.gif)
Leverage (finance)
Encyclopedia
In finance
, leverage (sometimes referred to as gearing in the United Kingdom) is a general term for any technique to multiply gains and losses. Common ways to attain leverage are borrowing money, buying fixed assets and using derivatives
. Important examples are:
, and has multiple definitions in each field.
of equity divided by volatility of an unlevered investment in the same assets. To understand the differences, consider the following positions, all funded with $100 of cash equity.
Degree of Financial Leverage (DFL)= EBIT / ( EBIT - Total Interest expense );
Degree of Combined Leverage (DCL)= DOL * DFL
Accounting leverage has the same definition as in investments. There are several ways to define operating leverage, the most common. is:
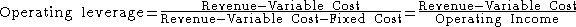
Financial leverage is usually defined as:
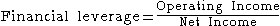
Operating leverage is an attempt to estimate the percentage change in operating income (earnings before interest and taxes
or EBIT) for a one percent change in revenue.
Financial leverage tries to estimate the percentage change in net income
for a one percent change in operating income.
The product of the two is called Total leverage, and estimates the percentage change in net income for a one percent change in revenue.
There are several variants of each of these definitions, and the financial statements are usually adjusted before the values are computed. Moreover, there are industry-specific conventions that differ somewhat from the treatment above.
, we have to study financial leverage. Financial leverage refers to the use of debt to acquire additional assets. Financial leverage may decrease or increase return on equity in different conditions. Financial over-leveraging means incurring a huge debt by borrowing funds at a lower rate of interest and utilizing the excess funds in high risk investments in order to maximize returns.
during a business downturn, while a less-levered corporation might survive. An investor who buys a stock on 50% margin will lose 40% of his money if the stock declines 20%.
There is an important implicit assumption in that account, however, which is that the underlying levered asset is the same as the unlevered one. If a company borrows money to modernize, or add to its product line, or expand internationally, the additional diversification might more than offset the additional risk from leverage. Or if an investor uses a fraction of his or her portfolio to margin stock index futures and puts the rest in a money market fund, he or she might have the same volatility and expected return as an investor in an unlevered equity index fund, with a limited downside. So while adding leverage to a given asset always adds risk, it is not the case that a levered company or investment is always riskier than an unlevered one. In fact, many highly-levered hedge funds have less return volatility than unlevered bond funds, and public utilities with lots of debt are usually less risky stocks than unlevered technology companies.
In finance, the general practice is to borrow money to buy an asset with a higher return than the interest on the debt. That at least might work out. People who consistently spend more than they make have a problem, but it's overspending (or underearning), not leverage. The same point is more controversial for governments.
People sometimes borrow money out of desperation rather than calculation. That also is not leverage. But it is true that leverage sometimes increases involuntarily. When Long-Term Capital Management
collapsed with over 100 to 1 leverage, it wasn't that the principals tried to run the firm at 100 to 1 leverage, it was that as equity eroded and they were unable to liquidate positions, the leverage level was beyond their control. One hundred to one leverage was a symptom of their problems, not the cause (although, of course, part of the cause was the 27 to 1 leverage the firm was running before it got into trouble, and the 55 to 1 leverage it had been forced up to by mid-August 1998 before the real troubles started). But the point is the fact that collapsing entities often have a lot of leverage does not mean that leverage causes collapses.
Involuntary leverage is a risk. It means that as things get bad, leverage goes up, multiplying losses as things continue to go down. This can lead to rapid ruin, even if the underlying asset value decline is mild or temporary. The risk can be mitigated by negotiating the terms of leverage, and by leveraging only liquid assets.
, either a creditor
or a derivative counterparty. It doesn't always do that, for example a company levering by acquiring a fixed asset has no further reliance on a counterparty. In the case of a creditor, most of the risk is usually on the creditor's side, but there can be risks to the borrower, such as demand repayment clauses or rights to seize collateral. If a derivative counterparty fails, unrealized gains on the contract may be jeopardized. These risks can be mitigated by negotiating terms, including mark-to-market collateral.
