
East Malaysia
Encyclopedia
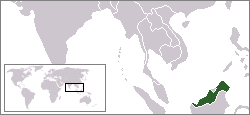
East Malaysia, also known as Malaysian Borneo, is the part of Malaysia located on the island of Borneo
Borneo
Borneo is the third largest island in the world and is located north of Java Island, Indonesia, at the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia....
. It consists of the Malaysian states
States of Malaysia
Malaysia is a federation which consists of thirteen states and three federal territories . Eleven states and two federal territories are located on the Malay Peninsula while the remaining two states and one federal territory are on the island of Borneo.-The states and federal territories:Malaysia...
of Sabah
Sabah
Sabah is one of 13 member states of Malaysia. It is located on the northern portion of the island of Borneo. It is the second largest state in the country after Sarawak, which it borders on its southwest. It also shares a border with the province of East Kalimantan of Indonesia in the south...
and Sarawak
Sarawak
Sarawak is one of two Malaysian states on the island of Borneo. Known as Bumi Kenyalang , Sarawak is situated on the north-west of the island. It is the largest state in Malaysia followed by Sabah, the second largest state located to the North- East.The administrative capital is Kuching, which...
, and the Federal Territory of Labuan
Labuan
Labuan is a federal territory in East Malaysia. It is an island off the coast of the state of Sabah. Labuan's capital is Victoria and is best known as an offshore financial centre offering international financial and business services via Labuan IBFC since 1990 as well as being an offshore support...
. It lies to the east from Peninsular Malaysia
Peninsular Malaysia
Peninsular Malaysia , also known as West Malaysia , is the part of Malaysia which lies on the Malay Peninsula. Its area is . It shares a land border with Thailand in the north. To the south is the island of Singapore. Across the Strait of Malacca to the west lies the island of Sumatra...
(West Malaysia), which is located on the Malay Peninsula
Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula or Thai-Malay Peninsula is a peninsula in Southeast Asia. The land mass runs approximately north-south and, at its terminus, is the southern-most point of the Asian mainland...
. The two are separated by the South China Sea
South China Sea
The South China Sea is a marginal sea that is part of the Pacific Ocean, encompassing an area from the Singapore and Malacca Straits to the Strait of Taiwan of around...
. While East Malaysia is less populated and less developed than West Malaysia, its land mass is larger and it has notably more natural resources, chiefly oil and gas reserves.
Physical geography
Borneo montane rain forests
The Borneo montane rain forests are an ecoregion, of Cloud forest, within the Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests Biome, of the island of Borneo in south-east Asia .-Location and description:...
towards the interior regions.
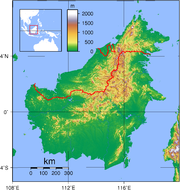
The total area of East Malaysia is 200,565 km2, representing approximately 61% of the total land area of Malaysia and 27% of the total area of Borneo
Borneo
Borneo is the third largest island in the world and is located north of Java Island, Indonesia, at the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia....
.
East Malaysia contains the five highest mountains in Malaysia – the highest being Mount Kinabalu
Mount Kinabalu
Mount Kinabalu is a prominent mountain on the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. It is located in the East Malaysian state of Sabah and is protected as Kinabalu National Park, a World Heritage Site. Kinabalu is the tallest peak in Borneo's Crocker Range and is the tallest mountain in the Malay...
at 4,095 m, which is also the highest mountain in Borneo and the 10th highest mountain peak in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
. It also contains the two longest rivers in Malaysia - Rajang River
Rajang River
The Rajang River is a river in Sarawak, Malaysia. The river is located in northwest of Borneo and it originates in the Iran Mountains. The river flows approximately 563 km to the South China Sea, making it the longest river in Malaysia....
and Kinabatangan River
Kinabatangan River
The Kinabatangan River is located in Sabah, eastern Malaysia, on the island of Borneo. It is the second longest river in Malaysia, with a length of 560 kilometers from its headwaters in the mountains of southwest Sabah, to its outlet at the Sulu Sea, east of Sandakan.Kinabatangan is known for its...
.
Banggi Island
Banggi Island
Banggi Island is located within the Kudat Division of Sabah in Malaysia. With an area of 440.7 square kilometres it is the third largest island in Malaysia after Langkawi Island and Betruit Island, followed Penang Island in fourth place. It is located off the northern coast of Sabah, near Marudu...
in Sabah
Sabah
Sabah is one of 13 member states of Malaysia. It is located on the northern portion of the island of Borneo. It is the second largest state in the country after Sarawak, which it borders on its southwest. It also shares a border with the province of East Kalimantan of Indonesia in the south...
and Betruit Island in Sarawak
Sarawak
Sarawak is one of two Malaysian states on the island of Borneo. Known as Bumi Kenyalang , Sarawak is situated on the north-west of the island. It is the largest state in Malaysia followed by Sabah, the second largest state located to the North- East.The administrative capital is Kuching, which...
are the two largest fully governed islands in Malaysia. The largest island is Borneo, which is shared with Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
and Brunei
Brunei
Brunei , officially the State of Brunei Darussalam or the Nation of Brunei, the Abode of Peace , is a sovereign state located on the north coast of the island of Borneo, in Southeast Asia...
. The second largest island is Sebatik Island
Sebatik Island
Sebatik Island is an island off the eastern coast of Borneo, partly within Indonesia and partly within Malaysia. It has an area of approximately 452.2 square kilometres...
, in Sabah, which is shared with Indonesia.
Of note, Sarawak contains the Mulu caves within Gunung Mulu National Park
Gunung Mulu National Park
Gunung Mulu National Park near Miri, Sarawak, Malaysian Borneo, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site that encompasses incredible caves and karst formations in a mountainous equatorial rainforest setting...
. Its Sarawak Chamber
Sarawak chamber
The Sarawak Chamber is a huge chamber in Gua Nasib Bagus , which is located in Gunung Mulu National Park, in the Malaysian state of Sarawak on the island of Borneo. It is considered to be the largest known underground chamber in the world....
has the largest known cave chamber in the world. The Mulu national park was declared a World Heritage Site
World Heritage Site
A UNESCO World Heritage Site is a place that is listed by the UNESCO as of special cultural or physical significance...
in November 2000.
Sabah's attractions includes World Heritage Site
World Heritage Site
A UNESCO World Heritage Site is a place that is listed by the UNESCO as of special cultural or physical significance...
Kinabalu Park
Kinabalu National Park
Kinabalu National Park or Taman Negara Kinabalu in Malay, established as one of the first national parks of Malaysia in 1964, is Malaysia's first World Heritage Site designated by UNESCO in December 2000 for its "outstanding universal values" and the role as one of the most important biological...
which has Mount Kinabalu
Mount Kinabalu
Mount Kinabalu is a prominent mountain on the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. It is located in the East Malaysian state of Sabah and is protected as Kinabalu National Park, a World Heritage Site. Kinabalu is the tallest peak in Borneo's Crocker Range and is the tallest mountain in the Malay...
, and Sipadan Island
Sipadan
Sipadan is the only oceanic island in Malaysia, rising from the seabed. It is located in the Celebes Sea off the east coast of Sabah, East Malaysia . It was formed by living corals growing on top of an extinct volcanic cone that took thousands of years to develop...
, a diving and bio-diversity hot-spot.
History
Some parts of present-day East Malaysia, especially the coastal regions, were once part of the thalassocracyThalassocracy
The term thalassocracy refers to a state with primarily maritime realms—an empire at sea, such as Athens or the Phoenician network of merchant cities...
of the Sultanate of Brunei. However, most parts of the interior region consisted of independent tribal societies.
In the mid 17th century, the north and eastern coast of Sabah was ceded to the Sultanate of Sulu while most of Sarawak remained part of Brunei. Beginning the mid 19th century, both Sabah and Sarawak became British protectorates and in 1946 both became separate British colonies.
Federation
Both Sabah (formerly British North Borneo) and Sarawak were separate British coloniesCrown colony
A Crown colony, also known in the 17th century as royal colony, was a type of colonial administration of the English and later British Empire....
from Malaya
British Malaya
British Malaya loosely described a set of states on the Malay Peninsula and the Island of Singapore that were brought under British control between the 18th and the 20th centuries...
, and did not become part of the Federation of Malaya
Federation of Malaya
The Federation of Malaya is the name given to a federation of 11 states that existed from 31 January 1948 until 16 September 1963. The Federation became independent on 31 August 1957...
in 1957. However, both voted to become part of the new Federation of Malaysia along with the Federation of Malaya
Federation of Malaya
The Federation of Malaya is the name given to a federation of 11 states that existed from 31 January 1948 until 16 September 1963. The Federation became independent on 31 August 1957...
and Singapore
Singapore
Singapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
in 1963. Previously, there were efforts to unite Brunei
Brunei
Brunei , officially the State of Brunei Darussalam or the Nation of Brunei, the Abode of Peace , is a sovereign state located on the north coast of the island of Borneo, in Southeast Asia...
, Sabah and Sarawak under the North Borneo Federation
North Borneo Federation
The North Borneo Federation, also known as Kalimantan Utara or North Kalimantan was a proposed political entity which would have comprised the British Colonies of Sarawak, British North Borneo and the protectorate of Brunei.By 1956, the governments of Sarawak, North Borneo, and the State of Brunei...
but that failed after the Brunei Revolt
Brunei Revolt
The Brunei Rebellion broke out on 8 December 1962. The rebels began co-ordinated attacks on the oil town of Seria and on police stations and government facilities around the protectorate...
occurred.
Sabah and Sarawak retained a higher degree of local government and legislative autonomy when compared to other states in West Malaysia. For example, both states have separate immigration controls, requiring Malaysian citizens from West Malaysia to carry passports or identity cards when visiting East Malaysia.
The island of Labuan
Labuan
Labuan is a federal territory in East Malaysia. It is an island off the coast of the state of Sabah. Labuan's capital is Victoria and is best known as an offshore financial centre offering international financial and business services via Labuan IBFC since 1990 as well as being an offshore support...
joined Malaysia and became part of Sabah in 1963 before becoming a Federal Territory
Federal Territory
The Federal Territories in Malaysia comprise three territories: Kuala Lumpur, Putrajaya and Labuan, governed directly by the federal government of Malaysia. Kuala Lumpur is the national capital of Malaysia, Putrajaya is the administrative capital, and Labuan is an offshore international financial...
in 1984. It was used to establish a centre for offshore finance
Offshore financial centre
An offshore financial centre , though not precisely defined, is usually a small, low-tax jurisdiction specializing in providing corporate and commercial services to non-resident offshore companies, and for the investment of offshore funds....
in 1990.
Administration
It has been a source of debate whether the states of Sabah and Sarawak joined the Federation of Malaysia as equal partners with Malaya and Singapore or whether they became merely equal partners of the states of Malaya (Peninsular Malaysia). The consensus seems to be that Sabah and Sarawak are merely one of the states in the federation with a slightly higher degree of autonomy compared to other states in Peninsular Malaysia. For example, the East Malaysian states have separate laws regulating the entry of citizens from other states in Malaysia, including the other East Malaysian state, whereas, in Peninsular, there are no restriction for interstate travel or migration, including visitors from East Malaysia. There are also separate land lawProperty law
Property law is the area of law that governs the various forms of ownership in real property and in personal property, within the common law legal system. In the civil law system, there is a division between movable and immovable property...
governing Sabah and Sarawak, instead of the National Land Code which governs the whole of Peninsular Malaysia.
With regard to the administration of justice, the courts in East Malaysia are part of the federal court system in Malaysia. The Constitution of Malaysia provides that there shall be two High Courts of coordinate jurisdiction – The High Court in Malaya and the High Court in Sabah and Sarawak (formerly the High Court in Borneo). The current Chief Judge of Sabah and Sarawak is Richard Malanjum
Richard Malanjum
Richard Malanjum is the fourth current Chief Judge of the High Court in Sabah and Sarawak in Malaysia. Before joining the judicial service, he was a practising lawyer and was the President of the Sabah Law Association, the bar association for the state of Sabah. Malanjum joined the judicial...
from Sabah. His office is the fourth highest in the Malaysian judicial system.
Population
The total population of East Malaysia in 2010 is estimated to be 6 million (3.5 million in Sabah and 2.5 million in Sarawak), which represents roughly 20% of the population of Malaysia. Significant amount of the population of East Malaysia today reside in towns and cities. The largest city and urban center is KuchingKuching
Kuching , officially the City of Kuching, and formerly the City of Sarawak, is the capital and most populous city of the East Malaysian state of Sarawak. It is the largest city on the island of Borneo, and the fourth largest city in Malaysia....
, which is also the capital of Sarawak and has a population of over 600,000 inhabitants. Kota Kinabalu
Kota Kinabalu
Kota Kinabalu , formerly known as Jesselton, is the capital of Sabah state in East Malaysia. It is also the capital of the West Coast Division of Sabah. The city is located on the northwest coast of Borneo facing the South China Sea. The Tunku Abdul Rahman National Park lies on one side and Mount...
is the second largest city and one of the most important cities in East Malaysia. Both Kuching and Kota Kinabalu together with Miri
Miri
Miri is a city in northern Sarawak, Malaysia, on the island of Borneo. It is the second largest city in Sarawak, with a population of about 300,000, and the government administrative centre of Miri District in Miri Division....
are the only three places with city status
City status
City status is the national recognition of an area as a city. Specifically, "city status" may refer to:*City rights in the Low Countries*City status in Ireland*City status in the United Kingdom*City status in the United States of America...
in East Malaysia. Other important towns include Sandakan
Sandakan
Sandakan is the second-largest city in Sabah, East Malaysia, on the north-eastern coast of Borneo. It is located on the east coast of the island and it is the administrative centre of Sandakan Division and was the former capital of British North Borneo...
and Tawau
Tawau
Tawau is the administrative center of Tawau Division, Malaysia and the third largest town of Sabah after Kota Kinabalu and Sandakan.-Geography:...
in Sabah and Sibu
Sibu
Sibu may refer to:*Sibu, Sarawak in Eastern Malaysia*Sibu Division*Sibu , an impact crater on Mars*Pulau Sibu, an island off the eastern coast of peninsular Malaysia*Sibu , name of a goddess in the Bribri tribe, in Costa Rica...
and Bintulu
Bintulu
Bintulu is a coastal town, and the capital of Bintulu District in the Bintulu Division of Sarawak, Malaysia. It is about 650 kilometers from Kuching and about 215 kilometers from either Sibu or Miri....
in Sarawak.
The earliest inhabitants of East Malaysia are the Dayak people
Dayak people
The Dayak or Dyak are the native people of Borneo. It is a loose term for over 200 riverine and hill-dwelling ethnic subgroups, located principally in the interior of Borneo, each with its own dialect, customs, laws, territory and culture, although common distinguishing traits are readily...
and other related ethnic groups such as the Dusun
Dusun
Dusun is the collective name of a tribe or ethnic and linguistic group in the Malaysian state of Sabah of North Borneo. Due to similarities in culture and language with the Kadazan ethnic group, a new unified term called "Kadazan-Dusun" was created. Collectively, they form the largest ethnic group...
people. These indigenous inhabitants form a significant portion of the population of East Malaysia, however they do not represent the majority population. There are significant migration into East Malaysia and Borneo from many parts of the Malay Archipelago
Malay Archipelago
The Malay Archipelago refers to the archipelago between mainland Southeastern Asia and Australia. The name was derived from the anachronistic concept of a Malay race....
since hundreds of years ago, including from Java, Lesser Sunda Islands, Sulawesi and Sulu. There are also recent migrations from further regions such as India and China.
The indigenous inhabitants are originally animists. Islamic influence had reached East Malaysia from as early as the 15th century while there are also Christian influence beginning the 19th century.
The indigenous inhabitants of East Malaysia are generally partisan and maintain culturally distinct dialects of the Malay language
Malay language
Malay is a major language of the Austronesian family. It is the official language of Malaysia , Indonesia , Brunei and Singapore...
, in addition to their own ethnic languages. Approximately 13% of the population of Sabah, and 26% of the population of Sarawak, is composed of ethnic Chinese Malaysians.
Transport
The Pan Borneo HighwayPan Borneo Highway
Pan Borneo Highway , also known as Trans Borneo Highway, , ' is a network of federal roads connecting Sarawak, Brunei and Sabah. The Pan Borneo Highway project is a joint project between the governments of Brunei and Malaysia...
connects Sabah and Sarawak as well as Brunei. East Malaysia is connected to Peninsular Malaysia via air transport with frequent flights between cities of East Malaysia and Peninsular Malaysia. These flights are provided by Malaysia Airlines
Malaysia Airlines
Malaysian Airline System Berhad , DBA Malaysia Airlines , is the government-owned flag carrier of Malaysia. Malaysia Airlines operates flights from its home base, Kuala Lumpur International Airport, and its eastern hub in Kota Kinabalu. It has its headquarters on the grounds of Sultan Abdul Aziz...
(MAS) and AirAsia
AirAsia
AirAsia Berhad is a Malaysian-based low-cost airline. AirAsia is Asia's largest low-fare, no-frills airline and a pioneer of low-cost travel in Asia. AirAsia group operates scheduled domestic and international flights to over 400 destinations spanning 25 countries. Its main hub is the Low-Cost...
. MAS operates flights from several countries to major cities in East Malaysia. Major airports in East Malaysia includes Kuching International Airport
Kuching International Airport
"RAF Kuching/RMAF Kuching" & "Kuching Airbase/Airfield" redirects here.Kuching International Airport is an international airport serving the entire southwestern region of Sarawak, Malaysia. It is located 11 km south of Kuching city centre. The airport also shares its runway with the RMAF...
and Kota Kinabalu International Airport
Kota Kinabalu International Airport
Kota Kinabalu International Airport serves the city of Kota Kinabalu, the state capital of Sabah, Malaysia. It is located about 8 km southwest of the city centre. It is the second busiest airport in Malaysia after Kuala Lumpur International Airport, handling 4.8 million passengers in 2009...
.
The rural areas in Borneo can only be accessible by air or by rivers. River transport is especially prevalent in Sarawak because there are many large and long rivers with Rajang River
Rajang River
The Rajang River is a river in Sarawak, Malaysia. The river is located in northwest of Borneo and it originates in the Iran Mountains. The river flows approximately 563 km to the South China Sea, making it the longest river in Malaysia....
being the most used river in Sarawak. Rivers are used by boats and ferries for transporting passengers and communications between inland areas and coastal towns. Timber is also transported via vessels and log carriers down the rivers of Sarawak.
External links
- Virtual Malaysia - The Official Portal of the Ministry of Tourism, Malaysia

