
Dromornis
Encyclopedia
Dromornis is a genus
of prehistoric birds
. They stood 3 meters tall and weighed half a ton. Dromornis lived in Australia
from the late Miocene
to the early Pliocene
, meaning that early humans never encountered this genus.
Dromornis had a huge beak and jaw capable of great force but did not have the beak or claws of a carnivore
.
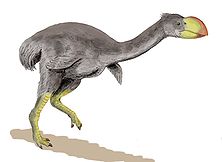 They are sometimes referred to as Mihirung birds. 'Mihirung paringmal' is an Aboriginal word from the Tjapwuring people of Western Victoria and it means 'giant bird'. Although they looked like giant emu
They are sometimes referred to as Mihirung birds. 'Mihirung paringmal' is an Aboriginal word from the Tjapwuring people of Western Victoria and it means 'giant bird'. Although they looked like giant emu
s, the Dromornis are more closely related to geese.
Dromornis stirtoni was three metres (10 feet) tall and weighed half a ton (500 kilos). It inhabited subtropical open woodlands in Australia
during the Late Miocene
and may have been carnivorous
. It was heavier than the Moa
and taller than Aepyornis
. The type specimen, a femur, was found in a 55 metre deep well at Peak Downs
, Queensland, and subsequently described by Richard Owen
in 1872. Due to the poor fossil record of Dromornis australis (the type species
of the genus) and the large time gap between the two Dromornis species, D. stirtoni may eventually be reassigned to the genus Bullockornis
.
This species had a long neck and stub-like wings, rendering it flightless. Its legs were powerful, but it is not believed to have been a fast runner. The bird's beak was large and immensely powerful, leading early researchers to believe that it was used to shear through tough plant stalks. However, recently others have argued that the size of the beak suggests that the bird was a carnivore.
Dromornis are part of a family of giant birds called Dromornithidae that lived from 15 million years ago until less than 30,000 years ago. Australia had been separated from the big southern landmass of Gondwana
for millions of years by this time. The animals of Australia had evolved very slowly in almost complete isolation from the animals of other continents. There were forests and a permanent water supply at Alcoota
where the Dromornis birds lived, although the climate was very unpredictable.
Genus
In biology, a genus is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia...
of prehistoric birds
Fossil birds
Birds are generally believed to have evolved from certain feathered theropod dinosaurs, and there is no real dividing line between birds and dinosaurs, except of course that some of the former survived the Cretaceous-Tertiary extinction event while the latter did not. For the purposes of this...
. They stood 3 meters tall and weighed half a ton. Dromornis lived in Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
from the late Miocene
Miocene
The Miocene is a geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about . The Miocene was named by Sir Charles Lyell. Its name comes from the Greek words and and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern sea invertebrates than the Pliocene. The Miocene follows the Oligocene...
to the early Pliocene
Pliocene
The Pliocene Epoch is the period in the geologic timescale that extends from 5.332 million to 2.588 million years before present. It is the second and youngest epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Miocene Epoch and is followed by the Pleistocene Epoch...
, meaning that early humans never encountered this genus.
Dromornis had a huge beak and jaw capable of great force but did not have the beak or claws of a carnivore
Carnivore
A carnivore meaning 'meat eater' is an organism that derives its energy and nutrient requirements from a diet consisting mainly or exclusively of animal tissue, whether through predation or scavenging...
.

Emu
The Emu Dromaius novaehollandiae) is the largest bird native to Australia and the only extant member of the genus Dromaius. It is the second-largest extant bird in the world by height, after its ratite relative, the ostrich. There are three subspecies of Emus in Australia...
s, the Dromornis are more closely related to geese.
Dromornis stirtoni was three metres (10 feet) tall and weighed half a ton (500 kilos). It inhabited subtropical open woodlands in Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
during the Late Miocene
Miocene
The Miocene is a geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about . The Miocene was named by Sir Charles Lyell. Its name comes from the Greek words and and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern sea invertebrates than the Pliocene. The Miocene follows the Oligocene...
and may have been carnivorous
Carnivore
A carnivore meaning 'meat eater' is an organism that derives its energy and nutrient requirements from a diet consisting mainly or exclusively of animal tissue, whether through predation or scavenging...
. It was heavier than the Moa
Moa
The moa were eleven species of flightless birds endemic to New Zealand. The two largest species, Dinornis robustus and Dinornis novaezelandiae, reached about in height with neck outstretched, and weighed about ....
and taller than Aepyornis
Aepyornis
Aepyornis is a genus of aepyornithid, one of two genera of ratite birds endemic to Madagascar known as elephant birds. This animal was the world's largest bird until its extinction, about 1000 years ago.-Description:...
. The type specimen, a femur, was found in a 55 metre deep well at Peak Downs
Peak Downs
Peak Downs may refer to:* Shire of Peak Downs, a Local Government Area of Queensland, Australia* Peak Downs Mine, a mine in Queensland, Australia...
, Queensland, and subsequently described by Richard Owen
Richard Owen
Sir Richard Owen, FRS KCB was an English biologist, comparative anatomist and palaeontologist.Owen is probably best remembered today for coining the word Dinosauria and for his outspoken opposition to Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection...
in 1872. Due to the poor fossil record of Dromornis australis (the type species
Type species
In biological nomenclature, a type species is both a concept and a practical system which is used in the classification and nomenclature of animals and plants. The value of a "type species" lies in the fact that it makes clear what is meant by a particular genus name. A type species is the species...
of the genus) and the large time gap between the two Dromornis species, D. stirtoni may eventually be reassigned to the genus Bullockornis
Bullockornis
Bullockornis, nicknamed the Demon Duck of Doom, is an extinct flightless bird that appeared to have lived in the Middle Miocene, approximately 15 million years ago, in what is now Australia....
.
This species had a long neck and stub-like wings, rendering it flightless. Its legs were powerful, but it is not believed to have been a fast runner. The bird's beak was large and immensely powerful, leading early researchers to believe that it was used to shear through tough plant stalks. However, recently others have argued that the size of the beak suggests that the bird was a carnivore.
Dromornis are part of a family of giant birds called Dromornithidae that lived from 15 million years ago until less than 30,000 years ago. Australia had been separated from the big southern landmass of Gondwana
Gondwana
In paleogeography, Gondwana , originally Gondwanaland, was the southernmost of two supercontinents that later became parts of the Pangaea supercontinent. It existed from approximately 510 to 180 million years ago . Gondwana is believed to have sutured between ca. 570 and 510 Mya,...
for millions of years by this time. The animals of Australia had evolved very slowly in almost complete isolation from the animals of other continents. There were forests and a permanent water supply at Alcoota
Alcoota
The Alcoota Fossil Beds are an important paleontological site located on Alcoota Station in Central Australia, 200km north-east of Alice Springs. It is notable for the occurrence of well-preserved, rare, Tertiary vertebrate fossils, which provide evidence of the evolution of the Northern...
where the Dromornis birds lived, although the climate was very unpredictable.

