Drug abuse
Encyclopedia
Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, refers to a maladaptive pattern of use of a substance that is not considered dependent. The term "drug abuse" does not exclude dependency, but is otherwise used in a similar manner in nonmedical contexts. The terms have a huge range of definitions related to taking a psychoactive drug
or performance enhancing drug for a non-therapeutic or non-medical effect. All of these definitions imply a negative judgment of the drug use in question (compare with the term responsible drug use
for alternative views). Some of the drugs most often associated with this term include alcohol
, amphetamines, barbiturate
s, benzodiazepine
s (particularly temazepam
, nimetazepam
, and flunitrazepam
), cocaine
, methaqualone
, and opioids. Use of these drugs may lead to criminal penalty in addition to possible physical, social, and psychological harm, both strongly depending on local jurisdiction. Other definitions of drug abuse fall into four main categories: public health definitions, mass communication and vernacular usage, medical definitions, and political and criminal justice definitions.
Substance abuse is a form of substance-related disorder.
 ]
]
Public health
practitioners have attempted to look at drug abuse from a broader perspective than the individual, emphasizing the role of society, culture and availability. Rather than accepting the loaded terms alcohol or drug "abuse," many public health professionals have adopted phrases such as "substance and alcohol type problems" or "harmful/problematic use" of drugs.
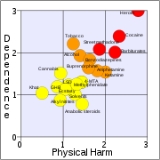
The Health Officers Council of British Columbia
— in their 2005 policy discussion paper, A Public Health Approach to Drug Control in Canada — has adopted a public health model of psychoactive substance use that challenges the simplistic black-and-white construction of the binary (or complementary) antonym
s "use" vs. "abuse". This model explicitly recognizes a spectrum of use, ranging from beneficial use to chronic dependence
(see diagram to the right).
's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
(DSM),the World Health Organization
's International Statistical Classification of Diseases and ICRIS Medical organization Related Health Problems
(ICD), no longer recognize 'drug abuse' as a current medical diagnosis. Instead, DSM has adopted substance abuse as a blanket term to include drug abuse and other things. ICD refrains from using either "substance abuse" or "drug abuse", instead using the term "harmful use" to cover physical or psychological harm to the user from use. Physical dependence, abuse of, and withdrawal from drugs and other miscellaneous substances is outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
(DSM-IV-TR) ). Its section Substance dependence
begins with:
However, other definitions differ; they may entail psychological or physical dependence
, and may focus on treatment and prevention in terms of the social consequences of substance uses.
, anxiolytic
, analgesic
, or stimulant
properties. Prescription misuse has been variably and inconsistently defined based on drug prescription status, the uses that occur without a prescription, intentional use to achieve intoxicating effects, route of administration, co-ingestion with alcohol
, and the presence or absence of abuse or dependence symptoms. Tolerance relates to the pharmacological property of substances in which chronic use leads to a change in the central nervous system, meaning that more of the substance is needed in order to produce desired effects. Stopping or reducing the use of this substance would cause withdrawal symptoms to occur.
points out that there are two issues with the term "drug abuse". First, what constitutes a "drug" is debatable. For instance, GHB
, a naturally occurring substance in the central nervous system is considered a drug, and is illegal in many countries, while nicotine
is not officially considered a drug in most countries. Second, the word "abuse" implies a recognized standard of use for any substance. Drinking an occasional glass of wine is considered acceptable in many Western countries, while drinking several bottles is seen as an abuse. Strict temperance advocates, which may or may not be religiously motivated, would see drinking even one glass as an abuse, and some groups even condemn caffeine
use in any quantity. Similarly, adopting the view that any (recreational) use of marijuana or amphetamines constitutes drug abuse implies that we have already decided that substance is harmful even in minute quantities.
, morbidity, injuries, unprotected sex, violence
, deaths, motor vehicle accidents, homicides, suicides, physical dependence
or psychological addiction
.
There is a high rate of suicide in alcoholics and other drug abusers. The reasons believed to cause the increased risk of suicide include the long-term abuse of alcohol and other drugs causing physiological distortion of brain chemistry as well as the social isolation. Another factor is the acute intoxicating effects of the drugs may make suicide more likely to occur. Suicide is also very common in adolescent alcohol abusers, with 1 in 4 suicides in adolescents being related to alcohol abuse. In the USA approximately 30 percent of suicides are related to alcohol abuse. Alcohol abuse is also associated with increased risks of committing criminal offences including child abuse
, domestic violence
, rapes, burglaries and assaults.
Drug abuse, including alcohol and prescription drugs can induce symptomatology which resembles mental illness. This can occur both in the intoxicated state and also during the withdrawal
state. In some cases these substance induced psychiatric disorders can persist long after detoxification, such as prolonged psychosis or depression after amphetamine or cocaine abuse. A protracted withdrawal syndrome can also occur with symptoms persisting for months after cessation of use. Benzodiazepines are the most notable drug for inducing prolonged withdrawal effects with symptoms sometimes persisting for years after cessation of use. Abuse of hallucinogens can trigger delusional and other psychotic phenomena long after cessation of use and cannabis
may trigger panic attacks during intoxication and with use it may cause a state similar to dysthymia. Severe anxiety and depression are commonly induced by sustained alcohol abuse which in most cases abates with prolonged abstinence. Even moderate alcohol sustained use may increase anxiety and depression levels in some individuals. In most cases these drug induced psychiatric disorders fade away with prolonged abstinence.