5% Projected Return on Investment
4% Cost of Debt
8:1 Leverage Debt:Equity
LONG-FORM MATH
Investment (8+1) * 5% = 45
less Interest (8) * 4% = 32
equals Equity 1 * 13%= 13
SHORT-FORM GENERIC CALCULATION
Interest Rate Differential (5-4) = 1%
Debt to Equity Multiple (8/1) = 8
Multiply Line1 * Line2 (1*8) = 8%
Add Investment Return + 5%
Equals Total Return (8+5) = 13%
, a fraction of deposits that was required to be held in liquid form, generally precious metals or government notes or deposits. This does not limit leverage. A capital requirement
is a fraction of assets that is required to be held in the form of equity or equity-like securities. Although these two are often confused, they are in fact opposite. A reserve requirement is a fraction of certain liabilities (from the right hand side of the balance sheet) that must be held as a certain kind of asset (from the left hand side of the balance sheet). A capital requirement is a fraction of assets (from the left hand side of the balance sheet) that must be held as a certain kind of liability or equity (from the right hand side of the balance sheet). Before the 1980s, regulators typically imposed judgmental capital requirements, a bank was supposed to be "adequately capitalized," but not objective rules.
National regulators began imposing formal capital requirements in the 1980s, and by 1988 most large multinational banks were held to the Basel I
standard. Basel I categorized assets into five risk buckets, and mandated minimum capital requirements for each. This limits accounting leverage. If a bank is required to hold 8% capital against an asset, that is the same as an accounting leverage limit of 1/.08 or 12.5 to 1.
While Basel I is generally credited with improving bank risk management it suffered from two main defects. It did not require capital for off-balance sheet risks (there was a clumsy provisions for derivatives, but not for other off-balance sheet exposures) and it encouraged banks to pick the riskiest assets in each bucket (for example, the capital requirement was the same for all corporate loans, whether to solid companies or ones near bankruptcy, and the requirement for government loans was zero).
Work on Basel II began in the early 1990s and it was implemented in stages beginning in 2005. Basel II attempted to limit economic leverage rather than accounting leverage. It required advanced banks to estimate the risk of their positions and allocate capital accordingly. While this is much more rational in theory, it is more subject to estimation error, both honest and opportunitistic. The poor performance of many banks in during the financial crisis of 2007-2009
led to calls to reimpose leverage limits, by which most people meant accounting leverage limits, if they understood the distinction at all. However, in view of the problems with Basel I, it seems likely that the some hybrid of accounting and notional leverage will be used, and the leverage limits will be imposed in addition to, not instead of, Basel II economic leverage limits.
, however, modern dictionaries (such as Random House Dictionary and Merriam-Webster's Dictionary of Law) refer to its use as a verb
as well. It was first adopted for use as a verb in American English
in 1957.
Finance
"Finance" is often defined simply as the management of money or “funds” management Modern finance, however, is a family of business activity that includes the origination, marketing, and management of cash and money surrogates through a variety of capital accounts, instruments, and markets created...
, leverage (sometimes referred to as gearing in the United Kingdom) is a general term for any technique to multiply gains and losses. Common ways to attain leverage are borrowing money, buying fixed assets and using derivatives
Derivative (finance)
A derivative instrument is a contract between two parties that specifies conditions—in particular, dates and the resulting values of the underlying variables—under which payments, or payoffs, are to be made between the parties.Under U.S...
. Important examples are:
- A public corporation may leverage its equityEquity (finance)In accounting and finance, equity is the residual claim or interest of the most junior class of investors in assets, after all liabilities are paid. If liability exceeds assets, negative equity exists...
by borrowing money. The more it borrows, the less equity capitalCapital (economics)In economics, capital, capital goods, or real capital refers to already-produced durable goods used in production of goods or services. The capital goods are not significantly consumed, though they may depreciate in the production process...
it needs, so any profits or losses are shared among a smaller base and are proportionately larger as a result. - A business entity can leverage its revenue by buying fixed assets. This will increase the proportion of fixed, as opposed to variable, costs, meaning that a change in revenueRevenueIn business, revenue is income that a company receives from its normal business activities, usually from the sale of goods and services to customers. In many countries, such as the United Kingdom, revenue is referred to as turnover....
will result in a larger change in operating income. - Hedge funds often leverage their assets by using derivatives. A fund might get any gains or losses on $20 million worth of crude oil by posting $1 million of cash as marginMargin (finance)In finance, a margin is collateral that the holder of a financial instrument has to deposit to cover some or all of the credit risk of their counterparty...
.
