Dutch colonization of the Americas
Encyclopedia
Dutch
trading posts and plantations in the Americas precede the much wider known colonization activities of the Dutch in Asia. Whereas the first Dutch fort in Asia was built in 1600 (in present-day Indonesia), the first forts and settlements on the Essequibo river in Guyana and on the Amazon date from the 1590s. Actual colonization, with Dutch settling in the new lands, was not as common as with other European nations. Many of the Dutch settlements were lost or abandoned by the end of that century, but the Netherlands managed to retain possession of Suriname
until it gained independence in 1975, as well as the Netherlands Antilles
and Aruba
, which remain within the Kingdom of the Netherlands
today.
where they had built a fort shortly after arriving in Sint Maarten) to the Spanish, they settled Curaçao
and Sint Eustatius. They regained half of Sint Maarten in 1648, from then on sharing the island with France. The border between the two portions of the island continued to be modified periodically, before being set for good in 1816.
Several other islands were captured and fortified to prevent Spanish
attacks in the ongoing Dutch war for independence from Spain and to exploit timber and salt resources: zfs,mh;xbm;
Until deep into the 19th century, the now Venezuelan islands of Aves
, the Aves archipelago
, Los Roques and La Orchila
were also considered by the Dutch government to be part of the Dutch West Indies.
The Netherlands Antilles
remained an overseas territory of the Netherlands. It was granted self-rule in 1954. In 1986, Aruba was granted autonomy, separately from the other islands. On October 10, 2010 the Netherlands Antilles was dismantled. The islands Curaçao and Sint Maarten became constituent countries of Kingdom of the Netherlands
. Bonaire, Saba, and Sint Eustatius became a special municipalities of the Netherlands.
existed:
before 1640 and later on Anegada
and Virgin Gorda
. The British took Tortola in 1672 and Anegada and Virgin Gorda in 1680.
.jpg)
In 1602, the government of the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands chartered the Dutch East India Company
(Vereenigde Oostindische Compagnie), or VOC with the mission of exploring it for a passage to the Indies
and claiming any uncharted areas for the United Provinces, which led to several significant expeditions. The two Dutch settlements in the Americas are, New Netherland
s and New Amsterdam
.
In 1609, the VOC commissioned English
explorer Henry Hudson
who, in an attempt to find the so-called northwest passage
to the Indies, discovered and claimed for the VOC parts of the present-day United States and Canada
. In the belief that it was the best route to explore, Hudson entered the Upper New York Bay
sailing up the Hudson River
which now bears his name. In 1614, Adriaen Block
led an expedition to the lower Hudson in the Tyger
, and then explored the East River
aboard the Onrust
, becoming the first known European to navigate the Hellegat
enter Long Island Sound. Block Island
and its sound
were named after him. Upon returning, Block compiled a map, the first to apply the name "New Netherland" to the area between English Virginia
and French Canada
, where he was later granted exclusive trading rights by the Dutch government.
After some early trading expeditions, the first Dutch settlement in the Americas was founded in 1615: Fort Nassau
, on Castle Island in the Hudson, near present-day Albany
. The settlement served mostly as a trade post for fur trade with the natives and was later replaced by Fort Oranje (in English: Fort Orange) at present-day Albany. Both forts were named in honor of the Dutch House of Orange-Nassau
.
In 1621, a new company was established with a trading monopoly in the Americas
and West Africa
: the Dutch West India Company
(Westindische Compagnie or WIC). The WIC sought recognition for the area in the New World – which had been called New Netherland
– as a province, which was granted in 1623. Soon after, the first colonists, mostly from present-day Belgium
and Germany, arrived in the new province. That same year the construction of several fortified trading posts began including the Fort Huys de Goede Hoop
(in English, Fort House of Good Hope), now known as Hartford, Connecticut
.
In 1626, Director-General of the WIC Peter Minuit
purchased the island of Manhattan
from Indians and started the construction of fort New Amsterdam
. In the same year, another Fort Nassau
(not the one near Albany) was built on the Delaware River
in southern New Jersey
. Other settlements were Fort Casimir
(Newcastle) and Fort Beversrede (Philadelphia). Fort Huys de Goede Hoop
was completed in 1633. By 1636, the English from Newtown now known as Cambridge, Massachusetts settled on the north side of the Little River, now buried under the Whitehead Highway of Hartford. By 1653, the English had overtaken this Dutch trading post. In 1655, the main settlement of New Sweden
, Fort Christina
, was captured after the Swedes
had briefly occupied Fort Casimir.
Many of the inhabitants of these settlements were not ethnically Dutch, but came from a variety of other European countries. A significant number of immigrants to New Netherland
were Protestants of English or French Huguenot
background, including the Louis Dubois
colony, which settled New Paltz, making a private treaty with the local Native Americans to purchase a large tract of land from the Hudson River
to the mountains. Later, under English rule, this self-governing colony, ruled by Dubois and 11 others on their unique duzine, continued to prosper and today the village boasts the oldest street in North America with the original stone houses.
In 1664, English troops under the command of the Duke of York and Albany
(later James II of England
) attacked the New Netherland colony. Being greatly outnumbered, Director-General Peter Stuyvesant
surrendered New Amsterdam
, with Fort Orange following soon. New Amsterdam was renamed New York
(from James's English title), Fort Orange was renamed Fort Albany
(from James's Scottish title).
The loss of the New Netherland province led to the Second Anglo–Dutch War during 1665–1667. This conflict ended with the Treaty of Breda in which the Dutch gave up their claim to New Netherland in exchange for Suriname
.
From 1673 to 1674, the territories were once again briefly captured by the Dutch in the Third Anglo–Dutch War, only to be returned to England at the Treaty of Westminster
. In 1674, Dutch navy captain Jurriaen Aernoutsz
also briefly captured two forts in the French colony of Acadia
, which he claimed as the Dutch territory of New Holland. However, Aernoutsz's appointed administrator, John Rhoades
, quickly lost control of the territory after Aernoutsz himself left for Curaçao
to seek out new settlers, and with effective control of Acadia remaining in the hands of France, Dutch sovereignty existed only on paper until the Netherlands surrendered their claim in the Treaties of Nijmegen
.
 From 1630 onward, the Dutch Republic
From 1630 onward, the Dutch Republic
came to control a large portion of Brazil. The Dutch West India Company
set up their headquarters in Recife
. The governor, Johan Maurits
invited artists and scientists to the colony to help to promote migration to the new South American colony. However, the Portuguese won a significant victory at the Second Battle of Guararapes
in 1649. On January 26, 1654, the Dutch Republic surrendered and signed the capitulation returning control of all North East Brazilian land to the Portuguese. After the end of the First Anglo–Dutch War in May 1654, the Dutch Republic demanded that New Holland (Dutch Brazil) was given back to them. Under threat of an occupation of Lisbon
and a reoccupation of North East Brazil
, the Portuguese being already involved in a war against Spain
acceded to the demand of the Dutch. However, the new Dutch political leader Johan de Witt
deemed commerce more important than territory, and saw to it that New Holland was sold back to Portugal on August 6, 1661 through the Treaty of the Hague
.
was conquered by Dutch pirate Sebastian de Cordes. He left the city after some months. Then in 1642 the VOC and the WIC sent a fleet of some ships to Chile
to conquer the city of Valdivia and the goldmines of the Spanish. The expedition was conducted by Hendrik Brouwer
, a Dutch general. In 1643 Brouwer conquered the Chiloé Archipelago
and the city of Valdivia. Brouwer died on the 7th of August of 1643, and the vice-general Elias Herckmans took control.
The second emigration
from the Netherlands
to Chile was in 1895. The so-called "Inspector General of Colonization and Immigration Chilean" a dozen Dutch families settled between 1895 and 1897 in Chiloé, particularly in Mechaico, Huillinco and Chacao. In the same period Hageman Egbert arrived in Chile. with his family, 14 April 1896, settling in Rio Gato, near Puerto Montt
. In addition, family Wennekool which inaugurated the Dutch colonization of Villarrica
.
In the early twentieth century, there arrived in Chile
a large group of Dutch people from South Africa
, which had been established where they worked mainly in construction of the railway. When the Boer War
, which would eventually lead to the British annexation of both republics in 1902. These emigrants decided to emigrate to Chile with the help of the Chilean government
.
On 4 May 1903, a group of over 200 Dutch emigrants sailed on the steamship "Oropesa" shipping company "Pacific Steam Navigation Company, from La Rochelle (La Pallice) in France. The majority of migrants were born in the Netherlands: 35% was from North Holland and South Holland
, 13% of North Brabant
, 9% of Zealand and equal number of Gelderland.
On June 5, arrived by train to their final destination, the city of Pitrufquén
, located south of Temuco
, near the hamlet of Donguil. Another group of Dutchmen arrived shortly after to Talcahuano, in the "Oravi" and the "Orissa". The Netherlands colony in Donguil was christened "New Transvaal Colony. There were established more than 500 families in order to start a new life. Between 7 February 1907 and February 18, 1909 above the last group of families Boers.
It is currently estimated at about 50,000 descendants of Dutch
, mostly located in Malleco, Gorbea
, Pitrufquén
, Faja Maisan and around Temuco
.
. The Dutch traded with the Indian peoples and, as in Suriname, established sugar
plantations worked by African slaves. While the coast remained under Dutch control, the English established plantations west of the Suriname River
. Conflict between the two countries meant parts of the region changed hands a number of times, but by 1796 Britain had control of the region. The Netherlands ceded the colonies of Essequibo
, Demerara
, and Berbice
to Britain in 1814.
. This colony was captured by the Dutch under Abraham Crijnsen during the Second Anglo–Dutch War. On July 31, 1667, under the Treaty of Breda the Dutch offered New Netherland
(including New Amsterdam
, modern-day New York City
) in exchange for their sugar factories on the coast of Surinam. In 1683 Suriname was sold to the Dutch West India Company and came to be known as Dutch Guiana
. The colony developed an agricultural economy based on African slavery
. During the Napoleonic Wars
, England controlled Suriname from 1799 until 1816, when it was returned to the Dutch. The Netherlands abolished slavery in 1863 and imported indentured labour force from the British Indian colonies and from the Dutch East Indies
to keep the economy going. Internal self governance was granted in 1954 and full independence in 1975. The prospect of independence prompted many to migrate to the Netherlands, especially from the large Hindustani minority. Political instability and economic decline after independence resulted in even more migration to the Netherlands and also to the USA. The Surinamese community in the Netherlands is now almost as large as the population in the country itself (about 450,000).
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
trading posts and plantations in the Americas precede the much wider known colonization activities of the Dutch in Asia. Whereas the first Dutch fort in Asia was built in 1600 (in present-day Indonesia), the first forts and settlements on the Essequibo river in Guyana and on the Amazon date from the 1590s. Actual colonization, with Dutch settling in the new lands, was not as common as with other European nations. Many of the Dutch settlements were lost or abandoned by the end of that century, but the Netherlands managed to retain possession of Suriname
Suriname
Suriname , officially the Republic of Suriname , is a country in northern South America. It borders French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west, Brazil to the south, and on the north by the Atlantic Ocean. Suriname was a former colony of the British and of the Dutch, and was previously known as...
until it gained independence in 1975, as well as the Netherlands Antilles
Netherlands Antilles
The Netherlands Antilles , also referred to informally as the Dutch Antilles, was an autonomous Caribbean country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands, consisting of two groups of islands in the Lesser Antilles: Aruba, Bonaire and Curaçao , in Leeward Antilles just off the Venezuelan coast; and Sint...
and Aruba
Aruba
Aruba is a 33 km-long island of the Lesser Antilles in the southern Caribbean Sea, located 27 km north of the coast of Venezuela and 130 km east of Guajira Peninsula...
, which remain within the Kingdom of the Netherlands
Kingdom of the Netherlands
The Kingdom of the Netherlands is a sovereign state and constitutional monarchy with territory in Western Europe and in the Caribbean. The four parts of the Kingdom—Aruba, Curaçao, the Netherlands, and Sint Maarten—are referred to as "countries", and participate on a basis of equality...
today.
Netherlands Antilles
Dutch colonization in the Caribbean started in the 1620s on St. Croix and Tobago (1628), followed in 1631 with settlements on Tortuga (now Île Tortue) and Sint Maarten. When the Dutch lost Sint Maarten (and AnguillaAnguilla
Anguilla is a British overseas territory and overseas territory of the European Union in the Caribbean. It is one of the most northerly of the Leeward Islands in the Lesser Antilles, lying east of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands and directly north of Saint Martin...
where they had built a fort shortly after arriving in Sint Maarten) to the Spanish, they settled Curaçao
Curaçao
Curaçao is an island in the southern Caribbean Sea, off the Venezuelan coast. The Country of Curaçao , which includes the main island plus the small, uninhabited island of Klein Curaçao , is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands...
and Sint Eustatius. They regained half of Sint Maarten in 1648, from then on sharing the island with France. The border between the two portions of the island continued to be modified periodically, before being set for good in 1816.
Several other islands were captured and fortified to prevent Spanish
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
attacks in the ongoing Dutch war for independence from Spain and to exploit timber and salt resources: zfs,mh;xbm;
- CuraçaoCuraçaoCuraçao is an island in the southern Caribbean Sea, off the Venezuelan coast. The Country of Curaçao , which includes the main island plus the small, uninhabited island of Klein Curaçao , is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands...
in 1634 - Saba in 1640
- Sint Eustatius in 1636
- Bonaire in 1634
- ArubaArubaAruba is a 33 km-long island of the Lesser Antilles in the southern Caribbean Sea, located 27 km north of the coast of Venezuela and 130 km east of Guajira Peninsula...
in 1637 - Sint Maarten in 1631
- TortolaTortolaTortola is the largest and most populated of the British Virgin Islands, a group of islands that form part of the archipelago of the Virgin Islands. Local tradition recounts that Christopher Columbus named it Tortola, meaning "land of the Turtle Dove". Columbus named the island Santa Ana...
, Virgin GordaVirgin GordaVirgin Gorda is the third-largest and second most populous of the British Virgin Islands . Located at approximately 18 degrees, 48 minutes North, and 64 degrees, 30 minutes West, it covers an area of about...
, Jost van DykeJost Van DykeAt roughly 8 square kilometers, and about 3 square miles Jost Van Dyke is the smallest of the four main islands of the British Virgin Islands, the northern portion of the archipelago of the Virgin Islands, located in the Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Sea. Jost Van Dyke lies about 8 km to the...
before 1640abw
Until deep into the 19th century, the now Venezuelan islands of Aves
Isla Aves
Isla de Aves , or Aves Island, is a Caribbean dependency of Venezuela. It has been the subject of numerous territorial disputes between the neighboring independent islands, such as Dominica, and European mother countries of surrounding dependent islands, such as the Netherlands. It lies to the west...
, the Aves archipelago
Las Aves Archipelago
The Las Aves Archipelagois a pristine archipelago in the Caribbean Sea, and is part of the Federal Dependencies of Venezuela. It is located north of the Venezuelan states of Aragua and Carabobo, between the Dutch island Bonaire in the west, and the Los Roques Archipelago in the east, at . The prime...
, Los Roques and La Orchila
La Orchila
La Orchila is a military base off the coast of Venezuela, north of Caracas. It has numerous beaches, including one where the sand is markedly pink ....
were also considered by the Dutch government to be part of the Dutch West Indies.
The Netherlands Antilles
Netherlands Antilles
The Netherlands Antilles , also referred to informally as the Dutch Antilles, was an autonomous Caribbean country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands, consisting of two groups of islands in the Lesser Antilles: Aruba, Bonaire and Curaçao , in Leeward Antilles just off the Venezuelan coast; and Sint...
remained an overseas territory of the Netherlands. It was granted self-rule in 1954. In 1986, Aruba was granted autonomy, separately from the other islands. On October 10, 2010 the Netherlands Antilles was dismantled. The islands Curaçao and Sint Maarten became constituent countries of Kingdom of the Netherlands
Kingdom of the Netherlands
The Kingdom of the Netherlands is a sovereign state and constitutional monarchy with territory in Western Europe and in the Caribbean. The four parts of the Kingdom—Aruba, Curaçao, the Netherlands, and Sint Maarten—are referred to as "countries", and participate on a basis of equality...
. Bonaire, Saba, and Sint Eustatius became a special municipalities of the Netherlands.
Tobago
The Netherlands made numerous attempts to colonize the island in the 17th century. Each time, the settlements were destroyed by rival European powers. Dutch settlements on TobagoTobago
Tobago is the smaller of the two main islands that make up the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located in the southern Caribbean, northeast of the island of Trinidad and southeast of Grenada. The island lies outside the hurricane belt...
existed:
- 1628–1637 destroyed by Spanish
- 1654–1666 conquered by British and destroyed by French
- 1672 destroyed by British
- 1676–1677 destroyed by French
Virgin Islands
The Dutch established a base on St. Croix in 1625, the same year that the British did. French Protestants joined the Dutch but conflict with the British colony led to its abandonment before 1650. The Dutch established a settlement on TortolaTortola
Tortola is the largest and most populated of the British Virgin Islands, a group of islands that form part of the archipelago of the Virgin Islands. Local tradition recounts that Christopher Columbus named it Tortola, meaning "land of the Turtle Dove". Columbus named the island Santa Ana...
before 1640 and later on Anegada
Anegada
Anegada is the northernmost of the British Virgin Islands, a group of islands which form part of the archipelago of the Virgin Islands. It lies approximately north of Virgin Gorda. Anegada is the only inhabited British Virgin Island formed from coral and limestone, rather than being of volcanic...
and Virgin Gorda
Virgin Gorda
Virgin Gorda is the third-largest and second most populous of the British Virgin Islands . Located at approximately 18 degrees, 48 minutes North, and 64 degrees, 30 minutes West, it covers an area of about...
