Demographics of Taiwan
Encyclopedia
This article is about the demographic
features of the population
in Taiwan
, including population density
, ethnicity
, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
The population in Taiwan was estimated in July 2011 at 23,188,087 spread across a total land area of 35,980 km², making it the sixteenth most densely populated country in the world with a population density of 641 people per km².
The original population of Taiwan consists of Taiwanese aborigines
who are genetically related to Austronesian peoples, with a mitochondrial DNA contribution from a Polynesian
maternal ancestor, and linguists classify their languages as Austronesian. Immigration of Han Chinese
to the Penghu islands started as early as the 1200s, while settlement of the main island occurred from the 1500s, stimulated by the import of workers from Fujian
by the Dutch in the 17th century. According to governmental statistics, 96% of Taiwan's population is now made up of Han Chinese
, while only 2% are Taiwanese aborigines
. Half the population are followers of one or a mixture of 25 recognized religions
. Around 93% of the religious population are followers of a mixture of Buddhism
, Taoism
, and Confucianism
, while a minority 4.5% are followers of Christianity
.
During the 20th century the population of Taiwan rose more than sevenfold, from 3.04 million in 1905 to 22.3 at December 31, 2000. This high growth was caused by a combination of factors, very high fertility rates up to the 1960s, and low mortality rates, and a surge in population as the Chinese Civil War
ended, and the Kuomintang forces retreated, bringing an influx of two million soldiers and civilians to Taiwan in 1948 - 1949. Consequently, the natural growth of Taiwan was very rapid, especially in the late 1940s and 1950s, with an effective growth rate as high as 36.8 per 1,000 during 1951-1956. Including the Kuomintang
forces, which accounted in 1950 for about 25% of all persons on Taiwan, immigration of mainland Chinese (now approximately 13% of the present population) at the end of the 1940s was a major factor in the high population growth of Taiwan. Some official government statistics for the period, including those reported on this page, do not seem consistent with the known size of the Kuomintang
influx.
Fertility rates decreased gradually thereafter, and in 1984 the rate reached the replacement level (2.1 children per women, which is needed to replace the existing population). Fertility rates have continued to decline and in 2010 Taiwan was experiencing a population growth of less than 0.2% and a fertility rate of only 0.9, which is the lowest rate ever recorded in Taiwan. The population of Taiwan is projected to reach a maximum of little over 23.4 million between 2020 and 2025, and will decrease thereafter.
The official national language
is Mandarin
, although a majority also speak Taiwanese (dialect of Min Nan
; a Southern Fujian
language) and Hakka. Japanese
speakers are becoming rare as the elderly generation who lived under Japanese rule
are dying out. Aboriginal languages are gradually becoming extinct as the aborigines have become acculturated despite a program by the ROC government to preserve the languages.
 According to May 2006 statistics from the Ministry of the Interior, the population of Taiwan was 22,805,547, 99.6% of which live on Taiwan island (Taiwan
According to May 2006 statistics from the Ministry of the Interior, the population of Taiwan was 22,805,547, 99.6% of which live on Taiwan island (Taiwan
, Taipei City and Kaohsiung City). The remaining 0.4% (82,618) live on offshore islands (Penghu, Jinmen, Mazu, Lanyu, and Green Island).
Taiwan is ranked the 50th most populous nation in the world.
Notes:
(台灣人 Táiwānrén) to clarify that they are from Taiwan, not from mainland China (大陸人 Dàlùrén; "mainlander/people from the mainland"). The people of Taiwan are officially "Chinese citizens" recognized by the Republic of China
government.
immigrants from the adjacent Fujian
province in mainland China
.
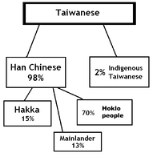
_demographics.png) Officially, the population of Taiwan consist of 98% Han Chinese
Officially, the population of Taiwan consist of 98% Han Chinese
, of which 84% identify as Benshengren (本省人 Běnshěngrén; literally "home-province person") while 15% are mainlanders or Waishengren (外省人 Wàishěngrén; literally "external-province person"). The remainder 2% are aborigines
(less than 500,000). A confounding factor is intermarriage between these ethnic groups - to the extent that it is doubtful whether the term "ethnicity" can be used at all.
and mainly plains tribe aboriginals who intermarried over the past four hundred years. Approximately two-thirds of those are descendants of early immigrants (70% of ethnic Hoklo
and 15% of ethnic Hakka
) from the adjacent Fujian
(Hokkien) and Guangdong
(Canton) province who crossed the Taiwan Strait
. Some settlers intermarried with Plains Aborigines. Both Hakka and Hoklo speakers regard themselves as Benshengren (本省人) and consider the mainland Chinese immigrants around the late 1940s during the Chinese Civil War
as Waishengren (外省人).
The ROC government officially recognizes fourteen aborigine tribes (原住民; yuánzhùmín; literally "original inhabitants"). These are: Ami, Atayal, Paiwan, Bunun
, Puyuma, Rukai, Tsou
, Saisiyat, Tao
(Yami), Thao, Kavalan
, Truku
, Seediq
, and Sakizaya
. Japanese colonial rule of Taiwan
classified and recognized nine tribes based on linguistic and cultural data; these criteria were modified and included in the official ROC ethnographies of Taiwanese people
. The Thao, Kavalan, Truku, Sakizaya, and Seediq tribes were recognized much later in 2001, 2002, 2004, 2007, and 2008 respectively by the ROC government. There are at least another dozen tribes that are not recognized by the government.
Unrecognized Taiwanese aboriginal tribes may include extinct tribes (mostly Plains aboriginal groups) or tribes currently classified with other groups. There are also 25,943 Aborigines who are currently not classified in any group.
Besides, there are People of the Mainland China Area, Hong Kong and Macao residents, and Nationals without registered household in the Taiwan Area.
Almost everyone in Taiwan born after the early 1950s can speak Mandarin
, which has been the official language and the medium of instruction in the schools for more than four decades. The Mandarin spoken in Taiwan has minor differences from that spoken in mainland China, South-east Asia and other regions of the world.
The majority speak a dialect form of Min Nan
(Southern Fujianese language), commonly referred to as Taiwanese, which was the most common language. The ethnic Hakka have a distinct Hakka dialect. Between 1900 and 1945 Japanese
was the medium of instruction and could be fluently spoken by many of those educated during that period. Chinese romanisation in Taiwan uses both Hanyu pinyin which has been officially adopted by the central government, and Tongyong pinyin
which some localities use. Wade-Giles
, used traditionally, is also found.
On Kinmen
(Quemoy), the language spoken is also Min Nan. On the Matsu Islands
, the Foochow dialect
, a Min Dong
(Eastern Fujianese) dialect, is spoken.
The most widely spoken Taiwanese aboriginal languages
today are Amis
, Atayal
, Bunun
, and Paiwan
.
guarantees freedom of religion as a right of all its citizens. , the Republic of China government recognizes 25 religions which are registered with the Civil Affairs Department of the Ministry of the Interior (MOI).
. These are not considered mutually exclusive, and many people practice a combination of the three. Confucianism
also is an honored school of thought and ethical codes. Christian
churches have been active in Taiwan for many centuries, a majority of which are Protestant
, with Presbyterian
s playing a particularly significant role. The ROC government has diplomatic relations with the Holy See
, which is the only European nation to formally recognize the ROC and is the ROC's longest lasting diplomatic ally, having established relations in 1942. Islam
is a static religion but has seen a surge in recent years as a result of foreign Muslims seeking work in Taiwan, most notably from Indonesia
. There is also a small group of Shinto
followers under the Tenrikyo
sect which began in the 1970s.
The table shows official statistics on religion issued by the Department of Civil Affairs, Ministry of the Interior ("MOI"), in 2005. The ROC government recognizes 26 religions in Taiwan. The statistics are reported by the various religious organizations to the MOI:
Statistics for the following religions and new religious movements are missing from the table above:
of which 2,631 were confirmed with AIDS
. There were 1,425 deaths leaving 10,029 people living with HIV/AIDS. This is less than 0.5% of the total population of Taiwan. Statistics by the Center for Disease Control show that the gender distribution of infected person was 90% male and 10% female.
for males aged 19–35 years of age with a service obligation of 12 months in 2008.
program initiated by the Ministry of Education in 1968. This consists of six years in elementary education and three years in junior high education. About 94.7% of junior high graduates continue their studies in either a senior high or vocational school . Reflecting a strong commitment to education, in FY 2001 16% of the ROC budget was allocated for education . The enrollment rate was 96.77% for the school year 2004-2005. For the school year 2005-2006, there were 5,283,855 students in both public and private schools, about a quarter of the entire population. The literacy rate is above 95%.
Taiwan has an extensive higher education system with more than 100 institutions of higher learning. Each year over 100,000 students take the joint college entrance exam; about 66.6% of the candidates are admitted to a college or university. Opportunities for graduate education are expanding in Taiwan, but many students travel abroad for advanced education, including 13,000 who study in the United States annually .
Since the mid-1990s, the government has introduced several education reforms in a bid to further improve education standards such as the replacement in 2002 of the 48-year long Joint University Entrance Examination (JUEE; 大學聯考; Dàxué liánkǎo) which had been set up in 1954.
Demographics
Demographics are the most recent statistical characteristics of a population. These types of data are used widely in sociology , public policy, and marketing. Commonly examined demographics include gender, race, age, disabilities, mobility, home ownership, employment status, and even location...
features of the population
Population
A population is all the organisms that both belong to the same group or species and live in the same geographical area. The area that is used to define a sexual population is such that inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with individuals...
in Taiwan
Taiwan
Taiwan , also known, especially in the past, as Formosa , is the largest island of the same-named island group of East Asia in the western Pacific Ocean and located off the southeastern coast of mainland China. The island forms over 99% of the current territory of the Republic of China following...
, including population density
Population density
Population density is a measurement of population per unit area or unit volume. It is frequently applied to living organisms, and particularly to humans...
, ethnicity
Ethnic group
An ethnic group is a group of people whose members identify with each other, through a common heritage, often consisting of a common language, a common culture and/or an ideology that stresses common ancestry or endogamy...
, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
The population in Taiwan was estimated in July 2011 at 23,188,087 spread across a total land area of 35,980 km², making it the sixteenth most densely populated country in the world with a population density of 641 people per km².
The original population of Taiwan consists of Taiwanese aborigines
Taiwanese aborigines
Taiwanese aborigines is the term commonly applied in reference to the indigenous peoples of Taiwan. Although Taiwanese indigenous groups hold a variety of creation myths, recent research suggests their ancestors may have been living on the islands for approximately 8,000 years before major Han...
who are genetically related to Austronesian peoples, with a mitochondrial DNA contribution from a Polynesian
Polynesians
The Polynesian peoples is a grouping of various ethnic groups that speak Polynesian languages, a branch of the Oceanic languages within the Austronesian languages, and inhabit Polynesia. They number approximately 1,500,000 people...
maternal ancestor, and linguists classify their languages as Austronesian. Immigration of Han Chinese
Han Chinese
Han Chinese are an ethnic group native to China and are the largest single ethnic group in the world.Han Chinese constitute about 92% of the population of the People's Republic of China , 98% of the population of the Republic of China , 78% of the population of Singapore, and about 20% of the...
to the Penghu islands started as early as the 1200s, while settlement of the main island occurred from the 1500s, stimulated by the import of workers from Fujian
Fujian
' , formerly romanised as Fukien or Huguing or Foukien, is a province on the southeast coast of mainland China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, and Guangdong to the south. Taiwan lies to the east, across the Taiwan Strait...
by the Dutch in the 17th century. According to governmental statistics, 96% of Taiwan's population is now made up of Han Chinese
Han Chinese
Han Chinese are an ethnic group native to China and are the largest single ethnic group in the world.Han Chinese constitute about 92% of the population of the People's Republic of China , 98% of the population of the Republic of China , 78% of the population of Singapore, and about 20% of the...
, while only 2% are Taiwanese aborigines
Taiwanese aborigines
Taiwanese aborigines is the term commonly applied in reference to the indigenous peoples of Taiwan. Although Taiwanese indigenous groups hold a variety of creation myths, recent research suggests their ancestors may have been living on the islands for approximately 8,000 years before major Han...
. Half the population are followers of one or a mixture of 25 recognized religions
Religion in Taiwan
A wide diversity of religions can be found on Taiwan, due to its multicultural history, and religious freedom written in the constitution of the Republic of China.-History:...
. Around 93% of the religious population are followers of a mixture of Buddhism
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
, Taoism
Taoism
Taoism refers to a philosophical or religious tradition in which the basic concept is to establish harmony with the Tao , which is the mechanism of everything that exists...
, and Confucianism
Confucianism
Confucianism is a Chinese ethical and philosophical system developed from the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius . Confucianism originated as an "ethical-sociopolitical teaching" during the Spring and Autumn Period, but later developed metaphysical and cosmological elements in the Han...
, while a minority 4.5% are followers of Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
.
During the 20th century the population of Taiwan rose more than sevenfold, from 3.04 million in 1905 to 22.3 at December 31, 2000. This high growth was caused by a combination of factors, very high fertility rates up to the 1960s, and low mortality rates, and a surge in population as the Chinese Civil War
Chinese Civil War
The Chinese Civil War was a civil war fought between the Kuomintang , the governing party of the Republic of China, and the Communist Party of China , for the control of China which eventually led to China's division into two Chinas, Republic of China and People's Republic of...
ended, and the Kuomintang forces retreated, bringing an influx of two million soldiers and civilians to Taiwan in 1948 - 1949. Consequently, the natural growth of Taiwan was very rapid, especially in the late 1940s and 1950s, with an effective growth rate as high as 36.8 per 1,000 during 1951-1956. Including the Kuomintang
Kuomintang
The Kuomintang of China , sometimes romanized as Guomindang via the Pinyin transcription system or GMD for short, and translated as the Chinese Nationalist Party is a founding and ruling political party of the Republic of China . Its guiding ideology is the Three Principles of the People, espoused...
forces, which accounted in 1950 for about 25% of all persons on Taiwan, immigration of mainland Chinese (now approximately 13% of the present population) at the end of the 1940s was a major factor in the high population growth of Taiwan. Some official government statistics for the period, including those reported on this page, do not seem consistent with the known size of the Kuomintang
Kuomintang
The Kuomintang of China , sometimes romanized as Guomindang via the Pinyin transcription system or GMD for short, and translated as the Chinese Nationalist Party is a founding and ruling political party of the Republic of China . Its guiding ideology is the Three Principles of the People, espoused...
influx.
Fertility rates decreased gradually thereafter, and in 1984 the rate reached the replacement level (2.1 children per women, which is needed to replace the existing population). Fertility rates have continued to decline and in 2010 Taiwan was experiencing a population growth of less than 0.2% and a fertility rate of only 0.9, which is the lowest rate ever recorded in Taiwan. The population of Taiwan is projected to reach a maximum of little over 23.4 million between 2020 and 2025, and will decrease thereafter.
The official national language
National language
A national language is a language which has some connection—de facto or de jure—with a people and perhaps by extension the territory they occupy. The term is used variously. A national language may for instance represent the national identity of a nation or country...
is Mandarin
Standard Chinese
Standard Chinese, or Modern Standard Chinese, also known as Mandarin or Putonghua, is the official language of the People's Republic of China and Republic of China , and is one of the four official languages of Singapore....
, although a majority also speak Taiwanese (dialect of Min Nan
Min Nan
The Southern Min languages, or Min Nan , are a family of Chinese languages spoken in southern Fujian, eastern Guangdong, Hainan, Taiwan, and southern Zhejiang provinces of China, and by descendants of emigrants from these areas in diaspora....
; a Southern Fujian
Fujian
' , formerly romanised as Fukien or Huguing or Foukien, is a province on the southeast coast of mainland China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, and Guangdong to the south. Taiwan lies to the east, across the Taiwan Strait...
language) and Hakka. Japanese
Japanese language
is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists .Japanese is an...
speakers are becoming rare as the elderly generation who lived under Japanese rule
Taiwan under Japanese rule
Between 1895 and 1945, Taiwan was a dependency of the Empire of Japan. The expansion into Taiwan was a part of Imperial Japan's general policy of southward expansion during the late 19th century....
are dying out. Aboriginal languages are gradually becoming extinct as the aborigines have become acculturated despite a program by the ROC government to preserve the languages.
Population

Taiwan
Taiwan , also known, especially in the past, as Formosa , is the largest island of the same-named island group of East Asia in the western Pacific Ocean and located off the southeastern coast of mainland China. The island forms over 99% of the current territory of the Republic of China following...
