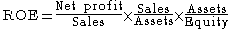DuPont analysis
Encyclopedia
DuPont analysis is an expression which breaks ROE (Return On Equity
) into three parts.
The name comes from the DuPont Corporation that started using this formula in the 1920s.
/Sales
)*(Sales
/Assets)*(Assets/Equity)= (Net Profit/Equity)
The Du Pont identity, however, is less useful for some industries, such as investment banking, that do not use certain concepts or for which the concepts are less meaningful. Variations may be used in certain industries, as long as they also respect the underlying structure of the Du Pont identity.
Du Pont analysis relies upon the accounting identity
, that is, a statement (formula) that is by definition true.

The return on equity (ROE) ratio is a measure of the rate of return to stockholders. Decomposing the ROE into various factors influencing company performance is often called the Du Pont system.
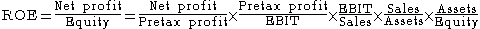
This decomposition presents various ratios used in fundamental analysis
.
ROE can also be stated as:
Profit margin is (Net profit ÷ Sales), so the ROE equation can be restated: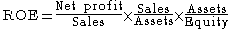
Return on equity
Return on equity measures the rate of return on the ownership interest of the common stock owners. It measures a firm's efficiency at generating profits from every unit of shareholders' equity . ROE shows how well a company uses investment funds to generate earnings growth...
) into three parts.
The name comes from the DuPont Corporation that started using this formula in the 1920s.
Basic formula
ROE = (Profit margin)*(Asset turnover)*(Equity multiplier) = (Net profitNet profit
Net profit or net revenue is a measure of the profitability of a venture after accounting for all costs. In a survey of nearly 200 senior marketing managers, 91 percent responded that they found the "net profit" metric very useful...
/Sales
Sales
A sale is the act of selling a product or service in return for money or other compensation. It is an act of completion of a commercial activity....
)*(Sales
Sales
A sale is the act of selling a product or service in return for money or other compensation. It is an act of completion of a commercial activity....
/Assets)*(Assets/Equity)= (Net Profit/Equity)
- Operating efficiency (measured by profit marginProfit marginProfit margin, net margin, net profit margin or net profit ratio all refer to a measure of profitability. It is calculated by finding the net profit as a percentage of the revenue.Net profit Margin = x100...
) - Asset use efficiency (measured by asset turnover)
- Financial leverageLeverage (finance)In finance, leverage is a general term for any technique to multiply gains and losses. Common ways to attain leverage are borrowing money, buying fixed assets and using derivatives. Important examples are:* A public corporation may leverage its equity by borrowing money...
(measured by equity multiplier)
ROE analysis
The Du Pont identity breaks down Return on Equity (that is, the returns that investors receive from the firm) into three distinct elements. This analysis enables the analyst to understand the source of superior (or inferior) return by comparison with companies in similar industries (or between industries).The Du Pont identity, however, is less useful for some industries, such as investment banking, that do not use certain concepts or for which the concepts are less meaningful. Variations may be used in certain industries, as long as they also respect the underlying structure of the Du Pont identity.
Du Pont analysis relies upon the accounting identity
Identity (mathematics)
In mathematics, the term identity has several different important meanings:*An identity is a relation which is tautologically true. This means that whatever the number or value may be, the answer stays the same. For example, algebraically, this occurs if an equation is satisfied for all values of...
, that is, a statement (formula) that is by definition true.
High turnover industries
Certain types of retail operations, particularly stores, may have very low profit margins on sales, and relatively moderate leverage. In contrast, though, groceries may have very high turnover, selling a significant multiple of their assets per year. The ROE of such firms may be particularly dependent on performance of this metric, and hence asset turnover may be studied extremely carefully for signs of under-, or, over-performance. For example, same store sales of many retailers is considered important as an indication that the firm is deriving greater profits from existing stores (rather than showing improved performance by continually opening new stores).High margin industries
Other industries, such as fashion, may derive a substantial portion of their competitive advantage from selling at a higher margin, rather than higher sales. For high-end fashion brands, increasing sales without sacrificing margin may be critical. The Du Pont identity allows analysts to determine which of the elements is dominant in any change of ROE.High leverage industries
Some sectors, such as the financial sector, rely on high leverage to generate acceptable ROE. In contrast, however, many other industries would see high levels of leverage as unacceptably risky. Du Pont analysis enables the third party (relying primarily on the financial statements) to compare leverage with other financial elements that determine ROE among similar companies.ROA and ROE ratio
The return on assets (ROA) ratio developed by DuPont for its own use is now used by many firms to evaluate how effectively assets are used. It measures the combined effects of profit margins and asset turnover.
The return on equity (ROE) ratio is a measure of the rate of return to stockholders. Decomposing the ROE into various factors influencing company performance is often called the Du Pont system.
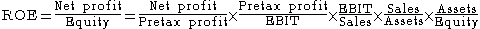
- Where
- Net profit = net profit after taxes
- Equity = shareholders' equity
- EBIT = Earnings before interest and taxesEarnings before interest and taxesIn accounting and finance, earnings before interest and taxes is a measure of a firm's profit that excludes interest and income tax expenses. Operating income is the difference between operating revenues and operating expenses...
- Sales = Net sales
This decomposition presents various ratios used in fundamental analysis
Fundamental analysis
Fundamental analysis of a business involves analyzing its financial statements and health, its management and competitive advantages, and its competitors and markets. When applied to futures and forex, it focuses on the overall state of the economy, interest rates, production, earnings, and...
.
- The company's taxTaxTo tax is to impose a financial charge or other levy upon a taxpayer by a state or the functional equivalent of a state such that failure to pay is punishable by law. Taxes are also imposed by many subnational entities...
burden is (Net profit ÷ Pretax profit). This is the proportion of the company's profits retained after paying income taxes. [NI/EBT] - The company's interest burden is (Pretax profit ÷ EBIT). This will be 1.00 for a firm with no debtDebtA debt is an obligation owed by one party to a second party, the creditor; usually this refers to assets granted by the creditor to the debtor, but the term can also be used metaphorically to cover moral obligations and other interactions not based on economic value.A debt is created when a...
or financial leverage. [EBT/EBIT] - The company's operating profit margin or return on sales (ROS) is (EBIT ÷ Sales). This is the operating profit per dollar of sales. [EBIT/Sales]
- The company's asset turnover (ATO) is (Sales ÷ Assets).
- The company's leverage ratio is (Assets ÷ Equity), which is equal to the firm's debt to equity ratioDebt to equity ratioThe debt-to-equity ratio is a financial ratio indicating the relative proportion of shareholders' equity and debt used to finance a company's assets. Closely related to leveraging, the ratio is also known as Risk, Gearing or Leverage...
+ 1. This is a measure of financial leverage. - The company's return on assets (ROA) is (Return on sales x Asset turnover).
- The company's compound leverage factor is (Interest burden x Leverage).
ROE can also be stated as:
-
- ROE = Tax burden x Interest burden x Margin x Turnover x Leverage
- ROE = Tax burden x ROA x Compound leverage factor
Profit margin is (Net profit ÷ Sales), so the ROE equation can be restated: