
Dynamic convex hull
Encyclopedia
The dynamic convex hull problem is a class of dynamic problem
s in computational geometry
. The problem consists in the maintenance, i.e., keeping track, of the convex hull
for the dynamically changing input data, i.e., when input data elements may be inserted, deleted, or modified. Problems of this class may be distinguished by the types of the input data and the allowed types of modification of the input data.
of the recomputation of the convex hull is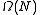 , since this time is required for a mere reporting of the output. This lower bound is attainable, because several general-purpose convex hull algorithms run in linear time when input points are ordered
, since this time is required for a mere reporting of the output. This lower bound is attainable, because several general-purpose convex hull algorithms run in linear time when input points are ordered
in some way and logarithmic-time methods for dynamic maintenance of ordered data are well-known.
This problem may be overcome by eliminating the restriction on the output representation. There are data structures that can maintain representations of the convex hull in an amount of time per update that is much smaller than linear. For many years the best algorithm of this type was that of Overmars and van Leeuwen (1981), which took time O(log2 n) per update, but it has since been improved by Timothy M. Chan
and others.
In a number of applications finding the convex hull is a step in an algorithm for the solution of the overall problem. The selected representation of the convex hull may influence on the computational complexity of further operations of the overall algorithm. For example, the point in polygon
query for a convex polygon represented by the ordered set of its vertices may be answered in logarithmic time, which would be impossible for convex hulls reported by the set of it vertices without any additional information. Therefore some research of dynamic convex hull algorithms involves the computational complexity of various geometric search problems with convex hulls stored in specific kinds of data structures. The mentioned approach of Overmars and van Leeuwen allows for logarithmic complexity of various common queries.
Dynamic problem (algorithms)
Dynamic problems in computational complexity theory are problems stated in terms of the changing input data. In the most general form a problem in this category is usually stated as follows:...
s in computational geometry
Computational geometry
Computational geometry is a branch of computer science devoted to the study of algorithms which can be stated in terms of geometry. Some purely geometrical problems arise out of the study of computational geometric algorithms, and such problems are also considered to be part of computational...
. The problem consists in the maintenance, i.e., keeping track, of the convex hull
Convex hull
In mathematics, the convex hull or convex envelope for a set of points X in a real vector space V is the minimal convex set containing X....
for the dynamically changing input data, i.e., when input data elements may be inserted, deleted, or modified. Problems of this class may be distinguished by the types of the input data and the allowed types of modification of the input data.
Planar point set
It is easy to construct an example for which the convex hull contains all input points, but after the insertion of a single point the convex hull becomes a triangle. And conversely, the deletion of a single point may produce the opposite drastic change of the size of the output. Therefore if the convex hull is required to be reported in traditional way as a polygon, the lower bound for the worst-case computational complexityComputational Complexity
Computational Complexity may refer to:*Computational complexity theory*Computational Complexity...
of the recomputation of the convex hull is
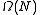 , since this time is required for a mere reporting of the output. This lower bound is attainable, because several general-purpose convex hull algorithms run in linear time when input points are ordered
, since this time is required for a mere reporting of the output. This lower bound is attainable, because several general-purpose convex hull algorithms run in linear time when input points are orderedSorting
Sorting is any process of arranging items in some sequence and/or in different sets, and accordingly, it has two common, yet distinct meanings:# ordering: arranging items of the same kind, class, nature, etc...
in some way and logarithmic-time methods for dynamic maintenance of ordered data are well-known.
This problem may be overcome by eliminating the restriction on the output representation. There are data structures that can maintain representations of the convex hull in an amount of time per update that is much smaller than linear. For many years the best algorithm of this type was that of Overmars and van Leeuwen (1981), which took time O(log2 n) per update, but it has since been improved by Timothy M. Chan
Timothy M. Chan
Timothy Moon-Yew Chan is Professor and University Research Chairin the David R. Cheriton School of Computer Science, University of Waterloo, Canada.He graduated with BA from Rice University in 1992, and completed his Ph.D...
and others.
In a number of applications finding the convex hull is a step in an algorithm for the solution of the overall problem. The selected representation of the convex hull may influence on the computational complexity of further operations of the overall algorithm. For example, the point in polygon
Point in polygon
In computational geometry, the point-in-polygon problem asks whether a given point in the plane lies inside, outside, or on the boundary of a polygon...
query for a convex polygon represented by the ordered set of its vertices may be answered in logarithmic time, which would be impossible for convex hulls reported by the set of it vertices without any additional information. Therefore some research of dynamic convex hull algorithms involves the computational complexity of various geometric search problems with convex hulls stored in specific kinds of data structures. The mentioned approach of Overmars and van Leeuwen allows for logarithmic complexity of various common queries.

