
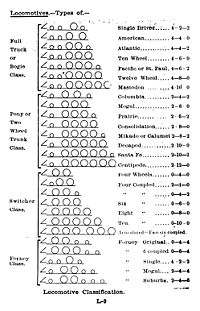
Whyte notation
Encyclopedia
Steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a railway locomotive that produces its power through a steam engine. These locomotives are fueled by burning some combustible material, usually coal, wood or oil, to produce steam in a boiler, which drives the steam engine...
s by wheel arrangement
Wheel arrangement
In rail transport, a wheel arrangement is a system of classifying the way in which wheels are distributed beneath a locomotive.. Several notations exist to describe the wheel assemblies of a locomotive by type, position, and connections, with the adopted notations varying by country...
was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte
Frederick Methvan Whyte
Frederick Methvan Whyte was a mechanical engineer of Dutch background who worked for the New York Central in the United States. He is most widely known as the person who developed Whyte notation to describe the different wheel arrangements of steam locomotives in 1900.In some railroad literature,...
and came into use in the early twentieth century encouraged by an editorial in American Engineer and Railroad Journal (December 1900). Whyte's system counts the number of leading wheel
Leading wheel
The leading wheel or leading axle of a steam locomotive is an unpowered wheel or axle located in front of the driving wheels. The axle or axles of the leading wheels are normally located in a truck...
s, then the number of driving wheel
Driving wheel
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons...
s, and finally the number of trailing wheel
Trailing wheel
On a steam locomotive, a trailing wheel or trailing axle is generally an unpowered wheel or axle located behind the driving wheels. The axle of the trailing wheels was usually located on a trailing truck...
s, groups of numbers being separated by dashes. Other classification schemes, like UIC classification
UIC classification
The UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements describes the wheel arrangement of locomotives, multiple units and trams. It is set out in the International Union of Railways "Leaflet 650 - Standard designation of axle arrangement on locomotives and multiple-unit sets". It is used in much...
and the French, Turkish and Swiss systems for steam locomotives, count axles rather than wheels.
Thus, in the Whyte Notation a locomotive with two leading axles (and thus four wheels) in front, then three driving axles (six wheels) and then one trailing axle (two wheels) is classified as a 4-6-2
4-6-2
4-6-2, in the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle .These locomotives are also known as Pacifics...
.
Articulated locomotives
Articulated locomotiveArticulated locomotive
Articulated locomotive usually means a steam locomotive with one or more engine units which can move independent of the main frame. This is done to allow a longer locomotive to negotiate tighter curves...
s such as Garratt
Garratt
A Garratt is a type of steam locomotive that is articulated in three parts. Its boiler is mounted on the centre frame, and two steam engines are mounted on separate frames, one on each end of the boiler. Articulation permits larger locomotives to negotiate curves and lighter rails that might...
s, which are effectively two locomotives joined by a common boiler
Boiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which water or other fluid is heated. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications.-Materials:...
, have a + between the arrangements of each engine. Thus, a "double Pacific" type Garratt is a 4-6-2+2-6-4.
Simpler articulated types such as Mallets, where there are no unpowered axles between powered axles, have extra groups of numbers in the middle. Thus a Union Pacific Big Boy
Union Pacific Big Boy
Big Boy was the name of the Union Pacific Railroad's 4000-class 4-8-8-4 articulated steam locomotives, built between 1941 and 1944 by American Locomotive Company...
is a 4-8-8-4; there are two leading axles, one group of four driving axles, another group of four driving axles, and then two trailing axles.
For Garratt locomotives the + sign is used even when there are no intermediate unpowered axles, e.g. the LMS Garratt
LMS Garratt
The London Midland and Scottish Railway Garratt was a class of Garratt 2-6-0+0-6-2 steam locomotive designed for heavy freight. A total of 33 were built from 1927, making them the most numerous class of Garratt in Britain.-Overview:...
2-6-0+0-6-2
2-6-0+0-6-2
In the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, a 2-6-0+0-6-2 is a Garratt articulated locomotive using a pair of 2-6-0 power units back to back, with the boiler and cab suspended between them...
. This is because the two engine units are more than just power bogies. They are complete engines, carrying fuel and water tanks. The + sign represents the bridge (carrying the boiler) which links the two engines.
Suffixes
The suffix T indicates a tank locomotiveTank locomotive
A tank locomotive or tank engine is a steam locomotive that carries its water in one or more on-board water tanks, instead of pulling it behind it in a tender. It will most likely also have some kind of bunker to hold the fuel. There are several different types of tank locomotive dependent upon...
; otherwise, a tender locomotive
Tender locomotive
A tender or coal-car is a special rail vehicle hauled by a steam locomotive containing the locomotive's fuel and water. Steam locomotives consume large quantities of water compared to the quantity of fuel, so tenders are necessary to keep the locomotive running over long distances. A locomotive...
is assumed. In British practice, this is sometimes extended to indicate the type of tank locomotive: T means side tank, PT pannier tank, ST saddle tank, WT well tank. T+T means a tank locomotive that has a tender for additional coal or water capacity.
In Europe, the suffix R can signify rack (0-6-0RT) or reversible (0-6-0TR), the latter case being the Bi-cabine locomotives used in France.
The suffix F indicates a fireless locomotive
Fireless locomotive
A fireless locomotive is a type of locomotive designed for use under conditions restricted by either the presence of flammable material or the need for cleanliness...
(0-4-0F). Note that this locomotive has no tender.
Other suffixes have been used at times, including ng for narrow-gauge locomotives (i.e., less than 56.5 in / 1435 mm) and CA or ca for compressed air (i.e. running on compressed air from a tank instead of steam from a boiler).
Internal combustion locomotives
In Britain, small diesel and petrolGasoline
Gasoline , or petrol , is a toxic, translucent, petroleum-derived liquid that is primarily used as a fuel in internal combustion engines. It consists mostly of organic compounds obtained by the fractional distillation of petroleum, enhanced with a variety of additives. Some gasolines also contain...
locomotives are usually classified in the same way as steam locomotives, e.g. 0-4-0, 0-6-0, 0-8-0. This may be followed by D for diesel or P for petrol, and another letter describing the transmission: E for electric, H hydraulic, M mechanical. Thus 0-6-0DE denotes a six-wheel diesel locomotive with electric transmission. Where the axles are coupled by chains or shafts (rather than side-rods), or are individually driven, the terms 4w, 6w or 8w are generally used. Thus 4wPE indicates a four-wheel petrol locomotive with electric transmission. For large diesel locomotives the UIC classification
UIC classification
The UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements describes the wheel arrangement of locomotives, multiple units and trams. It is set out in the International Union of Railways "Leaflet 650 - Standard designation of axle arrangement on locomotives and multiple-unit sets". It is used in much...
is used.
Limitations
The main limitation of the Whyte Notation in classifying locomotives was that it did not cover non-standard steam locomotive typessuch as Shay locomotiveShay locomotive
The Shay locomotive was the most widely used geared steam locomotive. The locomotives were built to the patents of Ephraim Shay, who has been credited with the popularization of the concept of a geared steam locomotive...
s, which use geared trucks rather than driving wheels. This led to the design of other forms of classification. The most commonly used system in Europe outside the United Kingdom is the UIC classification scheme, based on German practice, which can more completely define the exact layout of a locomotive.
Naming
In American (and to a lesser extent British) working practice, most wheel arrangements in common use were given individual names, often from the name of the first such locomotive built. For example the 2-2-02-2-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-2-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, two powered driving wheels on one axle, and no trailing wheels...
type arrangement is named Planet, after the 1830 locomotive
Planet (locomotive)
Planet was an early steam locomotive built in 1830 by Robert Stephenson and Company for the Liverpool and Manchester Railway. The ninth locomotive built for the L&MR, it was Stephenson's next major design change after the Rocket. It was the first locomotive to employ inside cylinders, and...
on which it was first used. (This naming convention is similar to the naming of warship classes.)
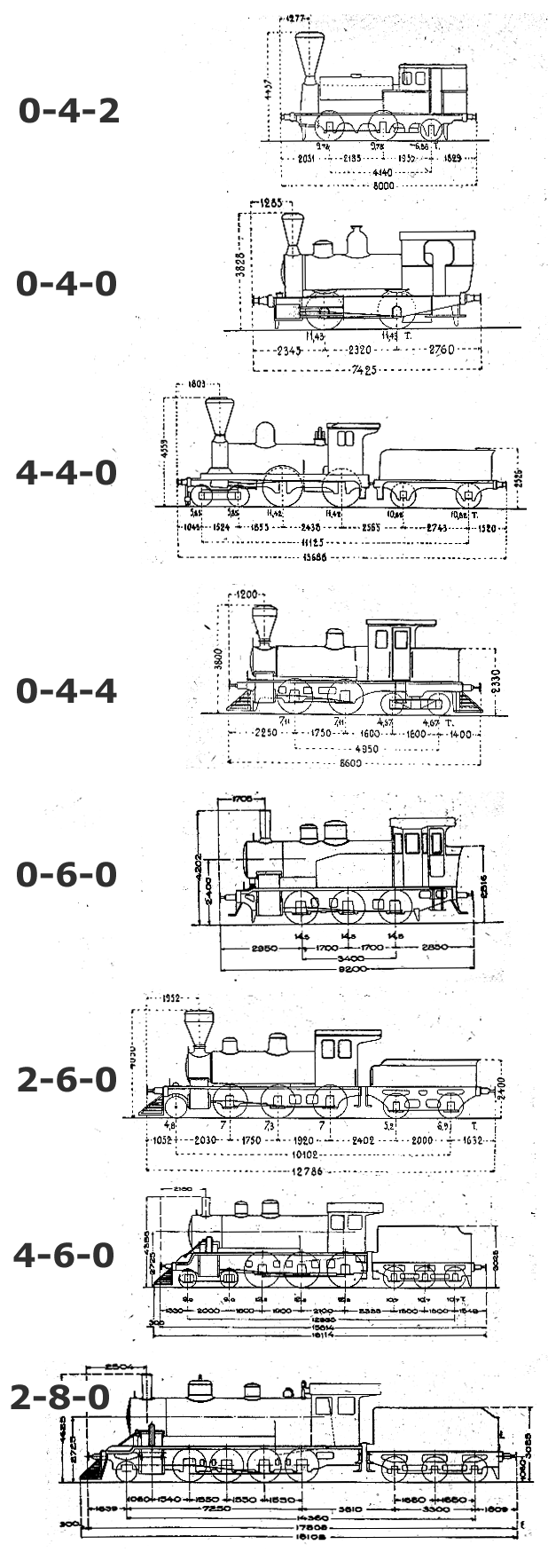
Common wheel arrangements
Here is a list of the most common wheel arrangements: in the illustration the front of the locomotive is to the left.| Arrangement (locomotive front is to the left) | |Whyte classification | |Name |
|---|---|---|
| Non-articulated locomotives | ||
 |
0-2-2 0-2-2 An 0-2-2, in the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, is one that has two coupled driving wheels followed by two trailing wheels, with no leading wheels... |
Northumbrian |
 |
2-2-0 2-2-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-2-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, two powered driving wheels on one axle, and no trailing wheels... |
Planet |
 |
2-2-2 2-2-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-2-2 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle two powered driving wheels on one axle, and two trailing wheels on one axle. The wheel arrangement both provided more stability and enabled a larger firebox... |
Single, Jenny Lind |
 |
2-2-4 2-2-4 In Whyte notation, a 2-2-4 is a railroad steam locomotive that has two leading wheels followed by two coupled driving wheels and four trailing wheels... |
|
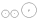 |
4-2-0 4-2-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-2-0 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, two powered and coupled driving wheels on one axle, and no trailing wheels... |
Jervis |
 |
4-2-2 4-2-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-2-2 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, two powered driving wheels on one axle, and two trailing wheels on one axle.... |
Bicycle |
 |
4-2-4 4-2-4 (locomotive) In Whyte notation, a 4-2-4 is a steam locomotive that has a four-wheel leading truck, one powered driving axle and a four-wheel unpowered trailing truck.Other equivalent classifications are:... |
|
 |
6-2-0 6-2-0 In the Whyte notation, a 6-2-0 is a railroad steam locomotive that has an unpowered three-axle leading truck followed by a single powered driving axle... |
Crampton |
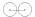 |
0-4-0 0-4-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 0-4-0 represents one of the simplest possible types, that with two axles and four coupled wheels, all of which are driven... |
Four-Coupled |
 |
0-4-2 0-4-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 0-4-2 represents the wheel arrangement with no leading wheels, four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle... |
|
 |
0-4-4 0-4-4 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 0-4-4 represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and four trailing wheels on two axles... |
Forney |
 |
2-4-0 2-4-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-4-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and no trailing wheels.... |
Porter, 'Old English' |
 |
2-4-2 2-4-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-4-2 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle... |
Columbia |
 |
2-4-4 2-4-4 In Whyte notation, a 2-4-4 is a steam locomotive with two unpowered leading wheels followed by four powered driving wheels and four unpowered trailing wheels.-Equivalent classifications:Other equivalent classifications are:... |
|
 |
4-4-0 4-4-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-4-0 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and no trailing wheels... |
American, Eight-wheeler |
 |
4-4-2 4-4-2 (locomotive) Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-4-2 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle... |
Atlantic |
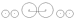 |
4-4-4 4-4-4 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-4-4 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and four trailing wheels on two axles. In the United States, this arrangement was named the... |
Reading, Jubilee (Canada) |
 |
0-6-0 0-6-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 0-6-0 represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and no trailing wheels... |
(one driving wheel per axle; used on Patiala State Monorail Trainways Patiala State Monorail Trainways Patiala State Monorail Trainways was a unique rail guided, partially road-borne railways system running in Patiala in the State of Punjab from 1907 to 1927.Unusual railways by Mr. J. R. Day and Mr. B. G... and also on the Listowel and Ballybunion Railway) |
 |
0-6-0 0-6-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 0-6-0 represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and no trailing wheels... |
Six-Coupled, Bourbonnais (France), USRA 0-6-0 USRA 0-6-0 The USRA 0-6-0 was a USRA standard class of steam locomotive designed under the control of the United States Railroad Administration, the nationalized railroad system in the United States during World War I... (United States) |
 |
0-6-2 0-6-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 0-6-2 represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle... |
|
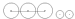 |
0-6-4 0-6-4 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 0-6-4 represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and four trailing wheels on two axles.... |
Forney six-coupled |
 |
2-6-0 2-6-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-6-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and no trailing wheels. This arrangement is commonly called a Mogul... |
Mogul |
 |
2-6-2 2-6-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-6-2 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels, six coupled driving wheels and two trailing wheels.Other equivalent classifications are:... |
Prairie |
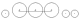 |
2-6-4 2-6-4 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, a 2-6-4 locomotive has two leading wheels, six coupled driving wheels and four trailing wheels... |
Adriatic |
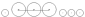 |
2-6-6 2-6-6 In the Whyte notation for describing steam locomotive wheel arrangement, a 2-6-6 is a locomotive with a two-wheeled leading truck, six driving wheels, and a six-wheeled trailing truck. All the locomotives produced of this arrangement have been tank locomotives, and the vast majority in the United... |
|
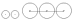 |
4-6-0 4-6-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-6-0 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles in a leading truck, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and no trailing wheels. This wheel arrangement became the second-most popular... |
Ten-Wheeler (not Britain) |
 |
4-6-2 4-6-2 4-6-2, in the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle .These locomotives are also known as Pacifics... |
Pacific |
 |
4-6-4 4-6-4 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-6-4 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles, and four trailing wheels on two axles .Other equivalent classifications are:UIC classification:... |
Hudson, Baltic |
 |
0-8-0 0-8-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 0-8-0 represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels... |
Eight-Coupled, USRA 0-8-0 USRA 0-8-0 The USRA 0-8-0 was a USRA standard class of steam locomotive designed under the control of the United States Railroad Administration, the nationalized railroad system in the United States during World War I... (United States) |
 |
0-8-2 0-8-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 0-8-2 represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle .... |
|
 |
0-8-4 0-8-4 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 0-8-4 represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and four trailing wheels on two axles .... |
|
 |
2-8-0 2-8-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-8-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels... |
Consolidation |
 |
2-8-2 2-8-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-8-2 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle... |
Mikado, Mike, MacArthur |
 |
2-8-4 2-8-4 In the Whyte notation, a 2-8-4 is a railroad steam locomotive that has one unpowered leading axle followed by four powered driving axles and two unpowered trailing axles. This locomotive type is most often referred to as a Berkshire, though the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway used the name Kanawha for... |
Berkshire, Kanawha |
 |
2-8-6 2-8-6 In the Whyte notation for describing steam locomotive wheel arrangement, a 2-8-6 is a locomotive with a two-wheel leading truck, eight driving wheels, and a six-wheel trailing truck... |
Used only on four Mason Bogie Mason Bogie The Mason Bogie is a type of articulated steam locomotive suited for sharp curves and uneven track, once commonly used on narrow gauge lines in the United States... locomotives |
 |
4-8-0 4-8-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-8-0 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels. The type was nicknamed the Mastodon or Twelve-wheeler in North America.... |
Mastodon, Twelve-Wheeler |
 |
4-8-2 4-8-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-8-2 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle... |
Mountain, Mohawk |
 |
4-8-4 4-8-4 Under the Whyte notation classification of steam locomotives, 4-8-4 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and four trailing wheels on two axles .Other equivalent classifications are:UIC classification: 2D2... |
Northern, Niagara, Confederation, Dixie, Greenbrier, Pocono, Potomac, Golden State, Western, General, Wyoming (Lehigh Valley Lehigh Valley Railroad The Lehigh Valley Railroad was one of a number of railroads built in the northeastern United States primarily to haul anthracite coal.It was authorized April 21, 1846 in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and incorporated September 20, 1847 as the Delaware, Lehigh, Schuylkill and Susquehanna Railroad... ), Governor, Big Apple, GS Series "Daylight" Southern Pacific class GS-4 The GS-4 was a streamlined 4-8-4 Northern type steam locomotive that served the Southern Pacific Company from 1941 to 1958. They were built by the Lima Locomotive Works and were numbered 4430 through 4457... (Southern Pacific) |
 |
4-8-6 4-8-6 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, a 4-8-6 locomotive would have had four leading wheels, eight coupled driving wheels and six trailing wheels.Other equivalent classifications are:... |
Proposed by Lima Lima Locomotive Works Lima Locomotive Works was an American firm that manufactured railroad locomotives from the 1870s through the 1950s. The company took the most distinctive part of its name from its main shops location in Lima, Ohio. The shops were located between the Baltimore & Ohio's Cincinnati-Toledo main line... , never built |
 |
6-8-6 6-8-6 In Whyte notation, a 6-8-6 is a steam locomotive with:* six unpowered leading wheels arranged into a three-axle leading truck,* eight powered driving wheels, and* six unpowered trailing wheels arranged into a three-axle trailing truck.... |
(PRR S2 PRR S2 The Pennsylvania Railroad's class S2 was a steam turbine locomotive. Only one prototype was built, #6200, delivered in 1944. The S2 was the sole example of the 6-8-6 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation, featuring a six-wheel leading truck, eight driving wheels, and a six-wheel trailing truck... steam turbine Steam turbine A steam turbine is a mechanical device that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam, and converts it into rotary motion. Its modern manifestation was invented by Sir Charles Parsons in 1884.... locomotive) |
 |
8-8-8 | (Breitspurbahn Breitspurbahn The Breitspurbahn was a planned broad-gauge railway, a personal pet project of Adolf Hitler during the Third Reich of Germany, supposed to run on 3 metre gauge track with double-deck coaches between major cities of Grossdeutschland, Hitler's expanded Germany.-History:Since reparations due after... ) |
 |
0-10-0 0-10-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 0-10-0 represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, ten powered and coupled driving wheels on five axles, and no trailing wheels... |
Ten-Coupled, (rarely) Decapod |
 |
0-10-2 0-10-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 0-10-2 represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, ten powered and coupled driving wheels on five axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle .... |
Union |
 |
2-10-0 2-10-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-10-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, ten powered and coupled driving wheels on five axles, and no trailing wheels... |
Decapod, Russian Decapod |
 |
2-10-2 2-10-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-10-2 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, ten powered and coupled driving wheels on five axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle, usually in a trailing truck... |
Santa Fe, Central, Decapod (only on the Southern Pacific) |
 |
2-10-4 2-10-4 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, a 2-10-4 locomotive has two leading wheels, ten driving wheels , and four trailing wheels... |
Texas, Colorado (CB&Q), Selkirk (Canada) |
 |
4-10-0 4-10-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-10-0 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels, ten powered and coupled driving wheels, and no trailing wheels. Central Pacific Railroad's El Gobernador, built in 1883, was the only locomotive with this wheel... |
Mastodon, Gobernador (in honor of El Gobernador El Gobernador El Gobernador was a 4-10-0 steam locomotive built by Central Pacific Railroad at the railroad's Sacramento, California shops. It was the last of Central Pacific's locomotives to receive an official name and was also the only locomotive of this wheel arrangement to operate on United States rails... ) |
 |
4-10-2 4-10-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-10-2 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles , ten powered and coupled driving wheels on five axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle... |
Southern Pacific Southern Pacific Railroad The Southern Pacific Transportation Company , earlier Southern Pacific Railroad and Southern Pacific Company, and usually simply called the Southern Pacific or Espee, was an American railroad.... , Overland |
 |
0-12-0 0-12-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 0-12-0 represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, twelve powered and coupled driving wheels on six axles, and no trailing wheels.-Equivalent classifications:... |
Twelve-Coupled |
 |
2-12-0 2-12-0 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-12-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle , twelve powered and coupled driving wheels on six axles, and no trailing wheels.... |
Centipede |
 |
2-12-2 2-12-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-12-2 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle , twelve powered and coupled driving wheels on six axles, and two trailing wheels on one axle .-Equivalent classifications:Other equivalent classifications... |
Javanic |
 |
2-12-4 2-12-4 In Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, a 2-12-4 is a locomotive with one pair of unpowered leading wheels, followed by six pairs of powered driving wheels, and two pairs of unpowered trailing wheels.... |
|
 |
4-12-2 4-12-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-12-2 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels, twelve coupled driving wheels, and two trailing wheels.Other equivalent classifications are:... |
Union Pacific |
 |
4-14-4 4-14-4 A 4-14-4, in the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, is a locomotive with four leading wheels, fourteen coupled driving wheels in a rigid frame, and four trailing wheels.... |
AA20 |
| Duplex Duplex locomotive A duplex locomotive is a steam locomotive that divides the driving force on its wheels by using two pairs of cylinders rigidly mounted to a single locomotive frame; it is not an articulated locomotive... locomotives |
||
 |
4-4-4-4 4-4-4-4 A 4-4-4-4 steam locomotive, in the Whyte notation for describing locomotive wheel arrangements, has a four-wheel leading truck, two sets of four driving wheels, and a four-wheel trailing truck.Other equivalent classifications are:... |
(PRR T1 PRR T1 The Pennsylvania Railroad's 52 T1 class duplex-drive 4-4-4-4 steam locomotives, introduced in 1942 and 1946 , were their last-built steam locomotives and their most controversial. They were ambitious, technologically sophisticated, powerful, fast, and uniquely streamlined by Raymond Loewy... ) |
 |
6-4-4-6 6-4-4-6 A 6-4-4-6 steam locomotive, in the Whyte notation for describing locomotive wheel arrangements, is one with six leading wheels, two sets of four driving wheels, and six trailing wheels.Other equivalent classifications are:... |
(PRR S1 PRR S1 The PRR S1 class steam locomotive was an experimental locomotive that was the largest rigid frame passenger locomotive ever built. The streamlined Art Deco styled shell of the locomotive was designed by Raymond Loewy.... ) |
 |
4-4-6-4 4-4-6-4 A 4-4-6-4, in the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, is one that has four leading wheels followed by four coupled driving wheels, a second set of six coupled driving wheels and four trailing wheels.... |
(PRR Q2 PRR Q2 The Pennsylvania Railroad's class Q2 comprised one prototype and twenty-five production duplex steam locomotives of 4-4-6-4 wheel arrangement.... ) |
 |
4-6-4-4 4-6-4-4 In Whyte notation, a 4-6-4-4 is a railroad steam locomotive that has four leading wheels followed by six coupled driving wheels, a second set of four driving wheels and four trailing wheels.Other equivalent classifications are:... |
(PRR Q1 PRR Q1 The Pennsylvania Railroad's class Q1 comprised a single experimental steam locomotive for freight service, #6130, built in March 1942. A duplex locomotive, it had a wheel arrangement of 4-6-4-4, comprising a four-wheel leading truck, two sets of driving wheels in a rigid locomotive frame, and a... ) |
| Mallet (simple and compound) articulated locomotives | ||
 |
0-4-4-0 0-4-4-0 In the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotive wheel arrangement, a 0-4-4-0 is a locomotive with no leading truck, two sets of four driving wheels, and no trailing truck. Examples of this type were constructed as Mallet, Meyer and Double Fairlie locomotives... |
Bavarian BB II Bavarian BB II The Bavarian Class BB II engines were Mallet saturated steam locomotives in the service of the Royal Bavarian State Railways .... |
 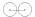 |
2-4-4-0 2-4-4-0 In the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotive wheel arrangement, a 2-4-4-0 is a locomotive with two leading truck, two sets of four driving wheels, and no trailing truck. Examples of this type were constructed as Mallet locomotives.... |
|
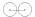  |
0-4-4-2 0-4-4-2 In Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, an 0-4-4-2 is a locomotive that has no leading wheels, two sets of four driving wheels and two trailing wheels.-Equivalent classifications:... |
|
 |
2-4-4-2 2-4-4-2 In Whyte notation, 2-4-4-2 refers to a railroad steam locomotive that has two leading wheels followed by four coupled driving wheels, a second set of four coupled driving wheels, and two trailing wheels.-Equivalent classifications:... |
|
 |
0-6-6-0 0-6-6-0 In Whyte notation, a 0-6-6-0 is a railroad steam locomotive that has two articulated sections, each with six coupled driving wheels, without any leading wheels or trailing wheels.-Equivalent classifications:Other equivalent classifications are:... |
Erie |
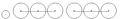 |
2-6-6-0 2-6-6-0 In Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, a 2-6-6-0 is a locomotive with one pair of unpowered leading wheels, followed by two sets of three pairs of powered driving wheels, and no trailing wheels... |
Denver & Salt Lake |
 |
2-6-6-2 2-6-6-2 In Whyte notation, 2-6-6-2 refers to a railroad steam locomotive that has two leading wheels followed by six coupled driving wheels, a second set of six coupled driving wheels, and two trailing wheels... |
|
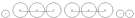 |
2-6-6-4 2-6-6-4 In the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotive wheel arrangement, a 2-6-6-4 is a locomotive with a two-wheel leading truck, two sets of six driving wheels, and a four-wheel trailing truck... |
Norfolk & Western |
 |
2-6-6-6 2-6-6-6 The 2-6-6-6 is an articulated locomotive type with 2 leading wheels, two sets of six driving wheels and six trailing wheels. Only two classes of the 2-6-6-6 type were built. One was the "Allegheny" class, built by the Lima Locomotive Works. The name comes from the locomotive's first service with... |
Allegheny, Blue Ridge |
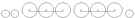 |
4-6-6-2 4-6-6-2 In Whyte notation, a 4-6-6-2 is a steam locomotive with four leading wheels in an unpowered bogie at the front of the locomotive followed by two sets of driving wheels with six wheels each , followed by two unpowered trailing wheels at the rear of the locomotive.Other equivalent classifications... |
(Southern Pacific class MM-2 Southern Pacific class MM-2 Southern Pacific Company's MM-2 class of steam locomotives was Southern Pacific's only class of 2-6-6-2 locomotives ordered and built as cab forward locomotives. They were built in 1911 by Baldwin Locomotive Works and entered service on SP beginning September 19, 1911. By 1914, they had all been... ) |
 |
4-6-6-4 4-6-6-4 In Whyte notation, a 4-6-6-4 is a railroad steam locomotive that has four leading wheels followed by six coupled driving wheels, a second set of six driving wheels and four trailing wheels.Other equivalent classifications are:... |
Challenger |
 |
2-6-8-0 2-6-8-0 A 2-6-8-0 steam locomotive, in the Whyte notation for describing locomotive wheel arrangements, has two leading wheels, a set of six driving wheels, a set of eight driving wheels, and no trailing wheels... |
(Southern Railway, Great Northern Railway) |
 |
0-8-8-0 0-8-8-0 In the Whyte notation for classifying the wheel arrangement of steam locomotives, an 0-8-8-0 is a locomotive with two sets of eight driving wheels and neither leading wheels nor trailing wheels... |
Angus |
 |
2-8-8-0 2-8-8-0 In the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, a 2-8-8-0 is a locomotive with a two-wheel leading truck, two sets of eight driving wheels, and no trailing truck.-Equivalent classifications:... |
Bull Moose |
 |
2-8-8-2 2-8-8-2 .A 2-8-8-2, in the Whyte notation for describing steam locomotive wheel arrangements, is an articulated locomotive with a two-wheel leading truck, two sets of eight driving wheels, and a two-wheel trailing truck. The equivalent UIC classification is, refined to Mallet locomotives, D1... |
Chesapeake |
 |
2-8-8-4 2-8-8-4 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, a 2-8-8-4 is a steam locomotive with two leading wheels, two sets of eight driving wheels, and a four-wheel trailing truck.Other equivalent classifications are:... |
Yellowstone |
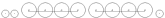 |
4-8-8-2 4-8-8-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, a 4-8-8-2 is a locomotive with four leading wheels, two sets of eight driving wheels, and a two-wheel trailing truck.Other equivalent classifications are:... |
Southern Pacific Southern Pacific Railroad The Southern Pacific Transportation Company , earlier Southern Pacific Railroad and Southern Pacific Company, and usually simply called the Southern Pacific or Espee, was an American railroad.... cab forward Cab forward The term cab forward refers to various rail and road vehicle designs which place the driver's compartment substantially farther towards the front than is common practice.- Rail locomotives :... classes AC-4 Southern Pacific class AC-4 Southern Pacific Railroad's AC-4 class of steam locomotives was the first class of cab forward locomotives built with the 4-8-8-2 wheel arrangement. They were designed as an improvement upon the railroad's existing MC class 2-8-8-2 locomotives having a larger firebox.The AC-4s were built in August... through AC-12 Southern Pacific class AC-12 Southern Pacific Railroad's AC-12 class of cab forward steam locomotives was the last class of steam locomotives ordered by Southern Pacific. They were built by Baldwin Locomotive Works during World War II, with the first, number 4275, entering service on October 27, 1943, and the last, 4294, on... (except AC-9 Southern Pacific class AC-9 The AC-9 was one of two Southern Pacific Railroad'sarticulated steam locomotive class that ran smokebox forward after 1920. Twelve AC-9 class locomotives were built by Lima in 1939 and were Southern Pacific's biggest steam engines... ) |
 |
4-8-8-4 4-8-8-4 In the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, a 4-8-8-4 is a locomotive with a four-wheel leading truck, two sets of eight driving wheels, and a four-wheel trailing truck.Other equivalent classifications are:... |
Big Boy Union Pacific Big Boy Big Boy was the name of the Union Pacific Railroad's 4000-class 4-8-8-4 articulated steam locomotives, built between 1941 and 1944 by American Locomotive Company... |
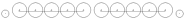 |
2-10-10-2 2-10-10-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotive wheel arrangements, a 2-10-10-2 is a locomotive with two leading wheels, two sets of ten driving wheels, and a pair of trailing wheels.Other equivalent classifications are:... |
(Santa Fe and Virginian railroads) |
 |
2-8-8-8-2 2-8-8-8-2 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, a 2-8-8-8-2 has two leading wheels, three sets of eight driving wheels, and two trailing wheels. Because of its length, such a locomotive must be an articulated locomotive. It is not longer than a normal articulated; the third... |
Triplex (Erie RR) |
 |
2-8-8-8-4 2-8-8-8-4 Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, a 2-8-8-8-4 has two leading wheels, three sets of eight driving wheels, and a four trailing wheels.Other equivalent classifications are:... |
Triplex (Virginian RR) |
| Garratt Garratt A Garratt is a type of steam locomotive that is articulated in three parts. Its boiler is mounted on the centre frame, and two steam engines are mounted on separate frames, one on each end of the boiler. Articulation permits larger locomotives to negotiate curves and lighter rails that might... articulated locomotives |
||
 |
0-4-0+0-4-0 0-4-0+0-4-0 A 0-4-0+0-4-0, in the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, is an articulated locomotive, usually of the Garratt type. It features no leading or trailing wheels at either end, having only two sets of four driving wheels... |
|
 |
2-6-2+2-6-2 2-6-2+2-6-2 A 2-6-2+2-6-2, in the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, is an articulated locomotive type used on Garratt and Fairlie locomotives... |
|
See also
- AAR wheel arrangementAAR wheel arrangementThe AAR wheel arrangement system is a method of classifying locomotive wheel arrangements that was developed by the Association of American Railroads. It is essentially a simplification of the European UIC classification, and it is widely used in North America to describe diesel and electric...
- Swiss locomotive and railcar classification
- Wheel arrangementWheel arrangementIn rail transport, a wheel arrangement is a system of classifying the way in which wheels are distributed beneath a locomotive.. Several notations exist to describe the wheel assemblies of a locomotive by type, position, and connections, with the adopted notations varying by country...
- UIC classificationUIC classificationThe UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements describes the wheel arrangement of locomotives, multiple units and trams. It is set out in the International Union of Railways "Leaflet 650 - Standard designation of axle arrangement on locomotives and multiple-unit sets". It is used in much...
:Category:Locomotives by wheel arrangement

