
EMule
Encyclopedia
eMule is a free
peer-to-peer file sharing
application for Microsoft Windows
. Started in May 2002 as an alternative to eDonkey2000
, eMule now connects to both the eDonkey network
and the Kad network
. The distinguishing features of eMule are the direct exchange of sources between client nodes, fast recovery of corrupted downloads, and the use of a credit system to reward frequent uploaders. Furthermore, eMule transmits data in zlib
-compressed form to save bandwidth.
eMule is coded in C++
using the Microsoft Foundation Classes. Since July 2002 eMule has been free software
, released under the GNU General Public License
; its popularity has led to eMule's codebase being used as the basis of cross-platform
clients aMule
, JMule
, xMule
, along with the release of many eMule mods (modifications of the original eMule) on the Internet.
As of December 2011, it is the most popular download on SourceForge
, with over 620 million downloads.
client. Over time more developers joined the effort. The source was first released at version 0.02 and published on SourceForge
on July 6, 2002.
eMule was first released as a binary on August 4, 2002 at version 0.05a. The 'Credit System' was implemented for the first time on September 14, 2002 in version 0.19a. The eMule project website started up on December 8, 2002.
Current versions (v0.40+) of eMule have added support for the Kad network
. This network has an implementation of the Kademlia
protocol, which does not rely on central servers as the eDonkey network
does, but is an implementation of a distributed hash table
.
Also added in recent versions were the ability to search using unicode
, allowing for searches for files in non-Latin alphabets, and the ability to search servers for files with complete sources of unfinished files on the eDonkey network
.
In new versions, a "Bad source list" was added. The application adds an IP address
to this list after one unsuccessful connection. After adding an IP to the "Bad source list", the application treats this IP as a "dead" IP. Unavailable IPs are banned for a time period from 15 to 45 minutes. Some users have complained that it leads to a loss of active sources and subsequently slows download speed.
Other recent additions include: the ability to run eMule from a user account with limited privileges (thus enhancing security), and Intelligent Corruption Handling (so that a corrupted chunk does not need to be re-downloaded entirely).
The 0.46b version added the creation and management of "eMule collection" files, which contain a set of links to files intended to be downloaded as a set.
From 2007, many ISPs have used bandwidth throttling
for usual P2P ports, resulting in slow performances. The 0.47b version adds protocol obfuscation and eMule will automatically select two port numbers at random in the startup wizard.
Although the nomenclature suggests that eMule is still in beta phase (version numbers below 1), it is now considered a stable product, and new versions are not released as often as they used to be; five to six months is now a typical time interval between releases.
as a hash list
comprising separate 9500 kilobyte chunks using the MD4
algorithm. The top-level MD4 hash, file size, filename, and several secondary search attributes such as bit rate and codec are stored on eD2k servers and the serverless Kad network
.
Users can search for filenames in the servers/kad and are presented with the filenames and the unique identifier consisting of the top-level MD4 hash for the file and the file's size that can be added to their downloads. The client then asks the servers where the other clients are using that hash. The servers return a set of IP/ports that indicate the locations of the clients that share the file.
eMule then asks the peers for the file. eMule will then be queued until an upload slot becomes available.
When a complete chunk of 9,728,000 bytes (9500 KiB) is downloaded and verified this data is also shared by the downloader, helping others to download the file as well.
It is also possible that a client knows other clients that are also sharing that same file. In that case a source exchange between the clients is made. This exchange of known peers is done directly between the peers.
Newer versions of eMule support AICH
- Advanced Intelligent Corruption Handling. It is meant to make eMule's corruption handling competitive with BitTorrent. SHA-1 hashes are computed for each 180kb sub-chunk and a whole SHA-1 hash tree
is formed. AICH is processed purely with peer-to-peer source exchanges. eMule requires 10 agreeing peers regarding the SHA-1 hash, so rare files generally do not benefit from AICH.
, behind a NAT
device that has not been correctly port forwarded, or whose IP address ends with a zero (e.g. 123.45.67.0) get a "Low ID" from the servers. They are still able to upload and download but need the help of servers or other kad
clients to be reached by other clients. Since they cannot be notified that they are in front of an upload queue, they have to poll
peers if an upload slot is available. Since they cannot connect to any other Low ID clients, they see only 40%-60% of the clients that a High ID can see. Their IP
/ports are not exchanged between other peers, limiting their possibilities for finding sources via eMule's pure-P2P source exchange.
