
Diphenyl ether
Encyclopedia
Diphenyl ether is the organic compound
with the formula O
(C
6H
5)2. The molecule is subject to reactions typical of other phenyl rings, including hydroxylation
, nitration
, halogenation
, sulfonation, and Friedel-Crafts alkylation or acylation
. This simple diaryl ether enjoys a variety of niche applications.
It is synthesized by a modification of the Williamson ether synthesis
, here the reaction of phenol
and bromobenzene in the presence of base
and a catalytic
amount of copper
:
Involving similar reactions, diphenyl ether is a significant side product in the high-pressure hydrolysis
of chlorobenzene
in the production of phenol.
, used as a heat transfer
medium. Such a mixture is well-suited for heat transfer applications because of the relatively large temperature range of its liquid state.
Diphenyl ether is a starting material in the production of phenoxathiin via the Ferrario reaction. Phenoxathiin is used in polyamide
and polyimide
production.
Because of its odor reminiscent of scented geranium, as well as its stability and low price, diphenyl ether is used widely in soap perfumes. Diphenyl ether is also used as a processing aid in the production of polyester
s.
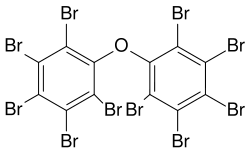
Several polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) are useful flame retardants. Of penta-, octa-, and decaBDE, the three most common PBDEs, only decaBDE is still in widespread use since its ban in the European Union in 2003. DecaBDE, also known as decabromodiphenyl oxide, is a high-volume industrial chemical with over 450,000 kilograms produced annually in the United States. Decabromodiphenyl oxide is sold under the trade name Saytex 102 as a flame retardant in the manufacture of paints and reinforced plastics.
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
with the formula O
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
(C
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
6H
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
5)2. The molecule is subject to reactions typical of other phenyl rings, including hydroxylation
Hydroxylation
Hydroxylation is a chemical process that introduces a hydroxyl group into an organic compound. In biochemistry, hydroxylation reactions are often facilitated by enzymes called hydroxylases. Hydroxylation is the first step in the oxidative degradation of organic compounds in air...
, nitration
Nitration
Nitration is a general chemical process for the introduction of a nitro group into a chemical compound. The dominant application of nitration is for the production of nitrobenzene, the precursor to methylene diphenyl diisocyanate...
, halogenation
Halogenation
Halogenation is a chemical reaction that incorporates a halogen atom into a molecule in substitution of hydrogen atom. Halogenation takes place in the gas phase. There are four types of halogenation: fluorination, chlorination, bromination, and iodination...
, sulfonation, and Friedel-Crafts alkylation or acylation
Friedel-Crafts reaction
The Friedel–Crafts reactions are a set of reactions developed by Charles Friedel and James Crafts in 1877. There are two main types of Friedel–Crafts reactions: alkylation reactions and acylation reactions. This reaction type is a form of electrophilic aromatic substitution...
. This simple diaryl ether enjoys a variety of niche applications.
Synthesis
Diphenyl ether and many of its properties were first reported as early as 1901.It is synthesized by a modification of the Williamson ether synthesis
Williamson ether synthesis
The Williamson ether synthesis is an organic reaction, forming an ether from an organohalide and an alcohol. This reaction was developed by Alexander Williamson in 1850. Typically it involves the reaction of an alkoxide ion with a primary alkyl halide via an SN2 reaction...
, here the reaction of phenol
Phenol
Phenol, also known as carbolic acid, phenic acid, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5OH. It is a white crystalline solid. The molecule consists of a phenyl , bonded to a hydroxyl group. It is produced on a large scale as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds...
and bromobenzene in the presence of base
Base (chemistry)
For the term in genetics, see base A base in chemistry is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions or more generally, donate electron pairs. A soluble base is referred to as an alkali if it contains and releases hydroxide ions quantitatively...
and a catalytic
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
amount of copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
:
- PhONa + PhBr → PhOPh + NaBr
Involving similar reactions, diphenyl ether is a significant side product in the high-pressure hydrolysis
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction during which molecules of water are split into hydrogen cations and hydroxide anions in the process of a chemical mechanism. It is the type of reaction that is used to break down certain polymers, especially those made by condensation polymerization...
of chlorobenzene
Chlorobenzene
Chlorobenzene is an aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5Cl. This colorless, flammable liquid is a common solvent and a widely used intermediate in the manufacture of other chemicals.-Uses:...
in the production of phenol.
Uses
The main application of diphenyl ether is as a eutectic mixture with biphenylBiphenyl
Biphenyl is an organic compound that forms colorless crystals. It has a distinctively pleasant smell. Biphenyl is an aromatic hydrocarbon with a molecular formula 2...
, used as a heat transfer
Heat transfer
Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the exchange of thermal energy from one physical system to another. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as heat conduction, convection, thermal radiation, and phase-change transfer...
medium. Such a mixture is well-suited for heat transfer applications because of the relatively large temperature range of its liquid state.
Diphenyl ether is a starting material in the production of phenoxathiin via the Ferrario reaction. Phenoxathiin is used in polyamide
Polyamide
A polyamide is a polymer containing monomers of amides joined by peptide bonds. They can occur both naturally and artificially, examples being proteins, such as wool and silk, and can be made artificially through step-growth polymerization or solid-phase synthesis, examples being nylons, aramids,...
and polyimide
Polyimide
Polyimide is a polymer of imide monomers. The structure of imide is as shown. Polyimides have been in mass production since 1955...
production.
Because of its odor reminiscent of scented geranium, as well as its stability and low price, diphenyl ether is used widely in soap perfumes. Diphenyl ether is also used as a processing aid in the production of polyester
Polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers which contain the ester functional group in their main chain. Although there are many polyesters, the term "polyester" as a specific material most commonly refers to polyethylene terephthalate...
s.
Several polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) are useful flame retardants. Of penta-, octa-, and decaBDE, the three most common PBDEs, only decaBDE is still in widespread use since its ban in the European Union in 2003. DecaBDE, also known as decabromodiphenyl oxide, is a high-volume industrial chemical with over 450,000 kilograms produced annually in the United States. Decabromodiphenyl oxide is sold under the trade name Saytex 102 as a flame retardant in the manufacture of paints and reinforced plastics.


