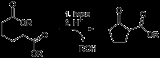
Dieckmann condensation
Overview
Intramolecular
Intramolecular in chemistry describes a process or characteristic limited within the structure of a single molecule, a property or phenomenon limited to the extent of a single molecule.- Examples :...
chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
of diester
Ester
Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...
s with base to give β-ketoesters. It is named after the German chemist Walter Dieckmann
Walter Dieckmann
Walter Dieckmann was a German chemist.Dieckmann studied at the University of Munich and became assisatant of Adolf von Baeyer....
(1869–1925). The equivalent intermolecular reaction is the Claisen condensation
Claisen condensation
The Claisen condensation is a carbon–carbon bond forming reaction that occurs between two esters or one ester and another carbonyl compound in the presence of a strong base, resulting in a β-keto ester or a β-diketone...
.
The acidic hydrogen between the two carbonyl
Carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups....
groups is deprotonated in step four. Protonation with a Brønsted-Lowry acid (H3O+ for example) re-forms the β-keto ester.
Unanswered Questions
Discussions