A Low ID client also consumes a lot more data on an eserver than a High ID client due to the lowidcallbacks. Also, a releaser or heavy uploader that uses a releaser mod such as MorphXT or Xtreme that is forced to operate on a Low ID (hotel room, job) also will find that he will have little control over his upload priorities (especially powershares) as the servers appear to limit their connection-forwarding for each client, thus turning his upload queue to a contention situation where the first to be able to get forwarding and find an open slot gets it.
All Clients uploading to you are rewarded by the credit system. It does not matter if the client supports the credit system or not. Non-supporting clients will grant you no credits when you upload to them. Credits are stored in the clients.met file. The unique user hash is used to identify the client. Your own credits are saved by the client who owes you the credit. This prevents faking the credits. Your own credits cannot be displayed.
The computation formula for the Official Credit System is composed of two ratios as follows:

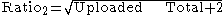
Both ratios are then compared and the lower one is used as the modifier. A few conditions exist:
An exception to this rule applies only when a peer is assigned a "Friend Slot" after being added to the client's Friends list. This automatically assigns a reserved upload slot for that peer so that he/she can begin downloading regardless of the Credit rating. Only one Friend Slot can be reserved so as to prevent any form of abuse such as upload discrimination.
. eMule supports AICH, making its corruption handling competitive with BitTorrent. eMule also supports source exchanges, allowing it to substantially reduce the loads on the servers and Kad. With a High ID and well-sourced downloads pre-acquired by server and/or Kad, eMule is able to sustain the peer sources on these files independent longer after disconnection from eD2k and Kad.
. Since eMule Plus forked off before the release of v0.30, the first official version to include Kad, eMule Plus does not support this feature. Other mods follow official eMule releases and make their own releases based on each new release of the official version. Since distributed mods are required to publicly share their source code by the GNU General Public License, useful features created by mod developers can be quickly incorporated into an official version. Among the eMule mods, MorphXT
began in january 2003 and is considered to be one of the earliest, and Xtreme
is one of the most popular.
nature of eMule, some third-parties have created modified versions of it, which frequently contain spyware
and other malware
programs. Some fake sites ask for credit card information or require you to sign up for a paid membership. The official e-mule is free.
These versions are usually found via rotating advertisements sometimes placed on legitimate sites.
or eMule) and the site emule.org.cn, which is named "Dianlv (eMule) Chinese Site" (电驴(eMule)中文网站).
Free software
Free software, software libre or libre software is software that can be used, studied, and modified without restriction, and which can be copied and redistributed in modified or unmodified form either without restriction, or with restrictions that only ensure that further recipients can also do...
peer-to-peer file sharing
Peer-to-peer file sharing
P2P or Peer-to-peer file sharing allows users to download files such as music, movies, and games using a P2P software client that searches for other connected computers. The "peers" are computer systems connected to each other through internet. Thus, the only requirements for a computer to join...
application for Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
. Started in May 2002 as an alternative to eDonkey2000
EDonkey2000
eDonkey2000 was a peer-to-peer file sharing application developed by US company MetaMachine, using the Multisource File Transfer Protocol...
, eMule now connects to both the eDonkey network
EDonkey network
The eDonkey network is a decentralized, mostly server-based, peer-to-peer file sharing network best suited to share big files among users, and to provide long term availability of files...
and the Kad network
Kad Network
The Kad network is a peer-to-peer network which implements the Kademlia P2P overlay protocol. The majority of users on the Kad Network are also connected to servers on the eDonkey network, and Kad Network clients typically query known nodes on the eDonkey network in order to find an initial node...
. The distinguishing features of eMule are the direct exchange of sources between client nodes, fast recovery of corrupted downloads, and the use of a credit system to reward frequent uploaders. Furthermore, eMule transmits data in zlib
Zlib
zlib is a software library used for data compression. zlib was written by Jean-Loup Gailly and Mark Adler and is an abstraction of the DEFLATE compression algorithm used in their gzip file compression program. Zlib is also a crucial component of many software platforms including Linux, Mac OS X,...
-compressed form to save bandwidth.
eMule is coded in C++
C++
C++ is a statically typed, free-form, multi-paradigm, compiled, general-purpose programming language. It is regarded as an intermediate-level language, as it comprises a combination of both high-level and low-level language features. It was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup starting in 1979 at Bell...
using the Microsoft Foundation Classes. Since July 2002 eMule has been free software
Free software
Free software, software libre or libre software is software that can be used, studied, and modified without restriction, and which can be copied and redistributed in modified or unmodified form either without restriction, or with restrictions that only ensure that further recipients can also do...
, released under the GNU General Public License
GNU General Public License
The GNU General Public License is the most widely used free software license, originally written by Richard Stallman for the GNU Project....
; its popularity has led to eMule's codebase being used as the basis of cross-platform
Cross-platform
In computing, cross-platform, or multi-platform, is an attribute conferred to computer software or computing methods and concepts that are implemented and inter-operate on multiple computer platforms...
clients aMule
AMule
aMule is a free peer-to-peer file sharing application that works with the EDonkey network and the Kad Network, offering similar features to eMule and adding others such as GeoIP . It was forked from the xMule source code on August 18, 2003, which itself is a fork of the lMule project, which was the...
, JMule
JMule
JMule is an open source file sharing client written in Java for eDonkey2000 networks. JMule is released under the terms of the GNU General Public License, it is based on Java platform and requires at least Java SE 6.0 for operation. At a more general level this is a project that try to accomplish...
, xMule
XMule
xMule — the X11 Mule — is a client for the eDonkey peer-to-peer file sharing network, originally intended to bring it to virtually all the major Unix platforms, with a particular emphasis on Linux...
, along with the release of many eMule mods (modifications of the original eMule) on the Internet.
As of December 2011, it is the most popular download on SourceForge
SourceForge
SourceForge Enterprise Edition is a collaborative revision control and software development management system. It provides a front-end to a range of software development lifecycle services and integrates with a number of free software / open source software applications .While originally itself...
, with over 620 million downloads.
History
The eMule project was started on May 13, 2002 by Hendrik Breitkreuz (also known as Merkur) who was dissatisfied with the original eDonkey2000EDonkey2000
eDonkey2000 was a peer-to-peer file sharing application developed by US company MetaMachine, using the Multisource File Transfer Protocol...
client. Over time more developers joined the effort. The source was first released at version 0.02 and published on SourceForge
SourceForge
SourceForge Enterprise Edition is a collaborative revision control and software development management system. It provides a front-end to a range of software development lifecycle services and integrates with a number of free software / open source software applications .While originally itself...
on July 6, 2002.
eMule was first released as a binary on August 4, 2002 at version 0.05a. The 'Credit System' was implemented for the first time on September 14, 2002 in version 0.19a. The eMule project website started up on December 8, 2002.
Current versions (v0.40+) of eMule have added support for the Kad network
Kad Network
The Kad network is a peer-to-peer network which implements the Kademlia P2P overlay protocol. The majority of users on the Kad Network are also connected to servers on the eDonkey network, and Kad Network clients typically query known nodes on the eDonkey network in order to find an initial node...
. This network has an implementation of the Kademlia
Kademlia
Kademlia is a distributed hash table for decentralized peer-to-peer computer networks designed by Petar Maymounkov and David Mazières in 2002. It specifies the structure of the network and the exchange of information through node lookups. Kademlia nodes communicate among themselves using UDP. A...
protocol, which does not rely on central servers as the eDonkey network
EDonkey network
The eDonkey network is a decentralized, mostly server-based, peer-to-peer file sharing network best suited to share big files among users, and to provide long term availability of files...
does, but is an implementation of a distributed hash table
Distributed hash table
A distributed hash table is a class of a decentralized distributed system that provides a lookup service similar to a hash table; pairs are stored in a DHT, and any participating node can efficiently retrieve the value associated with a given key...
.
Also added in recent versions were the ability to search using unicode
Unicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
, allowing for searches for files in non-Latin alphabets, and the ability to search servers for files with complete sources of unfinished files on the eDonkey network
EDonkey network
The eDonkey network is a decentralized, mostly server-based, peer-to-peer file sharing network best suited to share big files among users, and to provide long term availability of files...
.
