
Eaton Hodgkinson
Encyclopedia
Eaton A. Hodgkinson was an English
engineer
, a pioneer of the application of mathematics
to problems of structural design.
, near Great Budworth
, Cheshire
to a farming family. His father died when Hodgkinson was six years old and he was raised with his two sisters by his mother who maintained the farming business. She sent her son to Witton Grammar School in Northwich
where he studied the classics
with the intention that he would fulfill the family's ambition that he prepares for a career in the Church of England
. Unfortunately, the regime was unsuited to his tastes and talents which were already showing promise in mathematics. His mother moved him to a less prestigious private school in Northwich where his enthusiasm for mathematics was encouraged and fostered but, as the young Hodgkinson grew physically, he became indispensable on the family farm and soon left education to devote himself there.
However, farming was no more to his taste than Greek
and Latin
and his mother yearned to satisfy her son's appetites. Family friends advised that Hodgkinson might find some more suitable outlet in nearby Manchester
and so, in 1811, the family left for Salford to open a pawnbroking business. Hodgkinson used all his spare time in reading science
and mathematics and soon introduced himself into Manchester's scientific community, meeting, among others, his future collaborator, Sir William Fairbairn
. He became a pupil of John Dalton
, studying mathematics, and the two remained firm friends until Dalton's death in 1844. He retired early from the family business to devote a modest pension to his scientific work.
He married twice, to Catherine Johns and to a Miss Holditch. There were no children.
in Manchester
on the design of iron
beam
s, especially on the Water Street bridge for the Liverpool and Manchester Railway
in 1828-30. His improved cross section
was published by the Manchester Literary and Philosophical Society
in 1830 and influenced much nineteenth century structural engineering
. He derived the empirical formula for a concentrated load, W (in ton
s), at which a beam will fail as a function of its length between simple supports, L (in inches); its depth, d (in inches); and its bottom-flange area
, A (inch²):
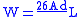
His expertise with beams led to his retention, along with Fairbairn, as consultant on the novel tubular design for the Britannia Bridge
. Fairbairn built and tested several prototypes, and developed the final form adopted for the bridge. Both Hodgkinson and Robert Stephenson
believed that extra chains would be needed to support the heavy spans, so the towers were built with spaces for the chains. Fairbairn, however, insisted that chains would not be necessary, and his opinion prevailed. He was right, and chains were never used, but the towers remain with their empty recesses.
in 1841 and, in 1847, he became professor of the mechanical principles of engineering at University College London
. In 1849, he was appointed by the UK Parliament to participate in a Royal Commission
to investigate the application of iron in railroad structures, performing some early investigations of metal fatigue
.
Towards the end of his life, his mental faculties failed and he died at Higher Broughton, Salford.
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
engineer
Engineer
An engineer is a professional practitioner of engineering, concerned with applying scientific knowledge, mathematics and ingenuity to develop solutions for technical problems. Engineers design materials, structures, machines and systems while considering the limitations imposed by practicality,...
, a pioneer of the application of mathematics
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
to problems of structural design.
Early life
Hodgkinson was born in the village of AndertonAnderton with Marbury
right|thumb|Map of civil parish of Anderton with Marbury within the former borough of Vale RoyalAnderton with Marbury is a civil parish in the unitary authority of Cheshire West and Chester and the ceremonial county of Cheshire, England. It had a population of 582 according to the 2001 census, and...
, near Great Budworth
Great Budworth
Great Budworth is a civil parish and village, approximately north of Northwich, England, within the unitary authority of Cheshire West and Chester and the ceremonial county of Cheshire. It lies off the A559 road, east of Comberbach, northwest of Higher Marston and southeast of Budworth Heath...
, Cheshire
Cheshire
Cheshire is a ceremonial county in North West England. Cheshire's county town is the city of Chester, although its largest town is Warrington. Other major towns include Widnes, Congleton, Crewe, Ellesmere Port, Runcorn, Macclesfield, Winsford, Northwich, and Wilmslow...
to a farming family. His father died when Hodgkinson was six years old and he was raised with his two sisters by his mother who maintained the farming business. She sent her son to Witton Grammar School in Northwich
Northwich
Northwich is a town and civil parish in the unitary authority of Cheshire West and Chester and the ceremonial county of Cheshire, England. It lies in the heart of the Cheshire Plain, at the confluence of the rivers Weaver and Dane...
where he studied the classics
Classics
Classics is the branch of the Humanities comprising the languages, literature, philosophy, history, art, archaeology and other culture of the ancient Mediterranean world ; especially Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome during Classical Antiquity Classics (sometimes encompassing Classical Studies or...
with the intention that he would fulfill the family's ambition that he prepares for a career in the Church of England
Church of England
The Church of England is the officially established Christian church in England and the Mother Church of the worldwide Anglican Communion. The church considers itself within the tradition of Western Christianity and dates its formal establishment principally to the mission to England by St...
. Unfortunately, the regime was unsuited to his tastes and talents which were already showing promise in mathematics. His mother moved him to a less prestigious private school in Northwich where his enthusiasm for mathematics was encouraged and fostered but, as the young Hodgkinson grew physically, he became indispensable on the family farm and soon left education to devote himself there.
However, farming was no more to his taste than Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
and Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
and his mother yearned to satisfy her son's appetites. Family friends advised that Hodgkinson might find some more suitable outlet in nearby Manchester
Manchester
Manchester is a city and metropolitan borough in Greater Manchester, England. According to the Office for National Statistics, the 2010 mid-year population estimate for Manchester was 498,800. Manchester lies within one of the UK's largest metropolitan areas, the metropolitan county of Greater...
and so, in 1811, the family left for Salford to open a pawnbroking business. Hodgkinson used all his spare time in reading science
Science
Science is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe...
and mathematics and soon introduced himself into Manchester's scientific community, meeting, among others, his future collaborator, Sir William Fairbairn
William Fairbairn
Sir William Fairbairn, 1st Baronet was a Scottish civil engineer, structural engineer and shipbuilder.-Early career:...