. The British took Tortola in 1672 and Anegada and Virgin Gorda in 1680.
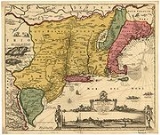
United States
.jpg)
In 1602, the government of the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands chartered the Dutch East India Company
Dutch East India Company
The Dutch East India Company was a chartered company established in 1602, when the States-General of the Netherlands granted it a 21-year monopoly to carry out colonial activities in Asia...
(Vereenigde Oostindische Compagnie), or VOC with the mission of exploring it for a passage to the Indies
Indies
The Indies is a term that has been used to describe the lands of South and Southeast Asia, occupying all of the present India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Nepal, Sri Lanka, the Maldives, and also Thailand, Cambodia, Laos, Vietnam, Brunei, Singapore, the Philippines, East Timor, Malaysia and...
and claiming any uncharted areas for the United Provinces, which led to several significant expeditions. The two Dutch settlements in the Americas are, New Netherland
New Netherland
New Netherland, or Nieuw-Nederland in Dutch, was the 17th-century colonial province of the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands on the East Coast of North America. The claimed territories were the lands from the Delmarva Peninsula to extreme southwestern Cape Cod...
s and New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam was a 17th-century Dutch colonial settlement that served as the capital of New Netherland. It later became New York City....
.
In 1609, the VOC commissioned English
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
explorer Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson was an English sea explorer and navigator in the early 17th century. Hudson made two attempts on behalf of English merchants to find a prospective Northeast Passage to Cathay via a route above the Arctic Circle...
who, in an attempt to find the so-called northwest passage
Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage is a sea route through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways amidst the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans...
to the Indies, discovered and claimed for the VOC parts of the present-day United States and Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
. In the belief that it was the best route to explore, Hudson entered the Upper New York Bay
Upper New York Bay
Upper New York Bay, or Upper Bay, is the traditional heart of the Port of New York and New Jersey, and often called New York Harbor. It is enclosed by the New York City boroughs of Manhattan, Brooklyn, and Staten Island and the Hudson County, New Jersey municipalities of Jersey City and Bayonne.It...
sailing up the Hudson River
Hudson River
The Hudson is a river that flows from north to south through eastern New York. The highest official source is at Lake Tear of the Clouds, on the slopes of Mount Marcy in the Adirondack Mountains. The river itself officially begins in Henderson Lake in Newcomb, New York...
which now bears his name. In 1614, Adriaen Block
Adriaen Block
Adriaen Block was a Dutch private trader and navigator who is best known for exploring the coastal and river valley areas between present-day New Jersey and Massachusetts during four voyages from 1611 to 1614, following the 1609 expedition by Henry Hudson...
led an expedition to the lower Hudson in the Tyger
Tyger (ship)
The Tyger was the ship used by Dutch captain Adriaen Block during his 1613 voyage to explore the East Coast of North America and the present day Hudson River...
, and then explored the East River
East River
The East River is a tidal strait in New York City. It connects Upper New York Bay on its south end to Long Island Sound on its north end. It separates Long Island from the island of Manhattan and the Bronx on the North American mainland...
aboard the Onrust
Onrust
The Onrust was a Dutch ship that was built by Adriaen Block and the crew of the Tyger, which had been destroyed by fire. The ship, a yacht, was the first decked vessel to be built entirely in America. The construction took one winter on Manhattan Island...
, becoming the first known European to navigate the Hellegat
Hell Gate
Hell Gate is a narrow tidal strait in the East River in New York City in the United States. It separates Astoria, Queens from Randall's Island/Wards Island ....
enter Long Island Sound. Block Island
Block Island
Block Island is part of the U.S. state of Rhode Island and is located in the Atlantic Ocean approximately south of the coast of Rhode Island, east of Montauk Point on Long Island, and is separated from the Rhode Island mainland by Block Island Sound. The United States Census Bureau defines Block...
and its sound
Block Island Sound
Block Island Sound is a strait in the open Atlantic Ocean, approximately wide, separating Block Island from the coast of Rhode Island in the United States...
were named after him. Upon returning, Block compiled a map, the first to apply the name "New Netherland" to the area between English Virginia
Colony and Dominion of Virginia
The Colony of Virginia was the English colony in North America that existed briefly during the 16th century, and then continuously from 1607 until the American Revolution...
and French Canada
New France
New France was the area colonized by France in North America during a period beginning with the exploration of the Saint Lawrence River by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Spain and Great Britain in 1763...
, where he was later granted exclusive trading rights by the Dutch government.
After some early trading expeditions, the first Dutch settlement in the Americas was founded in 1615: Fort Nassau
Fort Nassau
The name Fort Nassau was used by the Dutch in the 17th century for several fortifications, mostly trading stations, named for the House of Orange-Nassau...
, on Castle Island in the Hudson, near present-day Albany
Albany, New York
Albany is the capital city of the U.S. state of New York, the seat of Albany County, and the central city of New York's Capital District. Roughly north of New York City, Albany sits on the west bank of the Hudson River, about south of its confluence with the Mohawk River...
. The settlement served mostly as a trade post for fur trade with the natives and was later replaced by Fort Oranje (in English: Fort Orange) at present-day Albany. Both forts were named in honor of the Dutch House of Orange-Nassau
House of Orange-Nassau
The House of Orange-Nassau , a branch of the European House of Nassau, has played a central role in the political life of the Netherlands — and at times in Europe — since William I of Orange organized the Dutch revolt against Spanish rule, which after the Eighty Years' War...
.
In 1621, a new company was established with a trading monopoly in the Americas
Americas
The Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily...
and West Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
: the Dutch West India Company
Dutch West India Company
Dutch West India Company was a chartered company of Dutch merchants. Among its founding fathers was Willem Usselincx...