Measuring leverage
A good deal of confusion arises in discussions among people who use different definitions of leverage. The term is used differently in investments and corporate financeCorporate finance
Corporate finance is the area of finance dealing with monetary decisions that business enterprises make and the tools and analysis used to make these decisions. The primary goal of corporate finance is to maximize shareholder value while managing the firm's financial risks...
, and has multiple definitions in each field.
Investments
Accounting leverage is total assets divided by total assets minus total liabilities. Notional leverage is total notional amount of assets plus total notional amount of liabilities divided by equity. Economic leverage is volatilityVolatility (finance)
In finance, volatility is a measure for variation of price of a financial instrument over time. Historic volatility is derived from time series of past market prices...
of equity divided by volatility of an unlevered investment in the same assets. To understand the differences, consider the following positions, all funded with $100 of cash equity.
- Buy $100 of crude oil. Assets are $100 ($100 of oil), there are no liabilities. Accounting leverage is 1 to 1. Notional amount is $100 ($100 of oil), there are no liabilities and there is $100 of equity. Notional leverage is 1 to 1. The volatility of the equity is equal to the volatility of oil, since oil is the only asset and you own the same amount as your equity, so economic leverage is 1 to 1.
- Borrow $100 and buy $200 of crude oil. Assets are $200, liabilities are $100 so accounting leverage is 2 to 1. Notional amount is $200, equity is $100 so notional leverage is 2 to 1. The volatility of the position is twice the volatility of an unlevered position in the same assets, so economic leverage is 2 to 1.
- Buy $100 of crude oil, borrow $100 worth of gasoline and sell the gasoline for $100. You now have $100 cash, $100 of crude oil and owe $100 worth of gasoline. Your assets are $200, liabilities are $100 so accounting leverage is 2 to 1. You have $200 notional amount of assets plus $100 notional amount of liabilities, with $100 of equity, so your notional leverage is 3 to 1. The volatility of your position might be half the volatility of an unlevered investment in the same assets, since the price of oil and the price of gasoline are positively correlated, so your economic leverage might be 0.5 to 1.
- Buy $100 of a 10-year fixed-rate treasury bond, and enter into a fixed-for-floating 10-year interest rate swapInterest rate swapAn interest rate swap is a popular and highly liquid financial derivative instrument in which two parties agree to exchange interest rate cash flows, based on a specified notional amount from a fixed rate to a floating rate or from one floating rate to another...
to convert the payments to floating rate. The derivative is off-balance sheet, so it is ignored for accounting leverage. Accounting leverage is therefore 1 to 1. The notional amount of the swap does count for notional leverage, so notional leverage is 2 to 1. The swap removes most of the economic risk of the treasury bond, so economic leverage is near zero.
Corporate finance
Degree of Operating Leverage (DOL)= (EBIT + Fixed costs) / EBIT;Degree of Financial Leverage (DFL)= EBIT / ( EBIT - Total Interest expense );
Degree of Combined Leverage (DCL)= DOL * DFL
Accounting leverage has the same definition as in investments. There are several ways to define operating leverage, the most common. is:
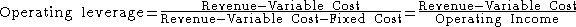
Financial leverage is usually defined as:
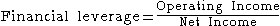
Operating leverage is an attempt to estimate the percentage change in operating income (earnings before interest and taxes
Earnings before interest and taxes
In accounting and finance, earnings before interest and taxes is a measure of a firm's profit that excludes interest and income tax expenses. Operating income is the difference between operating revenues and operating expenses...
or EBIT) for a one percent change in revenue.
Financial leverage tries to estimate the percentage change in net income
Net income
Net income is the residual income of a firm after adding total revenue and gains and subtracting all expenses and losses for the reporting period. Net income can be distributed among holders of common stock as a dividend or held by the firm as an addition to retained earnings...
for a one percent change in operating income.
The product of the two is called Total leverage, and estimates the percentage change in net income for a one percent change in revenue.
There are several variants of each of these definitions, and the financial statements are usually adjusted before the values are computed. Moreover, there are industry-specific conventions that differ somewhat from the treatment above.
Leverage and ROE
If we have to check real effect of leverage on ROEReturn on equity
Return on equity measures the rate of return on the ownership interest of the common stock owners. It measures a firm's efficiency at generating profits from every unit of shareholders' equity . ROE shows how well a company uses investment funds to generate earnings growth...