Drug abuse makes central nervous system
(CNS) effects, which produce changes in mood, levels of awareness or perceptions and sensations. Most of these drugs also alter systems other than the CNS. Some of these are often thought of as being abused. Some drugs appear to be more likely to lead to uncontrolled use than others.
Traditionally, new pharmacotherapies are quickly adopted in primary care settings, however; drugs for substance abuse treatment have faced many barriers. Naltrexone
, a drug originally marketed under the name "ReVia," and now marketed in intramuscular formulation as "Vivitrol" or in oral formulation as a generic, is a medication approved for the treatment of alcohol dependence. This drug has reached very few patients. This may be due to a number of factors, including resistance by Addiction Medicine
specialists and lack of resources.
The ability to recognize the signs of drug use or the symptoms of drug use in family members by parents and spouses has been affected significantly by the emergence of home drug test technology which helps identify recent use of common street and prescription drugs with near lab quality accuracy.
survey, a nationwide study on rates of substance use in the United States, show that 48.2% of 12th graders report having used an illicit drug at some point in their lives. In the 30 days prior to the survey, 41.2% of 12th graders had consumed alcohol and 19.2% of 12th graders had smoked tobacco cigarettes. In 2009 in the United States about 21% of high school students have taken prescription drugs without a prescription. And earlier in 2002, the World health Organization estimated that around 140 million people were alcohol dependent and another 400 million suffered alcohol-related problems.
Studies have shown that the large majority of adolescents will phase out of drug use before it becomes problematic. Thus, although rates of overall use are high, the percentage of adolescents who meet criteria for substance abuse is significantly lower (close to 5%). According to BBC, "Worldwide, the UN estimates there are more than 50 million regular users of morphine diacetate (heroin), cocaine and synthetic drugs."
In 1966, the American Medical Association
's Committee on Alcoholism and Addiction defined abuse of stimulants (amphetamines, primarily) in terms of 'medical supervision':
In 1973 the National Commission on Marijuana and Drug Abuse stated:
's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
(published in 1952) grouped alcohol and drug abuse under Sociopathic Personality Disturbances, which were thought to be symptoms of deeper psychological disorders or moral weakness.
The third edition, published in 1980, was the first to recognize substance abuse (including drug abuse) and substance dependence as conditions separate from substance abuse alone, bringing in social and cultural factors. The definition of dependence emphasised tolerance to drugs, and withdrawal from them as key components to diagnosis, whereas abuse was defined as "problematic use with social or occupational impairment" but without withdrawal or tolerance.
In 1987 the DSM-IIIR category "psychoactive substance abuse," which includes former concepts of drug abuse is defined as "a maladaptive pattern of use indicated by...continued use despite knowledge of having a persistent or recurrent social, occupational, psychological or physical problem that is caused or exacerbated by the use (or by) recurrent use in situations in which it is physically hazardous." It is a residual category, with dependence taking precedence when applicable. It was the first definition to give equal weight to behavioural and physiological factors in diagnosis.
By 1988, the DSM-IV defines substance dependence as "a syndrome involving compulsive use, with or without tolerance and withdrawal"; whereas substance abuse is "problematic use without compulsive use, significant tolerance, or withdrawal." Substance abuse can be harmful to your health and may even be deadly in certain scenarios
By 1994, The fourth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
(DSM) issued by the American Psychiatric Association
, the DSM-IV-TR, defines substance dependence as "when an individual persists in use of alcohol or other drugs despite problems related to use of the substance, substance dependence
may be diagnosed." followed by criteria for the diagnose
DSM-IV-TR defines substance abuse as:
The fifth edition of the DSM (DSM-5
), planned for release in 2013, is likely to have this terminology revisited yet again. Under consideration is a transition from the abuse/dependence terminology. At the moment, abuse is seen as an early form or less hazardous form of the disease characterized with the dependence criteria. However, the APA's 'dependence' term, as noted above, does not mean that physiologic dependence is present but rather means that a disease state is present, one that most would likely refer to as an addicted state. Many involved recognize that the terminology has often led to confusion, both within the medical community and with the general public. The American Psychiatric Association requests input as to how the terminology of this illness should be altered as it moves forward with DSM-5 discussion.
Most governments have designed legislation
to criminalize certain types of drug use. These drugs are often called "illegal drugs" but generally what is illegal is their unlicensed
production, distribution, and possession. These drugs are also called "controlled substances". Even for simple possession, legal punishment can be quite severe (including the death penalty in some countries). Laws vary across countries, and even within them, and have fluctuated widely throughout history.
Attempts by government-sponsored drug control policy to interdict drug supply and eliminate drug abuse have been largely unsuccessful.
