
Directivity
Encyclopedia
In electromagnetics
, directivity is a figure of merit
for an antenna
. It measures the power density the antenna radiates in the direction of its strongest emission, versus the power density radiated by an ideal isotropic radiator
(which emits uniformly in all directions) radiating the same total power.
An antenna's directivity is a component of its gain
; the other component is its (electrical) efficiency
. Directivity is an important measure because most emissions are intended to go in a particular direction or at least in a particular plane (horizontal or vertical); emissions in other directions or planes are wasteful (or worse
).
The directivity of an actual antenna can vary from 1.76 dBi for a short dipole
, to as much as 50 dBi for a large dish antenna.
 , and compares the radiation intensity
, and compares the radiation intensity
(power per unit solid angle
)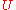 that an antenna creates in a particular direction against the average value over all directions:
that an antenna creates in a particular direction against the average value over all directions:

...where:
Directivity is represented as simply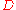 , and is the maximum directive gain value found among all possible solid angles:
, and is the maximum directive gain value found among all possible solid angles:

The equation can also be written as:
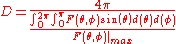
The word directivity is also sometimes used as a synonym for directive gain. This usage is readily understood, as the direction will be specified, or directional dependence implied. Later editions of the IEEE Dictionary specifically endorse this usage; nevertheless it has yet to be universally adopted.
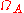 , is defined as the solid angle which all power would flow through if the antenna radiation intensity were constant and maximum value. If the beam solid angle is known, then directivity can be calculated as:
, is defined as the solid angle which all power would flow through if the antenna radiation intensity were constant and maximum value. If the beam solid angle is known, then directivity can be calculated as:
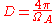
...which simply calculates the ratio of the beam solid angle to the total surface area of the sphere it intersects.
The beam solid angle can be approximated for antennas with one narrow major lobe and very negligible minor lobes, by simply multiplying the half-power beamwidth
s (in radians) in two perpendicular planes. The half-power beamwidth is simply the angle in which the radiation intensity is at least half of the peak radiation intensity.
The same calculations can be performed in degrees rather than in radians:
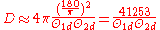
...where is the half-power beamwidth in one plane (degrees) and
is the half-power beamwidth in one plane (degrees) and 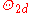 is the half-power beamwidth in a plane at a right angle to the other (degrees).
is the half-power beamwidth in a plane at a right angle to the other (degrees).
In planar arrays, a better approximation is:
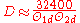
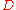 . Rather, the directivity is usually expressed as a decibel comparison to a reference antenna:
. Rather, the directivity is usually expressed as a decibel comparison to a reference antenna:

The reference antenna is usually the theoretical perfect isotropic radiator
which radiates uniformly in all directions and hence has a directivity of 1. The calculation is therefore simplified to:
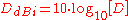
Another common reference antenna is the theoretical perfect half-wave dipole
which radiates perpendicular to itself with a directivity of 1.64:
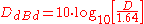
is taken under consideration, three additional measures can be calculated:
, as is a measure of the radiation pattern from a source indicating how much of the total energy from the source is radiating in a particular direction. In electro-acoustics, these patterns commonly include omni-directional, cardioid and hyper-cardioid microphone polar patterns. A loudspeaker with a high degree of directivity (narrow dispersion pattern) can be said to have a high Q.
Electromagnetism
Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three are the strong interaction, the weak interaction and gravitation...
, directivity is a figure of merit
Figure of merit
A figure of merit is a quantity used to characterize the performance of a device, system or method, relative to its alternatives. In engineering, figures of merit are often defined for particular materials or devices in order to determine their relative utility for an application...
for an antenna
Antenna (radio)
An antenna is an electrical device which converts electric currents into radio waves, and vice versa. It is usually used with a radio transmitter or radio receiver...
. It measures the power density the antenna radiates in the direction of its strongest emission, versus the power density radiated by an ideal isotropic radiator
Isotropic radiator
An isotropic radiator is a theoretical point source of electromagnetic or sound waves which radiates the same intensity of radiation in all directions. It has no preferred direction of radiation. It radiates uniformly in all directions over a sphere centred on the source...
(which emits uniformly in all directions) radiating the same total power.
An antenna's directivity is a component of its gain
Antenna gain
In electromagnetics, an antenna's power gain or simply gain is a key performance figure which combines the antenna's directivity and electrical efficiency. As a transmitting antenna, the figure describes how well the antenna converts input power into radio waves headed in a specified direction...
; the other component is its (electrical) efficiency
Antenna efficiency
In electromagnetics, antenna efficiency or radiation efficiency is a figure of merit for an antenna. It measures the electrical losses that occur throughout the antenna while it is operating at a given frequency, or averaged over its operation across a frequency band...
. Directivity is an important measure because most emissions are intended to go in a particular direction or at least in a particular plane (horizontal or vertical); emissions in other directions or planes are wasteful (or worse
Multipath
In wireless telecommunications, multipath is the propagation phenomenon that results in radio signals reaching the receiving antenna by two or more paths...
).
The directivity of an actual antenna can vary from 1.76 dBi for a short dipole
Dipole
In physics, there are several kinds of dipoles:*An electric dipole is a separation of positive and negative charges. The simplest example of this is a pair of electric charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign, separated by some distance. A permanent electric dipole is called an electret.*A...
, to as much as 50 dBi for a large dish antenna.
Definition
The directivity of an antenna is the maximum value of its directive gain. Directive gain is represented as , and compares the radiation intensity
, and compares the radiation intensityRadiation intensity
In electromagnetism, radiation intensity describes the power density that an antenna creates in a particular solid angle. A solid angle is a section of the surface of the imaginary sphere around the antenna....
(power per unit solid angle
Solid angle
The solid angle, Ω, is the two-dimensional angle in three-dimensional space that an object subtends at a point. It is a measure of how large that object appears to an observer looking from that point...
)
 that an antenna creates in a particular direction against the average value over all directions:
that an antenna creates in a particular direction against the average value over all directions:
...where:
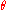 and
and 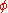 are the standard spherical coordinates angles
are the standard spherical coordinates angles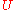 is the radiation intensityRadiation intensityIn electromagnetism, radiation intensity describes the power density that an antenna creates in a particular solid angle. A solid angle is a section of the surface of the imaginary sphere around the antenna....
is the radiation intensityRadiation intensityIn electromagnetism, radiation intensity describes the power density that an antenna creates in a particular solid angle. A solid angle is a section of the surface of the imaginary sphere around the antenna....
, which is the power density per unit solid angle such that: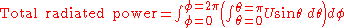
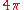 is the total solid angle for a sphere (also the surface area of a unit sphere, similar to
is the total solid angle for a sphere (also the surface area of a unit sphere, similar to  being the total angle for a circle and the perimeter of a unit circle).
being the total angle for a circle and the perimeter of a unit circle).- The denominator,
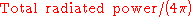 , represents the average radiated power density
, represents the average radiated power density
Directivity is represented as simply
 , and is the maximum directive gain value found among all possible solid angles:
, and is the maximum directive gain value found among all possible solid angles:
The equation can also be written as:
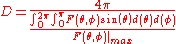
The word directivity is also sometimes used as a synonym for directive gain. This usage is readily understood, as the direction will be specified, or directional dependence implied. Later editions of the IEEE Dictionary specifically endorse this usage; nevertheless it has yet to be universally adopted.
Relation to beam width
The beam solid angle, represented as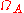 , is defined as the solid angle which all power would flow through if the antenna radiation intensity were constant and maximum value. If the beam solid angle is known, then directivity can be calculated as:
, is defined as the solid angle which all power would flow through if the antenna radiation intensity were constant and maximum value. If the beam solid angle is known, then directivity can be calculated as: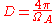
...which simply calculates the ratio of the beam solid angle to the total surface area of the sphere it intersects.
The beam solid angle can be approximated for antennas with one narrow major lobe and very negligible minor lobes, by simply multiplying the half-power beamwidth
Beamwidth
In telecommunication, the term beamwidth has the following meanings:1. In the radio regime, of an antenna pattern, the angle between the half-power points of the main lobe, when referenced to the peak effective radiated power of the main lobe....
s (in radians) in two perpendicular planes. The half-power beamwidth is simply the angle in which the radiation intensity is at least half of the peak radiation intensity.
The same calculations can be performed in degrees rather than in radians:
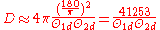
...where
 is the half-power beamwidth in one plane (degrees) and
is the half-power beamwidth in one plane (degrees) and 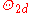 is the half-power beamwidth in a plane at a right angle to the other (degrees).
is the half-power beamwidth in a plane at a right angle to the other (degrees).In planar arrays, a better approximation is:
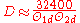
Expression in decibels
The directivity is rarely expressed as the unitless number . Rather, the directivity is usually expressed as a decibel comparison to a reference antenna:
. Rather, the directivity is usually expressed as a decibel comparison to a reference antenna:
The reference antenna is usually the theoretical perfect isotropic radiator
Isotropic radiator
An isotropic radiator is a theoretical point source of electromagnetic or sound waves which radiates the same intensity of radiation in all directions. It has no preferred direction of radiation. It radiates uniformly in all directions over a sphere centred on the source...
which radiates uniformly in all directions and hence has a directivity of 1. The calculation is therefore simplified to:
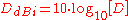
Another common reference antenna is the theoretical perfect half-wave dipole
Dipole
In physics, there are several kinds of dipoles:*An electric dipole is a separation of positive and negative charges. The simplest example of this is a pair of electric charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign, separated by some distance. A permanent electric dipole is called an electret.*A...
which radiates perpendicular to itself with a directivity of 1.64:
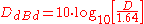
Accounting for polarization
When polarizationPolarization
Polarization is a property of certain types of waves that describes the orientation of their oscillations. Electromagnetic waves, such as light, and gravitational waves exhibit polarization; acoustic waves in a gas or liquid do not have polarization because the direction of vibration and...
is taken under consideration, three additional measures can be calculated:
Partial directive gain
Partial directive gain is the power density in a particular direction and for a particular component of the polarization, divided by the average power density for all directions and all polarizations. For any pair of orthogonal polarizations (such as left-hand-circular and right-hand-circular), the individual power densities simply add to give the total power density. Thus, if expressed as dimensionless ratios rather than in dB, the total directive gain is equal to the sum of the two partial directive gains.Partial directivity
Partial directivity is calculated in the same manner as the partial directive gain, but without consideration of antenna efficiency (i.e. assuming a lossless antenna). It is similarly additive for orthogonal polarizations.Partial gain
Partial gain is calculated in the same manner as gain, but considering only a certain polarization. It is similarly additive for orthogonal polarizations.In other fields
The term directivity is also used in acousticsAcoustics
Acoustics is the interdisciplinary science that deals with the study of all mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician while someone working in the field of acoustics...
, as is a measure of the radiation pattern from a source indicating how much of the total energy from the source is radiating in a particular direction. In electro-acoustics, these patterns commonly include omni-directional, cardioid and hyper-cardioid microphone polar patterns. A loudspeaker with a high degree of directivity (narrow dispersion pattern) can be said to have a high Q.