In new versions, a "Bad source list" was added. The application adds an IP address
IP address
An Internet Protocol address is a numerical label assigned to each device participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing...
to this list after one unsuccessful connection. After adding an IP to the "Bad source list", the application treats this IP as a "dead" IP. Unavailable IPs are banned for a time period from 15 to 45 minutes. Some users have complained that it leads to a loss of active sources and subsequently slows download speed.
Other recent additions include: the ability to run eMule from a user account with limited privileges (thus enhancing security), and Intelligent Corruption Handling (so that a corrupted chunk does not need to be re-downloaded entirely).
The 0.46b version added the creation and management of "eMule collection" files, which contain a set of links to files intended to be downloaded as a set.
From 2007, many ISPs have used bandwidth throttling
Bandwidth throttling
Bandwidth throttling is a reactive measure employed in communication networks to regulate network traffic and minimize bandwidth congestion. Bandwidth throttling can occur at different locations on the network. On a local area network , a sysadmin may employ bandwidth throttling to help limit...
for usual P2P ports, resulting in slow performances. The 0.47b version adds protocol obfuscation and eMule will automatically select two port numbers at random in the startup wizard.
Although the nomenclature suggests that eMule is still in beta phase (version numbers below 1), it is now considered a stable product, and new versions are not released as often as they used to be; five to six months is now a typical time interval between releases.
Basic concepts
Each file that is shared using eMule is hashedHash function
A hash function is any algorithm or subroutine that maps large data sets to smaller data sets, called keys. For example, a single integer can serve as an index to an array...
as a hash list
Hash list
In computer science, a hash list is typically a list of hashes of the data blocks in a file or set of files. Lists of hashes are used for many different purposes, such as fast table lookup and distributed databases...
comprising separate 9500 kilobyte chunks using the MD4
MD4
The MD4 Message-Digest Algorithm is a cryptographic hash function developed by Ronald Rivest in 1990. The digest length is 128 bits. The algorithm has influenced later designs, such as the MD5, SHA-1 and RIPEMD algorithms....
algorithm. The top-level MD4 hash, file size, filename, and several secondary search attributes such as bit rate and codec are stored on eD2k servers and the serverless Kad network
Kad Network
The Kad network is a peer-to-peer network which implements the Kademlia P2P overlay protocol. The majority of users on the Kad Network are also connected to servers on the eDonkey network, and Kad Network clients typically query known nodes on the eDonkey network in order to find an initial node...
.
Users can search for filenames in the servers/kad and are presented with the filenames and the unique identifier consisting of the top-level MD4 hash for the file and the file's size that can be added to their downloads. The client then asks the servers where the other clients are using that hash. The servers return a set of IP/ports that indicate the locations of the clients that share the file.
eMule then asks the peers for the file. eMule will then be queued until an upload slot becomes available.
When a complete chunk of 9,728,000 bytes (9500 KiB) is downloaded and verified this data is also shared by the downloader, helping others to download the file as well.
It is also possible that a client knows other clients that are also sharing that same file. In that case a source exchange between the clients is made. This exchange of known peers is done directly between the peers.
Newer versions of eMule support AICH
Aich
Aich may refer to:* AICH, Advanced Intelligent Corruption Handling, a corruption handling method used in eMule* Aich's Alloy, a type of brass* Aitch , a Bengali surname- See also :* Eich * Aicher* Aichinger...
- Advanced Intelligent Corruption Handling. It is meant to make eMule's corruption handling competitive with BitTorrent. SHA-1 hashes are computed for each 180kb sub-chunk and a whole SHA-1 hash tree
Hash tree
In cryptography and computer science Hash trees or Merkle trees are a type of data structure which contains a tree of summary information about a larger piece of data – for instance a file – used to verify its contents. Hash trees are a combination of hash lists and hash chaining, which in turn are...
is formed. AICH is processed purely with peer-to-peer source exchanges. eMule requires 10 agreeing peers regarding the SHA-1 hash, so rare files generally do not benefit from AICH.
Low ID
Users who cannot be reached from the outside because they are firewalledPersonal firewall
A personal firewall is an application which controls network traffic to and from a computer, permitting or denying communications based on a security policy. Typically it works as an application layer firewall....
