
Dynamic lot size model
Encyclopedia
In inventory theory
the Dynamic lot size model is a generalization of the economic order quantity
model that takes into account that demand for the product varies over time. The model was introduced by H.M. Wagner and T.H. Whitin in 1958.
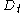 over a relevant time horizon (for example we might know how many widgets will be needed each week for the next 52 weeks). There is a setup cost
over a relevant time horizon (for example we might know how many widgets will be needed each week for the next 52 weeks). There is a setup cost 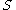 incurred for each order and there is an inventory holding cost
incurred for each order and there is an inventory holding cost 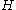 per item per period (S and H can also vary with time if desired). The problem is how many units to order now to minimize the sum of setup cost and inventory cost.
per item per period (S and H can also vary with time if desired). The problem is how many units to order now to minimize the sum of setup cost and inventory cost.
Wagner and Whitin gave an algorithm for finding the optimal solution by dynamic programming
. Because this method was perceived by some as too complex, a number of authors also developed approximate heuristics for the problem.
Inventory theory
Inventory theory is the sub-specialty within operations research that is concerned with the design of production/inventory systems to minimize costs...
the Dynamic lot size model is a generalization of the economic order quantity
Economic order quantity
Economic order quantity is the level of inventory that minimizes total inventory holding costs and ordering costs. It is one of the oldest classical production scheduling models. The framework used to determine this order quantity is also known as Wilson EOQ Model or Wilson Formula. The model was...
model that takes into account that demand for the product varies over time. The model was introduced by H.M. Wagner and T.H. Whitin in 1958.
Problem setup
We have available a forecast of product demand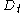 over a relevant time horizon (for example we might know how many widgets will be needed each week for the next 52 weeks). There is a setup cost
over a relevant time horizon (for example we might know how many widgets will be needed each week for the next 52 weeks). There is a setup cost 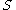 incurred for each order and there is an inventory holding cost
incurred for each order and there is an inventory holding cost 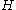 per item per period (S and H can also vary with time if desired). The problem is how many units to order now to minimize the sum of setup cost and inventory cost.
per item per period (S and H can also vary with time if desired). The problem is how many units to order now to minimize the sum of setup cost and inventory cost.Wagner and Whitin gave an algorithm for finding the optimal solution by dynamic programming
Dynamic programming
In mathematics and computer science, dynamic programming is a method for solving complex problems by breaking them down into simpler subproblems. It is applicable to problems exhibiting the properties of overlapping subproblems which are only slightly smaller and optimal substructure...
. Because this method was perceived by some as too complex, a number of authors also developed approximate heuristics for the problem.

