
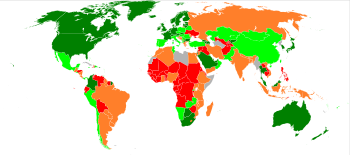
Ease of Doing Business Index
Encyclopedia
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for capital programmes.The World Bank's official goal is the reduction of poverty...
. Higher rankings indicate better, usually simpler, regulations for businesses and stronger protections of property rights. Empirical research funded by the World Bank to justify their work show that the effect of improving these regulations on economic growth is strong.
"Empirical research is needed to establish the optimal level of business regulation—for example, what the duration of court procedures should be and what the optimal degree of social protection is. The indicators compiled in the Doing Business project allow such research to take place. Since the start of the project in November 2001, more than 800 academic papers have used one or more indicators constructed in Doing Business and the related background papers by its authors."
Methodology
The index is based on the study of laws and regulations, with the input and verification by more than 8,000 government officials, lawyers, business consultants, accountants and other professionals in 183 economies who routinely advise on or administer legal and regulatory requirements.The Ease of Doing Business index is meant to measure regulations directly affecting businesses and does not directly measure more general conditions such as a nation's proximity to large markets, quality of infrastructure
Infrastructure
Infrastructure is basic physical and organizational structures needed for the operation of a society or enterprise, or the services and facilities necessary for an economy to function...
, inflation
Inflation
In economics, inflation is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation also reflects an erosion in the purchasing power of money – a...
, or crime
Crime
Crime is the breach of rules or laws for which some governing authority can ultimately prescribe a conviction...
. A nation's ranking on the index is based on the average of 10 subindices:
- Starting a BusinessStarting a Business IndexThe Starting a Business Index is a sub-index of the World Bank Ease of Doing Business Index.- Authors of the methodology :This methodology was developed by Simeon Djankov, Rafael La Porta, Florencio Lopez-De-Silanes and Andrei Shleifer in a paper The Regulation of Entry.- Ranking :Ranking of all...
- Procedures, time, cost and minimum capital to open a new business - Dealing with construction permits - Procedures, time and cost to build a warehouse
- Employing workers - Difficulty of hiring index, rigidity of hours of index, difficulty of redundancy index, rigidity of employment index, redundancy costs
- Registering property - Procedures, time and cost to register commercial real estate
- Getting credit - Strength of legal rights index, depth of credit information index
- Protecting investors - Indices on the extent of disclosure, extent of director liability and ease of shareholder suits
- Paying taxes - Number of taxes paid, hours per year spent preparing tax returns and total tax payable as share of gross profit
- Trading across borders - Number of documents, cost and time necessary to export and import
- Enforcing contracts - Procedures, time and cost to enforce a debt contract
- Closing a business - Index of recovery rate which is a function of time, cost and other factors such as lending rate and the likelihood of the company continuing to operate
For example, according to the Doing Business 2010 report, Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
ranked third on the first subindex "Starting a business" behind only New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
and Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
. In Australia there are 2 procedures required to start a business which take on average 2 days to complete. The official cost is 0.8% of the Gross National Income
Gross National Income
The GNI consists of: the personal consumption expenditures, the gross private investment, the government consumption expenditures, the net income from assets abroad , and the gross exports of goods and services, after deducting two components: the gross imports of goods and services, and the...
per capita
Per capita
Per capita is a Latin prepositional phrase: per and capita . The phrase thus means "by heads" or "for each head", i.e. per individual or per person...
. There is no minimum capital requirement. By contrast, in Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau
The Republic of Guinea-Bissau is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Senegal to the north, and Guinea to the south and east, with the Atlantic Ocean to its west....
which ranked among the worst (183rd out of 183) on this same subindex, there are 16 procedures required to start a business taking 213 days to complete. The official cost is 323.0% of the gross national income per capita. A minimum capital investment of 1006.6% of the gross national income per capita is required.
While fewer and simpler regulations often imply higher rankings, this is not always the case. Protecting the rights of creditors and investors, as well as establishing or upgrading property and credit registries, may mean that more regulation is needed.
Research and influence
More than 800 academic papers have used data from the index. The effect of improving regulations on economic growth is claimed to be very strong. Moving from the worst one-fourth of nations to the best one-fourth implies a 2.3 percentage point increase in annual growth.The various subcomponents of the index in themselves provide concrete suggestions for improvement. Many of them may be relatively easy to implement and uncontroversial (except perhaps among corrupt
Political corruption
Political corruption is the use of legislated powers by government officials for illegitimate private gain. Misuse of government power for other purposes, such as repression of political opponents and general police brutality, is not considered political corruption. Neither are illegal acts by...
officials who may gain from onerous regulations requiring bribes to bypass). As such, the index has influenced many nations to improve their regulations. Several have explicitly targeted to reach a minimum position on the index, for example the top 25 list. Between June 2008 and May 2009, Doing Business recorded 287 reforms in 131 economies, 20% more than in the year before. The 10 top reformers were Rwanda, Kyrgyz Republic, Macedonia (FYROM), Belarus, United Arab Emirates, Moldova, Colombia, Tajikistan, Egypt, Arab Rep.and Liberia.
The correlations between the subindices are low, which suggest that countries rarely score universally well or universally badly on the indicators. In other words, there is usually much room for partial reform even in the best ranking nations.
The annual Reformers' Club event brings together individuals from top reformer countries who have been instrumental in initiating and implementing business environment reform. These reformers are acknowledged for their success in improving the ease of doing business in their country. Presentations and case studies are available online.
Somewhat similar annual reports are the Indices of Economic Freedom
Indices of Economic Freedom
The annual survey Economic Freedom of the World is an indicator produced by the Fraser Institute, a Canadian think tank which attempts to measure the degree of economic freedom in the world's nations. This indicator has been used in peer-reviewed studies some of which have found a range of...
and the Global Competitiveness Report
Global Competitiveness Report
The Global Competitiveness Report is a yearly report published by the World Economic Forum. The first report was released in 1979. The 2011–2012 report covers 142 major and emerging economies....
. They, especially the later, look at many more factors that affect economic growth, like inflation and infrastructure. These factors may however be more subjective and diffuse since many are measured using surveys and they may be more difficult to change quickly compared to regulations.
According to some critics, however, some of the research lacks the rigor of a coherent economic theory, contains unstated ideological biases, and too much of it is undertaken by individuals closely associated with the index and reforms, so it is not sufficiently independent to be fully credible. This blanket criticism is often offered by those with their own ideological bias.
Criticism
The Doing Business methodology regarding labor regulations has been criticized because of the support for flexible employment regulations. For instance, the easier it is to dismiss a worker for economic reasons in a country, the more one goes up in the rankings. The Employing Workers index was revised in Doing Business 2008 to be in full compliance with the 188 International Labour OrganizationInternational Labour Organization
The International Labour Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that deals with labour issues pertaining to international labour standards. Its headquarters are in Geneva, Switzerland. Its secretariat — the people who are employed by it throughout the world — is known as the...
conventions. A country can have all ILO conventions ratified and still rank #1 on the Ease of Employing Workers. As a further step, according to the Report 2010, Doing business plans to develop a new worker protection indicator, a process that will benefit from the advice of a working group with broad stakeholder representation. The ILO, which has leadership on the core labor standards, will serve as an essential source of guidance in this process.
In 2008 the World Bank Group's Independent Evaluation Group, a semi-independent watchdog within the World Bank Group, published an evaluation of the Doing Business index. The report, titled Doing Business: An Independent Evaluation, contained both praise and criticism of Doing Business. The report recommended that Doing Business be clearer about what is and is not measured, disclose changes to published data, recruit more informants, and simplify the Paying Taxes indicator.
In April 2009 the World Bank issued a note with revisions to the Employing Workers index. The note explained that scoring for the Employing Workers indicator would be updated in Doing Business 2010 to give favorable scores for complying with relevant ILO conventions. The Employing Workers indicator was also removed as a guidepost for Country Policy and Institutional Assessments, which help determine resources provided to IDA countries.
A study commissioned by the Norwegian government alleges methodological weaknesses, an uncertainty in the ability of the indicators to capture the underlying business climate, and a general worry that many countries may find it easier to change their ranking in Doing Business than to change the underlying business environment.
Ranking
The most recent rankings come from the "Doing Business 2012" report.Singapore topped the ranking on Ease of Doing Business for the sixth year. Based on Singapore's experience, IDA International
IDA International
IDA International is a wholly owned privatised subsidiary of the Infocomm Development Authority of Singapore. Singapore is recognised worldwide as a leader in the use of infocomm to deliver better services to the public and businesses...
is collaborating with public agencies in several countries in the areas such as ICT strategy, national infocomm planning and solutions implementation that can help increase the ease of doing business.
| 2012 Rank | 2011 Rank | 2010 Rank | 2009 Rank | Country/Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |  Singapore Singapore |
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |  Hong Kong Hong Kong |
| 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |  New Zealand New Zealand |
| 4 | 5 | 4 | 4 |  United States United States |
| 5 | 6 | 6 | 5 |  Denmark Denmark |
| 6 | 8 | 10 | 10 |  Norway Norway |
| 7 | 4 | 5 | 6 |  United Kingdom United Kingdom |
| 8 | 16 | 19 | 23 |  South Korea South Korea |
| 9 | 15 | 14 | 11 |  Iceland Iceland |
| 10 | 9 | 7 | 7 |  Republic of Ireland Republic of Ireland |
| 11 | 13 | 16 | 14 |  Finland Finland |
| 12 | 11 | 13 | 15 |  Saudi Arabia Saudi Arabia |
| 13 | 7 | 8 | 8 |  Canada Canada |
| 14 | 14 | 18 | 17 |  Sweden Sweden |
| 15 | 10 | 9 | 9 |  Australia Australia |
| 16 | 12 | 13 | 16 |  Georgia (country) Georgia (country) |
| 17 | 19 | 12 | 12 |  Thailand Thailand |
| 18 | 21 | 23 | 21 |  Malaysia Malaysia |
| 19 | 22 | 25 | 27 |  Germany Germany |
| 20 | 18 | 15 | 13 |  Japan Japan |
| 21 | 24 | 27 | 29 |  Latvia Latvia |
| 22 | 38 | 32 | 69 |  Republic of Macedonia Republic of Macedonia |
| 23 | 20 | 17 | 24 |  Mauritius Mauritius |
| 24 | 17 | 24 | 22 |  Estonia Estonia |
| 25 | 33 | 46 | 61 |  Republic of China (Republic of China Republic of China (Republic of ChinaRepublic of China The Republic of China , commonly known as Taiwan , is a unitary sovereign state located in East Asia. Originally based in mainland China, the Republic of China currently governs the island of Taiwan , which forms over 99% of its current territory, as well as Penghu, Kinmen, Matsu and other minor... ) |
| 26 | 27 | 21 | 19 |  Switzerland Switzerland |
| 27 | 23 | 26 | 25 |  Lithuania Lithuania |
| 28 | 25 | 22 | 20 |  Belgium Belgium |
| 29 | 26 | 31 | 31 |  Early Modern France Early Modern France |
| 30 | 31 | 48 | 48 |  Portugal Portugal |
| 31 | 30 | 30 | 28 |  Netherlands Netherlands |