, behind a NAT
Network address translation
In computer networking, network address translation is the process of modifying IP address information in IP packet headers while in transit across a traffic routing device....
device that has not been correctly port forwarded, or whose IP address ends with a zero (e.g. 123.45.67.0) get a "Low ID" from the servers. They are still able to upload and download but need the help of servers or other kad
Kad Network
The Kad network is a peer-to-peer network which implements the Kademlia P2P overlay protocol. The majority of users on the Kad Network are also connected to servers on the eDonkey network, and Kad Network clients typically query known nodes on the eDonkey network in order to find an initial node...
clients to be reached by other clients. Since they cannot be notified that they are in front of an upload queue, they have to poll
Busy waiting
In software engineering, busy-waiting or spinning is a technique in which a process repeatedly checks to see if a condition is true, such as whether keyboard input is available, or if a lock is available. Spinning can also be used to generate an arbitrary time delay, a technique that was necessary...
peers if an upload slot is available. Since they cannot connect to any other Low ID clients, they see only 40%-60% of the clients that a High ID can see. Their IP
IP address
An Internet Protocol address is a numerical label assigned to each device participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing...
/ports are not exchanged between other peers, limiting their possibilities for finding sources via eMule's pure-P2P source exchange.
A Low ID client also consumes a lot more data on an eserver than a High ID client due to the lowidcallbacks. Also, a releaser or heavy uploader that uses a releaser mod such as MorphXT or Xtreme that is forced to operate on a Low ID (hotel room, job) also will find that he will have little control over his upload priorities (especially powershares) as the servers appear to limit their connection-forwarding for each client, thus turning his upload queue to a contention situation where the first to be able to get forwarding and find an open slot gets it.
Credit system
Credits are not global; they are exchanged between two specific clients. The credit system is used to reward users contributing to the network, i.e. uploading to other clients. The strict queue system in eMule is based on the waiting time a user has spent in the queue. The credit system provides a major modifier to this waiting time by taking the upload and download between the two clients into consideration. The more a user uploads to a client the faster he advances in this client's queue. The modifiers are calculated from the amount of transferred data between the two clients. The values used can be seen in the client's details dialog. To view this information, right-click on any user and choose View Details.All Clients uploading to you are rewarded by the credit system. It does not matter if the client supports the credit system or not. Non-supporting clients will grant you no credits when you upload to them. Credits are stored in the clients.met file. The unique user hash is used to identify the client. Your own credits are saved by the client who owes you the credit. This prevents faking the credits. Your own credits cannot be displayed.
The computation formula for the Official Credit System is composed of two ratios as follows:

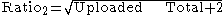
Both ratios are then compared and the lower one is used as the modifier. A few conditions exist:
- If the Uploaded Total is less than 1 MB, then the modifier will remain at 1.
- If the client uploads data but doesn't download any, the modifier will be fixed at 10.
- The modifier can only be between 1 and 10.
An exception to this rule applies only when a peer is assigned a "Friend Slot" after being added to the client's Friends list. This automatically assigns a reserved upload slot for that peer so that he/she can begin downloading regardless of the Credit rating. Only one Friend Slot can be reserved so as to prevent any form of abuse such as upload discrimination.
eMule compared to other P2P applications
One of the advantages of eMule is its large user base, currently averaging 3 to 4 million people, which share some 4 billion files, which makes it excellent for finding rare content. It is said to be the most complete implementation of the eD2k protocol and its extensions. However the transfer speed is generally slower than BitTorrent, although faster than anonymous networksAnonymous P2P
An anonymous P2P communication system is a peer-to-peer distributed application in which the nodes or participants are anonymous or pseudonymous...
. eMule supports AICH, making its corruption handling competitive with BitTorrent. eMule also supports source exchanges, allowing it to substantially reduce the loads on the servers and Kad. With a High ID and well-sourced downloads pre-acquired by server and/or Kad, eMule is able to sustain the peer sources on these files independent longer after disconnection from eD2k and Kad.
eMule mods
As a popular open source program, eMule has many variants, usually called mods. Some mods started as forks from official eMule versions, and then continued to develop independently rather than modifying newer official versions. An example of this type of mod is eMule PlusEMule Plus
eMule Plus is an open source eMule P2P compatible client created to improve its abilities and features, in both work efficiency and GUI.-Enhancements over eMule:* A modified GUI* Releaser Support eMule Plus is an open source eMule P2P compatible client created to improve its abilities and features,...
. Since eMule Plus forked off before the release of v0.30, the first official version to include Kad, eMule Plus does not support this feature. Other mods follow official eMule releases and make their own releases based on each new release of the official version. Since distributed mods are required to publicly share their source code by the GNU General Public License, useful features created by mod developers can be quickly incorporated into an official version. Among the eMule mods, MorphXT
MorphXT
eMule MorphXT is a peer-to-peer file sharing application for Microsoft Windows released under the GNU General Public License , as is its parent software eMule.eMule connects to both the eDonkey network and the Kad network...
began in january 2003 and is considered to be one of the earliest, and Xtreme
Xtreme Mod
eMule Xtreme Mod is a free peer-to-peer file sharing application for Microsoft Windows based on eMule, released under the GNU General Public License, coded in Microsoft Visual C++. It connects to the eDonkey network and the Kad network...
is one of the most popular.
Fake eMule sites and malware
Due to the popularity and open sourceOpen source
The term open source describes practices in production and development that promote access to the end product's source materials. Some consider open source a philosophy, others consider it a pragmatic methodology...
nature of eMule, some third-parties have created modified versions of it, which frequently contain spyware
Spyware
Spyware is a type of malware that can be installed on computers, and which collects small pieces of information about users without their knowledge. The presence of spyware is typically hidden from the user, and can be difficult to detect. Typically, spyware is secretly installed on the user's...
and other malware
Malware
Malware, short for malicious software, consists of programming that is designed to disrupt or deny operation, gather information that leads to loss of privacy or exploitation, or gain unauthorized access to system resources, or that otherwise exhibits abusive behavior...
programs. Some fake sites ask for credit card information or require you to sign up for a paid membership. The official e-mule is free.
These versions are usually found via rotating advertisements sometimes placed on legitimate sites.
Chinese mods of eMule client
VeryCD's easyMule is a popular eMule client among Chinese users. It has a simplified interface and lacks some advanced settings available in the standard eMule client. As of version 1.1 it only supports searching through the VeryCD database, though external eD2k links are accepted. Some criticized VeryCD for their misleading name "Dianlv" ' onMouseout='HidePop("2174")' href="/topics/EDonkey">eDonkeyEDonkey
eDonkey may refer to:* eDonkey network , a popular file sharing network** eDonkey2000, a discontinued file sharing program that used the eDonkey network...
or eMule) and the site emule.org.cn, which is named "Dianlv (eMule) Chinese Site" (电驴(eMule)中文网站).
See also
- eDonkey networkEDonkey networkThe eDonkey network is a decentralized, mostly server-based, peer-to-peer file sharing network best suited to share big files among users, and to provide long term availability of files...
- Kad networkKad NetworkThe Kad network is a peer-to-peer network which implements the Kademlia P2P overlay protocol. The majority of users on the Kad Network are also connected to servers on the eDonkey network, and Kad Network clients typically query known nodes on the eDonkey network in order to find an initial node...
- Comparison of eDonkey softwareComparison of eDonkey softwareThe following tables compare general and technical information for a number of available applications supporting the eDonkey network.- General :- Features :...
- Comparison of file sharing applicationsComparison of file sharing applicationsFile sharing is a method of distributing electronically stored information such as computer programs and digital media. Below is a list of file sharing applications....
External links
- eMule Protocol Specification by Danny Bickson and Yoram Kulbak from Hebrew University of JerusalemHebrew University of JerusalemThe Hebrew University of Jerusalem ; ; abbreviated HUJI) is Israel's second-oldest university, after the Technion – Israel Institute of Technology. The Hebrew University has three campuses in Jerusalem and one in Rehovot. The world's largest Jewish studies library is located on its Edmond J...
- Glasnost test eMule traffic shapingTraffic shapingTraffic shaping is the control of computer network traffic in order to optimize or guarantee performance, improve latency, and/or increase usable bandwidth for some kinds of packets by delaying other kinds of packets that meet certain criteria...
(Max Planck Institute for Software SystemsMax Planck Institute for Software SystemsThe Max Planck Institute for Software Systems is a computer science research institute co-located in Saarbrücken and Kaiserslautern, Germany. The institute is chartered to conduct basic research in all areas related to the design, analysis, modeling, implementation and evaluation of complex...
)