(Westindische Compagnie or WIC). The WIC sought recognition for the area in the New World – which had been called New Netherland
New Netherland
New Netherland, or Nieuw-Nederland in Dutch, was the 17th-century colonial province of the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands on the East Coast of North America. The claimed territories were the lands from the Delmarva Peninsula to extreme southwestern Cape Cod...
– as a province, which was granted in 1623. Soon after, the first colonists, mostly from present-day Belgium
Belgium
Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
and Germany, arrived in the new province. That same year the construction of several fortified trading posts began including the Fort Huys de Goede Hoop
Fort Hoop
Fort Hoop was a settlement in the seventeenth century colonial province of New Netherland that eventually developed into Hartford, Connecticut.-History:...
(in English, Fort House of Good Hope), now known as Hartford, Connecticut
Hartford, Connecticut
Hartford is the capital of the U.S. state of Connecticut. The seat of Hartford County until Connecticut disbanded county government in 1960, it is the second most populous city on New England's largest river, the Connecticut River. As of the 2010 Census, Hartford's population was 124,775, making...
.
In 1626, Director-General of the WIC Peter Minuit
Peter Minuit
Peter Minuit, Pieter Minuit, Pierre Minuit or Peter Minnewit was a Walloon from Wesel, in present-day North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, then part of the Duchy of Cleves. He was the Director-General of the Dutch colony of New Netherland from 1626 until 1633, and he founded the Swedish colony of...
purchased the island of Manhattan
Manhattan
Manhattan is the oldest and the most densely populated of the five boroughs of New York City. Located primarily on the island of Manhattan at the mouth of the Hudson River, the boundaries of the borough are identical to those of New York County, an original county of the state of New York...
from Indians and started the construction of fort New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam was a 17th-century Dutch colonial settlement that served as the capital of New Netherland. It later became New York City....
. In the same year, another Fort Nassau
Fort Nassau
The name Fort Nassau was used by the Dutch in the 17th century for several fortifications, mostly trading stations, named for the House of Orange-Nassau...
(not the one near Albany) was built on the Delaware River
Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river on the Atlantic coast of the United States.A Dutch expedition led by Henry Hudson in 1609 first mapped the river. The river was christened the South River in the New Netherland colony that followed, in contrast to the North River, as the Hudson River was then...
in southern New Jersey
Gloucester City, New Jersey
Gloucester City is a city in Camden County, New Jersey, United States. As of the United States 2010 Census, the city population was 11,456.-Geography:Gloucester City is located at ....
. Other settlements were Fort Casimir
Fort Casimir
Fort Casimir was a Dutch settlement in 17th century colonial province of New Netherland. It was located on a no-longer existing barrier island at the end of Chestnut Street in what is now New Castle, Delaware...
(Newcastle) and Fort Beversrede (Philadelphia). Fort Huys de Goede Hoop
Fort Hoop
Fort Hoop was a settlement in the seventeenth century colonial province of New Netherland that eventually developed into Hartford, Connecticut.-History:...
was completed in 1633. By 1636, the English from Newtown now known as Cambridge, Massachusetts settled on the north side of the Little River, now buried under the Whitehead Highway of Hartford. By 1653, the English had overtaken this Dutch trading post. In 1655, the main settlement of New Sweden
New Sweden
New Sweden was a Swedish colony along the Delaware River on the Mid-Atlantic coast of North America from 1638 to 1655. Fort Christina, now in Wilmington, Delaware, was the first settlement. New Sweden included parts of the present-day American states of Delaware, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania....
, Fort Christina
Fort Christina
Fort Christina was the first Swedish settlement in North America and the principal settlement of the New Sweden colony...
, was captured after the Swedes
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
had briefly occupied Fort Casimir.
Many of the inhabitants of these settlements were not ethnically Dutch, but came from a variety of other European countries. A significant number of immigrants to New Netherland
New Netherland
New Netherland, or Nieuw-Nederland in Dutch, was the 17th-century colonial province of the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands on the East Coast of North America. The claimed territories were the lands from the Delmarva Peninsula to extreme southwestern Cape Cod...
were Protestants of English or French Huguenot
Huguenot
The Huguenots were members of the Protestant Reformed Church of France during the 16th and 17th centuries. Since the 17th century, people who formerly would have been called Huguenots have instead simply been called French Protestants, a title suggested by their German co-religionists, the...
background, including the Louis Dubois
Louis Dubois
Louis DuBois was a Huguenot colonist in New Netherland who, with two of his sons and nine other refugees, founded the village of New Paltz, New York...
colony, which settled New Paltz, making a private treaty with the local Native Americans to purchase a large tract of land from the Hudson River
Hudson River
The Hudson is a river that flows from north to south through eastern New York. The highest official source is at Lake Tear of the Clouds, on the slopes of Mount Marcy in the Adirondack Mountains. The river itself officially begins in Henderson Lake in Newcomb, New York...
to the mountains. Later, under English rule, this self-governing colony, ruled by Dubois and 11 others on their unique duzine, continued to prosper and today the village boasts the oldest street in North America with the original stone houses.
In 1664, English troops under the command of the Duke of York and Albany
Duke of York
The Duke of York is a title of nobility in the British peerage. Since the 15th century, it has, when granted, usually been given to the second son of the British monarch. The title has been created a remarkable eleven times, eight as "Duke of York" and three as the double-barreled "Duke of York and...
(later James II of England
James II of England
James II & VII was King of England and King of Ireland as James II and King of Scotland as James VII, from 6 February 1685. He was the last Catholic monarch to reign over the Kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland...
) attacked the New Netherland colony. Being greatly outnumbered, Director-General Peter Stuyvesant
Peter Stuyvesant
Peter Stuyvesant , served as the last Dutch Director-General of the colony of New Netherland from 1647 until it was ceded provisionally to the English in 1664, after which it was renamed New York...
surrendered New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam was a 17th-century Dutch colonial settlement that served as the capital of New Netherland. It later became New York City....