In spite of the huge efforts by the U.S., drug supply and purity has reached an all time high, with the vast majority of resources spent on interdiction and law enforcement instead of public health
. In the United States
, the number of nonviolent drug offenders in prison exceeds by 100,000 the total incarcerated population in the EU, despite the fact that the EU has 100 million more citizens.
Despite drug legislation (or perhaps because of it), large, organized criminal drug cartel
s operate worldwide. Advocates of decriminalization argue that drug prohibition makes drug dealing a lucrative business, leading to much of the associated criminal activity.
estimated that the social and economic cost of drug abuse to the UK economy in terms of crime, absenteeism and sickness is in excess of £20 billion a year. and in just the year 1995, America spent nearly $109.8 billion on drug abuse.
However, it does not estimate what portion of those crimes are unintended consequences of drug prohibition (crimes to sustain expensive drug consumption, risky production and dangerous distribution), nor what is the cost of enforcement. Those aspects are necessary for a full analysis of the economics of prohibition.
The Home Office has a recent history of taking a hard line on controlled drugs, including those with no known fatalities and even medical benefits, in direct opposition to the scientific community.
literature, behavioral psychology, and from randomized clinical trials, several evidenced based interventions have emerged:
According to some nurse practitioners, stopping substance abuse can reduce the risk of dying early and also reduce some health risks like heart disease, lung disease, and strokes.
In children and adolescents, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and family therapy
currently have the most research evidence for the treatment of substance abuse problems. These treatments can be administered in a variety of different formats, each of which has varying levels of research support
It has been suggested that social skills
training adjunctive to inpatient treatment of alcohol dependence is probably efficacious.
Psychoactive drug
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, or psychotropic is a chemical substance that crosses the blood–brain barrier and acts primarily upon the central nervous system where it affects brain function, resulting in changes in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition, and behavior...
or performance enhancing drug for a non-therapeutic or non-medical effect. All of these definitions imply a negative judgment of the drug use in question (compare with the term responsible drug use
Responsible drug use
Responsible drug use is a harm reduction strategy based on a belief that illegal recreational drug use can be responsible in terms of reduced or eliminated risk of negative impact on the lives of both the user and others....
for alternative views). Some of the drugs most often associated with this term include alcohol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
, amphetamines, barbiturate
Barbiturate
Barbiturates are drugs that act as central nervous system depressants, and can therefore produce a wide spectrum of effects, from mild sedation to total anesthesia. They are also effective as anxiolytics, as hypnotics, and as anticonvulsants...
s, benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepine
A benzodiazepine is a psychoactive drug whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring...
s (particularly temazepam
Temazepam
Temazepam is an intermediate-acting 3-hydroxy benzodiazepine. It is mostly prescribed for the short-term treatment of sleeplessness in patients who have difficulty maintaining sleep...
, nimetazepam
Nimetazepam
Nimetazepam is an intermediate-acting hypnotic drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It was first synthesized by a team at Hoffmann-La Roche in 1962. It possesses hypnotic, anxiolytic, sedative, and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. Nimetazepam is also an anticonvulsant. It is sold in 5 mg...
, and flunitrazepam
Flunitrazepam
Flunitrazepam is marketed as a potent hypnotic, sedative, anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, amnestic, and skeletal muscle relaxant drug most commonly known as Rohypnol...
), cocaine
Cocaine
Cocaine is a crystalline tropane alkaloid that is obtained from the leaves of the coca plant. The name comes from "coca" in addition to the alkaloid suffix -ine, forming cocaine. It is a stimulant of the central nervous system, an appetite suppressant, and a topical anesthetic...
, methaqualone
Methaqualone
Methaqualone is a sedative-hypnotic drug that is similar in effect to barbiturates, a general central nervous system depressant. The sedative-hypnotic activity was first noted by Indian researchers in the 1950s and in 1962 methaqualone itself was patented in the US by Wallace and Tiernan...
, and opioids. Use of these drugs may lead to criminal penalty in addition to possible physical, social, and psychological harm, both strongly depending on local jurisdiction. Other definitions of drug abuse fall into four main categories: public health definitions, mass communication and vernacular usage, medical definitions, and political and criminal justice definitions.
Substance abuse is a form of substance-related disorder.
Public health definitions

Public health
Public health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals" . It is concerned with threats to health based on population health...
practitioners have attempted to look at drug abuse from a broader perspective than the individual, emphasizing the role of society, culture and availability. Rather than accepting the loaded terms alcohol or drug "abuse," many public health professionals have adopted phrases such as "substance and alcohol type problems" or "harmful/problematic use" of drugs.
The Health Officers Council of British Columbia
British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost of Canada's provinces and is known for its natural beauty, as reflected in its Latin motto, Splendor sine occasu . Its name was chosen by Queen Victoria in 1858...