| 32 | 32 | 28 | 26 |  Austria Austria |
| 33 | 40 | 33 | 47 |  United Arab Emirates United Arab Emirates |
| 34 | 29 | 29 | 30 |  Israel Israel |
| 35 | 34 | 34 | 32 |  South Africa South Africa |
| 36 | 50 | 39 | 37 |  Qatar Qatar |
| 37 | 42 | 53 | 57 |  Slovenia Slovenia |
| 38 | 28 | 20 | 18 |  Bahrain Bahrain |
| 39 | 43 | 49 | 40 |  Chile Chile |
| 40 | 37 | 40 | 36 |  Cyprus Cyprus |
| 41 | 36 | 56 | 65 |  Peru Peru |
| 42 | 39 | 37 | 49 |  Colombia Colombia |
| 43 | 47 | 35 | 33 |  Puerto Rico Puerto Rico |
| 44 | 49 | 62 | 51 |  Spain Spain |
| 45 | 58 | 67 | 143 |  Rwanda Rwanda |
| 46 | 55 | 69 | 73 |  Tunisia Tunisia |
| 47 | 59 | 63 | 64 |  Kazakhstan Kazakhstan |
| 48 | 41 | 42 | 35 | |
| 49 | 57 | 65 | 60 |  Oman Oman |
| 50 | 45 | 64 | 53 |  Luxembourg Luxembourg |
| 51 | 46 | 47 | 41 |  Hungary Hungary |
| 52 | 53 | 36 | 34 |  Saint Lucia Saint Lucia |
| 53 | 35 | 51 | 55 |  Mexico Mexico |
| 54 | 52 | 45 | 39 |  Botswana Botswana |
| 55 | 48 | 43 | 50 |  Armenia Armenia |
| 56 | 66 | 71 | 77 |  Kingdom of Montenegro Kingdom of Montenegro |
| 57 | 64 | 50 | 44 |  Antigua and Barbuda Antigua and Barbuda |
| 58 | 71 | 52 | 46 |  Tonga Tonga |
| 59 | 51 | 44 | 42 |  Kingdom of Bulgaria Kingdom of Bulgaria |
| 60 | 61 | 57 | 68 |  Samoa Samoa |
| 61 | 72 | 77 | 83 |  Panama Panama |
| 62 | 70 | 72 | 72 |  Poland Poland |
| 63 | 67 | 92 | 87 |  Ghana Ghana |
| 64 | 63 | 74 | 66 |  Czech Republic Czech Republic |
| 65 | 88 | 83 | 76 |  Dominica Dominica |
| 66 | 54 | 38 | 38 |  Azerbaijan Azerbaijan |
| 67 | 74 | 61 | 52 |  Kuwait Kuwait |
| 68 | 97 | 81 | 78 |  Trinidad and Tobago Trinidad and Tobago |
| 69 | 68 | 58 | 82 |  Belarus Belarus |
| 70 | 44 | 41 | 80 |  Kyrgyzstan Kyrgyzstan |
| 71 | 65 | 73 | 63 |  Turkey Turkey |
| 72 | 56 | 55 | 45 |  Kingdom of Romania Kingdom of Romania |
| 73 | 92 | 91 | 88 |  Grenada Grenada |
| 74 | 96 | 104 | 96 |  Solomon Islands Solomon Islands |
| 75 | 75 | 70 | 62 |  Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Saint Vincent and the Grenadines |
| 76 | 60 | 59 | 58 |  Vanuatu Vanuatu |
| 77 | 62 | 54 | 43 |  Fiji Fiji |
| 78 | 69 | 66 | 54 |  Namibia Namibia |
| 79 | 85 | 87 | 71 |  Maldives Maldives |
| 80 | 84 | 103 | 110 |  Independent State of Croatia Independent State of Croatia |
| 81 | 90 | 94 | 108 |  Moldova Moldova |
| 82 | 82 | 82 | 89 |  Albania Albania |
| 83 | 112 | 96 | 94 |  Brunei Brunei |
| 84 | 76 | 90 | 99 |  Zambia Zambia |
| 85 | 77 | 68 | 59 |  The Bahamas The Bahamas |
| 86 | 73 | 60 | 56 |  Mongolia Mongolia |
| 87 | 80 | 78 | 74 |  Italy Italy |
| 88 | 81 | 75 | 67 |  Jamaica Jamaica |
| 89 | 102 | 105 | 97 |  Sri Lanka Sri Lanka |
| 90 | 124 | 114 | 109 |  Uruguay Uruguay |
| 91 | 79 | 89 | 86 |  Mainland China Mainland China |
| 92 | 89 | 88 | 90 |  Serbia Serbia |
| 93 | 99 | 80 | 75 |  Belize Belize |
| 94 | 114 | 128 | 130 |  Morocco Morocco |
| 95 | 87 | 76 | 70 |  Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Kitts and Nevis |