, with Fort Orange following soon. New Amsterdam was renamed New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
(from James's English title), Fort Orange was renamed Fort Albany
Fort Frederick (Albany)
Fort Frederick was a fort in Albany, New York from 1676-1789. Sitting atop State Street Hill it replaced the earlier decaying Fort Orange along the Hudson River. The fort was named for Frederick Louis, son of King George II. The fort was referred to as Fort Albany in the 1936 novel Drums Along the...
(from James's Scottish title).
The loss of the New Netherland province led to the Second Anglo–Dutch War during 1665–1667. This conflict ended with the Treaty of Breda in which the Dutch gave up their claim to New Netherland in exchange for Suriname
Suriname
Suriname , officially the Republic of Suriname , is a country in northern South America. It borders French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west, Brazil to the south, and on the north by the Atlantic Ocean. Suriname was a former colony of the British and of the Dutch, and was previously known as...
.
From 1673 to 1674, the territories were once again briefly captured by the Dutch in the Third Anglo–Dutch War, only to be returned to England at the Treaty of Westminster
Treaty of Westminster (1674)
The Treaty of Westminster of 1674 was the peace treaty that ended the Third Anglo-Dutch War. Signed by the Netherlands and England, it provided for the return of the colony of New Netherland to England and renewed the Treaty of Breda of 1667...
. In 1674, Dutch navy captain Jurriaen Aernoutsz
Jurriaen Aernoutsz
Jurriaen Aernoutsz was a Dutch colonial navy captain, who briefly captured a section of the French colony of Acadia in 1674 AD, establishing the brief Dutch Occupation of Acadia....
also briefly captured two forts in the French colony of Acadia
Acadia
Acadia was the name given to lands in a portion of the French colonial empire of New France, in northeastern North America that included parts of eastern Quebec, the Maritime provinces, and modern-day Maine. At the end of the 16th century, France claimed territory stretching as far south as...
, which he claimed as the Dutch territory of New Holland. However, Aernoutsz's appointed administrator, John Rhoades
John Rhoades
John Rhoades was a fur trader from New England, who was part of Jurriaen Aernoutsz's short-lived conquest of Acadia in 1674.A resident of Massachusetts, Rhoades met with Aernoutsz shortly after the latter's arrival in New York City, and used his familiarity with the region to convince Aernoutsz to...
, quickly lost control of the territory after Aernoutsz himself left for Curaçao
Curaçao
Curaçao is an island in the southern Caribbean Sea, off the Venezuelan coast. The Country of Curaçao , which includes the main island plus the small, uninhabited island of Klein Curaçao , is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands...
to seek out new settlers, and with effective control of Acadia remaining in the hands of France, Dutch sovereignty existed only on paper until the Netherlands surrendered their claim in the Treaties of Nijmegen
Treaties of Nijmegen
The Treaties of Peace of Nijmegen were a series of treaties signed in the Dutch city of Nijmegen between August 1678 and December 1679...
.
Brazil

Dutch Republic
The Dutch Republic — officially known as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands , the Republic of the United Netherlands, or the Republic of the Seven United Provinces — was a republic in Europe existing from 1581 to 1795, preceding the Batavian Republic and ultimately...
came to control a large portion of Brazil. The Dutch West India Company
Dutch West India Company
Dutch West India Company was a chartered company of Dutch merchants. Among its founding fathers was Willem Usselincx...
set up their headquarters in Recife
Recife
Recife is the fifth-largest metropolitan area in Brazil with 4,136,506 inhabitants, the largest metropolitan area of the North/Northeast Regions, the 5th-largest metropolitan influence area in Brazil, and the capital and largest city of the state of Pernambuco. The population of the city proper...
. The governor, Johan Maurits
John Maurice of Nassau
John Maurice of Nassau was count and prince of Nassau-Siegen.He was born in Dillenburg...
invited artists and scientists to the colony to help to promote migration to the new South American colony. However, the Portuguese won a significant victory at the Second Battle of Guararapes
Second Battle of Guararapes
The Second Battle of Guararapes was the second and decisive battle in a conflict called Pernambucana Insurrection, between Dutch and Portuguese forces in 1649 at Jaboatão dos Guararapes in the state of Pernambuco, ending the Dutch occupation of Brazil....
in 1649. On January 26, 1654, the Dutch Republic surrendered and signed the capitulation returning control of all North East Brazilian land to the Portuguese. After the end of the First Anglo–Dutch War in May 1654, the Dutch Republic demanded that New Holland (Dutch Brazil) was given back to them. Under threat of an occupation of Lisbon
Lisbon
Lisbon is the capital city and largest city of Portugal with a population of 545,245 within its administrative limits on a land area of . The urban area of Lisbon extends beyond the administrative city limits with a population of 3 million on an area of , making it the 9th most populous urban...
and a reoccupation of North East Brazil
Northeast Region, Brazil
The Northeast Region of Brazil is composed of the following states: Maranhão, Piauí, Ceará, Rio Grande do Norte, Paraíba, Pernambuco, Alagoas, Sergipe and Bahia, and it represents 18.26% of the Brazilian territory....
, the Portuguese being already involved in a war against Spain
Portuguese Restoration War
Portuguese Restoration War was the name given by nineteenth-century 'romantic' historians to the war between Portugal and Spain that began with the Portuguese revolution of 1640 and ended with the Treaty of Lisbon . The revolution of 1640 ended the sixty-year period of dual monarchy in Portugal...
acceded to the demand of the Dutch. However, the new Dutch political leader Johan de Witt
Johan de Witt
Johan de Witt, heer van Zuid- en Noord-Linschoten, Snelrewaard, Hekendorp and IJsselveere was a key figure in Dutch politics in the mid 17th century, when its flourishing sea trade in a period of globalization made the United Provinces a leading European power during the Dutch Golden Age...
deemed commerce more important than territory, and saw to it that New Holland was sold back to Portugal on August 6, 1661 through the Treaty of the Hague
Treaty of The Hague (1661)
The Treaty of The Hague was signed in 1661 between representatives of the Dutch Empire and the Portuguese Empire...