. He became a pupil of John Dalton
John Dalton
John Dalton FRS was an English chemist, meteorologist and physicist. He is best known for his pioneering work in the development of modern atomic theory, and his research into colour blindness .-Early life:John Dalton was born into a Quaker family at Eaglesfield, near Cockermouth, Cumberland,...
, studying mathematics, and the two remained firm friends until Dalton's death in 1844. He retired early from the family business to devote a modest pension to his scientific work.
He married twice, to Catherine Johns and to a Miss Holditch. There were no children.
Scientific work
Hodgkinson worked with Sir William FairbairnWilliam Fairbairn
Sir William Fairbairn, 1st Baronet was a Scottish civil engineer, structural engineer and shipbuilder.-Early career:...
in Manchester
Manchester
Manchester is a city and metropolitan borough in Greater Manchester, England. According to the Office for National Statistics, the 2010 mid-year population estimate for Manchester was 498,800. Manchester lies within one of the UK's largest metropolitan areas, the metropolitan county of Greater...
on the design of iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
beam
Beam (structure)
A beam is a horizontal structural element that is capable of withstanding load primarily by resisting bending. The bending force induced into the material of the beam as a result of the external loads, own weight, span and external reactions to these loads is called a bending moment.- Overview...
s, especially on the Water Street bridge for the Liverpool and Manchester Railway
Liverpool and Manchester Railway
The Liverpool and Manchester Railway was the world's first inter-city passenger railway in which all the trains were timetabled and were hauled for most of the distance solely by steam locomotives. The line opened on 15 September 1830 and ran between the cities of Liverpool and Manchester in North...
in 1828-30. His improved cross section
Cross section (geometry)
In geometry, a cross-section is the intersection of a figure in 2-dimensional space with a line, or of a body in 3-dimensional space with a plane, etc...
was published by the Manchester Literary and Philosophical Society
Manchester Literary and Philosophical Society
The Manchester Literary and Philosophical Society, popularly known as the Lit & Phil, is a learned society in Manchester, England.Established in 1781 as the Literary and Philosophical Society of Manchester, by Thomas Percival, Thomas Barnes and Thomas Henry, other prominent members have included...
in 1830 and influenced much nineteenth century structural engineering
Structural engineering
Structural engineering is a field of engineering dealing with the analysis and design of structures that support or resist loads. Structural engineering is usually considered a specialty within civil engineering, but it can also be studied in its own right....
. He derived the empirical formula for a concentrated load, W (in ton
Ton
The ton is a unit of measure. It has a long history and has acquired a number of meanings and uses over the years. It is used principally as a unit of weight, and as a unit of volume. It can also be used as a measure of energy, for truck classification, or as a colloquial term.It is derived from...
s), at which a beam will fail as a function of its length between simple supports, L (in inches); its depth, d (in inches); and its bottom-flange area
Area
Area is a quantity that expresses the extent of a two-dimensional surface or shape in the plane. Area can be understood as the amount of material with a given thickness that would be necessary to fashion a model of the shape, or the amount of paint necessary to cover the surface with a single coat...
, A (inch²):
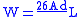
His expertise with beams led to his retention, along with Fairbairn, as consultant on the novel tubular design for the Britannia Bridge
Britannia Bridge
Britannia Bridge is a bridge across the Menai Strait between the island of Anglesey and the mainland of Wales. It was originally designed and built by Robert Stephenson as a tubular bridge of wrought iron rectangular box-section spans for carrying rail traffic...
. Fairbairn built and tested several prototypes, and developed the final form adopted for the bridge. Both Hodgkinson and Robert Stephenson
Robert Stephenson
Robert Stephenson FRS was an English civil engineer. He was the only son of George Stephenson, the famed locomotive builder and railway engineer; many of the achievements popularly credited to his father were actually the joint efforts of father and son.-Early life :He was born on the 16th of...
believed that extra chains would be needed to support the heavy spans, so the towers were built with spaces for the chains. Fairbairn, however, insisted that chains would not be necessary, and his opinion prevailed. He was right, and chains were never used, but the towers remain with their empty recesses.
Later years
Hodgkinson was elected a Fellow of the Royal SocietyRoyal Society
The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, known simply as the Royal Society, is a learned society for science, and is possibly the oldest such society in existence. Founded in November 1660, it was granted a Royal Charter by King Charles II as the "Royal Society of London"...
in 1841 and, in 1847, he became professor of the mechanical principles of engineering at University College London
University College London
University College London is a public research university located in London, United Kingdom and the oldest and largest constituent college of the federal University of London...
. In 1849, he was appointed by the UK Parliament to participate in a Royal Commission
Royal Commission
In Commonwealth realms and other monarchies a Royal Commission is a major ad-hoc formal public inquiry into a defined issue. They have been held in various countries such as the United Kingdom, Australia, Canada, New Zealand, and Saudi Arabia...
to investigate the application of iron in railroad structures, performing some early investigations of metal fatigue
Metal Fatigue
Metal Fatigue , is a futuristic science fiction, real-time strategy computer game developed by Zono Incorporated and published by Psygnosis and TalonSoft .-Plot:...
.
Towards the end of his life, his mental faculties failed and he died at Higher Broughton, Salford.

