Diphosphorus
Encyclopedia
Diphosphorus, P2, is the diatomic
form of phosphorus
. Unlike its nitrogen group
neighbor nitrogen
, which forms a stable N2 molecule with a nitrogen to nitrogen triple bond
, phosphorus prefers a tetrahedral form P4 because P-P pi-bonds are high in energy. Diphosphorus is, therefore, very reactive with a bond-dissociation energy (117 kcal
/mol
or 490 kJ/mol) half that of dinitrogen.
Diphosphorus has been generated by heating white phosphorus at 1100 kelvin
s. Nevertheless, some advancements have been obtained in generating the diatomic molecule in homogeneous solution, under normal conditions with the use by some transition metal
complexes
(based on, for example, tungsten
and niobium
).
The molecule attracted attention in 2006, when a new method for its synthesis at milder temperatures emerged.
This method is a variation on nitrogen expulsion in azide
s with formation of a nitrene
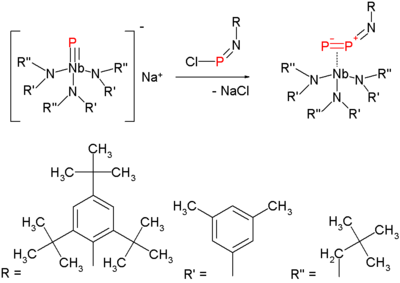
. The synthesis of the diphosphorus precursor consists of reacting a terminal niobium
phosphide
with a chloroiminophosphane:
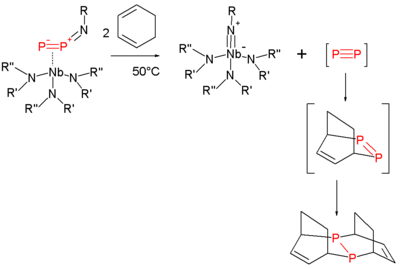
Heating this compound at 50 °C in 1,3-cyclohexadiene
serving as a solvent
and as a trapping reagent expulses diphosphorus, which is reactive, as it is forms a double Diels-Alder adduct
and the niobium imido compound:
The same imido compound also forms when the thermolysis is performed in toluene
but then the fate of diphosphorus is unknown.
P2 has been suggested to form as an intermediate in the photolysis of P4 and in the presence of 2,3-dimethylbutadiene the diphosphane is again formed To date, no direct evidence of P2 formation via P4 photolysis exists.
Diatomic
Diatomic molecules are molecules composed only of two atoms, of either the same or different chemical elements. The prefix di- means two in Greek. Common diatomic molecules are hydrogen , nitrogen , oxygen , and carbon monoxide . Seven elements exist in the diatomic state in the liquid and solid...
form of phosphorus
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks...
. Unlike its nitrogen group
Nitrogen group
The nitrogen group is a periodic table group consisting of nitrogen , phosphorus , arsenic , antimony , bismuth and ununpentium ....
neighbor nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
, which forms a stable N2 molecule with a nitrogen to nitrogen triple bond
Triple bond
A triple bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two chemical elements involving six bonding electrons instead of the usual two in a covalent single bond. The most common triple bond, that between two carbon atoms, can be found in alkynes. Other functional groups containing a triple bond are...
, phosphorus prefers a tetrahedral form P4 because P-P pi-bonds are high in energy. Diphosphorus is, therefore, very reactive with a bond-dissociation energy (117 kcal
Calorie
The calorie is a pre-SI metric unit of energy. It was first defined by Nicolas Clément in 1824 as a unit of heat, entering French and English dictionaries between 1841 and 1867. In most fields its use is archaic, having been replaced by the SI unit of energy, the joule...
/mol
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
or 490 kJ/mol) half that of dinitrogen.
Diphosphorus has been generated by heating white phosphorus at 1100 kelvin
Kelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
s. Nevertheless, some advancements have been obtained in generating the diatomic molecule in homogeneous solution, under normal conditions with the use by some transition metal
Transition metal
The term transition metal has two possible meanings:*The IUPAC definition states that a transition metal is "an element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell." Group 12 elements are not transition metals in this definition.*Some...
complexes
Complex (chemistry)
In chemistry, a coordination complex or metal complex, is an atom or ion , bonded to a surrounding array of molecules or anions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents...
(based on, for example, tungsten
Tungsten
Tungsten , also known as wolfram , is a chemical element with the chemical symbol W and atomic number 74.A hard, rare metal under standard conditions when uncombined, tungsten is found naturally on Earth only in chemical compounds. It was identified as a new element in 1781, and first isolated as...
and niobium
Niobium
Niobium or columbium , is a chemical element with the symbol Nb and atomic number 41. It's a soft, grey, ductile transition metal, which is often found in the pyrochlore mineral, the main commercial source for niobium, and columbite...
).
The molecule attracted attention in 2006, when a new method for its synthesis at milder temperatures emerged.
This method is a variation on nitrogen expulsion in azide
Azide
Azide is the anion with the formula N3−. It is the conjugate base of hydrazoic acid. N3− is a linear anion that is isoelectronic with CO2 and N2O. Per valence bond theory, azide can be described by several resonance structures, an important one being N−=N+=N−...
s with formation of a nitrene
Nitrene
In chemistry, a nitrene is the nitrogen analogue of a carbene. The nitrogen atom has only 6 valence electrons and is therefore considered an electrophile...
. The synthesis of the diphosphorus precursor consists of reacting a terminal niobium
Niobium
Niobium or columbium , is a chemical element with the symbol Nb and atomic number 41. It's a soft, grey, ductile transition metal, which is often found in the pyrochlore mineral, the main commercial source for niobium, and columbite...
phosphide
Phosphide
In chemistry, a phosphide is a compound of phosphorus with a less electronegative element or elements. Binary compounds are formed with the majority of less electronegative elements with the exception of Hg, Pb, Sb, Bi, Te, Po...
with a chloroiminophosphane:
Heating this compound at 50 °C in 1,3-cyclohexadiene
1,3-Cyclohexadiene
1,3-Cyclohexadiene is a highly flammable cycloalkene that occurs as a colorless clear liquid. Its refractive index is 1.475 .It can be used as a hydrogen donor in transfer hydrogenation, since its conversion to benzene + hydrogen is in fact exothermic .Despite this apparent instability with respect...
serving as a solvent
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
and as a trapping reagent expulses diphosphorus, which is reactive, as it is forms a double Diels-Alder adduct
Diels-Alder reaction
The Diels–Alder reaction is an organic chemical reaction between a conjugated diene and a substituted alkene, commonly termed the dienophile, to form a substituted cyclohexene system. The reaction can proceed even if some of the atoms in the newly formed ring are not carbon...
and the niobium imido compound:
The same imido compound also forms when the thermolysis is performed in toluene
Toluene
Toluene, formerly known as toluol, is a clear, water-insoluble liquid with the typical smell of paint thinners. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, i.e., one in which a single hydrogen atom from the benzene molecule has been replaced by a univalent group, in this case CH3.It is an aromatic...
but then the fate of diphosphorus is unknown.
P2 has been suggested to form as an intermediate in the photolysis of P4 and in the presence of 2,3-dimethylbutadiene the diphosphane is again formed To date, no direct evidence of P2 formation via P4 photolysis exists.
External links
- Ron Dagani, "A Mild Route To P2, Chemical & Engineering NewsChemical & Engineering NewsChemical & Engineering News is a weekly magazine published by the American Chemical Society, providing professional and technical information in the fields of chemistry and chemical engineering...
September 4, 2006 Link