— in their 2005 policy discussion paper, A Public Health Approach to Drug Control in Canada — has adopted a public health model of psychoactive substance use that challenges the simplistic black-and-white construction of the binary (or complementary) antonym
Antonym
In lexical semantics, opposites are words that lie in an inherently incompatible binary relationship as in the opposite pairs male : female, long : short, up : down, and precede : follow. The notion of incompatibility here refers to the fact that one word in an opposite pair entails that it is not...
s "use" vs. "abuse". This model explicitly recognizes a spectrum of use, ranging from beneficial use to chronic dependence
Substance dependence
The section about substance dependence in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders does not use the word addiction at all. It explains:...
(see diagram to the right).
Medical definitions
In the modern medical profession, the three most used diagnostic tools in the world, the American Psychiatric AssociationAmerican Psychiatric Association
The American Psychiatric Association is the main professional organization of psychiatrists and trainee psychiatrists in the United States, and the most influential worldwide. Its some 38,000 members are mainly American but some are international...
's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders is published by the American Psychiatric Association and provides a common language and standard criteria for the classification of mental disorders...
(DSM),the World Health Organization
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
's International Statistical Classification of Diseases and ICRIS Medical organization Related Health Problems
ICD
The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems is a medical classification that provides codes to classify diseases and a wide variety of signs, symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or disease...
(ICD), no longer recognize 'drug abuse' as a current medical diagnosis. Instead, DSM has adopted substance abuse as a blanket term to include drug abuse and other things. ICD refrains from using either "substance abuse" or "drug abuse", instead using the term "harmful use" to cover physical or psychological harm to the user from use. Physical dependence, abuse of, and withdrawal from drugs and other miscellaneous substances is outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders is published by the American Psychiatric Association and provides a common language and standard criteria for the classification of mental disorders...
(DSM-IV-TR) ). Its section Substance dependence
Substance dependence
The section about substance dependence in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders does not use the word addiction at all. It explains:...
begins with:
-
- "Substance dependence When an individual persists in use of alcohol or other drugs despite problems related to use of the substance, substance dependenceSubstance dependenceThe section about substance dependence in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders does not use the word addiction at all. It explains:...
may be diagnosed. Compulsive and repetitive use may result in tolerance to the effect of the drug and withdrawal symptoms when use is reduced or stopped. These, along with Substance Abuse are considered Substance Use Disorders...."
- "Substance dependence When an individual persists in use of alcohol or other drugs despite problems related to use of the substance, substance dependence
However, other definitions differ; they may entail psychological or physical dependence
Substance dependence
The section about substance dependence in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders does not use the word addiction at all. It explains:...
, and may focus on treatment and prevention in terms of the social consequences of substance uses.
Drug misuse
Drug misuse is a term used commonly for prescription medications with clinical efficacy but abuse potential and known adverse effects linked to improper use, such as psychiatric medications with sedativeSedative
A sedative or tranquilizer is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or excitement....
, anxiolytic
Anxiolytic
An anxiolytic is a drug used for the treatment of anxiety, and its related psychological and physical symptoms...
, analgesic
Analgesic
An analgesic is any member of the group of drugs used to relieve pain . The word analgesic derives from Greek an- and algos ....
, or stimulant
Stimulant
Stimulants are psychoactive drugs which induce temporary improvements in either mental or physical function or both. Examples of these kinds of effects may include enhanced alertness, wakefulness, and locomotion, among others...
properties. Prescription misuse has been variably and inconsistently defined based on drug prescription status, the uses that occur without a prescription, intentional use to achieve intoxicating effects, route of administration, co-ingestion with alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
, and the presence or absence of abuse or dependence symptoms. Tolerance relates to the pharmacological property of substances in which chronic use leads to a change in the central nervous system, meaning that more of the substance is needed in order to produce desired effects. Stopping or reducing the use of this substance would cause withdrawal symptoms to occur.
As a value judgment
Philip JenkinsPhilip Jenkins
Philip Jenkins is as of 2010 the Edwin Erle Sparks Professor of Humanities at Pennsylvania State University . He was Professor and a Distinguished Professor of History and Religious studies at the same institution; and also assistant, associate and then full professor of Criminal Justice and...
points out that there are two issues with the term "drug abuse". First, what constitutes a "drug" is debatable. For instance, GHB
Gamma-Hydroxybutyric acid
γ-Hydroxybutyric acid , also known as 4-hydroxybutanoic acid and sodium oxybate when used for medicinal purposes, is a naturally occurring substance found in the central nervous system, wine, beef, small citrus fruits, and almost all animals in small amounts. It is also categorized as an illegal...
, a naturally occurring substance in the central nervous system is considered a drug, and is illegal in many countries, while nicotine
Nicotine
Nicotine is an alkaloid found in the nightshade family of plants that constitutes approximately 0.6–3.0% of the dry weight of tobacco, with biosynthesis taking place in the roots and accumulation occurring in the leaves...
is not officially considered a drug in most countries. Second, the word "abuse" implies a recognized standard of use for any substance. Drinking an occasional glass of wine is considered acceptable in many Western countries, while drinking several bottles is seen as an abuse. Strict temperance advocates, which may or may not be religiously motivated, would see drinking even one glass as an abuse, and some groups even condemn caffeine
Caffeine
Caffeine is a bitter, white crystalline xanthine alkaloid that acts as a stimulant drug. Caffeine is found in varying quantities in the seeds, leaves, and fruit of some plants, where it acts as a natural pesticide that paralyzes and kills certain insects feeding on the plants...
use in any quantity. Similarly, adopting the view that any (recreational) use of marijuana or amphetamines constitutes drug abuse implies that we have already decided that substance is harmful even in minute quantities.
