
Direction vector
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, a direction vector that describes a line segment
D is any vector

where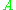 and
and 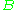 are two distinct points on the line D. If v is a direction vector for D, so is kv for any nonzero scalar
are two distinct points on the line D. If v is a direction vector for D, so is kv for any nonzero scalar
k; and these are in fact all of the direction vectors for the line D. Under some definitions, the direction vector is required to be a unit vector, in which case each line has exactly two direction vectors, which are negatives of each other (equal in magnitude, opposite in direction).
can be described as the set of solutions to an equation of the form

where a, b, c are real number
s. Then one direction vector of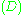 is
is 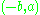 . Any multiple of
. Any multiple of 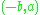 is also a direction vector.
is also a direction vector.
For example, suppose the equation of a line is . Then
. Then 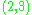 ,
, 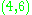 , and
, and  are all direction vectors for this line.
are all direction vectors for this line.
(any number of dimensions), given a point a and a nonzero vector v, a line is defined parametrically
by (a+tv), where the parameter t varies between -∞ and +∞. This line has v as a direction vector.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, a direction vector that describes a line segment
Line (geometry)
The notion of line or straight line was introduced by the ancient mathematicians to represent straight objects with negligible width and depth. Lines are an idealization of such objects...
D is any vector

where
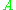 and
and 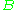 are two distinct points on the line D. If v is a direction vector for D, so is kv for any nonzero scalar
are two distinct points on the line D. If v is a direction vector for D, so is kv for any nonzero scalarScalar (mathematics)
In linear algebra, real numbers are called scalars and relate to vectors in a vector space through the operation of scalar multiplication, in which a vector can be multiplied by a number to produce another vector....
k; and these are in fact all of the direction vectors for the line D. Under some definitions, the direction vector is required to be a unit vector, in which case each line has exactly two direction vectors, which are negatives of each other (equal in magnitude, opposite in direction).
Direction vector for a line in R2
Any line in two-dimensional Euclidean spaceEuclidean space
In mathematics, Euclidean space is the Euclidean plane and three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, as well as the generalizations of these notions to higher dimensions...
can be described as the set of solutions to an equation of the form

where a, b, c are real number
Real number
In mathematics, a real number is a value that represents a quantity along a continuum, such as -5 , 4/3 , 8.6 , √2 and π...
s. Then one direction vector of
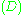 is
is 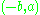 . Any multiple of
. Any multiple of 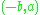 is also a direction vector.
is also a direction vector.For example, suppose the equation of a line is
 . Then
. Then 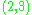 ,
, 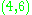 , and
, and  are all direction vectors for this line.
are all direction vectors for this line.Parametric equation for a line
In Euclidean spaceEuclidean space
In mathematics, Euclidean space is the Euclidean plane and three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, as well as the generalizations of these notions to higher dimensions...
(any number of dimensions), given a point a and a nonzero vector v, a line is defined parametrically
Parametric equation
In mathematics, parametric equation is a method of defining a relation using parameters. A simple kinematic example is when one uses a time parameter to determine the position, velocity, and other information about a body in motion....
by (a+tv), where the parameter t varies between -∞ and +∞. This line has v as a direction vector.
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Direction." From MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource. http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Direction.html
- Glossary, Nipissing University
- Finding the vector equation of a line
- Lines in a plane - Orthogonality, Distances, MATH-tutorial
- Coordinate Systems, Points, Lines and Planes

