Dinitrogen pentoxide
Encyclopedia
Dinitrogen pentoxide is the chemical compound
with the formula
N2O5. Also known as nitrogen pentoxide, N2O5 is one of the binary nitrogen
oxide
s, a family of compounds that only contain nitrogen and oxygen. It is an unstable and potentially dangerous oxidizer that once was used as a reagent
when dissolved in chloroform
for nitration
s but has largely been superseded by NO2BF4 (nitronium tetrafluoroborate
).
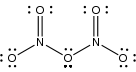
N2O5 is a rare example of a compound that adopts two structures depending on the conditions: most commonly it is a salt, but under some conditions it is a polar molecule:
. A recommended laboratory synthesis entails dehydrating nitric acid
(HNO3) with phosphorus(V) oxide
:
In the reverse process, N2O5 reacts with water (hydrolyses
) to produce nitric acid. Thus, nitrogen pentoxide is the anhydride of nitric acid:
N2O5 exists as colourless crystals that sublime slightly above room temperature. The salt eventually decomposes at room temperature into NO2
and O2
.
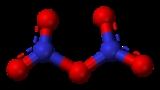
 Solid N2O5 is a salt
Solid N2O5 is a salt
, consisting of separated anions and cations. The cation is the linear nitronium ion NO2+ and the anion is the planar nitrate
NO3− ion. Thus, the solid could be called nitronium nitrate. Both nitrogen
centers have oxidation state +5.
The intact molecule O2N–O–NO2 exists in the gas phase (obtained by subliming N2O5) and when the solid is extracted into nonpolar solvent
s such as CCl4
. In the gas phase, the O–N–O angle is 133° and the N–O–N angle is 114°. When gaseous N2O5 is cooled rapidly ("quenched"), one can obtain the metastable molecular form, which exothermically converts to the ionic form above −70 °C.
, has been used as a reagent to introduce the NO2 functionality. This nitration
reaction is represented as follows:
where Ar represents an arene
moiety.
N2O5 is of interest for the preparation of explosives.
and BF3
). NO2BF4 has been used to nitrate a variety of organic compounds, especially arenes and heterocycles. Interestingly, the reactivity of the NO2+ can be further enhanced with strong acids that generate the "super-electrophile" HNO22+.
salts. The decomposition of dinitrogen pentoxide produces the highly toxic nitrogen dioxide
gas.
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
with the formula
Chemical formula
A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
N2O5. Also known as nitrogen pentoxide, N2O5 is one of the binary nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
oxide
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
s, a family of compounds that only contain nitrogen and oxygen. It is an unstable and potentially dangerous oxidizer that once was used as a reagent
Reagent
A reagent is a "substance or compound that is added to a system in order to bring about a chemical reaction, or added to see if a reaction occurs." Although the terms reactant and reagent are often used interchangeably, a reactant is less specifically a "substance that is consumed in the course of...
when dissolved in chloroform
Chloroform
Chloroform is an organic compound with formula CHCl3. It is one of the four chloromethanes. The colorless, sweet-smelling, dense liquid is a trihalomethane, and is considered somewhat hazardous...
for nitration
Nitration
Nitration is a general chemical process for the introduction of a nitro group into a chemical compound. The dominant application of nitration is for the production of nitrobenzene, the precursor to methylene diphenyl diisocyanate...
s but has largely been superseded by NO2BF4 (nitronium tetrafluoroborate
Nitronium tetrafluoroborate
Nitronium tetrafluoroborate is an inorganic compound with formula NO2BF4. It is a salt of nitronium cation and tetrafluoroborate anion. It is a colorless crystalline solid, which reacts heavily with water to form the corrosive acids HF and HNO3. As such, it must be handled under water-free conditions...
).
N2O5 is a rare example of a compound that adopts two structures depending on the conditions: most commonly it is a salt, but under some conditions it is a polar molecule:
- N2O5 [NO2+][NO3−]
Syntheses and properties
N2O5 was first reported by Deville in 1840, who prepared it by treating AgNO3 with Cl2Chlorine
Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine...
. A recommended laboratory synthesis entails dehydrating nitric acid
Nitric acid
Nitric acid , also known as aqua fortis and spirit of nitre, is a highly corrosive and toxic strong acid.Colorless when pure, older samples tend to acquire a yellow cast due to the accumulation of oxides of nitrogen. If the solution contains more than 86% nitric acid, it is referred to as fuming...
(HNO3) with phosphorus(V) oxide
Phosphorus pentoxide
Phosphorus pentoxide is a chemical compound with molecular formula P4O10 . This white crystalline solid is the anhydride of phosphoric acid. It is a powerful desiccant.-Structure:...
