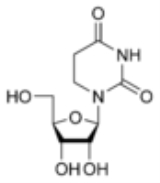
Dihydrouridine
Encyclopedia
Dihydrouridine is a pyrimidine
which is the result of adding two hydrogen
atoms to a uridine
, making it a fully saturated pyrimidine ring with no remaining double bonds. D is found in tRNA and rRNA molecules as a nucleoside
; the corresponding nucleobase
is 5,6-Dihydrouracil.
Because it is non-planar, D disturbs the stacking interactions in helices and destabilizes the RNA structure. D also stabilizes the C2’-endo sugar conformation, which is more flexible then the C3’-endo conformation, and this effect is propagated to the 5’-neighboring residue. Thus, while pseudouridine
and 2’-O-methylations stabilize the local RNA structure
, D does the opposite.
tRNA of organisms that grow at low temperatures (psychrophiles) have high 5,6-dihydrouridine levels (40-70% more on average) which provides the necessary, local, flexibility of the tRNA at or below the freezing point.
Pyrimidine
Pyrimidine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound similar to benzene and pyridine, containing two nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 of the six-member ring...
which is the result of adding two hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
atoms to a uridine
Uridine
Uridine is a molecule that is formed when uracil is attached to a ribose ring via a β-N1-glycosidic bond.If uracil is attached to a deoxyribose ring, it is known as a deoxyuridine....
, making it a fully saturated pyrimidine ring with no remaining double bonds. D is found in tRNA and rRNA molecules as a nucleoside
Nucleoside
Nucleosides are glycosylamines consisting of a nucleobase bound to a ribose or deoxyribose sugar via a beta-glycosidic linkage...
; the corresponding nucleobase
Nucleobase
Nucleobases are a group of nitrogen-based molecules that are required to form nucleotides, the basic building blocks of DNA and RNA. Nucleobases provide the molecular structure necessary for the hydrogen bonding of complementary DNA and RNA strands, and are key components in the formation of stable...
is 5,6-Dihydrouracil.
Because it is non-planar, D disturbs the stacking interactions in helices and destabilizes the RNA structure. D also stabilizes the C2’-endo sugar conformation, which is more flexible then the C3’-endo conformation, and this effect is propagated to the 5’-neighboring residue. Thus, while pseudouridine
Pseudouridine
Pseudouridine is the C-glycoside isomer of the nucleoside uridine, and it is the most prevalent of the over one hundred different modified nucleosides found in RNA. Ψ is found in all species and in many classes of RNA except mRNA...
and 2’-O-methylations stabilize the local RNA structure
RNA structure
Biomolecular structure is the structure of biomolecules, mainly proteins and the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. The structure of these molecules is frequently decomposed into primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure, and quaternary structure. The scaffold for this structure is...
, D does the opposite.
tRNA of organisms that grow at low temperatures (psychrophiles) have high 5,6-dihydrouridine levels (40-70% more on average) which provides the necessary, local, flexibility of the tRNA at or below the freezing point.