, Taipei City and Kaohsiung City). The remaining 0.4% (82,618) live on offshore islands (Penghu, Jinmen, Mazu, Lanyu, and Green Island).
Taiwan is ranked the 50th most populous nation in the world.
| Rank | Name | Chinese name | Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Taiwan Taiwan Taiwan , also known, especially in the past, as Formosa , is the largest island of the same-named island group of East Asia in the western Pacific Ocean and located off the southeastern coast of mainland China. The island forms over 99% of the current territory of the Republic of China following... |
臺灣 or 台灣 | 18,590,635 ¹ |
| 2 | Taipei City | 臺北市 or 台北市 | 2,620,693 |
| 3 | Kaohsiung City | 高雄市 | 1,511,601 |
| 4 | Fukien Province | 福建省 | 82,618 ² |
| Total | 22,805,547 |
Notes:
| 1. | Excludes the cities of Taipei and Kaohsiung, which were split off from the Taiwan Taiwan Taiwan , also known, especially in the past, as Formosa , is the largest island of the same-named island group of East Asia in the western Pacific Ocean and located off the southeastern coast of mainland China. The island forms over 99% of the current territory of the Republic of China following... in 1967 and 1979 respectively. |
| 2. | Covers only the modern counties of Kinmen and Lienchiang, which are under the effective jurisdiction of the Fukien Province. |
Population census
| Year | Males (thousands) | Females (thousands) | Total population (thousands) | Average annual growth rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1905 | 1,611 | 1,429 | 3,040 | |
| 1915 | 1,813 | 1,669 | 3,480 | 1.4 |
| 1920 | 1,894 | 1,762 | 3,655 | 1.0 |
| 1925 | 2,053 | 1,941 | 3,993 | 1.8 |
| 1930 | 2,353 | 2,239 | 4,593 | 2.8 |
| 1935 | 2,660 | 2,553 | 5,212 | 2.6 |
| 1940 | 2,971 | 2,901 | 5,872 | 2.4 |
| 1956 | 4,772 | 4,596 | 9,368 | 3.0 |
| 1966 | 7,153 | 6,352 | 13,505 | 3.7 |
| 1970 (sampling) | 7,723 | 7,047 | 14,770 | 2.3 |
| 1975 (sampling) | 8,439 | 7,840 | 16,279 | 2.0 |
| 1980 | 9,405 | 8,624 | 18,030 | 2.1 |
| 1990 | 10,618 | 9,775 | 20,394 | 1.2 |
| 2000 | 11,386 | 10,915 | 22,301 | 0.9 |
| 2010 (end of year estimate) | 23,162 | 0.4 |
Net migration rate
During 2004-2010 Taiwan's migration rate was positive. On average the annual net migration amounted to 22,000 people during that period, which is equivalent to a rate of 1.0 per 1000 inhabitants per year.Age structure
| Age range | 1980 | census 1990 | census 2000 | 2010 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–14 years | 32.1% | 26.9% | 21.2% | 15.65% |
| 15–64 years | 63.6% | 67.0% | 70.2% | 73.61% |
| 65 years and over | 4.3% | 6.1% | 8.6% | 10.74% |
Sex ratio
- at birth: 1.1 male(s)/female
- under 15 years: 1.09 male(s)/female
- 15-64 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
- 65 years and over: 0.99 male(s)/female
- total population: 1.04 male(s)/female (2006 est.)
Nationality
Some identify themselves as TaiwaneseTaiwanese people
Taiwanese people may refer to individuals who either claim or are imputed cultural identity focused on the island of Taiwan and/or Taiwan Area which have been governed by the Republic of China since 1945...
(台灣人 Táiwānrén) to clarify that they are from Taiwan, not from mainland China (大陸人 Dàlùrén; "mainlander/people from the mainland"). The people of Taiwan are officially "Chinese citizens" recognized by the Republic of China
Republic of China
The Republic of China , commonly known as Taiwan , is a unitary sovereign state located in East Asia. Originally based in mainland China, the Republic of China currently governs the island of Taiwan , which forms over 99% of its current territory, as well as Penghu, Kinmen, Matsu and other minor...
government.
Ethnicity (Overview)
The majority of the population are said to be descendants of Han ChineseHan Chinese
Han Chinese are an ethnic group native to China and are the largest single ethnic group in the world.Han Chinese constitute about 92% of the population of the People's Republic of China , 98% of the population of the Republic of China , 78% of the population of Singapore, and about 20% of the...
immigrants from the adjacent Fujian
Fujian
' , formerly romanised as Fukien or Huguing or Foukien, is a province on the southeast coast of mainland China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, and Guangdong to the south. Taiwan lies to the east, across the Taiwan Strait...
province in mainland China
Mainland China
Mainland China, the Chinese mainland or simply the mainland, is a geopolitical term that refers to the area under the jurisdiction of the People's Republic of China . According to the Taipei-based Mainland Affairs Council, the term excludes the PRC Special Administrative Regions of Hong Kong and...
.
_demographics.png)
Han Chinese
Han Chinese are an ethnic group native to China and are the largest single ethnic group in the world.Han Chinese constitute about 92% of the population of the People's Republic of China , 98% of the population of the Republic of China , 78% of the population of Singapore, and about 20% of the...
, of which 84% identify as Benshengren (本省人 Běnshěngrén; literally "home-province person") while 15% are mainlanders or Waishengren (外省人 Wàishěngrén; literally "external-province person"). The remainder 2% are aborigines
Taiwanese aborigines
Taiwanese aborigines is the term commonly applied in reference to the indigenous peoples of Taiwan. Although Taiwanese indigenous groups hold a variety of creation myths, recent research suggests their ancestors may have been living on the islands for approximately 8,000 years before major Han...
(less than 500,000). A confounding factor is intermarriage between these ethnic groups - to the extent that it is doubtful whether the term "ethnicity" can be used at all.
Han Chinese
98% of Taiwanese are descendants of a mixture of Han ChineseHan Chinese
Han Chinese are an ethnic group native to China and are the largest single ethnic group in the world.Han Chinese constitute about 92% of the population of the People's Republic of China , 98% of the population of the Republic of China , 78% of the population of Singapore, and about 20% of the...
and mainly plains tribe aboriginals who intermarried over the past four hundred years. Approximately two-thirds of those are descendants of early immigrants (70% of ethnic Hoklo
Hoklo people
The Hoklo people are Han Chinese people whose traditional Ancestral homes are in southern Fujian of South China...
and 15% of ethnic Hakka
Hakka people
The Hakka , sometimes Hakka Han, are Han Chinese who speak the Hakka language and have links to the provincial areas of Guangdong, Jiangxi, Guangxi, Sichuan, Hunan and Fujian in China....
) from the adjacent Fujian
Fujian
' , formerly romanised as Fukien or Huguing or Foukien, is a province on the southeast coast of mainland China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, and Guangdong to the south. Taiwan lies to the east, across the Taiwan Strait...
(Hokkien) and Guangdong
Guangdong
Guangdong is a province on the South China Sea coast of the People's Republic of China. The province was previously often written with the alternative English name Kwangtung Province...
(Canton) province who crossed the Taiwan Strait
Taiwan Strait
The Taiwan Strait or Formosa Strait, formerly known as the Black Ditch, is a 180-km-wide strait separating Mainland China and Taiwan. The strait is part of the South China Sea and connects to East China Sea to the northeast...
. Some settlers intermarried with Plains Aborigines. Both Hakka and Hoklo speakers regard themselves as Benshengren (本省人) and consider the mainland Chinese immigrants around the late 1940s during the Chinese Civil War
Chinese Civil War
The Chinese Civil War was a civil war fought between the Kuomintang , the governing party of the Republic of China, and the Communist Party of China , for the control of China which eventually led to China's division into two Chinas, Republic of China and People's Republic of...
as Waishengren (外省人).