.
Chile
In 1600 , the Chilean city of ValdiviaValdivia, Chile
Valdivia is a city and commune in southern Chile administered by the Municipality of Valdivia. The city is named after its founder Pedro de Valdivia and is located at the confluence of the Calle-Calle, Valdivia and Cau-Cau Rivers, approximately east of the coastal towns of Corral and Niebla...
was conquered by Dutch pirate Sebastian de Cordes. He left the city after some months. Then in 1642 the VOC and the WIC sent a fleet of some ships to Chile
Chile
Chile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
to conquer the city of Valdivia and the goldmines of the Spanish. The expedition was conducted by Hendrik Brouwer
Hendrik Brouwer
Hendrik Brouwer was a Dutch explorer, admiral, and colonial administrator both in Japan and the Dutch East Indies....
, a Dutch general. In 1643 Brouwer conquered the Chiloé Archipelago
Chiloé Archipelago
Chiloé Archipelago consists of several islands lying off the coast of Chile. It is separated from mainland Chile by Chacao Channel in the north, the Sea of Chiloé in the east and Gulf of Corcovado to the southeast. All of the archipelago except Desertores Islands, which are part of Palena...
and the city of Valdivia. Brouwer died on the 7th of August of 1643, and the vice-general Elias Herckmans took control.
The second emigration
Emigration
Emigration is the act of leaving one's country or region to settle in another. It is the same as immigration but from the perspective of the country of origin. Human movement before the establishment of political boundaries or within one state is termed migration. There are many reasons why people...
from the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
to Chile was in 1895. The so-called "Inspector General of Colonization and Immigration Chilean" a dozen Dutch families settled between 1895 and 1897 in Chiloé, particularly in Mechaico, Huillinco and Chacao. In the same period Hageman Egbert arrived in Chile. with his family, 14 April 1896, settling in Rio Gato, near Puerto Montt
Puerto Montt
Puerto Montt is a port city and commune in southern Chile, located at the northern end of the Reloncaví Sound in the Llanquihue Province, Los Lagos Region. The commune spans an area of and had a population of 175,938 in 2002. It is located 1,055 km to the south of the capital, Santiago...
. In addition, family Wennekool which inaugurated the Dutch colonization of Villarrica
Villarrica, Chile
Villarrica is a city and commune in southern Chile located on the western shore of Villarrica Lake in the Province of Cautín, Araucanía Region south of Santiago and close to the Villarrica Volcano ski center to the south east. Residents of Villarrica are known as Villarriquences.Tourism, grain and...
.
In the early twentieth century, there arrived in Chile
Chile
Chile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
a large group of Dutch people from South Africa
South Africa
The Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
, which had been established where they worked mainly in construction of the railway. When the Boer War
Boer War
The Boer Wars were two wars fought between the British Empire and the two independent Boer republics, the Oranje Vrijstaat and the Republiek van Transvaal ....
, which would eventually lead to the British annexation of both republics in 1902. These emigrants decided to emigrate to Chile with the help of the Chilean government
Government
Government refers to the legislators, administrators, and arbitrators in the administrative bureaucracy who control a state at a given time, and to the system of government by which they are organized...
.
On 4 May 1903, a group of over 200 Dutch emigrants sailed on the steamship "Oropesa" shipping company "Pacific Steam Navigation Company, from La Rochelle (La Pallice) in France. The majority of migrants were born in the Netherlands: 35% was from North Holland and South Holland
South Holland
South Holland is a province situated on the North Sea in the western part of the Netherlands. The provincial capital is The Hague and its largest city is Rotterdam.South Holland is one of the most densely populated and industrialised areas in the world...
, 13% of North Brabant
North Brabant
North Brabant , sometimes called Brabant, is a province of the Netherlands, located in the south of the country, bordered by Belgium in the south, the Meuse River in the north, Limburg in the east and Zeeland in the west.- History :...
, 9% of Zealand and equal number of Gelderland.
On June 5, arrived by train to their final destination, the city of Pitrufquén
Pitrufquén
Pitrufquén is a Chilean city and commune in Cautín Province, Araucanía Region. The city is located 30 km south of Temuco and lies immediately south of the Toltén River, along Chile Highway 5.-History:...
, located south of Temuco
Temuco
Temuco is a city and commune, capital of the Cautín Province and of the Araucanía Region in southern Chile. The name comes from the Mapudungun language, meaning "temu water"; "temu" is a tree used by Mapuches for medicinal purposes. The city is located 670 km south of Santiago...
, near the hamlet of Donguil. Another group of Dutchmen arrived shortly after to Talcahuano, in the "Oravi" and the "Orissa". The Netherlands colony in Donguil was christened "New Transvaal Colony. There were established more than 500 families in order to start a new life. Between 7 February 1907 and February 18, 1909 above the last group of families Boers.
It is currently estimated at about 50,000 descendants of Dutch
Dutch people
The Dutch people are an ethnic group native to the Netherlands. They share a common culture and speak the Dutch language. Dutch people and their descendants are found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in Suriname, Chile, Brazil, Canada, Australia, South Africa, New Zealand, and the United...
, mostly located in Malleco, Gorbea
Gorbea, Chile
Gorbea is a Chilean city and commune located in Cautín Province, Araucanía Region.-Demographics:According to the 2002 census of the National Statistics Institute, Gorbea spans an area of and has 15,222 inhabitants . Of these, 9,413 lived in urban areas and 5,809 in rural areas...
, Pitrufquén
Pitrufquén
Pitrufquén is a Chilean city and commune in Cautín Province, Araucanía Region. The city is located 30 km south of Temuco and lies immediately south of the Toltén River, along Chile Highway 5.-History:...
, Faja Maisan and around Temuco
Temuco
Temuco is a city and commune, capital of the Cautín Province and of the Araucanía Region in southern Chile. The name comes from the Mapudungun language, meaning "temu water"; "temu" is a tree used by Mapuches for medicinal purposes. The city is located 670 km south of Santiago...
.
Guyana
The Dutch West Indian Company built a fort in 1616 on the Essequibo RiverEssequibo River
The Esequibo River is the largest river in Guyana, and the largest river between the Orinoco and Amazon. Rising in the Acarai Mountains near the Brazil-Guyana border, the Essequibo flows to the north for 1,010 km through forest and savanna into the Atlantic Ocean.-Geography:There are countless...
. The Dutch traded with the Indian peoples and, as in Suriname, established sugar
Sugar
Sugar is a class of edible crystalline carbohydrates, mainly sucrose, lactose, and fructose, characterized by a sweet flavor.Sucrose in its refined form primarily comes from sugar cane and sugar beet...
plantations worked by African slaves. While the coast remained under Dutch control, the English established plantations west of the Suriname River
Suriname River
The Suriname River is 480 km long and flows through the country Suriname. Its sources are located in the Guiana Highlands on the border between the Wilhelmina Mountains and the Eilerts de Haan Mountains...
. Conflict between the two countries meant parts of the region changed hands a number of times, but by 1796 Britain had control of the region. The Netherlands ceded the colonies of Essequibo
Essequibo (colony)
Essequibo was from 1616 to 1814 a Dutch colony in the region of the Essequibo river on the north coast of South America. The colony formed a part of the colonies that are known under the collective name of Dutch Guyana.- History :...
, Demerara
Demerara
Demerara was a region in South America in what is now Guyana that was colonised by the Dutch in 1611. The British invaded and captured the area in 1796...
, and Berbice
Berbice
Berbice is a region along the Berbice River in Guyana, which was between 1627 and 1815 a colony of the Netherlands. After having been ceded to the United Kingdom in the latter year, it was merged with Essequibo and Demerara to form the colony of British Guiana in 1831...
to Britain in 1814.
Suriname
The European colony in Suriname was founded in the 1650s by Lord Willoughby, the governor of BarbadosBarbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles. It is in length and as much as in width, amounting to . It is situated in the western area of the North Atlantic and 100 kilometres east of the Windward Islands and the Caribbean Sea; therein, it is about east of the islands of Saint...
. This colony was captured by the Dutch under Abraham Crijnsen during the Second Anglo–Dutch War. On July 31, 1667, under the Treaty of Breda the Dutch offered New Netherland
New Netherland
New Netherland, or Nieuw-Nederland in Dutch, was the 17th-century colonial province of the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands on the East Coast of North America. The claimed territories were the lands from the Delmarva Peninsula to extreme southwestern Cape Cod...
(including New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam was a 17th-century Dutch colonial settlement that served as the capital of New Netherland. It later became New York City....
, modern-day New York City
New York City
New York is the most populous city in the United States and the center of the New York Metropolitan Area, one of the most populous metropolitan areas in the world. New York exerts a significant impact upon global commerce, finance, media, art, fashion, research, technology, education, and...
) in exchange for their sugar factories on the coast of Surinam. In 1683 Suriname was sold to the Dutch West India Company and came to be known as Dutch Guiana
Dutch Guiana
Dutch Guiana, also known as Netherlands Guyana or Dutch Guyana , is the name given to various Dutch colonies on the northern coast of South America, created by the Dutch West India Company...
. The colony developed an agricultural economy based on African slavery
Slavery
Slavery is a system under which people are treated as property to be bought and sold, and are forced to work. Slaves can be held against their will from the time of their capture, purchase or birth, and deprived of the right to leave, to refuse to work, or to demand compensation...
. During the Napoleonic Wars
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars were a series of wars declared against Napoleon's French Empire by opposing coalitions that ran from 1803 to 1815. As a continuation of the wars sparked by the French Revolution of 1789, they revolutionised European armies and played out on an unprecedented scale, mainly due to...
, England controlled Suriname from 1799 until 1816, when it was returned to the Dutch. The Netherlands abolished slavery in 1863 and imported indentured labour force from the British Indian colonies and from the Dutch East Indies
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies was a Dutch colony that became modern Indonesia following World War II. It was formed from the nationalised colonies of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Netherlands government in 1800....
to keep the economy going. Internal self governance was granted in 1954 and full independence in 1975. The prospect of independence prompted many to migrate to the Netherlands, especially from the large Hindustani minority. Political instability and economic decline after independence resulted in even more migration to the Netherlands and also to the USA. The Surinamese community in the Netherlands is now almost as large as the population in the country itself (about 450,000).
See also
- Atlantic WorldAtlantic worldThe Atlantic World is an organizing concept for the historical study of the Atlantic Ocean rim from the beginning of the Age of Exploration to the anad modern era. In many ways the history of the "Atlantic world" culminates in the "Atlantic Revolutions" of the late 18th century and early 19th century...
- Dutch EmpireDutch EmpireThe Dutch Empire consisted of the overseas territories controlled by the Dutch Republic and later, the modern Netherlands from the 17th to the 20th century. The Dutch followed Portugal and Spain in establishing an overseas colonial empire, but based on military conquest of already-existing...
- Dutch West India CompanyDutch West India CompanyDutch West India Company was a chartered company of Dutch merchants. Among its founding fathers was Willem Usselincx...
- New York history
- New AmsterdamNew AmsterdamNew Amsterdam was a 17th-century Dutch colonial settlement that served as the capital of New Netherland. It later became New York City....
- New NetherlandNew NetherlandNew Netherland, or Nieuw-Nederland in Dutch, was the 17th-century colonial province of the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands on the East Coast of North America. The claimed territories were the lands from the Delmarva Peninsula to extreme southwestern Cape Cod...
- Netherlands AntillesNetherlands AntillesThe Netherlands Antilles , also referred to informally as the Dutch Antilles, was an autonomous Caribbean country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands, consisting of two groups of islands in the Lesser Antilles: Aruba, Bonaire and Curaçao , in Leeward Antilles just off the Venezuelan coast; and Sint...
Literature
- Israel, J.I., Dutch primacy in world trade, 1585–1740, Oxford University Press, 1989

