
Dimer
Encyclopedia
Monomer
A monomer is an atom or a small molecule that may bind chemically to other monomers to form a polymer; the term "monomeric protein" may also be used to describe one of the proteins making up a multiprotein complex...
s joined by bonds that can be either strong or weak.
Organic chemistry
Molecular dimers are often formed by the reaction of two identical compounds e.g.: 2A → A-A. In this example, monomerMonomer
A monomer is an atom or a small molecule that may bind chemically to other monomers to form a polymer; the term "monomeric protein" may also be used to describe one of the proteins making up a multiprotein complex...
"A" is said to dimerise to give the dimer "A-A". An example is Diaminocarbenes, which dimerise to give tetraaminoethylene
Tetraaminoethylene
Tetraaminoethylene is a hypothetical organic compound with formula C2N4H8 or 2C=C2. Like all geminal polyamines, this compound has never been synthesised and is believed to be extremely unstable....
s:
- 2 C(NR2)2 → (R2N)2C=C(NR2)2
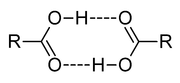
Acetic acid
Acetic acid
Acetic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CO2H . It is a colourless liquid that when undiluted is also called glacial acetic acid. Acetic acid is the main component of vinegar , and has a distinctive sour taste and pungent smell...
forms a dimer in the gas phase, the monomer units are held together by hydrogen bond
Hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is the attractive interaction of a hydrogen atom with an electronegative atom, such as nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine, that comes from another molecule or chemical group. The hydrogen must be covalently bonded to another electronegative atom to create the bond...
s. Under special conditions, most OH-containing molecules form dimers, e.g. the water dimer
Water dimer
The water dimer consists of two water molecules loosely bound by a hydrogen bond. It is the smallest water cluster. Because it is the simplest model system for studying hydrogen bonding in water, it has been the target of so many theoretical studies that it has been called "a theoretical Guinea...
.
Dicyclopentadiene
Dicyclopentadiene
Dicyclopentadiene, abbreviated DCPD, is a chemical compound with formula C10H12. At room temperature, it is a white crystalline solid with a camphor-like odor. Its energy density is 10,975 Wh/l....
is an unsymmetrical dimer of two cyclopentadiene
Cyclopentadiene
Cyclopentadiene is an organic compound with the formula C5H6. This colorless liquid has a strong and unpleasant odor. At room temperature, this cyclic diene dimerizes over the course of hours to give dicyclopentadiene via a Diels–Alder reaction...
molecules that have reacted in a Diels-Alder reaction
Diels-Alder reaction
The Diels–Alder reaction is an organic chemical reaction between a conjugated diene and a substituted alkene, commonly termed the dienophile, to form a substituted cyclohexene system. The reaction can proceed even if some of the atoms in the newly formed ring are not carbon...
to give the product. Upon heating, it "cracks" (undergoes a retro-Diels-Alder reaction) to give identical monomers:
- C10H12 → 2 C5H6
The term homodimer is used when the two molecules are identical (e.g. A-A) and heterodimer when they are not (e.g. A-B). The reverse of dimerisation is often called dissociation
Dissociation (chemistry)
Dissociation in chemistry and biochemistry is a general process in which ionic compounds separate or split into smaller particles, ions, or radicals, usually in a reversible manner...
.