Aboriginal
The total population of aborigines was estimated in May 2006 to be 468,602 which is about 2% of the total population of Taiwan. The aborigines inhabit the eastern half of Taiwan which consists mostly of mountainous terrain.| Living in the Eastern plains | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|
| 220,513 (47.1%) | 111,372 | 109,141 |
| Living in the mountains | Male | Female |
| 248,089 (52.9%) | 122,016 | 126,073 |
| 468,602 | 233,388 | 235,214 |
- Note: Source data obtained from ROC Ministry of the Interior website (Spreadsheet data: m1-04.xls)
The ROC government officially recognizes fourteen aborigine tribes (原住民; yuánzhùmín; literally "original inhabitants"). These are: Ami, Atayal, Paiwan, Bunun
Bunun People
The Bunun , also historically known as the Vonum, are a tribe of Taiwanese aborigines and are best known for their sophisticated polyphonic vocal music. They speak the Bunun language. Unlike other aboriginal tribes in Taiwan, the Bunun are widely dispersed across the island. In the year 2000 the...
, Puyuma, Rukai, Tsou
Tsou people
The Tsou are an indigenous people of central southern Republic of China . They are spread across three administrative entities of the Republic of China — Nantou County, Chiayi County and Kaohsiung City....
, Saisiyat, Tao
Tao people
The Tao , originally recognized as Yami , are a Taiwanese aboriginal people, native to tiny outlying Orchid Island in Taiwan. The Tao are an Austronesian people linguistically and culturally closer to the Ivatan people of the Batanes islands in the Philippines than to other aboriginal peoples on...
(Yami), Thao, Kavalan
Kavalan people
The Kavalan or Kuvalan are an indigenous people of Taiwan, part of the larger Taiwanese aborigine ethnic group. The Kavalan originally inhabited modern-day Yilan County. Most of them moved to the coastal area of Hualien County and Taitung County in the 19th century...
, Truku
Truku people
The Truku people are an Indigenous Taiwanese tribe. Taroko is also the name of the area of Taiwan where the Truku tribe resides. The Executive Yuan, Republic of China has officially recognized the Truku since January 15, 2004. The Truku are the 12th aboriginal tribe in Taiwan to receive this...
, Seediq
Seediq people
The Seediq are a Taiwanese aboriginal people who live primarily in Nantou County and Hualien County. Their language is also known as Seediq. They were officially recognised as Taiwan's 14th indigenous group on 23 April 2008...
, and Sakizaya
Sakizaya people
The Sakizaya are Taiwanese Aborigines with a population of approximately 5,000–10,000...
. Japanese colonial rule of Taiwan
Taiwan under Japanese rule
Between 1895 and 1945, Taiwan was a dependency of the Empire of Japan. The expansion into Taiwan was a part of Imperial Japan's general policy of southward expansion during the late 19th century....
classified and recognized nine tribes based on linguistic and cultural data; these criteria were modified and included in the official ROC ethnographies of Taiwanese people
Taiwanese people
Taiwanese people may refer to individuals who either claim or are imputed cultural identity focused on the island of Taiwan and/or Taiwan Area which have been governed by the Republic of China since 1945...
. The Thao, Kavalan, Truku, Sakizaya, and Seediq tribes were recognized much later in 2001, 2002, 2004, 2007, and 2008 respectively by the ROC government. There are at least another dozen tribes that are not recognized by the government.
| English name | Chinese name | Pinyin Pinyin Pinyin is the official system to transcribe Chinese characters into the Roman alphabet in China, Malaysia, Singapore and Taiwan. It is also often used to teach Mandarin Chinese and spell Chinese names in foreign publications and used as an input method to enter Chinese characters into... transliteration | |Population at census 2000 | Population | Date of recognition | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amis (Pangcah) |
阿美 | Āměi | 148,992 | 183,799 | Japanese colonial era | One of the 9 tribes originally recognized by the Japanese colonial government. Tribal name means "north." |
| Paiwan | 排灣 | Páiwān | 70,331 | 88,323 | Japanese colonial era | One of the 9 tribes originally recognized by the Japanese colonial government. |
| Atayal (Tayal) |
泰雅 | Tàiyǎ | 91,883 | 80,061 | Japanese colonial era | One of the 9 tribes originally recognized by the Japanese colonial government. Tribal name means "brave person." |
| Bunun Bunun People The Bunun , also historically known as the Vonum, are a tribe of Taiwanese aborigines and are best known for their sophisticated polyphonic vocal music. They speak the Bunun language. Unlike other aboriginal tribes in Taiwan, the Bunun are widely dispersed across the island. In the year 2000 the... |
布農 | Bùnóng | 41,038 | 51,447 | Japanese colonial era | One of the 9 tribes originally recognized by the Japanese colonial government. |
| Truku Truku people The Truku people are an Indigenous Taiwanese tribe. Taroko is also the name of the area of Taiwan where the Truku tribe resides. The Executive Yuan, Republic of China has officially recognized the Truku since January 15, 2004. The Truku are the 12th aboriginal tribe in Taiwan to receive this... (Taroko) |
太魯閣 | Tàilǔgé | - | 25,857 | January 14, 2004 | Originally classified as Atayal Atayal The Atayal , also known as the Tayal and the Tayan, are one tribe of Taiwanese aborigines. In the year 2000 the Atayal tribe numbered 91,883. This was approximately 23.1% of Taiwan's total indigenous population, making them the second-largest tribal group... . |
| Rukai | 魯凱 | Lǔkǎi | 12,084 | 11,911 | Japanese colonial era | One of the 9 tribes originally recognized by the Japanese colonial government. |
| Puyuma | 卑南 | Bēinán | 9,606 | 11,850 | Japanese colonial era | One of the 9 tribes originally recognized by the Japanese colonial government. |
| Tsou Tsou people The Tsou are an indigenous people of central southern Republic of China . They are spread across three administrative entities of the Republic of China — Nantou County, Chiayi County and Kaohsiung City.... (Cou) |
鄒 | Zōu | 6,169 | 6,733 | Japanese colonial era | One of the 9 tribes originally recognized by the Japanese colonial government. |
| Seediq Seediq people The Seediq are a Taiwanese aboriginal people who live primarily in Nantou County and Hualien County. Their language is also known as Seediq. They were officially recognised as Taiwan's 14th indigenous group on 23 April 2008... |
賽德克 | Sàidékè | - | 6,606 | April 23, 2008 | Originally classified as Atayal Atayal The Atayal , also known as the Tayal and the Tayan, are one tribe of Taiwanese aborigines. In the year 2000 the Atayal tribe numbered 91,883. This was approximately 23.1% of Taiwan's total indigenous population, making them the second-largest tribal group... . |
| Saisiyat (Saysiat) |
賽夏 | Sàixià | 5,311 | 5,900 | Japanese colonial era | One of the 9 tribes originally recognized by the Japanese colonial government. |
| Tao Tao people The Tao , originally recognized as Yami , are a Taiwanese aboriginal people, native to tiny outlying Orchid Island in Taiwan. The Tao are an Austronesian people linguistically and culturally closer to the Ivatan people of the Batanes islands in the Philippines than to other aboriginal peoples on... (Yami) |
達悟 | Dáwù | 3,872 | 3,748 | Japanese colonial era | One of the 9 tribes originally recognized by the Japanese colonial government. Also known as 雅美 (Yǎmĕi) or 耶美 (Yémĕi). Tribal name means "person." |
| Kavalan Kavalan people The Kavalan or Kuvalan are an indigenous people of Taiwan, part of the larger Taiwanese aborigine ethnic group. The Kavalan originally inhabited modern-day Yilan County. Most of them moved to the coastal area of Hualien County and Taitung County in the 19th century... |
噶瑪蘭 | Gámǎlán | - | 1,218 | 2002 | Some Kavalan are classified as Amis Amis Amis may refer to:* Amis people , a tribe of Taiwanese aborigines* Amis language, an indigenous language of Taiwan* AMIS , an Internet service provider in Slovenia and CroatiaThe acronym AMIS may stand for:... . |
| Thao | 邵 | Shào | - | 693 | 2001 | Originally thought to be Plains aborigines living among the Tsou. |
| Sakizaya Sakizaya people The Sakizaya are Taiwanese Aborigines with a population of approximately 5,000–10,000... |
撒奇萊雅 | Sāqíláiyǎ | - | 442 | January 17, 2007 | Reclassified as Amis Amis Amis may refer to:* Amis people , a tribe of Taiwanese aborigines* Amis language, an indigenous language of Taiwan* AMIS , an Internet service provider in Slovenia and CroatiaThe acronym AMIS may stand for:... during the Japanese colonial era. |
| Others | 8,249 | |||||
| Total | 397,535 | |||||
Unrecognized Taiwanese aboriginal tribes may include extinct tribes (mostly Plains aboriginal groups) or tribes currently classified with other groups. There are also 25,943 Aborigines who are currently not classified in any group.
