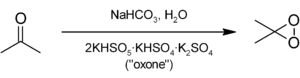Dimethyldioxirane
Encyclopedia
Dimethyldioxirane is a dioxirane
derived from acetone
. It is the most commonly used dioxirane
in organic synthesis
.
is the active ingredient:
The preparation of DMDO is rather inefficient (typical yields < 3%) and typically only yields a relatively dilute solution in acetone (approximately 0.15 M). However, this is of no consequence, since DMDO is prepared from extremely cheap starting materials: acetone
, sodium bicarbonate
, and potassium peroxymonosulfate
(commercially known as "oxone"). A freshly prepared solution of DMDO in acetone will last approximately one to two weeks in the freezer. Frequent titrations (typically by 1H NMR with thioanisole) are required.
s. One particular advantage of using DMDO is that the only byproduct of oxidation is acetone, a fairly innocuous and volatile compound. DMDO oxidations are particularly mild, sometimes allowing oxidations which might not otherwise be possible. In fact, DMDO is considered the reagent of choice for epoxidation, and in nearly all circumstances is as good as or better than peroxyacids such as meta-Chloroperoxybenzoic acid
(m-CPBA).
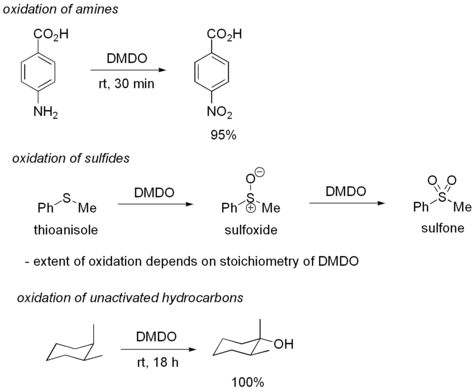
Despite its high reactivity, DMDO displays good selectivity for olefins. Typically, electron deficient olefins are oxidized more slowly than electron rich ones. DMDO will also oxidize several other functional groups. For example, DMDO will oxidize primary amine
s to nitro compound
s and sulfide
s to sulfoxide
s. In some cases, DMDO will even oxidize unactivated C-H bonds:
DMDO can also be used to convert nitro compound
s to carbonyl compounds (Nef reaction
).
Dioxirane
A dioxirane is a molecule containing a three-membered ring composed of one carbon and two oxygens. Somewhat unstable, they are used in organic synthesis as oxidizing reagents. The only dioxirane in common use is dimethyldioxirane , the oxirane derived from acetone....
derived from acetone
Acetone
Acetone is the organic compound with the formula 2CO, a colorless, mobile, flammable liquid, the simplest example of the ketones.Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important solvent in its own right, typically as the solvent of choice for cleaning purposes in the laboratory...
. It is the most commonly used dioxirane
Dioxirane
A dioxirane is a molecule containing a three-membered ring composed of one carbon and two oxygens. Somewhat unstable, they are used in organic synthesis as oxidizing reagents. The only dioxirane in common use is dimethyldioxirane , the oxirane derived from acetone....
in organic synthesis
Organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the construction of organic compounds via organic reactions. Organic molecules can often contain a higher level of complexity compared to purely inorganic compounds, so the synthesis of organic compounds has...
.
Synthesis
DMDO is not commercially available because of its instability. DMDO can be prepared by the reaction of acetone with oxone, where the potassium peroxymonosulfatePotassium peroxymonosulfate
Potassium peroxymonosulfate is widely used as an oxidizing agent...
is the active ingredient:
The preparation of DMDO is rather inefficient (typical yields < 3%) and typically only yields a relatively dilute solution in acetone (approximately 0.15 M). However, this is of no consequence, since DMDO is prepared from extremely cheap starting materials: acetone
Acetone
Acetone is the organic compound with the formula 2CO, a colorless, mobile, flammable liquid, the simplest example of the ketones.Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important solvent in its own right, typically as the solvent of choice for cleaning purposes in the laboratory...
, sodium bicarbonate
Sodium bicarbonate
Sodium bicarbonate or sodium hydrogen carbonate is the chemical compound with the formula Na HCO3. Sodium bicarbonate is a white solid that is crystalline but often appears as a fine powder. It has a slightly salty, alkaline taste resembling that of washing soda . The natural mineral form is...
, and potassium peroxymonosulfate
Potassium peroxymonosulfate
Potassium peroxymonosulfate is widely used as an oxidizing agent...
(commercially known as "oxone"). A freshly prepared solution of DMDO in acetone will last approximately one to two weeks in the freezer. Frequent titrations (typically by 1H NMR with thioanisole) are required.
Uses
The most common use for DMDO is the oxidation of alkenes to epoxideEpoxidation with dioxiranes
Epoxidation with dioxiranes refers to the synthesis of epoxides from alkenes using three-membered cyclic peroxides, also known as dioxiranes.Dioxiranes are three-membered cyclic peroxides containing a weak oxygen-oxygen bond. Although they are able to effect oxidations of heteroatom functionality...
s. One particular advantage of using DMDO is that the only byproduct of oxidation is acetone, a fairly innocuous and volatile compound. DMDO oxidations are particularly mild, sometimes allowing oxidations which might not otherwise be possible. In fact, DMDO is considered the reagent of choice for epoxidation, and in nearly all circumstances is as good as or better than peroxyacids such as meta-Chloroperoxybenzoic acid
Meta-Chloroperoxybenzoic acid
meta-Chloroperoxybenzoic acid is a peroxycarboxylic acid used widely as an oxidant in organic synthesis. mCPBA is often preferred to other peroxy acids because of its relative ease of handling...
(m-CPBA).
Despite its high reactivity, DMDO displays good selectivity for olefins. Typically, electron deficient olefins are oxidized more slowly than electron rich ones. DMDO will also oxidize several other functional groups. For example, DMDO will oxidize primary amine
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
s to nitro compound
Nitro compound
Nitro compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups . They are often highly explosive, especially when the compound contains more than one nitro group and is impure. The nitro group is one of the most common explosophores used globally...
s and sulfide
Sulfide
A sulfide is an anion of sulfur in its lowest oxidation state of 2-. Sulfide is also a slightly archaic term for thioethers, a common type of organosulfur compound that are well known for their bad odors.- Properties :...
s to sulfoxide
Sulfoxide
A sulfoxide is a chemical compound containing a sulfinyl functional group attached to two carbon atoms. Sulfoxides can be considered as oxidized sulfides...
s. In some cases, DMDO will even oxidize unactivated C-H bonds:
DMDO can also be used to convert nitro compound
Nitro compound
Nitro compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups . They are often highly explosive, especially when the compound contains more than one nitro group and is impure. The nitro group is one of the most common explosophores used globally...
s to carbonyl compounds (Nef reaction
Nef reaction
The Nef reaction is an organic reaction describing the acid hydrolysis of a salt of a primary or secondary nitroalkane to an aldehyde or a ketone and nitrous oxide ....
).