| 96 | 111 | 100 | 104 |  Jordan Jordan |
| 97 | 101 | 110 | 117 |  Guatemala Guatemala |
| 98 | 78 | 93 | 91 |  Vietnam Vietnam |
| 99 | 105 | 99 | 103 |  Yemen Yemen |
| 100 | 109 | 109 | 100 |  Greece Greece |
| 101 | 103 | 102 | 95 |  Papua New Guinea Papua New Guinea |
| 102 | 106 | 124 | 122 |  Paraguay Paraguay |
| 103 | 95 | 111 | 105 |  Seychelles Seychelles |
| 104 | 113 | 108 | 101 |  Lebanon Lebanon |
| 105 | 83 | 85 | 85 |  Pakistan Pakistan |
| 106 | 108 | 98 | 93 |  Marshall Islands Marshall Islands |
| 107 | 116 | 123 | 123 |  Nepal Nepal |
| 108 | 91 | 86 | 102 |  Dominican Republic Dominican Republic |
| 109 | 98 | 95 | 84 |  Kenya Kenya |
| 110 | 94 | 106 | 116 |  Egypt Egypt |
| 111 | 104 | 107 | 111 |  Ethiopia Ethiopia |
| 112 | 86 | 84 | 81 |  El Salvador El Salvador |
| 113 | 115 | 118 | 112 |  Argentina Argentina |
| 114 | 100 | 101 | 98 |  Guyana Guyana |
| 115 | 93 | 79 | 79 |  Kiribati Kiribati |
| 116 | 120 | 97 | 92 |  Palau Palau |
| 117 | 119 | 113 | 107 |  Republic of Kosovo Republic of Kosovo |
| 118 | 117 | 117 | 113 |  Nicaragua Nicaragua |
| 119 | 132 | 146 | 147 |  Cape Verde Cape Verde |
| 120 | 123 | 120 | 118 |  Russia Russia |
| 121 | 125 | 121 | 120 |  Costa Rica Costa Rica |
| 122 | 107 | 119 | 115 |  Bangladesh Bangladesh |
| 123 | 122 | 112 | 106 |  Uganda Uganda |
| 124 | 118 | 115 | 114 |  Swaziland Swaziland |
| 125 | 110 | 116 | 119 |  Bosnia and Herzegovina Bosnia and Herzegovina |
| 126 | 127 | 129 | 127 |  Brazil Brazil |
| 127 | 128 | 131 | 126 |  Tanzania Tanzania |
| 128 | 131 | 141 | 136 |  Honduras Honduras |
| 129 | 121 | 122 | 129 |  Indonesia Indonesia |
| 130 | 130 | 138 | 133 |  Ecuador Ecuador |
| 131 | 135 | 139 | 137 |  West Bank and Gaza West Bank and Gaza |
| 132 | 134 | 133 | 132 |  India India |
| 133 | 137 | 125 | 121 |  Nigeria Nigeria |
| 134 | 144 | 143 | 138 | |
| 135 | 154 | 154 | 149 |  Sudan Sudan |
| 136 | 148 | 144 | 141 |  Philippines Philippines |
| 137 | 140 | 134 | 144 |  Madagascar Madagascar |
| 138 | 147 | 145 | 139 |  Cambodia Cambodia |
| 139 | 126 | 135 | 140 |  Mozambique Mozambique |
| 140 | 141 | 127 | 125 |  Federated States of Micronesia Federated States of Micronesia |
| 141 | 143 | 148 | 156 |  Sierra Leone Sierra Leone |
| 142 | 142 | 126 | 124 |  Bhutan Bhutan |
| 143 | 138 | 130 | 128 |  Lesotho Lesotho |
| 144 | 129 | 137 | 142 |  Iran Iran |
| 145 | 133 | 132 | 131 |  Malawi Malawi |
| 146 | 153 | 156 | 162 |  Mali Mali |
| 147 | 139 | 152 | 164 |  Tajikistan Tajikistan |
| 148 | 136 | 136 | 134 |  Algeria Algeria |
| 149 | 146 | 140 | 135 | |
| 150 | 151 | 147 | 155 |  Burkina Faso Burkina Faso |
| 151 | 155 | 149 | 159 |  Liberia Liberia |
| 152 | 145 | 142 | 145 |  Ukraine Ukraine |
| 153 | 149 | 161 | 158 |  Bolivia Bolivia |
| 154 | 152 | 157 | 152 |  Senegal Senegal |
| 155 | 164 | 170 | 169 |  Equatorial Guinea Equatorial Guinea |
| 156 | 156 | 158 | 151 |  Gabon Gabon |
| 157 | 159 | 162 | 153 |  Comoros Comoros |