| English name | Chinese name | Pinyin Pinyin Pinyin is the official system to transcribe Chinese characters into the Roman alphabet in China, Malaysia, Singapore and Taiwan. It is also often used to teach Mandarin Chinese and spell Chinese names in foreign publications and used as an input method to enter Chinese characters into... |
|---|---|---|
| Babuza | 巴布薩 | Bābùsà |
| Basay | 巴賽 | Bāsài |
| Hoanya | 洪雅 | Hé'ānyǎ |
| Kanakanabu | 卡那卡那富 | Kǎnàkǎnàfù |
| Kaxabu Kaxabu people The Kaxabu people are a variant of the Pazeh/Kaxabu ethno-linguistic group of Taiwanese Aborigines.-See also:*Kingdom of Middag*Formosan languages*Taiwanese aborigines... |
噶哈巫 | Géhāwū |
| Ketagalan | 凱達格蘭 | Kǎidágélán |
| Luilang | 雷朗 | Léilǎng |
| Makatao | 馬卡道 | Mǎkǎdào |
| Papora (Papora) |
巴布拉 | Bābùlā |
| Pazeh Pazeh people The Pazeh people, including the Kaxabu, are the descendants of the Tsouic Pazeh speaking indigenous people from the central Taiwanese areas of Taichung and Miaoli... (Pazih) |
巴宰 (巴澤海) | Bāzǎi (Bāzéhǎi) |
| Qauqaut | 猴猴 | Hóuhóu |
| Saaroa | 沙阿魯阿 | Shāālǔā |
| Siraya | 西拉雅 | Xīlāyǎ |
| Taokas Taokas people Taokas is one of a number of indigenous ethno-linguistic groups that inhabited the plains of western Taiwan. The Taokas were located in the areas around today's Hsinchu City/Hsinchu County, Miaoli County, and Taichung City region. Several Taokas groups have been historically linked to many revolts... |
道卡斯 | Dàokǎsī |
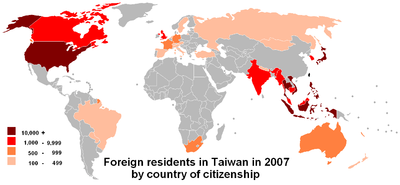
Foreign residents

| Nationality / Origin | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 148,737 | 34.6% | |
| 2 | 86,317 | 20.1% | |
| 3 | 74,483 | 17.3% | |
| 4 | 68,618 | 15.9% | |
| 5 | 11,087 | 2.5% | |
| 6 | 10,383 | 2.4% | |
| 7 | 9,735 | 2.2% | |
| 8 | 3,428 | 0.8% | |
| 9 | 2,410 | 0.6% | |
| 10 | 1,538 | 0.4% | |
| 11 | 1,388 | 0.3% | |
| 12 | 1,091 | 0.3% | |
| - | Other | 11,157 | 2.6% |
| Total | 430,372 | 100.0% | |
|
|||
Besides, there are People of the Mainland China Area, Hong Kong and Macao residents, and Nationals without registered household in the Taiwan Area.
| People | Temporary residency | Permanent residency |
|---|---|---|
| Mainland China | 241,455 | 128,744 |
| Hong Kong and Macao | 34,241 | 21,218 |
| nationals without registered household | 136,846 | 204,808 |
|
||
Languages
- Overview: Mandarin (official), Taiwanese Minnan, Hakka dialects, Taiwanese aboriginal languagesFormosan languagesThe Formosan languages are the languages of the indigenous peoples of Taiwan. Taiwanese aborigines currently comprise about 2% of the island's population. However, far fewer can still speak their ancestral language, after centuries of language shift...
Almost everyone in Taiwan born after the early 1950s can speak Mandarin
Standard Chinese
Standard Chinese, or Modern Standard Chinese, also known as Mandarin or Putonghua, is the official language of the People's Republic of China and Republic of China , and is one of the four official languages of Singapore....
, which has been the official language and the medium of instruction in the schools for more than four decades. The Mandarin spoken in Taiwan has minor differences from that spoken in mainland China, South-east Asia and other regions of the world.
The majority speak a dialect form of Min Nan
Min Nan
The Southern Min languages, or Min Nan , are a family of Chinese languages spoken in southern Fujian, eastern Guangdong, Hainan, Taiwan, and southern Zhejiang provinces of China, and by descendants of emigrants from these areas in diaspora....
(Southern Fujianese language), commonly referred to as Taiwanese, which was the most common language. The ethnic Hakka have a distinct Hakka dialect. Between 1900 and 1945 Japanese
Japanese language
is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists .Japanese is an...
was the medium of instruction and could be fluently spoken by many of those educated during that period. Chinese romanisation in Taiwan uses both Hanyu pinyin which has been officially adopted by the central government, and Tongyong pinyin
Tongyong Pinyin
Tongyong Pinyin was the official Romanization of Mandarin Chinese in the Republic of China between 2002 and 2008. The system was unofficially used between 2000 and 2002, when a new romanization system for the Republic of China was being evaluated for adoption. The ROC's Ministry of Education...
which some localities use. Wade-Giles
Wade-Giles
Wade–Giles , sometimes abbreviated Wade, is a romanization system for the Mandarin Chinese language. It developed from a system produced by Thomas Wade during the mid-19th century , and was given completed form with Herbert Giles' Chinese–English dictionary of 1892.Wade–Giles was the most...
, used traditionally, is also found.
On Kinmen
Kinmen
Kinmen , also known as Quemoy , is a small archipelago of several islands administered by the Republic of China : Greater Kinmen, Lesser Kinmen, and some islets. Administratively, it is Kinmen County of Fujian Province, ROC. The county is claimed by the People's Republic of China as part of its...
(Quemoy), the language spoken is also Min Nan. On the Matsu Islands
Matsu Islands
The Matsu Islands are a minor archipelago of 19 islands and islets in the Taiwan Strait administered as Lienchiang County , Fujian Province of the Republic of China . Only a small area of what is historically Lienchiang County is under the control of the ROC...
, the Foochow dialect
Fuzhou dialect
Fuzhou dialect , also known as Foochow dialect, Foochow, Foochowese, Fuzhounese, or Fuzhouhua, is considered the standard dialect of Min Dong, which is a branch of Min Chinese mainly spoken in the eastern part of Fujian Province. Native speakers also call it ' , meaning the language spoken in...
, a Min Dong
Min Dong
The Eastern Min language, or Min Dong is the language mainly spoken in the eastern part of Fujian Province in China, in and near Fuzhou and Ningde. Fuzhou is the province's capital and largest city...
(Eastern Fujianese) dialect, is spoken.
The most widely spoken Taiwanese aboriginal languages
Formosan languages
The Formosan languages are the languages of the indigenous peoples of Taiwan. Taiwanese aborigines currently comprise about 2% of the island's population. However, far fewer can still speak their ancestral language, after centuries of language shift...
today are Amis
Amis language
Amis is the Formosan language of the Amis Ami, an indigenous tribal people living along the east coast of Taiwan . It is spoken from Hualien in the north to Taitung in the south, with another population near the southern end of the island, though the northern varieties are sometimes considered a...
, Atayal
Atayal language
The Atayal language is spoken by the Atayal people of Taiwan. Squliq and C’uli’ are two major dialects...
, Bunun
Bunun language
The Bunun language is spoken by the Bunun people of Taiwan. It is one of the Formosan languages, a geographic group of Austronesian languages, and is subdivided in five dialects: Isbukun, Takbunuaz, Takivatan, Takibaka and Takituduh. Isbukun, the dominant dialect, is mainly spoken in the south of...
, and Paiwan
Paiwan language
Paiwan is a native language of Taiwan, spoken by the Paiwan people, one tribe of the Taiwanese aborigines. Paiwan is a Formosan language of the Austronesian language family...
.
Religion
Article 13 of the Constitution of the Republic of ChinaConstitution of the Republic of China
The Constitution of the Republic of China is the fundamental law of the Republic of China . Drafted by the Kuomintang as part of its third stage of national development , it established a centralized Republic with five branches of government...
guarantees freedom of religion as a right of all its citizens. , the Republic of China government recognizes 25 religions which are registered with the Civil Affairs Department of the Ministry of the Interior (MOI).
