
Driving wheel
Encyclopedia
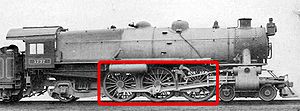

Steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a railway locomotive that produces its power through a steam engine. These locomotives are fueled by burning some combustible material, usually coal, wood or oil, to produce steam in a boiler, which drives the steam engine...
, a driving wheel is a powered wheel
Wheel
A wheel is a device that allows heavy objects to be moved easily through rotating on an axle through its center, facilitating movement or transportation while supporting a load, or performing labor in machines. Common examples found in transport applications. A wheel, together with an axle,...
which is driven by the locomotive
Locomotive
A locomotive is a railway vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. The word originates from the Latin loco – "from a place", ablative of locus, "place" + Medieval Latin motivus, "causing motion", and is a shortened form of the term locomotive engine, first used in the early 19th...
's piston
Piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tight by piston rings. In an engine, its purpose is to transfer force from...
s (or turbine
Turbine
A turbine is a rotary engine that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work.The simplest turbines have one moving part, a rotor assembly, which is a shaft or drum with blades attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades, or the blades react to the flow, so that they move and...
, in the case of a steam turbine locomotive
Steam turbine locomotive
A steam turbine locomotive is a steam locomotive which transmits steam power to the wheels via a steam turbine. Numerous attempts at this type of locomotive were made, mostly without success...
). On a conventional, non-articulated locomotive, the driving wheels are all coupled together with side rods (also known as coupling rod
Coupling rod
right|thumb|connecting rod and coupling rods attached to a small locomotive driving wheelA coupling rod or side rod connects the driving wheels of a locomotive. Steam locomotives in particular usually have them, but some diesel and electric locomotives, especially older ones and shunters, also have...
s); normally one pair is directly driven by the main rod (or connecting rod
Connecting rod
In a reciprocating piston engine, the connecting rod or conrod connects the piston to the crank or crankshaft. Together with the crank, they form a simple mechanism that converts linear motion into rotating motion....
) which is connected to the end of the piston rod
Piston rod
In a piston engine, a piston rod joins a piston to a connecting rod.Many internal combustion engines, and in particular all current automobile engines, do not have true piston rods, and the term piston rod is often used as a synonym for connecting rod in the context of these engines.All engines...
; power is transmitted to the others through the side rods.
On Diesel
Diesel locomotive
A diesel locomotive is a type of railroad locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engine, a reciprocating engine operating on the Diesel cycle as invented by Dr. Rudolf Diesel...
and Electric locomotive
Electric locomotive
An electric locomotive is a locomotive powered by electricity from overhead lines, a third rail or an on-board energy storage device...
s the driving wheels may be directly driven by the traction motor
Traction motor
Traction motor refers to an electric motor providing the primary rotational torque of a machine, usually for conversion into linear motion ....
s. Coupling rods are not usually used, and it is quite common for each axle to have its own motor. Jackshaft drive and coupling rods were used in the past (e.g. in the Swiss Crocodile locomotive
Crocodile (locomotive)
Crocodile electric locomotives are so called because they have long "noses" at each end, reminiscent of the snout of a crocodile . These contain the motors and drive axles, and are connected by an articulated center section. The center section usually contains the crew compartments, pantographs...
) but their use is now confined to shunting locomotives
Switcher
A switcher or shunter is a small railroad locomotive intended not for moving trains over long distances but rather for assembling trains ready for a road locomotive to take over, disassembling a train that has been...
.
On an articulated locomotive
Articulated locomotive
Articulated locomotive usually means a steam locomotive with one or more engine units which can move independent of the main frame. This is done to allow a longer locomotive to negotiate tighter curves...
or a duplex locomotive
Duplex locomotive
A duplex locomotive is a steam locomotive that divides the driving force on its wheels by using two pairs of cylinders rigidly mounted to a single locomotive frame; it is not an articulated locomotive...
driving wheels are grouped into sets which are linked together within the set.
Diameter

Leading wheel
The leading wheel or leading axle of a steam locomotive is an unpowered wheel or axle located in front of the driving wheels. The axle or axles of the leading wheels are normally located in a truck...
or trailing wheel
Trailing wheel
On a steam locomotive, a trailing wheel or trailing axle is generally an unpowered wheel or axle located behind the driving wheels. The axle of the trailing wheels was usually located on a trailing truck...
s. Since a conventional steam locomotive is directly driven, one of the few ways to 'gear
Gear ratio
The gear ratio of a gear train is the ratio of the angular velocity of the input gear to the angular velocity of the output gear, also known as the speed ratio of the gear train. The gear ratio can be computed directly from the numbers of teeth of the various gears that engage to form the gear...
' a locomotive for a particular performance goal is to size the driving wheels appropriately. Freight locomotives generally had driving wheels between 40 and 60 in (1,016 and 1,524 mm) in diameter; dual-purpose locomotives generally between 60 and 70 in (1,524 and 1,778 mm), and passenger locomotives between 70 and 100 in (1,778 and 2,540 mm) or so. Some long wheelbase locomotives (four or more coupled axles) were equipped with blind drivers. These were driving wheels without the usual flange
Flange
A flange is an external or internal ridge, or rim , for strength, as the flange of an iron beam such as an I-beam or a T-beam; or for attachment to another object, as the flange on the end of a pipe, steam cylinder, etc., or on the lens mount of a camera; or for a flange of a rail car or tram wheel...
s, which allowed them to negotiate tighter curves without binding.
The driving wheels on express passenger locomotives have come down in diameter over the years, e.g. from 8 in 1 in (2,463.8 mm) on the GNR Stirling 4-2-2
GNR Stirling 4-2-2
The Great Northern Railway No. 1 class Stirling Single is a class of steam locomotive designed for express passenger work. Designed by Patrick Stirling, they are characterised by a single pair of large driving wheels which led to the nickname "eight-footer"...
of 1870 to 6 in 2 in (1,879.6 mm) on the SR Merchant Navy Class
SR Merchant Navy class
The SR Merchant Navy class , was a class of air-smoothed 4-6-2 Pacific steam locomotives designed for the Southern Railway of the United Kingdom by Oliver Bulleid...
of 1941. This is because improvements in valve design allowed for higher piston speeds.
Balancing