Signs and symptoms
Depending on the actual compound, drug abuse including alcohol may lead to health problems, social problemsSocial problems
Social problems are problems and difficulties that people often face in society. These include:*crime*corruption*poverty*homelessness*hunger*disease*drug addiction*alcoholism*schizophrenia*depression*pollution...
, morbidity, injuries, unprotected sex, violence
Violence
Violence is the use of physical force to apply a state to others contrary to their wishes. violence, while often a stand-alone issue, is often the culmination of other kinds of conflict, e.g...
, deaths, motor vehicle accidents, homicides, suicides, physical dependence
Physical dependence
Physical dependence refers to a state resulting from chronic use of a drug that has produced tolerance and where negative physical symptoms of withdrawal result from abrupt discontinuation or dosage reduction...
or psychological addiction
Substance dependence
The section about substance dependence in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders does not use the word addiction at all. It explains:...
.
There is a high rate of suicide in alcoholics and other drug abusers. The reasons believed to cause the increased risk of suicide include the long-term abuse of alcohol and other drugs causing physiological distortion of brain chemistry as well as the social isolation. Another factor is the acute intoxicating effects of the drugs may make suicide more likely to occur. Suicide is also very common in adolescent alcohol abusers, with 1 in 4 suicides in adolescents being related to alcohol abuse. In the USA approximately 30 percent of suicides are related to alcohol abuse. Alcohol abuse is also associated with increased risks of committing criminal offences including child abuse
Child abuse
Child abuse is the physical, sexual, emotional mistreatment, or neglect of a child. In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Department of Children And Families define child maltreatment as any act or series of acts of commission or omission by a parent or...
, domestic violence
Domestic violence
Domestic violence, also known as domestic abuse, spousal abuse, battering, family violence, and intimate partner violence , is broadly defined as a pattern of abusive behaviors by one or both partners in an intimate relationship such as marriage, dating, family, or cohabitation...
, rapes, burglaries and assaults.
Drug abuse, including alcohol and prescription drugs can induce symptomatology which resembles mental illness. This can occur both in the intoxicated state and also during the withdrawal
Withdrawal
Withdrawal can refer to any sort of separation, but is most commonly used to describe the group of symptoms that occurs upon the abrupt discontinuation/separation or a decrease in dosage of the intake of medications, recreational drugs, and alcohol...
state. In some cases these substance induced psychiatric disorders can persist long after detoxification, such as prolonged psychosis or depression after amphetamine or cocaine abuse. A protracted withdrawal syndrome can also occur with symptoms persisting for months after cessation of use. Benzodiazepines are the most notable drug for inducing prolonged withdrawal effects with symptoms sometimes persisting for years after cessation of use. Abuse of hallucinogens can trigger delusional and other psychotic phenomena long after cessation of use and cannabis
Cannabis
Cannabis is a genus of flowering plants that includes three putative species, Cannabis sativa, Cannabis indica, and Cannabis ruderalis. These three taxa are indigenous to Central Asia, and South Asia. Cannabis has long been used for fibre , for seed and seed oils, for medicinal purposes, and as a...
may trigger panic attacks during intoxication and with use it may cause a state similar to dysthymia. Severe anxiety and depression are commonly induced by sustained alcohol abuse which in most cases abates with prolonged abstinence. Even moderate alcohol sustained use may increase anxiety and depression levels in some individuals. In most cases these drug induced psychiatric disorders fade away with prolonged abstinence.
Drug abuse makes central nervous system
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
(CNS) effects, which produce changes in mood, levels of awareness or perceptions and sensations. Most of these drugs also alter systems other than the CNS. Some of these are often thought of as being abused. Some drugs appear to be more likely to lead to uncontrolled use than others.
Traditionally, new pharmacotherapies are quickly adopted in primary care settings, however; drugs for substance abuse treatment have faced many barriers. Naltrexone
Naltrexone
Naltrexone is an opioid receptor antagonist used primarily in the management of alcohol dependence and opioid dependence. It is marketed in generic form as its hydrochloride salt, naltrexone hydrochloride, and marketed under the trade names Revia and Depade...
, a drug originally marketed under the name "ReVia," and now marketed in intramuscular formulation as "Vivitrol" or in oral formulation as a generic, is a medication approved for the treatment of alcohol dependence. This drug has reached very few patients. This may be due to a number of factors, including resistance by Addiction Medicine
Addiction Medicine
Addiction medicine is a medical specialty that deals with the treatment of addiction. The specialty often crosses over into other areas, since various aspects of addiction fall within the fields of public health, psychology, social work, psychiatry, and internal medicine, among others...
specialists and lack of resources.
The ability to recognize the signs of drug use or the symptoms of drug use in family members by parents and spouses has been affected significantly by the emergence of home drug test technology which helps identify recent use of common street and prescription drugs with near lab quality accuracy.
Epidemiology
The initiation of drug and alcohol use is most likely to occur during adolescence, and some experimentation with substances by older adolescents is common. For example, results from 2010 Monitoring the FutureMonitoring the Future
The Monitoring the Future study, also known as the National High School Senior Survey, is a long-term epidemiological study that surveys trends in legal and illicit drug use among American adolescents and adults as well as personal levels of perceived risk and disapproval for each drug...
survey, a nationwide study on rates of substance use in the United States, show that 48.2% of 12th graders report having used an illicit drug at some point in their lives. In the 30 days prior to the survey, 41.2% of 12th graders had consumed alcohol and 19.2% of 12th graders had smoked tobacco cigarettes. In 2009 in the United States about 21% of high school students have taken prescription drugs without a prescription. And earlier in 2002, the World health Organization estimated that around 140 million people were alcohol dependent and another 400 million suffered alcohol-related problems.
Studies have shown that the large majority of adolescents will phase out of drug use before it becomes problematic. Thus, although rates of overall use are high, the percentage of adolescents who meet criteria for substance abuse is significantly lower (close to 5%). According to BBC, "Worldwide, the UN estimates there are more than 50 million regular users of morphine diacetate (heroin), cocaine and synthetic drugs."

APA, AMA, and NCDA
In 1932, the American Psychiatric Association created a definition that used legality, social acceptability, and cultural familiarity as qualifying factors:In 1966, the American Medical Association
American Medical Association
The American Medical Association , founded in 1847 and incorporated in 1897, is the largest association of medical doctors and medical students in the United States.-Scope and operations:...
's Committee on Alcoholism and Addiction defined abuse of stimulants (amphetamines, primarily) in terms of 'medical supervision':
In 1973 the National Commission on Marijuana and Drug Abuse stated:
...drug abuse may refer to any type of drug or chemical without regard to its pharmacologic actions. It is an eclectic concept having only one uniform connotation: societal disapproval. ... The Commission believes that the term drug abuse must be deleted from official pronouncements and public policy dialogue. The term has no functional utility and has become no more than an arbitrary codeword for that drug use which is presently considered wrong.
DSM
The first edition of the American Psychiatric AssociationAmerican Psychiatric Association
The American Psychiatric Association is the main professional organization of psychiatrists and trainee psychiatrists in the United States, and the most influential worldwide. Its some 38,000 members are mainly American but some are international...
's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders is published by the American Psychiatric Association and provides a common language and standard criteria for the classification of mental disorders...
(published in 1952) grouped alcohol and drug abuse under Sociopathic Personality Disturbances, which were thought to be symptoms of deeper psychological disorders or moral weakness.
The third edition, published in 1980, was the first to recognize substance abuse (including drug abuse) and substance dependence as conditions separate from substance abuse alone, bringing in social and cultural factors. The definition of dependence emphasised tolerance to drugs, and withdrawal from them as key components to diagnosis, whereas abuse was defined as "problematic use with social or occupational impairment" but without withdrawal or tolerance.
In 1987 the DSM-IIIR category "psychoactive substance abuse," which includes former concepts of drug abuse is defined as "a maladaptive pattern of use indicated by...continued use despite knowledge of having a persistent or recurrent social, occupational, psychological or physical problem that is caused or exacerbated by the use (or by) recurrent use in situations in which it is physically hazardous." It is a residual category, with dependence taking precedence when applicable. It was the first definition to give equal weight to behavioural and physiological factors in diagnosis.
By 1988, the DSM-IV defines substance dependence as "a syndrome involving compulsive use, with or without tolerance and withdrawal"; whereas substance abuse is "problematic use without compulsive use, significant tolerance, or withdrawal." Substance abuse can be harmful to your health and may even be deadly in certain scenarios
By 1994, The fourth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders is published by the American Psychiatric Association and provides a common language and standard criteria for the classification of mental disorders...
(DSM) issued by the American Psychiatric Association
American Psychiatric Association
The American Psychiatric Association is the main professional organization of psychiatrists and trainee psychiatrists in the United States, and the most influential worldwide. Its some 38,000 members are mainly American but some are international...
, the DSM-IV-TR, defines substance dependence as "when an individual persists in use of alcohol or other drugs despite problems related to use of the substance, substance dependence
Substance dependence
The section about substance dependence in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders does not use the word addiction at all. It explains:...
may be diagnosed." followed by criteria for the diagnose
DSM-IV-TR defines substance abuse as:
- A. A maladaptive pattern of substance use leading to clinically significant impairment or distress, as manifested by one (or more) of the following, occurring within a 12-month period:
-
-
- Recurrent substance use resulting in a failure to fulfill major role obligations at work, school, or home (e.g., repeated absences or poor work performance related to substance use; substance-related absences, suspensions or expulsions from school; neglect of children or household)
- Recurrent substance use in situations in which it is physically hazardous (e.g., driving an automobile or operating a machine when impaired by substance use)
- Recurrent substance-related legal problems (e.g., arrests for substance-related disorderly conduct)
- Continued substance use despite having persistent or recurrent social or interpersonal problems caused or exacerbated by the effects of the substance (e.g., arguments with spouse about consequences of intoxication, physical fights)
- B. The symptoms have never met the criteria for Substance Dependence for this class of substance.
-
The fifth edition of the DSM (DSM-5
DSM-5
The next edition of the American Psychiatric Association's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders , commonly called DSM-5 , is currently in consultation, planning and preparation...
), planned for release in 2013, is likely to have this terminology revisited yet again. Under consideration is a transition from the abuse/dependence terminology. At the moment, abuse is seen as an early form or less hazardous form of the disease characterized with the dependence criteria. However, the APA's 'dependence' term, as noted above, does not mean that physiologic dependence is present but rather means that a disease state is present, one that most would likely refer to as an addicted state. Many involved recognize that the terminology has often led to confusion, both within the medical community and with the general public. The American Psychiatric Association requests input as to how the terminology of this illness should be altered as it moves forward with DSM-5 discussion.
Legal approaches
- Related articles: Drug control law, Prohibition (drugs)Prohibition (drugs)The prohibition of drugs through sumptuary legislation or religious law is a common means of attempting to prevent drug use. Prohibition of drugs has existed at various levels of government or other authority from the Middle Ages to the present....
, Arguments for and against drug prohibitionArguments for and against drug prohibitionArguments about the prohibition of drugs, and over drug policy reform, are subjects of considerable controversy. The following is a presentation of major drug policy arguments, including those for drug law enforcement on one side of the debate, and arguments for drug law reform on the other.-...
Most governments have designed legislation
Legislation
Legislation is law which has been promulgated by a legislature or other governing body, or the process of making it...
to criminalize certain types of drug use. These drugs are often called "illegal drugs" but generally what is illegal is their unlicensed
License
The verb license or grant licence means to give permission. The noun license or licence refers to that permission as well as to the document recording that permission.A license may be granted by a party to another party as an element of an agreement...
production, distribution, and possession. These drugs are also called "controlled substances". Even for simple possession, legal punishment can be quite severe (including the death penalty in some countries). Laws vary across countries, and even within them, and have fluctuated widely throughout history.
Attempts by government-sponsored drug control policy to interdict drug supply and eliminate drug abuse have been largely unsuccessful.
In spite of the huge efforts by the U.S., drug supply and purity has reached an all time high, with the vast majority of resources spent on interdiction and law enforcement instead of public health
Public health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals" . It is concerned with threats to health based on population health...
. In the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, the number of nonviolent drug offenders in prison exceeds by 100,000 the total incarcerated population in the EU, despite the fact that the EU has 100 million more citizens.
Despite drug legislation (or perhaps because of it), large, organized criminal drug cartel
Drug cartel
Drug cartels are criminal organizations developed with the primary purpose of promoting and controlling drug trafficking operations. They range from loosely managed agreements among various drug traffickers to formalized commercial enterprises. The term was applied when the largest trafficking...
s operate worldwide. Advocates of decriminalization argue that drug prohibition makes drug dealing a lucrative business, leading to much of the associated criminal activity.
Cost
The UK Home OfficeHome Office
The Home Office is the United Kingdom government department responsible for immigration control, security, and order. As such it is responsible for the police, UK Border Agency, and the Security Service . It is also in charge of government policy on security-related issues such as drugs,...
estimated that the social and economic cost of drug abuse to the UK economy in terms of crime, absenteeism and sickness is in excess of £20 billion a year. and in just the year 1995, America spent nearly $109.8 billion on drug abuse.
However, it does not estimate what portion of those crimes are unintended consequences of drug prohibition (crimes to sustain expensive drug consumption, risky production and dangerous distribution), nor what is the cost of enforcement. Those aspects are necessary for a full analysis of the economics of prohibition.
The Home Office has a recent history of taking a hard line on controlled drugs, including those with no known fatalities and even medical benefits, in direct opposition to the scientific community.
Treatment
Treatment for substance abuse is critical for many around the world. Often a formal intervention is necessary to convince the substance abuser to submit to any form of treatment. Behavioral interventions and medications exist that have helped many people reduce, or discontinue, their substance abuse. From the applied behavior analysisApplied Behavior Analysis
Applied behavior analysis is a science that involves using modern behavioral learning theory to modify behaviors. Behavior analysts reject the use of hypothetical constructs and focus on the observable relationship of behavior to the environment...
literature, behavioral psychology, and from randomized clinical trials, several evidenced based interventions have emerged:
- Behavioral Marital TherapyIntegrative behavioral couples therapyBehavioral marital therapy, sometimes called Behavioral couple, or couples, therapy, has its origins in behaviorism and is a form of behavior therapy. The theory is rooted in social learning theory and behavior analysis. As a model, it is constantly being revised as new research...
- Motivational InterviewingMotivational interviewingMotivational interviewing refers to a counseling approach in part developed by clinical psychologists Professor William R Miller, Ph.D. and Professor Stephen Rollnick, Ph.D. The concept of motivational interviewing evolved from experience in the treatment of problem drinkers, and was first...
- Community Reinforcement ApproachCommunity reinforcement and family trainingCommunity reinforcement approach and community reinforcement and family training approach are behavior therapy approaches to treating substance abuse.-Research:...
- Exposure therapyExposure therapyExposure therapy is a technique in behavior therapy intended to treat anxiety disorders and involves the exposure to the feared object or context without any danger in order to overcome their anxiety. Procedurally it is similar to the fear extinction paradigm in rodent work...
- Contingency ManagementContingency ManagementContingency management is a type of treatment used in the mental health or substance abuse fields. Patients are rewarded for their behavior; generally, adherence to or failure to adhere to program rules and regulations or their treatment plan...
- Pharmacological therapy - A number of medications have been approved for the treatment of substance abuse. These include replacement therapies such as buprenorphineBuprenorphineBuprenorphine is a semi-synthetic opioid that is used...
and methadoneMethadoneMethadone is a synthetic opioid, used medically as an analgesic and a maintenance anti-addictive for use in patients with opioid dependency. It was developed in Germany in 1937...
as well as antagonist medications like disulfiramDisulfiramDisulfiram is a drug discovered in the 1920s and used to support the treatment of chronic alcoholism by producing an acute sensitivity to alcohol. Trade names for disulfiram in different countries are Antabuse and Antabus manufactured by Odyssey Pharmaceuticals...
and naltrexoneNaltrexoneNaltrexone is an opioid receptor antagonist used primarily in the management of alcohol dependence and opioid dependence. It is marketed in generic form as its hydrochloride salt, naltrexone hydrochloride, and marketed under the trade names Revia and Depade...
in either short acting, or the newer long acting form (under the brand name Vivitrol). Several other medications, often ones originally used in other contexts, have also been shown to be effective including bupropionBupropionBupropion is an atypical antidepressant and smoking cessation aid. The drug is a non-tricyclic antidepressant and differs from most commonly prescribed antidepressants such as SSRIs, as its primary pharmacological action is thought to be norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibition...
(Zyban or Wellbutrin), ModafinilModafinilModafinil is an analeptic drug manufactured by Cephalon, and is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of narcolepsy, shift work sleep disorder, and excessive daytime sleepiness associated with obstructive sleep apnea...
(Provigil) and more.
According to some nurse practitioners, stopping substance abuse can reduce the risk of dying early and also reduce some health risks like heart disease, lung disease, and strokes.
In children and adolescents, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and family therapy
Family therapy
Family therapy, also referred to as couple and family therapy, family systems therapy, and family counseling, is a branch of psychotherapy that works with families and couples in intimate relationships to nurture change and development. It tends to view change in terms of the systems of...
currently have the most research evidence for the treatment of substance abuse problems. These treatments can be administered in a variety of different formats, each of which has varying levels of research support
It has been suggested that social skills
Social skills
A social skill is any skill facilitating interaction and communication with others. Social rules and relations are created, communicated, and changed in verbal and nonverbal ways. The process of learning such skills is called socialization...
training adjunctive to inpatient treatment of alcohol dependence is probably efficacious.
See also
- Addictive personalityAddictive personalityAn addictive personality refers to a particular set of personality traits that make an individual predisposed to addictions. People who are substance dependent are characterized by: a physical or psychological dependency that negatively impacts the quality of life...
- Combined drug intoxicationCombined drug intoxicationCombined drug intoxication , also known as multiple drug intake or lethal polydrug/polypharmacy intoxication, is an unnatural cause of human death...
- Drug addiction
- Drug overdoseDrug overdoseThe term drug overdose describes the ingestion or application of a drug or other substance in quantities greater than are recommended or generally practiced...
- Poly drug usePoly drug usePolydrug use refers to the use of two or more psychoactive drugs in combination to achieve a particular effect. In many cases one drug is used as a base or primary drug, with additional drugs to leaven or compensate for the side effects of the primary drug and make the experience more enjoyable...
- Polysubstance abuse
- Risk factors in pregnancyRisk factors in pregnancyFactors increasing the risk of pregnancy beyond the normal level of risk may be present in a woman's medical profile either before she becomes pregnant or during the pregnancy. These pre-existing factors may relate to physical and/or mental health, and/or to social issues, or a combination...
- List of drug-related deaths
- List of controlled drugs in the United Kingdom
- Substances controlled for their drug effects by the US federal governmentControlled Substances ActThe Controlled Substances Act was enacted into law by the Congress of the United States as Title II of the Comprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970. The CSA is the federal U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture, importation, possession, use and distribution of certain...
- Self-medicationSelf-medicationSelf-medication is a term used to describe the use of drugs or other self-soothing forms of behavior to treat untreated and often undiagnosed mental distress, stress and anxiety, including mental illnesses and/or psychological trauma...

