
Dini test
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, the Dini and Dini-Lipschitz tests are highly precise tests that can be used to prove that the Fourier series
of a function
converges at a given point. These tests are named after Ulisse Dini and Rudolf Lipschitz
.
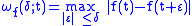
Notice that we consider here f to be a periodic function, e.g. if t = 0 and ε is negative then we define f(ε) = f(2π + ε).
The global modulus of continuity (or simply the modulus of continuity
) is defined by
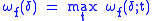
With these definitions we may state the main results
Theorem (Dini's test): Assume a function f satisfies at a point t that
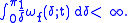
Then the Fourier series of f converges at t to f(t).
For example, the theorem holds with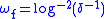 but does not hold with
but does not hold with 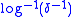 .
.
Theorem (the Dini-Lipschitz test): Assume a function f satisfies
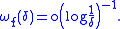
Then the Fourier series of f converges uniformly to f.
In particular, any function of a Hölder class satisfies the Dini-Lipschitz test.
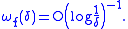
and the Fourier series of f diverges. For the Dini test, the statement of precision is slightly longer: it says that for any function Ω such that
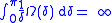
there exists a function f such that
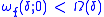
and the Fourier series of f diverges at 0.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, the Dini and Dini-Lipschitz tests are highly precise tests that can be used to prove that the Fourier series
Fourier series
In mathematics, a Fourier series decomposes periodic functions or periodic signals into the sum of a set of simple oscillating functions, namely sines and cosines...
of a function
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function associates one quantity, the argument of the function, also known as the input, with another quantity, the value of the function, also known as the output. A function assigns exactly one output to each input. The argument and the value may be real numbers, but they can...
converges at a given point. These tests are named after Ulisse Dini and Rudolf Lipschitz
Rudolf Lipschitz
Rudolf Otto Sigismund Lipschitz was a German mathematician and professor at the University of Bonn from 1864. Peter Gustav Dirichlet was his teacher. He supervised the early work of Felix Klein....
.
Definition
Let f be a function on [0,2π], let t be some point and let δ be a positive number. We define the local modulus of continuity at the point t by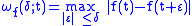
Notice that we consider here f to be a periodic function, e.g. if t = 0 and ε is negative then we define f(ε) = f(2π + ε).
The global modulus of continuity (or simply the modulus of continuity
Modulus of continuity
In mathematical analysis, a modulus of continuity is a function\omega:[0,\infty]\to[0,\infty]used to measure quantitatively the uniform continuity of functions. So, a function f:I\to\R admits \omega as a modulus of continuity if and only if|f-f|\leq\omega,for all x and y in the domain of f...
) is defined by
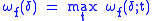
With these definitions we may state the main results
Theorem (Dini's test): Assume a function f satisfies at a point t that
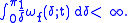
Then the Fourier series of f converges at t to f(t).
For example, the theorem holds with
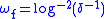 but does not hold with
but does not hold with 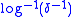 .
.Theorem (the Dini-Lipschitz test): Assume a function f satisfies
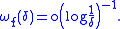
Then the Fourier series of f converges uniformly to f.
In particular, any function of a Hölder class satisfies the Dini-Lipschitz test.
Precision
Both tests are best of their kind. For the Dini-Lipschitz test, it is possible to construct a function f with its modulus of continuity satisfying the test with O instead of o, i.e.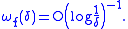
and the Fourier series of f diverges. For the Dini test, the statement of precision is slightly longer: it says that for any function Ω such that
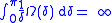
there exists a function f such that
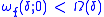
and the Fourier series of f diverges at 0.