| 158 | 161 | 155 | 148 |  Suriname Suriname |
| 159 | 165 | 166 | 161 |  Mauritania Mauritania |
| 160 | 167 | 160 | 168 |  Afghanistan Afghanistan |
| 161 | 168 | 171 | 167 |  Cameroon Cameroon |
| 162 | 160 | 165 | 166 |  Togo Togo |
| 163 | 178 | 180 | 180 |  São Tomé and Príncipe São Tomé and Príncipe |
| 164 | 166 | 153 | 150 |  Iraq Iraq |
| 165 | 171 | 167 | 165 |  Laos Laos |
| 166 | 150 | 150 | 146 |  Uzbekistan Uzbekistan |
| 167 | 169 | 168 | 163 |  Côte d'Ivoire Côte d'Ivoire |
| 168 | 174 | 164 | 173 |  East Timor East Timor |
| 169 | 181 | 176 | 177 |  Burundi Burundi |
| 170 | 158 | 163 | 157 |  Djibouti Djibouti |
| 171 | 157 | 159 | 160 |  Zimbabwe Zimbabwe |
| 172 | 163 | 169 | 170 |  Angola Angola |
| 173 | 173 | 174 | 174 |  Niger Niger |
| 174 | 162 | 151 | 154 |  Haiti Haiti |
| 175 | 170 | 172 | 172 |  Benin Benin |
| 176 | 176 | 181 | 181 |  Guinea-Bissau Guinea-Bissau |
| 177 | 172 | 177 | 178 |  Venezuela Venezuela |
| 178 | 175 | 182 | 182 |  Democratic Republic of the Congo Democratic Republic of the Congo |
| 179 | 179 | 173 | 171 |  Guinea Guinea |
| 180 | 180 | 175 | 175 |  Eritrea Eritrea |
| 181 | 177 | 179 | 179 |  Republic of the Congo Republic of the Congo |
| 182 | 182 | 183 | 183 |  Central African Republic Central African Republic |
| 183 | 183 | 178 | 176 |  Chad Chad |
North Korea
North Korea
The Democratic People’s Republic of Korea , , is a country in East Asia, occupying the northern half of the Korean Peninsula. Its capital and largest city is Pyongyang. The Korean Demilitarized Zone serves as the buffer zone between North Korea and South Korea...
, Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan , formerly also known as Turkmenia is one of the Turkic states in Central Asia. Until 1991, it was a constituent republic of the Soviet Union, the Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic . Turkmenistan is one of the six independent Turkic states...
, Somalia
Somalia
Somalia , officially the Somali Republic and formerly known as the Somali Democratic Republic under Socialist rule, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. Since the outbreak of the Somali Civil War in 1991 there has been no central government control over most of the country's territory...
, Libya
Libya
Libya is an African country in the Maghreb region of North Africa bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, and Algeria and Tunisia to the west....
, Cuba
Cuba
The Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
and the disputed territory Western Sahara
Western Sahara
Western Sahara is a disputed territory in North Africa, bordered by Morocco to the north, Algeria to the northeast, Mauritania to the east and south, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. Its surface area amounts to . It is one of the most sparsely populated territories in the world, mainly...
are not ranked.
External links
- doingbusiness.org – Doing business map