, we have to study financial leverage. Financial leverage refers to the use of debt to acquire additional assets. Financial leverage may decrease or increase return on equity in different conditions. Financial over-leveraging means incurring a huge debt by borrowing funds at a lower rate of interest and utilizing the excess funds in high risk investments in order to maximize returns.
Leverage and risk
The most obvious risk of leverage is that it multiplies losses. A corporation that borrows too much money might face bankruptcyBankruptcy
Bankruptcy is a legal status of an insolvent person or an organisation, that is, one that cannot repay the debts owed to creditors. In most jurisdictions bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the debtor....
during a business downturn, while a less-levered corporation might survive. An investor who buys a stock on 50% margin will lose 40% of his money if the stock declines 20%.
There is an important implicit assumption in that account, however, which is that the underlying levered asset is the same as the unlevered one. If a company borrows money to modernize, or add to its product line, or expand internationally, the additional diversification might more than offset the additional risk from leverage. Or if an investor uses a fraction of his or her portfolio to margin stock index futures and puts the rest in a money market fund, he or she might have the same volatility and expected return as an investor in an unlevered equity index fund, with a limited downside. So while adding leverage to a given asset always adds risk, it is not the case that a levered company or investment is always riskier than an unlevered one. In fact, many highly-levered hedge funds have less return volatility than unlevered bond funds, and public utilities with lots of debt are usually less risky stocks than unlevered technology companies.
Popular risks
There is a popular prejudice against leverage rooted in the observation that people who borrow a lot of money often end up badly. But the issue here is those people are not leveraging anything, they're borrowing money for consumption.In finance, the general practice is to borrow money to buy an asset with a higher return than the interest on the debt. That at least might work out. People who consistently spend more than they make have a problem, but it's overspending (or underearning), not leverage. The same point is more controversial for governments.
People sometimes borrow money out of desperation rather than calculation. That also is not leverage. But it is true that leverage sometimes increases involuntarily. When Long-Term Capital Management
Long-Term Capital Management
Long-Term Capital Management L.P. was a speculative hedge fund based in Greenwich, Connecticut that utilized absolute-return trading strategies combined with high leverage...
collapsed with over 100 to 1 leverage, it wasn't that the principals tried to run the firm at 100 to 1 leverage, it was that as equity eroded and they were unable to liquidate positions, the leverage level was beyond their control. One hundred to one leverage was a symptom of their problems, not the cause (although, of course, part of the cause was the 27 to 1 leverage the firm was running before it got into trouble, and the 55 to 1 leverage it had been forced up to by mid-August 1998 before the real troubles started). But the point is the fact that collapsing entities often have a lot of leverage does not mean that leverage causes collapses.
Involuntary leverage is a risk. It means that as things get bad, leverage goes up, multiplying losses as things continue to go down. This can lead to rapid ruin, even if the underlying asset value decline is mild or temporary. The risk can be mitigated by negotiating the terms of leverage, and by leveraging only liquid assets.
Forced position reductions
A common misconception is that levered entities are forced to reduce positions as they lose money. This is only true if the entity is run at maximum leverage. For example, if a person has $100, borrows another $100 and buys $200 worth of oil, he has 2 to 1 accounting leverage. If the price of oil declines 25%, he has $50 of equity supporting $150 worth of oil, 3 to 1 accounting leverage. If 2 to 1 is the maximum his counterparties will allow him, he has to sell one-third of his position to pay his debt down to $50. Now if oil goes back up to the original price, he has only $83 of equity. He lost 17 percent of his equity, even though the price of oil ended up back at its original price. Now if the price of oil declines 25%, the investor has to put up an additional $50 of margin, but she still has $40 of unencumbered cash. She may or may not wish to reduce the position, but she is not forced to do so. The point is that it is using maximum leverage that can force position reductions, not simply using leverage. It often surprises people to learn that hedge funds running at 10 to 1 or higher notional leverage ratios hold 80 percent or 90 percent cash.Model risk
Another risk of leverage is model risk. Many investors run high levels of notional leverage but low levels of economic leverage (in fact, these are the type of strategies hedge funds are named for, although not all hedge fund pursue them). Economic leverage depends on model assumptions. For example, a fund with $100 might feel comfortable holding $1,000 long positions in crude oil futures and $1,000 of short positions in gasoline futures. The notional leverage is 20 to 1 (accounting leverage is zero) but the fund might estimate economic leverage is only 1 to 1, that is the fund may assume a 10% fall in the price of oil will cause a 9% fall in the price of gasoline, so the fund will lose only 10% net ($100 loss on the oil long and $90 profit on the gasoline short). If that assumption is incorrect, the fund may have much more economic leverage than it thinks. For example, if refinery capacity is shut down by a hurricane, the price of oil may fall (less demand from refineries) while the price of gasoline might rise (less supply from refineries). A 5% fall in the price of oil and a 5% rise in the price of gasoline could wipe out the fund.Counterparty risk
Leverage may involve a counterpartyCounterparty
A counterparty is a legal and financial term. It means a party to a contract. A counterparty is usually the entity with whom one negotiates on a given agreement, and the term can refer to either party or both, depending on context....
, either a creditor
Creditor
A creditor is a party that has a claim to the services of a second party. It is a person or institution to whom money is owed. The first party, in general, has provided some property or service to the second party under the assumption that the second party will return an equivalent property or...
or a derivative counterparty. It doesn't always do that, for example a company levering by acquiring a fixed asset has no further reliance on a counterparty. In the case of a creditor, most of the risk is usually on the creditor's side, but there can be risks to the borrower, such as demand repayment clauses or rights to seize collateral. If a derivative counterparty fails, unrealized gains on the contract may be jeopardized. These risks can be mitigated by negotiating terms, including mark-to-market collateral.
Mathematical Example
Calculate equity return given:5% Projected Return on Investment
4% Cost of Debt
8:1 Leverage Debt:Equity
LONG-FORM MATH
Investment (8+1) * 5% = 45
less Interest (8) * 4% = 32
equals Equity 1 * 13%= 13
SHORT-FORM GENERIC CALCULATION
Interest Rate Differential (5-4) = 1%
Debt to Equity Multiple (8/1) = 8
Multiply Line1 * Line2 (1*8) = 8%
Add Investment Return + 5%
Equals Total Return (8+5) = 13%
Leverage and bank regulation
Prior to the 1980s, quantitative limits on bank leverage were rare. Banks in most countries had a reserve requirementReserve requirement
The reserve requirement is a central bank regulation that sets the minimum reserves each commercial bank must hold of customer deposits and notes...
, a fraction of deposits that was required to be held in liquid form, generally precious metals or government notes or deposits. This does not limit leverage. A capital requirement
Capital requirement
Capital requirement refers to -The standardized requirements in place for banks and other depository institutions, which determines how much capital is required to be held for a certain level of assets through regulatory agencies such as the Bank for International Settlements, Federal Deposit...
is a fraction of assets that is required to be held in the form of equity or equity-like securities. Although these two are often confused, they are in fact opposite. A reserve requirement is a fraction of certain liabilities (from the right hand side of the balance sheet) that must be held as a certain kind of asset (from the left hand side of the balance sheet). A capital requirement is a fraction of assets (from the left hand side of the balance sheet) that must be held as a certain kind of liability or equity (from the right hand side of the balance sheet). Before the 1980s, regulators typically imposed judgmental capital requirements, a bank was supposed to be "adequately capitalized," but not objective rules.
National regulators began imposing formal capital requirements in the 1980s, and by 1988 most large multinational banks were held to the Basel I
Basel I
Basel I is the round of deliberations by central bankers from around the world, and in 1988, the Basel Committee in Basel, Switzerland, published a set of minimal capital requirements for banks. This is also known as the 1988 Basel Accord, and was enforced by law in the Group of Ten countries...
standard. Basel I categorized assets into five risk buckets, and mandated minimum capital requirements for each. This limits accounting leverage. If a bank is required to hold 8% capital against an asset, that is the same as an accounting leverage limit of 1/.08 or 12.5 to 1.
While Basel I is generally credited with improving bank risk management it suffered from two main defects. It did not require capital for off-balance sheet risks (there was a clumsy provisions for derivatives, but not for other off-balance sheet exposures) and it encouraged banks to pick the riskiest assets in each bucket (for example, the capital requirement was the same for all corporate loans, whether to solid companies or ones near bankruptcy, and the requirement for government loans was zero).
Work on Basel II began in the early 1990s and it was implemented in stages beginning in 2005. Basel II attempted to limit economic leverage rather than accounting leverage. It required advanced banks to estimate the risk of their positions and allocate capital accordingly. While this is much more rational in theory, it is more subject to estimation error, both honest and opportunitistic. The poor performance of many banks in during the financial crisis of 2007-2009
Subprime mortgage crisis
The U.S. subprime mortgage crisis was one of the first indicators of the late-2000s financial crisis, characterized by a rise in subprime mortgage delinquencies and foreclosures, and the resulting decline of securities backed by said mortgages....
led to calls to reimpose leverage limits, by which most people meant accounting leverage limits, if they understood the distinction at all. However, in view of the problems with Basel I, it seems likely that the some hybrid of accounting and notional leverage will be used, and the leverage limits will be imposed in addition to, not instead of, Basel II economic leverage limits.
Leverage and the financial crisis of 2007–2009
The financial crisis of 2007–2009, like many previous financial crises, was blamed in part on "excessive leverage." However, the word is used in several different senses.- Consumers in the United States and many other developed countries borrowed large amounts of money, $2.6 trillion in the United States alone. For most of this, "leverage" is a euphemismEuphemismA euphemism is the substitution of a mild, inoffensive, relatively uncontroversial phrase for another more frank expression that might offend or otherwise suggest something unpleasant to the audience...
as the borrowing was used to support consumption rather than to lever anything. Only people who borrowed for investment, such as speculative house purchases or buying stocks, were using leverage in the financial sense. - Financial institutions were highly levered. Lehman BrothersLehman BrothersLehman Brothers Holdings Inc. was a global financial services firm. Before declaring bankruptcy in 2008, Lehman was the fourth largest investment bank in the USA , doing business in investment banking, equity and fixed-income sales and trading Lehman Brothers Holdings Inc. (former NYSE ticker...
, for example, in its last annual financial statements, showed accounting leverage of 30.7 times ($691 billion in assets divided by $22 billion in stockholders’ equity). Bankruptcy examiner Anton R. ValukasAnton R. ValukasAnton R. Valukas was the United States Attorney for the Northern District of Illinois from 1985 to 1989. In 2007, he became the chairman of Chicago law firm Jenner & Block, in which capacity he gained notoriety in 2009, when he was appointed bankruptcy examiner in the bankruptcy of Lehman...
determined that the true accounting leverage was higher, it had been understated due to dubious accounting treatments including the so-called repo 105Repo 105Repo 105 is a repurchase agreement which results in an accounting maneuver where a short-term loan is classified as a sale. The cash obtained through this "sale" is then used to pay down debt, allowing the company to appear to reduce its leverage by temporarily paying down liabilities—just long...
(Allowed by Ernst & YoungErnst & YoungErnst & Young is one of the largest professional services networks in the world and one of the "Big Four" accountancy firms, along with Deloitte, KPMG and PricewaterhouseCoopers ....
). Accounting leverage is the ratio usually cited by the press. - Notional leverage more than twice as high, due to off-balance sheet transactions. At the end of 2007, Lehman had $738 billion of notional derivatives in addition to the assets above, plus significant off-balance sheet exposures to special purpose entities, structured investment vehicles and conduits, plus various lending commitments, contractual payments and contingent obligations.
- On the other hand, almost half of Lehman’s balance sheet consisted of closely offsetting positions and very low risk assets, such as regulatory deposits. The company emphasized "net leverage", which excluded these assets. On that basis, Lehman held $373 billion of "net assets" and a "net leverage ratio" of 16.1. This is not a standardized computation, but it probably corresponds more closely to what most people think of when they hear a leverage ratio.
Use of Language
Levering has come to be known as Leveraging, in financial communities. This may have originally been a slang adaptation, since leverage was a nounNoun
In linguistics, a noun is a member of a large, open lexical category whose members can occur as the main word in the subject of a clause, the object of a verb, or the object of a preposition .Lexical categories are defined in terms of how their members combine with other kinds of...
, however, modern dictionaries (such as Random House Dictionary and Merriam-Webster's Dictionary of Law) refer to its use as a verb
Verb
A verb, from the Latin verbum meaning word, is a word that in syntax conveys an action , or a state of being . In the usual description of English, the basic form, with or without the particle to, is the infinitive...
as well. It was first adopted for use as a verb in American English
American English
American English is a set of dialects of the English language used mostly in the United States. Approximately two-thirds of the world's native speakers of English live in the United States....
in 1957.

