
Delta modulation
Encyclopedia
Delta modulationis an analog-to-digital
and digital-to-analog signal
conversion technique used for transmission of voice information where quality is not of primary importance. DM is the simplest form of differential pulse-code modulation (DPCM) where the difference between successive samples is encoded into n-bit data streams. In delta modulation, the transmitted data is reduced to a 1-bit data stream.
Its main features are:
To achieve high signal-to-noise ratio
, delta modulation must use oversampling
techniques, that is, the analog signal is sampled at a rate several times higher than the Nyquist rate
.
Derived forms of delta modulation
are continuously variable slope delta modulation
, delta-sigma modulation
, and differential modulation. Differential pulse-code modulation is the super set of DM.
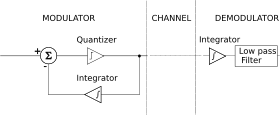 The modulator is made by a quantizer which converts the difference between the input signal and the average of the previous steps. In its simplest form, the quantizer can be realized with a comparator referenced to 0 (two levels quantizer), whose output is 1 or 0 if the input signal is positive or negative. It is also a bit-quantizer as it quantizes only a bit at a time. The demodulator is simply an integrator (like the one in the feedback loop) whose output rises or falls with each 1 or 0 received. The integrator itself constitutes a low-pass filter.
The modulator is made by a quantizer which converts the difference between the input signal and the average of the previous steps. In its simplest form, the quantizer can be realized with a comparator referenced to 0 (two levels quantizer), whose output is 1 or 0 if the input signal is positive or negative. It is also a bit-quantizer as it quantizes only a bit at a time. The demodulator is simply an integrator (like the one in the feedback loop) whose output rises or falls with each 1 or 0 received. The integrator itself constitutes a low-pass filter.
The two sources of noise in delta modulation are "slope overload", when steps are too small to track the original waveform, and "granularity", when steps are too large.
But a 1971 study shows that slope overload is less objectionable compared to granularity than one might expect based solely on SNR measures.
(CVSD) is a modification of DM in which the step size is not fixed.
Rather, when several consecutive bits have the same direction value, the encoder and decoder assume that slope overload is occurring, and the step size becomes progressively larger.
Otherwise, the step size becomes gradually smaller over time.
ADM reduces slope error,at the expense of increasing quantizing error.This error can be reduced by using a low pass filter.
Digital signal
A digital signal is a physical signal that is a representation of a sequence of discrete values , for example of an arbitrary bit stream, or of a digitized analog signal...
and digital-to-analog signal
Analog signal
An analog or analogue signal is any continuous signal for which the time varying feature of the signal is a representation of some other time varying quantity, i.e., analogous to another time varying signal. It differs from a digital signal in terms of small fluctuations in the signal which are...
conversion technique used for transmission of voice information where quality is not of primary importance. DM is the simplest form of differential pulse-code modulation (DPCM) where the difference between successive samples is encoded into n-bit data streams. In delta modulation, the transmitted data is reduced to a 1-bit data stream.
Its main features are:
- the analog signal is approximated with a series of segments
- each segment of the approximated signal is compared to the original analog wave to determine the increase or decrease in relative amplitude
- the decision process for establishing the state of successive bits is determined by this comparison
- only the change of informationInformationInformation in its most restricted technical sense is a message or collection of messages that consists of an ordered sequence of symbols, or it is the meaning that can be interpreted from such a message or collection of messages. Information can be recorded or transmitted. It can be recorded as...
is sent, that is, only an increase or decrease of the signal amplitude from the previous sample is sent whereas a no-change condition causes the modulated signal to remain at the same 0 or 1 state of the previous sample.
To achieve high signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. It is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power. A ratio higher than 1:1 indicates more signal than noise...
, delta modulation must use oversampling
Oversampling
In signal processing, oversampling is the process of sampling a signal with a sampling frequency significantly higher than twice the bandwidth or highest frequency of the signal being sampled...
techniques, that is, the analog signal is sampled at a rate several times higher than the Nyquist rate
Nyquist rate
In signal processing, the Nyquist rate, named after Harry Nyquist, is two times the bandwidth of a bandlimited signal or a bandlimited channel...
.