:
- P4O10 + 12 HNO3 → 4 H3PO4 + 6 N2O5
In the reverse process, N2O5 reacts with water (hydrolyses
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction during which molecules of water are split into hydrogen cations and hydroxide anions in the process of a chemical mechanism. It is the type of reaction that is used to break down certain polymers, especially those made by condensation polymerization...
) to produce nitric acid. Thus, nitrogen pentoxide is the anhydride of nitric acid:
- N2O5 + H2O → 2 HNO3
N2O5 exists as colourless crystals that sublime slightly above room temperature. The salt eventually decomposes at room temperature into NO2
Nitrogen dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide is the chemical compound with the formula it is one of several nitrogen oxides. is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of nitric acid, millions of tons of which are produced each year. This reddish-brown toxic gas has a characteristic sharp, biting odor and is a prominent...
and O2
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
.
Structure

Salt
In chemistry, salts are ionic compounds that result from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base. They are composed of cations and anions so that the product is electrically neutral...
, consisting of separated anions and cations. The cation is the linear nitronium ion NO2+ and the anion is the planar nitrate
Nitrate
The nitrate ion is a polyatomic ion with the molecular formula NO and a molecular mass of 62.0049 g/mol. It is the conjugate base of nitric acid, consisting of one central nitrogen atom surrounded by three identically-bonded oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement. The nitrate ion carries a...
NO3− ion. Thus, the solid could be called nitronium nitrate. Both nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
centers have oxidation state +5.
The intact molecule O2N–O–NO2 exists in the gas phase (obtained by subliming N2O5) and when the solid is extracted into nonpolar solvent
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
s such as CCl4
Carbon tetrachloride
Carbon tetrachloride, also known by many other names is the organic compound with the formula CCl4. It was formerly widely used in fire extinguishers, as a precursor to refrigerants, and as a cleaning agent...
. In the gas phase, the O–N–O angle is 133° and the N–O–N angle is 114°. When gaseous N2O5 is cooled rapidly ("quenched"), one can obtain the metastable molecular form, which exothermically converts to the ionic form above −70 °C.
Reactions and applications
Dinitrogen pentoxide, for example as a solution in chloroformChloroform
Chloroform is an organic compound with formula CHCl3. It is one of the four chloromethanes. The colorless, sweet-smelling, dense liquid is a trihalomethane, and is considered somewhat hazardous...
, has been used as a reagent to introduce the NO2 functionality. This nitration
Nitration
Nitration is a general chemical process for the introduction of a nitro group into a chemical compound. The dominant application of nitration is for the production of nitrobenzene, the precursor to methylene diphenyl diisocyanate...
reaction is represented as follows:
- N2O5 + Ar–H → HNO3 + Ar–NO2
where Ar represents an arene
Arene
Arene or Arênê or Arène may refer to:*an aromatic hydrocarbon*Arene , a genus of marine snails in the family Areneidae*Arene , the wife of Aphareus and mother of Idas and Lynceus in Greek mythology...
moiety.
N2O5 is of interest for the preparation of explosives.
NO2BF4
Replacement of the NO3− portion of N2O5 with BF4− gives NO2BF4 (CAS#13826-86-3). This salt retains the high reactivity of NO2+, but it is thermally stable, decomposing at ca. 180°C (into NO2FNitryl fluoride
Nitryl fluoride, NO2F, is a colourless gas and strong oxidizing agent, which is used as an oxidizer in rocket propellants and as a fluorinating agent. It is a molecular species, not ionic, consistent with its low boiling point...
and BF3
Boron trifluoride
Boron trifluoride is the chemical compound with the formula BF3. This pungent colourless toxic gas forms white fumes in moist air. It is a useful Lewis acid and a versatile building block for other boron compounds.-Structure and bonding:...
). NO2BF4 has been used to nitrate a variety of organic compounds, especially arenes and heterocycles. Interestingly, the reactivity of the NO2+ can be further enhanced with strong acids that generate the "super-electrophile" HNO22+.
Hazards
N2O5 is a strong oxidizer that forms explosive mixtures with organic compounds and ammoniumAmmonium
The ammonium cation is a positively charged polyatomic cation with the chemical formula NH. It is formed by the protonation of ammonia...
salts. The decomposition of dinitrogen pentoxide produces the highly toxic nitrogen dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide is the chemical compound with the formula it is one of several nitrogen oxides. is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of nitric acid, millions of tons of which are produced each year. This reddish-brown toxic gas has a characteristic sharp, biting odor and is a prominent...
gas.