Statistics on registered religions (2005)
About 81.3% of the population can be considered religious believers, most of whom identify themselves as Buddhists or Taoists. At the same time there is a strong belief in folk religionFolk religion
Folk religion consists of ethnic or regional religious customs under the umbrella of an organized religion, but outside of official doctrine and practices...
. These are not considered mutually exclusive, and many people practice a combination of the three. Confucianism
Confucianism
Confucianism is a Chinese ethical and philosophical system developed from the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius . Confucianism originated as an "ethical-sociopolitical teaching" during the Spring and Autumn Period, but later developed metaphysical and cosmological elements in the Han...
also is an honored school of thought and ethical codes. Christian
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
churches have been active in Taiwan for many centuries, a majority of which are Protestant
Protestantism
Protestantism is one of the three major groupings within Christianity. It is a movement that began in Germany in the early 16th century as a reaction against medieval Roman Catholic doctrines and practices, especially in regards to salvation, justification, and ecclesiology.The doctrines of the...
, with Presbyterian
Presbyterian Church in Taiwan
The Presbyterian Church in Taiwan was planted in Taiwan in the 19th century by Dr James Laidlaw Maxwell Snr of the Presbyterian Church of England and Dr George Leslie Mackay of the Presbyterian Church in Canada....
s playing a particularly significant role. The ROC government has diplomatic relations with the Holy See
Holy See
The Holy See is the episcopal jurisdiction of the Catholic Church in Rome, in which its Bishop is commonly known as the Pope. It is the preeminent episcopal see of the Catholic Church, forming the central government of the Church. As such, diplomatically, and in other spheres the Holy See acts and...
, which is the only European nation to formally recognize the ROC and is the ROC's longest lasting diplomatic ally, having established relations in 1942. Islam
Islam in Taiwan
Islam in Taiwan is a slowly growing religion with an estimated 100 converts annually. There are about 45,000 registered Muslims in Taiwan, as of 2007. There are 88,500 Indonesian Muslims working in Taiwan...
is a static religion but has seen a surge in recent years as a result of foreign Muslims seeking work in Taiwan, most notably from Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
. There is also a small group of Shinto
Shinto
or Shintoism, also kami-no-michi, is the indigenous spirituality of Japan and the Japanese people. It is a set of practices, to be carried out diligently, to establish a connection between present day Japan and its ancient past. Shinto practices were first recorded and codified in the written...
followers under the Tenrikyo
Tenrikyo
Tenrikyo is a monotheistic religion originating in revelations to a 19th-century Japanese woman named Nakayama Miki, known as Oyasama by followers...
sect which began in the 1970s.
The table shows official statistics on religion issued by the Department of Civil Affairs, Ministry of the Interior ("MOI"), in 2005. The ROC government recognizes 26 religions in Taiwan. The statistics are reported by the various religious organizations to the MOI:
| Religion | Members | % of total population | Temples & churches |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buddhism Buddhism Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th... (including Tantric Buddhism) |
8,086,000 | 35.1% | 4,006 |
| Taoism Taoism Taoism refers to a philosophical or religious tradition in which the basic concept is to establish harmony with the Tao , which is the mechanism of everything that exists... |
7,600,000 | 33.0% | 18,274 |
| Yi Guan Dao | 810,000 | 3.5% | 3,260 |
| Protestantism Protestantism Protestantism is one of the three major groupings within Christianity. It is a movement that began in Germany in the early 16th century as a reaction against medieval Roman Catholic doctrines and practices, especially in regards to salvation, justification, and ecclesiology.The doctrines of the... |
605,000 | 2.6% | 3,609 |
| Catholicism Roman Catholic Church The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the world's largest Christian church, with over a billion members. Led by the Pope, it defines its mission as spreading the gospel of Jesus Christ, administering the sacraments and exercising charity... |
298,000 | 1.3% | 1,151 |
| Lord of Universe Church Lord of Universe Church The Lord of Universe Church is an international religious organization based in the Republic of China which is devoted to the "T'ienti Teachings" proclaimed by the late Lee Yü-chieh. It is a splinter religion from Tiender which is closely related to Confucianism and Taoism... |
298,000 | 1.3% | 50 |
| Maitreya Great Tao | 250,000 | 1.1% | 2,200 |
| Tian De Jiao | 200,000 | 0.9% | 14 |
| Li-ism Li-ism Liism , also known as Reasonable Religion , is a syncretism of Confucianism, Taoism, and Buddhism, with a focus on Guan Yin worship. It has its origins in the White Lotus. According to legend, it was founded in 1621. It was practiced secretly until the Republic of China was founded in 1911... |
186,000 | 0.8% | 138 |
| Syuan Yuan Jiao Syuan Yuan Jiao Syuan Yuan Jiao is a new religion founded in Taiwan in 1957 by Wang Han-sheng. It is a synthesis of Confucianism, Daoism, and Mohism.... |
152,700 | 0.7% | 22 |
| Islam Islam Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~... |
58,000 | 0.3% | 6 |
| Tenrikyo Tenrikyo Tenrikyo is a monotheistic religion originating in revelations to a 19th-century Japanese woman named Nakayama Miki, known as Oyasama by followers... |
35,000 | 0.2% | 153 |
| Universe Maitreya Emperor Jiao | 35,000 | 0.2% | 12 |
| Hai Zih Dao | 30,000 | 0.1% | 55 |
| Confucianism Confucianism Confucianism is a Chinese ethical and philosophical system developed from the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius . Confucianism originated as an "ethical-sociopolitical teaching" during the Spring and Autumn Period, but later developed metaphysical and cosmological elements in the Han... |
26,700 | 0.1% | 139 |
| Church of Scientology Church of Scientology The Church of Scientology is an organization devoted to the practice and the promotion of the Scientology belief system. The Church of Scientology International is the Church of Scientology's parent organization, and is responsible for the overall ecclesiastical management, dissemination and... |
20,000 | 0.1% | 7 |
| Bahá'í Faith Bahá'í Faith in Taiwan The Bahá'í Faith in Taiwan, 巴哈伊教, began after the religion entered areas of China and nearby Japan. The first Bahá'ís arrived in Taiwan in 1949 and the first of these to have become a Bahá'í was Mr. Jerome Chu in 1945 while visiting the United States. By May 1955 there were eighteen Bahá'ís in... |
16,000 | 0.1% | 13 |
| The Chinese Heritage and Mission Religion | 5,000 | < 0.1% | 5 |
| Zhonghua Sheng Jiao | 3,200 | < 0.1% | 7 |
| Mahikarikyo | 1,000 | < 0.1% | 9 |
| Pre-cosmic Salvationism | 1,000 | < 0.1% | 6 |
| Huang Zhong Huang Zhong Huang Zhong was a military general serving under the warlord Liu Bei during the late Han Dynasty period of Chinese history. He was most noted for his victory in the Battle of Mount Dingjun, in which his force routed that of Xiahou Yuan, who was slain during battle... |
1,000 | < 0.1% | 1 |
| Da Yi Jiao | 1,000 | < 0.1% | 1 |
| Total religious population | 18,718,600 | 81.3% | 33,138 |
| Total population | 23,036,087 | 100% | - |
Statistics for the following religions and new religious movements are missing from the table above:
- Xian Tian Jiu Jiao
- The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
- Holy Spirit Association for the Unification of World Christianity
- Source: Taipei Times.