Derived forms of delta modulation
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
are continuously variable slope delta modulation
Continuously variable slope delta modulation
Continuously variable slope delta modulation is a voice coding method. It is a delta modulation with variable step size Continuously variable slope delta modulation (CVSD or CVSDM) is a voice coding method. It is a delta modulation with variable step size Continuously variable slope delta...
, delta-sigma modulation
Delta-sigma modulation
Delta-sigma modulation is a method for encoding high-resolution or analog signals into lower-resolution digital signals. The conversion is done using error feedback, where the difference between the two signals is measured and used to improve the conversion...
, and differential modulation. Differential pulse-code modulation is the super set of DM.
Principle
Rather than quantizing the absolute value of the input analog waveform, delta modulation quantizes the difference between the current and the previous step, as shown in the block diagram in Fig. 1.
Transfer characteristics
The transfer characteristics of a delta modulated system follows a signum function,as it quantizes only two levels and also one-bit at a time.The two sources of noise in delta modulation are "slope overload", when steps are too small to track the original waveform, and "granularity", when steps are too large.
But a 1971 study shows that slope overload is less objectionable compared to granularity than one might expect based solely on SNR measures.
Output signal power
In delta modulation there is no restriction on the amplitude of the signal waveform, because the number of levels is not fixed. On the other hand, there is a limitation on the slope of the signal waveform which must be observed if slope overload is to be avoided. However, if the signal waveform changes slowly, there is nominally no limit to the signal power which may be transmitted.Bit-rate
If the communication channel is of limited bandwidth,there is the possibility of interference in either DM or PCM. Hence, 'DM' and 'PCM' operate at same bit-rate.Adaptive delta modulation
Adaptive delta modulation (ADM) or continuously variable slope delta modulationContinuously variable slope delta modulation
Continuously variable slope delta modulation is a voice coding method. It is a delta modulation with variable step size Continuously variable slope delta modulation (CVSD or CVSDM) is a voice coding method. It is a delta modulation with variable step size Continuously variable slope delta...
(CVSD) is a modification of DM in which the step size is not fixed.
Rather, when several consecutive bits have the same direction value, the encoder and decoder assume that slope overload is occurring, and the step size becomes progressively larger.
Otherwise, the step size becomes gradually smaller over time.
ADM reduces slope error,at the expense of increasing quantizing error.This error can be reduced by using a low pass filter.
Comparison of PCM and DM
- Signal-to-noise ratio of DM is larger than signal-to-noise ratio of PCM.
- For an ADM signal-to-noise ratio is comparable to Signal-to-noise ratio of companded PCM.
- In PCM,that it transmits all the bits which are used to code a sample, whereas in DM transmits only one bit for one sample.
- In PCM system Highest Bandwidth is required since the number of bits are high,but in DM system lowest bandwidth is only required.
- PCM system is complex in design when compared to DM system.
- No feedback exists in case of PCM system, but feedback exists in DM system.
Applications
Delta modulation, in particular pure DM has very few practical uses. However it is an interesting concept.See also
- Adaptive differential pulse-code modulation
- Analog-to-digital converterAnalog-to-digital converterAn analog-to-digital converter is a device that converts a continuous quantity to a discrete time digital representation. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement...
- CodecCodecA codec is a device or computer program capable of encoding or decoding a digital data stream or signal. The word codec is a portmanteau of "compressor-decompressor" or, more commonly, "coder-decoder"...
- Pulse-code modulationPulse-code modulationPulse-code modulation is a method used to digitally represent sampled analog signals. It is the standard form for digital audio in computers and various Blu-ray, Compact Disc and DVD formats, as well as other uses such as digital telephone systems...
- Pulse-density modulationPulse-density modulationPulse-density modulation, or PDM, is a form of modulation used to represent an analog signal with digital data. In a PDM signal, specific amplitude values are not encoded into pulses of different size as they would be in PCM. Instead, it is the relative density of the pulses that corresponds to...
- Delta-sigma modulationDelta-sigma modulationDelta-sigma modulation is a method for encoding high-resolution or analog signals into lower-resolution digital signals. The conversion is done using error feedback, where the difference between the two signals is measured and used to improve the conversion...
- Direct Stream DigitalDirect Stream DigitalDirect-Stream Digital is the trademark name used by Sony and Philips for their system of recreating audible signals which uses pulse-density modulation encoding, a technology to store audio signals on digital storage media which is used for the Super Audio CD .The signal is stored as delta-sigma...
- Delta-sigma modulation