Whyte notation
In the Whyte notationWhyte notation
The Whyte notation for classifying steam locomotives by wheel arrangement was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte and came into use in the early twentieth century encouraged by an editorial in American Engineer and Railroad Journal...
, driving wheels are designated by the middle number or numbers in the set. The UIC classification
UIC classification
The UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements describes the wheel arrangement of locomotives, multiple units and trams. It is set out in the International Union of Railways "Leaflet 650 - Standard designation of axle arrangement on locomotives and multiple-unit sets". It is used in much...
system counts the number of axles rather than the number of wheels and driving wheels are designated by letters rather than numbers. The suffix 'o' is used to indicate independently powered axles.
The number of driving wheels on locomotives varied quite a bit. Some early locomotives had as few as two driving wheels (one axle). The largest number of total driving wheels was 24 (twelve axles) on the 2-8-8-8-2
2-8-8-8-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, a 2-8-8-8-2 has two leading wheels, three sets of eight driving wheels, and two trailing wheels. Because of its length, such a locomotive must be an articulated locomotive. It is not longer than a normal articulated; the third...
and 2-8-8-8-4
2-8-8-8-4
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, a 2-8-8-8-4 has two leading wheels, three sets of eight driving wheels, and a four trailing wheels.Other equivalent classifications are:...
locomotives. The largest number of coupled driving wheels was 14 (seven axles) on the ill-fated AA20 4-14-4
4-14-4
A 4-14-4, in the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, is a locomotive with four leading wheels, fourteen coupled driving wheels in a rigid frame, and four trailing wheels....
locomotive.
Other uses of the term driving wheel
The term driving wheel is sometimes used to denote the drive sprocketSprocket
A sprocket or sprocket-wheel is a profiled wheel with teeth, cogs, or even sprockets that mesh with a chain, track or other perforated or indented material. The name 'sprocket' applies generally to any wheel upon which are radial projections that engage a chain passing over it...
which moves the track
Caterpillar track
Continuous tracks or caterpillar tracks are a system of vehicle propulsion in which modular metal plates linked into a continuous band are driven by two or more wheels...
on tracked vehicles such as tank
Tank
A tank is a tracked, armoured fighting vehicle designed for front-line combat which combines operational mobility, tactical offensive, and defensive capabilities...
s and bulldozer
Bulldozer
A bulldozer is a crawler equipped with a substantial metal plate used to push large quantities of soil, sand, rubble, etc., during construction work and typically equipped at the rear with a claw-like device to loosen densely-compacted materials.Bulldozers can be found on a wide range of sites,...
s.
In popular culture
The Canadian band Cowboy JunkiesCowboy Junkies
Cowboy Junkies are a Canadian alternative country/blues/folk rock band. The group was formed in Toronto in 1985 by Margo Timmins , Michael Timmins , Peter Timmins and Alan Anton ....
perform a song called "Lost My Driving Wheel", with the lyrics "I feel like an old engine/ That's lost my driving wheel" and can't go any further.
Many versions the American folk song In the Pines reference a decapitated man's head being found in a driving wheel.
See also
- AAR wheel arrangementAAR wheel arrangementThe AAR wheel arrangement system is a method of classifying locomotive wheel arrangements that was developed by the Association of American Railroads. It is essentially a simplification of the European UIC classification, and it is widely used in North America to describe diesel and electric...
- Drive axles in the article AxleAxleAn axle is a central shaft for a rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to its surroundings, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearings or bushings are provided at the mounting points where the axle...
- Sprocket wheelSprocketA sprocket or sprocket-wheel is a profiled wheel with teeth, cogs, or even sprockets that mesh with a chain, track or other perforated or indented material. The name 'sprocket' applies generally to any wheel upon which are radial projections that engage a chain passing over it...
- UIC classificationUIC classificationThe UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements describes the wheel arrangement of locomotives, multiple units and trams. It is set out in the International Union of Railways "Leaflet 650 - Standard designation of axle arrangement on locomotives and multiple-unit sets". It is used in much...
- Whyte notationWhyte notationThe Whyte notation for classifying steam locomotives by wheel arrangement was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte and came into use in the early twentieth century encouraged by an editorial in American Engineer and Railroad Journal...