Births and deaths
| Average population (x 1000) | Live births | Deaths | Natural change | Crude birth rate (per 1000) | Crude death rate (per 1000) | Natural change (per 1000) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1906 | 3 060 | 119 107 | 102 000 | 16 000 | 38.6 | 33.4 | 5.2 |
| 1907 | 3 090 | 121 756 | 100 000 | 21 000 | 39.1 | 32.4 | 6.7 |
| 1908 | 3 120 | 119 800 | 100 000 | 19 000 | 38.2 | 31.9 | 6.3 |
| 1909 | 3 160 | 127 286 | 98 000 | 29 000 | 40.2 | 31.1 | 9.1 |
| 1910 | 3 210 | 132 141 | 88 000 | 45 000 | 41.3 | 27.5 | 13.8 |
| 1911 | 3 270 | 135 658 | 86 000 | 51 000 | 41.8 | 26.2 | 15.6 |
| 1912 | 3 330 | 136 622 | 83 000 | 55 000 | 41.3 | 25.0 | 16.3 |
| 1913 | 3 390 | 136 967 | 85 000 | 53 000 | 40.8 | 25.0 | 15.8 |
| 1914 | 3 440 | 141 450 | 95 000 | 47 000 | 41.4 | 27.6 | 13.8 |
| 1915 | 3 480 | 137 669 | 110 000 | 29 000 | 40.0 | 31.5 | 8.5 |
| 1916 | 3 510 | 128 605 | 100 000 | 31 000 | 37.3 | 28.6 | 8.7 |
| 1917 | 3 560 | 142 414 | 96 000 | 50 000 | 40.9 | 27.0 | 13.9 |
| 1918 | 3 590 | 139 465 | 122 000 | 21 000 | 39.7 | 34.1 | 5.6 |
| 1919 | 3 630 | 136 707 | 97 000 | 43 000 | 38.5 | 26.8 | 11.7 |
| 1920 | 3 655 | 141 313 | 117 000 | 27 000 | 39.5 | 32.1 | 7.4 |
| 1921 | 3 720 | 155 159 | 90 000 | 69 000 | 42.8 | 24.2 | 18.6 |
| 1922 | 3 790 | 154 531 | 93 000 | 65 000 | 41.8 | 24.6 | 17.2 |
| 1923 | 3 860 | 146 984 | 82 000 | 69 000 | 39.1 | 21.3 | 17.8 |
| 1924 | 3 930 | 158 688 | 96 000 | 67 000 | 41.4 | 24.5 | 16.9 |
| 1925 | 3 993 | 159 423 | 95 000 | 68 000 | 40.8 | 23.9 | 16.9 |
| 1926 | 4 100 | 175 802 | 92 000 | 87 000 | 43.7 | 22.4 | 21.3 |
| 1927 | 4 210 | 177 422 | 93 000 | 89 000 | 43.2 | 22.1 | 21.1 |
| 1928 | 4 330 | 183 699 | 95 000 | 94 000 | 43.7 | 22.0 | 21.7 |
| 1929 | 4 460 | 190 031 | 96 000 | 100 000 | 44.0 | 21.6 | 22.4 |
| 1930 | 4 593 | 198 186 | 89 000 | 117 000 | 44.8 | 19.4 | 25.4 |
| 1931 | 4 710 | 208 137 | 100 000 | 116 000 | 45.8 | 21.3 | 24.5 |
| 1932 | 4 867 | 204 913 | 99 000 | 115 000 | 44.0 | 20.4 | 23.6 |
| 1933 | 4 995 | 211 737 | 98 000 | 123 000 | 44.3 | 19.7 | 24.6 |
| 1934 | 5 128 | 219 189 | 105 166 | 123 510 | 44.6 | 20.5 | 24.1 |
| 1935 | 5 255 | 225 980 | 106 905 | 129 040 | 44.9 | 20.3 | 24.6 |
| 1936 | 5 384 | 223 961 | 106 332 | 127 725 | 43.5 | 19.8 | 23.7 |
| 1937 | 5 530 | 237 090 | 109 096 | 138 570 | 44.8 | 19.7 | 25.1 |
| 1938 | 5 678 | 235 821 | 111 723 | 133 117 | 43.1 | 19.7 | 23.4 |
| 1939 | 5 821 | 244 707 | 115 044 | 139 119 | 43.7 | 19.8 | 23.9 |
| 1940 | 5 987 | 246 691 | 116 239 | 141 232 | 43.0 | 19.4 | 23.6 |
| 1941 | 6 163 | 241 894 | 99 858 | 153 447 | 41.1 | 16.2 | 24.9 |
| 1942 | 6 339 | 242 796 | 112 161 | 143 243 | 40.3 | 17.7 | 22.6 |
| 1943 | 6 507 | 247 427 | 122 001 | 138 662 | 40.0 | 18.8 | 21.2 |
| 1944 | |||||||
| 1945 | |||||||
| 1946 | |||||||
| 1947 | 6 294 | 241 071 | 114 000 | 127 000 | 38.3 | 18.1 | 20.2 |
| 1948 | 6 648 | 264 000 | 95 000 | 169 000 | 39.7 | 14.3 | 25.4 |
| 1949 | 7 099 | 300 843 | 93 000 | 208 000 | 42.4 | 13.1 | 29.3 |
| 1950 | 7 468 | 323 643 | 86 000 | 238 000 | 43.4 | 11.5 | 31.9 |
| 1951 | 7 695 | 385 383 | 89 000 | 296 000 | 50.0 | 11.6 | 38.5 |
| 1952 | 8 000 | 372 905 | 79 000 | 294 000 | 46.6 | 9.9 | 36.8 |
| 1953 | 8 297 | 374 536 | 78 000 | 297 000 | 45.2 | 9.4 | 35.8 |
| 1954 | 8 617 | 383 574 | 71 000 | 313 000 | 44.6 | 8.2 | 36.3 |
| 1955 | 8 924 | 403 683 | 77 000 | 327 000 | 45.3 | 8.6 | 36.6 |
| 1956 | 9 242 | 414 036 | 74 000 | 340 000 | 44.8 | 8.0 | 36.8 |
| 1957 | 9 539 | 394 870 | 81 000 | 314 000 | 41.4 | 8.5 | 32.9 |
| 1958 | 9 858 | 410 885 | 75 000 | 336 000 | 41.7 | 7.6 | 34.1 |
| 1959 | 10 227 | 421 458 | 74 000 | 347 000 | 41.2 | 7.2 | 33.9 |
| 1960 | 10 602 | 419 442 | 74 000 | 345 000 | 39.5 | 7.0 | 32.5 |
| 1961 | 10 983 | 420 254 | 74 000 | 346 254 | 38.3 | 6.7 | 31.5 |
| 1962 | 11 312 | 423 469 | 72 000 | 351 469 | 37.4 | 6.4 | 31.1 |
| 1963 | 11 680 | 424 250 | 71 000 | 353 250 | 36.3 | 6.1 | 30.2 |
| 1964 | 12 088 | 416 926 | 69 000 | 347 926 | 34.5 | 5.7 | 28.8 |
| 1965 | 12 442 | 406 604 | 67 887 | 338 717 | 32.7 | 5.5 | 27.2 |
| 1966 | 12 812 | 415 108 | 69 778 | 345 330 | 32.4 | 5.4 | 27.0 |
| 1967 | 13 147 | 374 282 | 71 861 | 302 421 | 28.5 | 5.5 | 23.0 |
| 1968 | 13 474 | 394 260 | 73 650 | 320 610 | 29.3 | 5.5 | 23.8 |
| 1969 | 13 995 | 390 728 | 70 549 | 320 179 | 27.9 | 5.0 | 22.9 |
| 1970 | 14 507 | 394 015 | 71 135 | 322 883 | 27.2 | 4.9 | 22.3 |
| 1971 | 14 837 | 380 424 | 70 954 | 309 470 | 25.6 | 4.8 | 20.9 |
| 1972 | 15 145 | 365 749 | 71 486 | 294 263 | 24.1 | 4.7 | 19.4 |
| 1973 | 15 424 | 366 942 | 73 477 | 293 465 | 23.8 | 4.8 | 19.0 |
| 1974 | 15 699 | 355 933 | 74 760 | 293 063 | 23.4 | 4.8 | 18.7 |
| 1975 | 15 999 | 357 653 | 75 061 | 292 586 | 23.0 | 4.7 | 18.3 |
| 1976 | 16 298 | 424 075 | 77 000 | 347 075 | 26.0 | 4.7 | 21.3 |
| 1977 | 16 601 | 393 633 | 79 000 | 316 796 | 23.7 | 4.8 | 19.1 |
| 1978 | 16 951 | 411 637 | 79 000 | 330 203 | 24.3 | 4.7 | 19.5 |
| 1979 | 17 337 | 421 720 | 82 000 | 340 518 | 24.3 | 4.7 | 19.6 |
| 1980 | 17 608 | 413 881 | 84 333 | 329 548 | 23.5 | 4.8 | 18.7 |
| 1981 | 17 972 | 414 069 | 87 192 | 326 877 | 23.0 | 4.9 | 18.2 |
| 1982 | 18 261 | 405 263 | 87 578 | 317 685 | 22.2 | 4.8 | 17.4 |
| 1983 | 18 538 | 383 439 | 90 951 | 292 488 | 20.7 | 4.9 | 15.8 |
| 1984 | 18 873 | 371 008 | 89 915 | 281 093 | 19.7 | 4.8 | 14.9 |
| 1985 | 19 135 | 346 208 | 92 348 | 253 860 | 18.1 | 4.8 | 13.3 |
| 1986 | 19 356 | 309 230 | 95 057 | 214 173 | 16.0 | 4.9 | 11.1 |
| 1987 | 19 564 | 314 024 | 96 319 | 217 705 | 16.1 | 4.9 | 11.1 |
| 1988 | 19 788 | 342 031 | 102 113 | 239 918 | 17.3 | 5.2 | 12.1 |
| 1989 | 20 004 | 315 299 | 103 288 | 212 011 | 15.8 | 5.2 | 10.6 |
| 1990 | 20 230 | 335 618 | 105 669 | 229 949 | 16.6 | 5.2 | 11.4 |
| 1991 | 20 455 | 321 932 | 106 284 | 215 648 | 15.7 | 5.2 | 10.5 |
| 1992 | 20 655 | 321 632 | 110 516 | 211 116 | 15.6 | 5.4 | 10.2 |
| 1993 | 20 848 | 325 613 | 110 901 | 214 712 | 15.6 | 5.3 | 10.3 |
| 1994 | 21 087 | 322 938 | 113 866 | 209 072 | 15.3 | 5.4 | 9.9 |
| 1995 | 21 268 | 329 581 | 119 112 | 210 469 | 15.5 | 5.6 | 9.9 |
| 1996 | 21 441 | 325 545 | 122 489 | 203 056 | 15.2 | 5.7 | 9.5 |
| 1997 | 21 634 | 326 002 | 121 000 | 205 002 | 15.1 | 5.6 | 9.5 |
| 1998 | 21 836 | 271 450 | 123 180 | 148 270 | 12.4 | 5.6 | 6.8 |
| 1999 | 22 011 | 283 661 | 126 113 | 157 548 | 12.9 | 5.7 | 7.2 |
| 2000 | 22 185 | 305 312 | 125 957 | 179 355 | 13.8 | 5.7 | 8.1 |
| 2001 | 22 342 | 260 354 | 127 647 | 132 707 | 11.7 | 5.7 | 5.9 |
| 2002 | 22 464 | 247 530 | 128 636 | 118 894 | 11.0 | 5.7 | 5.3 |
| 2003 | 22 554 | 227 070 | 130 801 | 96 269 | 10.1 | 5.8 | 4.3 |
| 2004 | 22 647 | 216 419 | 135 092 | 81 327 | 9.6 | 6.0 | 3.6 |
| 2005 | 22 730 | 205 854 | 139 398 | 66 456 | 9.1 | 6.1 | 2.9 |
| 2006 | 22 824 | 204 459 | 135 839 | 68 620 | 9.0 | 6.0 | 3.0 |
| 2007 | 22 918 | 204 414 | 141 111 | 63 303 | 8.9 | 6.2 | 2.8 |
| 2008 | 22 998 | 198 733 | 143 624 | 55 109 | 8.6 | 6.2 | 2.4 |
| 2009 | 23 079 | 191 310 | 143 582 | 47 728 | 8.3 | 6.2 | 2.1 |
| 2010 | 23 141 | 166 886 | 145 772 | 21 114 | 7.2 | 6.3 | 0.9 |
Fertility rate
The fertility rate of Taiwan is one of the lowest fertility rates ever recorded in the world in historical times. It reached its lowest level in 2010: 0.90 children per female. In 1980, the rate was still well above replacement level (2.515), but it dropped to 1.88 in 1985, 1.81 in 1990, 1.78 in 1995, 1.68 in 2000, 1.12 in 2005.Infant mortality rate
- total: 6.29 deaths/1,000 live births
- male: 6.97 deaths/1,000 live births
- female: 5.55 deaths/1,000 live births (2006 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
Taiwan is ranked 51st in the world for highest life expectancy at birth.| Gender | Life expectancy in 2009 |
|---|---|
| Male | 75.88 years |
| Female | 82.46 years |
HIV/AIDS
The first reported case of HIV/AIDS was recorded in December 1984 and the first local infection recorded in February 1986. As of May 2006, there were 11,486 recorded cases of HIVHIV
Human immunodeficiency virus is a lentivirus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome , a condition in humans in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive...
of which 2,631 were confirmed with AIDS
AIDS
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is a disease of the human immune system caused by the human immunodeficiency virus...
. There were 1,425 deaths leaving 10,029 people living with HIV/AIDS. This is less than 0.5% of the total population of Taiwan. Statistics by the Center for Disease Control show that the gender distribution of infected person was 90% male and 10% female.
| Data | Population |
|---|---|
| Adult prevalence | 11,486 |
| People living with HIV/AIDS | 10,029 |
| Deaths | 1,425 |
- Source: Center for Disease Control (CDC), Republic of China - May 2006 est.(PDF file)
Military manpower
The Republic of China has a compulsory military draftConscription
Conscription is the compulsory enlistment of people in some sort of national service, most often military service. Conscription dates back to antiquity and continues in some countries to the present day under various names...
for males aged 19–35 years of age with a service obligation of 12 months in 2008.
Available manpower
Defined as 19–49 years of age.| Gender | Population |
|---|---|
| Male | 5,883,828 |
| Female | 5,680,773 |
| Total | 11,564,601 |
Fit for military service
Of the available manpower, the following are fit for military service. Defined as 19–49 years of age.| Gender | Population |
|---|---|
| Male | 4,749,537 |
| Female | 4,644,607 |
| Total | 9,394,144 |
Education
Taiwan has a nine-year compulsory educationCompulsory education
Compulsory education refers to a period of education that is required of all persons.-Antiquity to Medieval Era:Although Plato's The Republic is credited with having popularized the concept of compulsory education in Western intellectual thought, every parent in Judea since Moses's Covenant with...
program initiated by the Ministry of Education in 1968. This consists of six years in elementary education and three years in junior high education. About 94.7% of junior high graduates continue their studies in either a senior high or vocational school . Reflecting a strong commitment to education, in FY 2001 16% of the ROC budget was allocated for education . The enrollment rate was 96.77% for the school year 2004-2005. For the school year 2005-2006, there were 5,283,855 students in both public and private schools, about a quarter of the entire population. The literacy rate is above 95%.
Taiwan has an extensive higher education system with more than 100 institutions of higher learning. Each year over 100,000 students take the joint college entrance exam; about 66.6% of the candidates are admitted to a college or university. Opportunities for graduate education are expanding in Taiwan, but many students travel abroad for advanced education, including 13,000 who study in the United States annually .
Since the mid-1990s, the government has introduced several education reforms in a bid to further improve education standards such as the replacement in 2002 of the 48-year long Joint University Entrance Examination (JUEE; 大學聯考; Dàxué liánkǎo) which had been set up in 1954.
Distribution of students
| Sector | Education | Years of study | Typical Age range | Students | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-school | Kindergarten | (2 years) | 4–6 years old | 224,220 | 4.2% |
| Compulsory | Elementary | 6 years | 6–12 years old | 1,831,913 | 34.7% |
| Junior High | 3 years | 12–15 years old | 951,236 | 18% | |
| Senior Secondary | Senior High | 3 years | 15–18 years old | 420,608 | 8% |
| Senior Vocation | 3 years | 15–18 years old | 331,604 | 6.3% | |
| Higher Education | Junior College | 2–5 years | 15–20 years old | 37,068 | 0.7% |
| University & College | 4–7 years (up to 13 years) |
18–25 years old (up to 31 years old) |
1,259,490 | 23.8% | |
| Other | Special School | up to 14 years | 4–18 years old | 6,361 | 0.1% |
| Supplementary School | n/a | n/a | 200,573 | 3.8% | |
| Open University | n/a | n/a | 20,782 | 0.4% | |
| Total | 5,283,855 | 100% |
- Source: Number of students at each level (SY 2005-2006), Ministry of Education, Republic of China.
Literacy
Definition of literacy is those aged 15 and over who can read and write.| Gender | Population |
|---|---|
| Male | n/a |
| Female | n/a |
| Total | n/a |
| Literacy rate | 96.1% |
- Source: CIA World Factbook (2003 est.)

