
Discrete signal
Encyclopedia
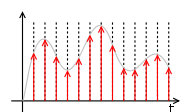
A discrete signal or discrete-time signal is a time series
Time series
In statistics, signal processing, econometrics and mathematical finance, a time series is a sequence of data points, measured typically at successive times spaced at uniform time intervals. Examples of time series are the daily closing value of the Dow Jones index or the annual flow volume of the...
consisting of a sequence
Sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an ordered list of objects . Like a set, it contains members , and the number of terms is called the length of the sequence. Unlike a set, order matters, and exactly the same elements can appear multiple times at different positions in the sequence...
of qualities. In other words, it is a type series that is a function over a domain
Domain (mathematics)
In mathematics, the domain of definition or simply the domain of a function is the set of "input" or argument values for which the function is defined...
of discrete integral.
Unlike a continuous-time signal
Continuous signal
A continuous signal or a continuous-time signal is a varying quantity whose domain, which is often time, is a continuum . That is, the function's domain is an uncountable set. The function itself need not be continuous...
, a discrete-time signal is a function of a continuous argument; however, it may have been obtained by sampling from a discrete-time signal, and then each value in the sequence is called a sample. When a discrete-time signal obtained by sampling is a sequence corresponding to uniformly spaced times, it has an associated sampling rate
Sampling rate
The sampling rate, sample rate, or sampling frequency defines the number of samples per unit of time taken from a continuous signal to make a discrete signal. For time-domain signals, the unit for sampling rate is hertz , sometimes noted as Sa/s...
; the sampling rate is not apparent in the data sequence, and so needs to be associated as a separate data item.
Acquisition
Discrete signals may have several origins, but can usually be classified into one of two groups:- By acquiring values of an analog signalAnalog signalAn analog or analogue signal is any continuous signal for which the time varying feature of the signal is a representation of some other time varying quantity, i.e., analogous to another time varying signal. It differs from a digital signal in terms of small fluctuations in the signal which are...
at constant or variable rate. This process is called samplingSampling (signal processing)In signal processing, sampling is the reduction of a continuous signal to a discrete signal. A common example is the conversion of a sound wave to a sequence of samples ....
. - By recording the number of events of a given kind over finite time periods. For example, this could be the number of people taking a certain elevator every day.
Digital signals
A digital signalDigital signal
A digital signal is a physical signal that is a representation of a sequence of discrete values , for example of an arbitrary bit stream, or of a digitized analog signal...
is a discrete-time signal for which not only the time but also the amplitude has been made discrete; in other words, its samples take on only values from a discrete set.
The process of converting a continuous-valued discrete-time signal to a digital (discrete-valued discrete-time) signal is known as analog-to-digital conversion. It usually proceeds by replacing each original sample value by an approximation selected from a given discrete set (for example by truncating or rounding, but much more sophisticated methods exist), a process known as quantization
Quantization (signal processing)
Quantization, in mathematics and digital signal processing, is the process of mapping a large set of input values to a smaller set – such as rounding values to some unit of precision. A device or algorithmic function that performs quantization is called a quantizer. The error introduced by...
. This process loses information, and so discrete-valued signals are only an approximation of the converted continuous-valued discrete-time signal, itself only an approximation of the original continuous-valued continuous-time signal.
Common practical digital signals are represented as 8-bit
8-bit
The first widely adopted 8-bit microprocessor was the Intel 8080, being used in many hobbyist computers of the late 1970s and early 1980s, often running the CP/M operating system. The Zilog Z80 and the Motorola 6800 were also used in similar computers...
(256 levels), 16-bit
16-bit
-16-bit architecture:The HP BPC, introduced in 1975, was the world's first 16-bit microprocessor. Prominent 16-bit processors include the PDP-11, Intel 8086, Intel 80286 and the WDC 65C816. The Intel 8088 was program-compatible with the Intel 8086, and was 16-bit in that its registers were 16...
(65,536 levels), 32-bit
32-bit
The range of integer values that can be stored in 32 bits is 0 through 4,294,967,295. Hence, a processor with 32-bit memory addresses can directly access 4 GB of byte-addressable memory....
(4.3 billion levels), and so on, though any number of quantization levels is possible, not just powers of two
Power of two
In mathematics, a power of two means a number of the form 2n where n is an integer, i.e. the result of exponentiation with as base the number two and as exponent the integer n....
.
See also
- AliasingAliasingIn signal processing and related disciplines, aliasing refers to an effect that causes different signals to become indistinguishable when sampled...
- Anti-aliasing filterAnti-aliasing filterAn anti-aliasing filter is a filter used before a signal sampler, to restrict the bandwidth of a signal to approximately satisfy the sampling theorem....
- Digital-to-analog converterDigital-to-analog converterIn electronics, a digital-to-analog converter is a device that converts a digital code to an analog signal . An analog-to-digital converter performs the reverse operation...
- Digital controlDigital controlDigital control is a branch of control theory that uses digital computers to act as system controllers.Depending on the requirements, a digital control system can take the form of a microcontroller to an ASIC to a standard desktop computer....
- Digital frequencyDigital frequencyDigital frequency is the analogue for discrete signals as frequency is to continuous signals.Since a discrete signal is a sequence it contains no direct information as to determine the frequency of the corresponding continuous signal.Just like in frequency, a digital frequency can have values in...
- Nyquist–Shannon sampling theoremNyquist–Shannon sampling theoremThe Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem, after Harry Nyquist and Claude Shannon, is a fundamental result in the field of information theory, in particular telecommunications and signal processing. Sampling is the process of converting a signal into a numeric sequence...
- Whittaker–Shannon interpolation formulaWhittaker–Shannon interpolation formulaThe Whittaker–Shannon interpolation formula or sinc interpolation is a method to reconstruct a continuous-time bandlimited signal from a set of equally spaced samples.-Definition:...
- Sampling (signal processing)Sampling (signal processing)In signal processing, sampling is the reduction of a continuous signal to a discrete signal. A common example is the conversion of a sound wave to a sequence of samples ....
- Ideal samplerIdeal samplerIn signal processing, an ideal sampler is a theoretical operation whose input is a continuous signal and whose output is a sequence of instantaneous values of the signal at discrete moments of time, which is called a discrete signal....

