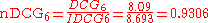Discounted cumulative gain
Encyclopedia
Discounted cumulative gain (DCG) is a measure of effectiveness of a Web
search engine
algorithm
or related applications, often used in information retrieval
. Using a graded relevance
scale of documents in a search engine result set, DCG measures the usefulness, or gain, of a document based on its position in the result list. The gain is accumulated from the top of the result list to the bottom with the gain of each result discounted at lower ranks.
DCG originates from an earlier, more primitive, measure called Cumulative Gain.
 is defined as:
is defined as:

Where is the graded relevance of the result at position
is the graded relevance of the result at position  .
.
The value computed with the CG function is unaffected by changes in the ordering of search results. That is, moving a highly relevant document above a higher ranked, less relevant, document
above a higher ranked, less relevant, document 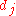 does not change the computed value for CG. Based on the two assumptions made above about the usefulness of search results, DCG is used in place of CG for a more accurate measure.
does not change the computed value for CG. Based on the two assumptions made above about the usefulness of search results, DCG is used in place of CG for a more accurate measure.
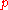 is defined as:
is defined as:
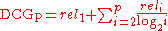
There has not been shown any theoretically sound justification for using a logarithmic
reduction factor other than the fact that it produces a smooth reduction. An alternative formulation of DCG places stronger emphasis on retrieving relevant documents:
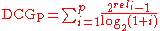
The function is equivalent to the previous DCG function when the relevance values of documents are binary
;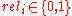 .
.
. Comparing a search engine's performance from one query to the next cannot be consistently achieved using DCG alone, so the cumulative gain at each position for a chosen value of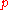 should be normalized across queries. This is done by sorting documents of a result list by relevance, producing an ideal
should be normalized across queries. This is done by sorting documents of a result list by relevance, producing an ideal
DCG at position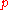 . For a query, the normalized discounted cumulative gain, or nDCG, is computed as:
. For a query, the normalized discounted cumulative gain, or nDCG, is computed as:
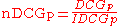
The nDCG values for all queries can be averaged to obtain a measure of the average performance of a search engine's ranking algorithm. Note that in a perfect ranking algorithm, the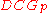 will be the same as the
will be the same as the  producing an nDCG of 1.0. All nDCG calculations are then relative values on the interval 0.0 to 1.0 and so are cross-query comparable.
producing an nDCG of 1.0. All nDCG calculations are then relative values on the interval 0.0 to 1.0 and so are cross-query comparable.
The main difficulty encountered in using nDCG is the unavailability of an ideal ordering of results when only partial relevance feedback
is available.
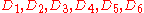
the user provides the following relevance scores:
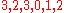
That is: document 1 has a relevance of 3, document 2 has a relevance of 2, etc. The Cumulative Gain of this search result listing is:
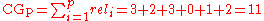
Changing the order of any two documents does not affect the CG measure. If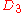 and
and  are switched, the CG remains the same, 11. DCG is used to emphasize highly relevant documents appearing early in the result list. Using the logarithmic scale for reduction, the DCG for each result in order is:
are switched, the CG remains the same, 11. DCG is used to emphasize highly relevant documents appearing early in the result list. Using the logarithmic scale for reduction, the DCG for each result in order is:
So the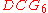 of this ranking is:
of this ranking is:
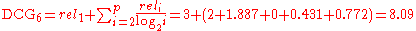
Now a switch of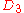 and
and 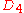 results in a reduced DCG because a less relevant document is placed higher in the ranking; that is, a more relevant document is discounted more by being placed in a lower rank.
results in a reduced DCG because a less relevant document is placed higher in the ranking; that is, a more relevant document is discounted more by being placed in a lower rank.
The performance of this query to another is incomparable in this form since the other query may have more results, resulting in a larger overall DCG which may not necessarily be better. In order to compare, the DCG values must be normalized.
To normalize DCG values, an ideal ordering for the given query is needed. For this example, that ordering would be the monotonically decreasing sort of the relevance judgments provided by the experiment participant, which is:

The DCG of this ideal ordering, or IDCG, is then:
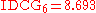
And so the nDCG for this query is given as:
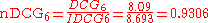
World Wide Web
The World Wide Web is a system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet...
search engine
Search engine
A search engine is an information retrieval system designed to help find information stored on a computer system. The search results are usually presented in a list and are commonly called hits. Search engines help to minimize the time required to find information and the amount of information...
algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
or related applications, often used in information retrieval
Information retrieval
Information retrieval is the area of study concerned with searching for documents, for information within documents, and for metadata about documents, as well as that of searching structured storage, relational databases, and the World Wide Web...
. Using a graded relevance
Relevance (information retrieval)
In information science and information retrieval, relevance denotes how well a retrieved document or set of documents meets the information need of the user.-Types:...
scale of documents in a search engine result set, DCG measures the usefulness, or gain, of a document based on its position in the result list. The gain is accumulated from the top of the result list to the bottom with the gain of each result discounted at lower ranks.
Mathematical Details
Two assumptions are made in using DCG and its related measures.- Highly relevant documents are more useful when appearing earlier in a search engine result list (have higher ranks)
- Highly relevant documents are more useful than marginally relevant documents, which are in turn more useful than irrelevant documents.
DCG originates from an earlier, more primitive, measure called Cumulative Gain.
Cumulative Gain
Cumulative Gain (CG) is the predecessor of DCG and does not include the position of a result in the consideration of the usefulness of a result set. In this way, it is the sum of the graded relevance values of all results in a search result list. The CG at a particular rank position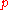 is defined as:
is defined as:
Where
 is the graded relevance of the result at position
is the graded relevance of the result at position 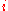 .
.The value computed with the CG function is unaffected by changes in the ordering of search results. That is, moving a highly relevant document
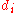 above a higher ranked, less relevant, document
above a higher ranked, less relevant, document 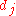 does not change the computed value for CG. Based on the two assumptions made above about the usefulness of search results, DCG is used in place of CG for a more accurate measure.
does not change the computed value for CG. Based on the two assumptions made above about the usefulness of search results, DCG is used in place of CG for a more accurate measure.Discounted Cumulative Gain
The premise of DCG is that highly relevant documents appearing lower in a search result list should be penalized as the graded relevance value is reduced logarithmically proportional to the position of the result. The discounted CG accumulated at a particular rank position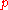 is defined as:
is defined as: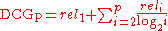
There has not been shown any theoretically sound justification for using a logarithmic
Logarithm
The logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, has to be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of 1000 to base 10 is 3, because 1000 is 10 to the power 3: More generally, if x = by, then y is the logarithm of x to base b, and is written...
reduction factor other than the fact that it produces a smooth reduction. An alternative formulation of DCG places stronger emphasis on retrieving relevant documents:
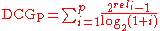
The function is equivalent to the previous DCG function when the relevance values of documents are binary
Binary function
In mathematics, a binary function, or function of two variables, is a function which takes two inputs.Precisely stated, a function f is binary if there exists sets X, Y, Z such that\,f \colon X \times Y \rightarrow Z...
;
 .
.Normalized DCG
Search result lists vary in length depending on the queryWeb search query
A web search query is a query that a user enters into web search engine to satisfy his or her information needs. Web search queries are distinctive in that they are unstructured and often ambiguous; they vary greatly from standard query languages which are governed by strict syntax rules.- Types...
. Comparing a search engine's performance from one query to the next cannot be consistently achieved using DCG alone, so the cumulative gain at each position for a chosen value of
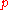 should be normalized across queries. This is done by sorting documents of a result list by relevance, producing an ideal
should be normalized across queries. This is done by sorting documents of a result list by relevance, producing an idealIdeal
-In philosophy:* Ideal , values that one actively pursues as goals* Platonic ideal, a philosophical idea of trueness of form, associated with Plato-In mathematics:* Ideal , special subsets of a ring considered in abstract algebra...
DCG at position
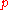 . For a query, the normalized discounted cumulative gain, or nDCG, is computed as:
. For a query, the normalized discounted cumulative gain, or nDCG, is computed as: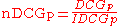
The nDCG values for all queries can be averaged to obtain a measure of the average performance of a search engine's ranking algorithm. Note that in a perfect ranking algorithm, the
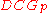 will be the same as the
will be the same as the  producing an nDCG of 1.0. All nDCG calculations are then relative values on the interval 0.0 to 1.0 and so are cross-query comparable.
producing an nDCG of 1.0. All nDCG calculations are then relative values on the interval 0.0 to 1.0 and so are cross-query comparable.The main difficulty encountered in using nDCG is the unavailability of an ideal ordering of results when only partial relevance feedback
Relevance feedback
Relevance feedback is a feature of some information retrieval systems. The idea behind relevance feedback is to take the results that are initially returned from a given query and to use information about whether or not those results are relevant to perform a new query...
is available.
Example
Presented with a list of documents in response to a search query, an experiment participant is asked to judge the relevance of each document to the query. Each document is to be judged on a scale of 0-3 with 0 meaning irrelevant, 3 meaning completely relevant, and 1 and 2 meaning "somewhere in between". For the documents ordered by the ranking algorithm as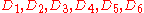
the user provides the following relevance scores:

That is: document 1 has a relevance of 3, document 2 has a relevance of 2, etc. The Cumulative Gain of this search result listing is:
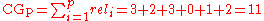
Changing the order of any two documents does not affect the CG measure. If
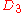 and
and  are switched, the CG remains the same, 11. DCG is used to emphasize highly relevant documents appearing early in the result list. Using the logarithmic scale for reduction, the DCG for each result in order is:
are switched, the CG remains the same, 11. DCG is used to emphasize highly relevant documents appearing early in the result list. Using the logarithmic scale for reduction, the DCG for each result in order is: 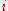 |
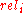 |
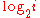 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 0 | N/A |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 | 1.59 | 1.887 |
| 4 | 0 | 2.0 | 0 |
| 5 | 1 | 2.32 | 0.431 |
| 6 | 2 | 2.59 | 0.772 |
So the
 of this ranking is:
of this ranking is: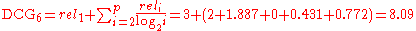
Now a switch of
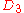 and
and 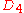 results in a reduced DCG because a less relevant document is placed higher in the ranking; that is, a more relevant document is discounted more by being placed in a lower rank.
results in a reduced DCG because a less relevant document is placed higher in the ranking; that is, a more relevant document is discounted more by being placed in a lower rank.The performance of this query to another is incomparable in this form since the other query may have more results, resulting in a larger overall DCG which may not necessarily be better. In order to compare, the DCG values must be normalized.
To normalize DCG values, an ideal ordering for the given query is needed. For this example, that ordering would be the monotonically decreasing sort of the relevance judgments provided by the experiment participant, which is:

The DCG of this ideal ordering, or IDCG, is then:
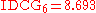
And so the nDCG for this query is given as: