
Dukhin number
Encyclopedia
Dukhin number is a dimensionless quantity that characterizes the contribution of the surface conductivity
to various electrokinetic and electroacoustic
effects, as well as to electrical conductivity and permittivity
of fluid heterogeneous systems.
It was introduced by Lyklema in “Fundamentals of Interface and Colloid Science”.
IUPAC Technical Report prepared by a group of most known world experts on this subject uses this term explicitly.
Dukhin number is a ratio of the surface conductivity
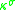 to the fluid bulk electrical conductivity Km multiplied by particle size a :
to the fluid bulk electrical conductivity Km multiplied by particle size a :

There is another expression of this number that is valid when surface conductivity is associated only with ions motion above slipping plane in the double layer
. In this case, value of the surface conductivity depends on ζ-potential, which leads to the following expression for the Dukhin number for symmetrical electrolyte with equal ions diffusion coefficient:
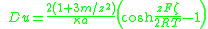
where parameter m characterizes contribution of electro-osmosis
into motion of ions within DL:
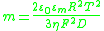
There are several ways to measure Dukhin number.
Surface conductivity
Surface conductivity is an additional conductivity of an electrolyte in the vicinity of charged surfaces. Close to charged surfaces a layer of counter ions of opposite polarity exists which is attracted by the surface charges. This layer of higher ionic concentration is a part of the interfacial ...
to various electrokinetic and electroacoustic
Electroacoustic music
Electroacoustic music originated in Western art music during its modern era following the incorporation of electric sound production into compositional practice. The initial developments in electroacoustic music composition during the mid-20th century are associated with the activities of composers...
effects, as well as to electrical conductivity and permittivity
Permittivity
In electromagnetism, absolute permittivity is the measure of the resistance that is encountered when forming an electric field in a medium. In other words, permittivity is a measure of how an electric field affects, and is affected by, a dielectric medium. The permittivity of a medium describes how...
of fluid heterogeneous systems.
It was introduced by Lyklema in “Fundamentals of Interface and Colloid Science”.
IUPAC Technical Report prepared by a group of most known world experts on this subject uses this term explicitly.
Dukhin number is a ratio of the surface conductivity
Surface conductivity
Surface conductivity is an additional conductivity of an electrolyte in the vicinity of charged surfaces. Close to charged surfaces a layer of counter ions of opposite polarity exists which is attracted by the surface charges. This layer of higher ionic concentration is a part of the interfacial ...
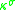 to the fluid bulk electrical conductivity Km multiplied by particle size a :
to the fluid bulk electrical conductivity Km multiplied by particle size a :
There is another expression of this number that is valid when surface conductivity is associated only with ions motion above slipping plane in the double layer
Double layer
Double layer may refer to:* Double layer , a structure in a plasma and consists of two parallel layers with opposite electrical charge* Double layer , a structure that appears on the surface of an object when it is placed into a liquid...
. In this case, value of the surface conductivity depends on ζ-potential, which leads to the following expression for the Dukhin number for symmetrical electrolyte with equal ions diffusion coefficient:
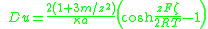
where parameter m characterizes contribution of electro-osmosis
Electro-osmosis
Electroosmotic flow is the motion of liquid induced by an applied potential across a porous material, capillary tube, membrane, microchannel, or any other fluid conduit...
into motion of ions within DL:
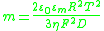
- F is Faraday constant
- T is absolute temperature
- R is gas constantGas constantThe gas constant is a physical constant which is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law and the Nernst equation. It is equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, but expressed in units of energy The gas constant (also known as the molar, universal,...
- C is ions concentration in bulk
- z is ionIonAn ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
valencyValence (chemistry)In chemistry, valence, also known as valency or valence number, is a measure of the number of bonds formed by an atom of a given element. "Valence" can be defined as the number of valence bonds... - ζ is electrokinetic potential
- ε0 is vacuumVacuumIn everyday usage, vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter, such that its gaseous pressure is much less than atmospheric pressure. The word comes from the Latin term for "empty". A perfect vacuum would be one with no particles in it at all, which is impossible to achieve in...
dielectricDielectricA dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material, as in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric...
permittivityPermittivityIn electromagnetism, absolute permittivity is the measure of the resistance that is encountered when forming an electric field in a medium. In other words, permittivity is a measure of how an electric field affects, and is affected by, a dielectric medium. The permittivity of a medium describes how... - εm is fluid dielectric permittivity
- η is dynamic viscosity
- D is diffusion coefficient
There are several ways to measure Dukhin number.

