
Economy of Chile
Encyclopedia
The economy of Chile
is ranked as an upper-middle income economy by the World Bank
, and is one of South America
's most stable and prosperous nations, leading Latin American nations in human development
, competitiveness, income per capita, globalization, economic freedom, and low perception of corruption. However, it has a high economic inequality
, as measured by the Gini index.
In May 2010 Chile became the first South American country to join the OECD
. In 2006, Chile became the country with the highest nominal GDP per capita in Latin America. Chile has an inequality-adjusted human development index of 0.634, compared to 0.509 and 0.562 for neighbouring Brazil and Argentina, respectively. 5.3% of the population lives on less than US $2 a day.
The Global Competitiveness Report
for 2009-2010 ranks Chile as being the 30th most competitive country in the world and the first in Latin America, well above from Brazil (56th), Mexico (60th) and Argentina which ranks 85th. The Ease of doing business index
created by the World Bank
lists Chile as 43rd in the world that encompasses better, usually simpler, regulations for businesses and stronger protections of property rights. The privatized national pension system
(AFP) has encouraged domestic investment and contributed to an estimated total domestic savings rate of approximately 21% of GDP.
. During early colonial times there were gold exports to Perú from placer deposit
s which soon depleted. Trade restrictions and monopolies established by the Spanish crown are credited for having held back economic development for much of the colonial times. As effect of these restrictions the country incorporated very few new crops and animal breeds after initial conquest. Other sectors that were held back by restrictions were the wine and mining industries. The Bourbon reforms
in the 18th century eased many monopolies and trade restrictions.
In the 1830s Chile consolidated under the ideas of Diego Portales
as a stable state open to foreign trade. Foreign investment in Chile grew over the 19th century. After the War of the Pacific
the Chilean treasury grew by 900%. The League of Nations
labeled Chile the country hardest hit by the Great Depression
because 80% of government revenue came from exports of copper and nitrates, which were in low demand. After the Great Depression Chilean economic policies changed toward import substitution industrialization and the Production Development Corporation
was established.
Under the influence of the Chicago Boys
the Pinochet regime made of Chile a leading country in establishing neoliberal policies which are attributed to have lifted the country to become one of the richest in Latin America. Despite a general selling of state property the regime retained the lucrative state owned mining company CODELCO
which stands for about 30% of government income.
According to the CIA World Factbook, during the early 1990s, Chile's "reputation as a role model for economic reform" was strengthened when the democratic government of Patricio Aylwin
, who took over from the military in 1990, deepened the economic reform initiated by the military government. Growth in real GDP averaged 8% from 1991–1997, but fell to half that level in 1998 because of tight monetary policies (implemented to keep the current account deficit in check) and because of lower export earnings, the latter which was a product of the Asian financial crisis. Chile's economy has since recovered and has seen growth rates of 5-7% over the past several years.
After a decade of impressive growth rates, Chile began to experience a moderate economic downturn in 1999, brought on by unfavorable global economic conditions related to the Asian financial crisis, which began in 1997. The economy remained sluggish until 2003, when it began to show clear signs of recovery, achieving 4.0% real GDP growth. The Chilean economy finished 2004 with growth of 6.0%. Real GDP growth reached 5.7% in 2005 before falling back to 4.0% in 2006. GDP expanded by 5.1% in 2007.
, logging
and fishing
accounts only for 4.9% of the GDP as of 2007 and employed 13.6% of the country's labor force
. Some major agriculture products of Chile includes grapes, apples, pears, onions, wheat, corn, oats, peaches, garlic, asparagus, beans, beef, poultry, wool, fish and timber.
Chile’s position in the Southern Hemisphere
leads to an agricultural season cycle opposite to those of the principal consumer markets, primarily located in the Northern Hemisphere. Chile’s extreme north-south orientation produces 7 different macro-regions distinguished by climate and geographical features, which allows the country itself to stagger harvests and results in extended harvesting seasons. However, the mountainous landscape of Chile
limits the extent and intensity of agriculture so that arable land corresponds only to 2.62% of the total territory. Through Chile’s trade agreements, its agricultural products have gained access to a market controlling 77% of the world’s GDP and by approximately 2012, 74% of Chilean agribusiness exports will be duty free.
Chiles principal growing region
and agricultural heartland is the Central Valley
delimited by the Chilean Coast Range
in the west, the Andes
in the east Aconcagua River
by the north and Bío-Bío River
by the south. In the northern half of Chile cultivation is highly dependent on irrigation
. South of the Central Valley cultivation is gradually replaced by aquaculture
, silviculture
, sheep and cattle
farming.
in the world. As of August 2007, Chile’s share of worldwide salmon industry sales was 38.2%, rising from just 10% in 1990. The average growth rate of the industry for the 20 years between 1984 and 2004 was 42% per year. The presence of large foreign firms in the salmon industry has brought what probably most contributes to Chile’s burgeoning salmon production, technology. Technology transfer has allowed Chile to build its global competitiveness and innovation and has led to the expansion of production as well as to an increase in average firm size in the industry.
comprise the vast majority of Chile's forestry exports. Within the forestry sector, the largest contributor to total production is pulp
, followed by wood-based panels and lumber
. Due to popular and increasing demands for Chile’s forestry products, the government is currently focusing on increasing the already vast acreage of Chile’s Pine and Eucalyptus plantations as well as opening new industrial plants.
 The mining sector in Chile is one of the pillars of Chilean economy. The Chilean government strongly supports foreign investment in the sector and has modified its mining industry laws and regulations to create a favorable investing environment for foreigners. Thanks to a large amount of copper resources, progressive legislation and a healthy investment environment, Chile has become the copper mining capital of the world, producing over 1/3 of the global copper output.
The mining sector in Chile is one of the pillars of Chilean economy. The Chilean government strongly supports foreign investment in the sector and has modified its mining industry laws and regulations to create a favorable investing environment for foreigners. Thanks to a large amount of copper resources, progressive legislation and a healthy investment environment, Chile has become the copper mining capital of the world, producing over 1/3 of the global copper output.
received about 2.25 million foreign visitors in 2006, up to 2.50 million in 2007
The percentages of foreign tourists arrivals by land, air and sea were, respectively, 55.3%, 40.5% and 4.2% for that year. The two main gateways for international tourists visiting Chile are Comodoro Arturo Merino Benítez International Airport
and Paso Los Libertadores
.
Chile a great diversity of natural landscapes, from the Mars-like landscapes of the hyperarid Atacama Desert
to the glacier-fed fjords of the Chilean Patagonia
, passing by the winelands backdropped by the Andes
of the Central Valley
and the old-growth forests of the Lakes District. Easter Island
and Juan Fernández Archipelago, including Robinson Crusoe Island
, are also major attractions.
Many of the most visited attractions in Chile are protected areas. The extensive Chilean protected areas
system includes 32 national parks, 48 natural reserves and 15 natural monuments.
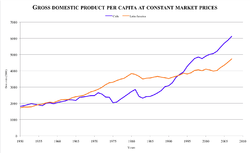 According to the CIA World Factbook, Chile's "sound economic policies," maintained consistently since the 1980s, "have contributed to steady economic growth in Chile and have more than halved poverty rates." The 1973-90 military government sold many state-owned companies, and the three democratic governments since 1990 have continued privatization, though at a slower pace. The government's role in the economy is mostly limited to regulation, although the state continues to operate copper giant CODELCO and a few other enterprises (there is one state-run bank). Chile is strongly committed to free trade and has welcomed large amounts of foreign investment. Chile has signed free trade agreements (FTAs) with a whole network of countries, including an FTA with the United States that was signed in 2003 and implemented in January 2004.
According to the CIA World Factbook, Chile's "sound economic policies," maintained consistently since the 1980s, "have contributed to steady economic growth in Chile and have more than halved poverty rates." The 1973-90 military government sold many state-owned companies, and the three democratic governments since 1990 have continued privatization, though at a slower pace. The government's role in the economy is mostly limited to regulation, although the state continues to operate copper giant CODELCO and a few other enterprises (there is one state-run bank). Chile is strongly committed to free trade and has welcomed large amounts of foreign investment. Chile has signed free trade agreements (FTAs) with a whole network of countries, including an FTA with the United States that was signed in 2003 and implemented in January 2004.
Chile's independent Central Bank
pursues an inflation target of between 2% and 4%. Inflation has not exceeded 5% since 1998. Chile registered an inflation rate of 3.2% in 2006. The Chilean peso's rapid appreciation against the U.S. dollar in recent years has helped dampen inflation. Most wage settlements and loans are indexed, reducing inflation's volatility. Under the compulsory private pension system, most formal sector employees pay 10% of their salaries into privately managed funds.
As of 2006, Chile invested only 0.6% of its annual GDP in research and development (R&D). Even then, two-thirds of that was government spending. Beyond its general economic and political stability, the government has also encouraged the use of Chile as an "investment platform" for multinational corporations planning to operate in the region, but this will have limited value given the developing business climate in Chile itself. Chile's approach to foreign direct investment is codified in the country's Foreign Investment Law, which gives foreign investors the same treatment as Chileans. Registration is reported to be simple and transparent, and foreign investors are guaranteed access to the official foreign exchange market to repatriate their profits and capital.
Faced with an international economic downturn the government announced a $4 billion economic stimulus plan to spur employment and growth, and despite the global financial crisis, aimed for an expansion of between 2 percent and 3 percent of GDP for 2009. Nonetheless, economic analysts disagreed with government estimates and predicted economic growth at a median of 1.5 percent. According to the CIA World FactBook, the GDP contracted an estimated -1.7% in 2009.
The Chilean Government has formed a Council on Innovation and Competition, which is tasked with identifying new sectors and industries to promote. It is hoped that this, combined with some tax reforms to encourage domestic and foreign investment in research and development
, will bring in additional FDI to new parts of the economy.
Chile maintains one of the best credit ratings (S&P A+) in Latin America. There are three main ways for Chilean firms to raise funds abroad: bank loans, issuance of bonds, and the selling of stocks on U.S. markets through American Depository Receipts (ADRs). Nearly all of the funds raised through these means go to finance domestic Chilean investment. The government is required by law to run a fiscal surplus of at least 1% of GDP. In 2006, the Government of Chile ran a surplus of $11.3 billion, equal to almost 8% of GDP. The Government of Chile continues to pay down its foreign debt, with public debt only 3.9% of GDP at the end of 2006.
The main destinations for Chilean exports were the Americas (US $39 billion), Asia (US $27.8 billion) and Europe (US $22.2 billion). Seen as shares of Chile's export markets, 42% of exports went to the Americas, 30% to Asia and 24% to Europe. Within Chile's diversified network of trade relationships, its most important partner remained the United States. Total trade with the U.S. was US $14.8 billion in 2006. Since the U.S.-Chile Free Trade Agreement went into effect on January 1, 2004, U.S.-Chilean trade has increased by 154%. Internal Government of Chile figures show that even when factoring out inflation and the recent high price of copper, bilateral trade between the U.S. and Chile has grown over 60% since then.
Total trade with Europe also grew in 2006, expanding by 42%. The Netherlands and Italy were Chile's main European trading partners. Total trade with Asia also grew significantly at nearly 31%. Trade with Korea and Japan grew significantly, but China remained Chile's most important trading partner in Asia. Chile's total trade with China reached U.S. $8.8 billion in 2006, representing nearly 66% of the value of its trade relationship with Asia.
The growth of exports in 2006 was mainly caused by a strong increase in sales to the United States, the Netherlands, and Japan. These three markets alone accounted for an additional US $5.5 billion worth of Chilean exports. Chilean exports to the United States totaled US $9.3 billion, representing a 37.7% increase compared to 2005 (US $6.7 billion). Exports to the European Union were US $15.4 billion, a 63.7% increased compared to 2005 (US $9.4 billion). Exports to Asia increased from US $15.2 billion in 2005 to US $19.7 billion in 2006, a 29.9% increase.
During 2006, Chile imported US $26 billion from the Americas, representing 54% of total imports, followed by Asia at 22%, and Europe at 16%. Mercosur members were the main suppliers of imports to Chile at US $9.1 billion, followed by the United States with US $5.5 billion and the European Union with US $5.2 billion. From Asia, China was the most important exporter to Chile, with goods valued at US $3.6 billion. Year-on-year growth in imports was especially strong from a number of countries-Ecuador (123.9%), Thailand (72.1%), Korea (52.6%), and China (36.9%).
Chile's overall trade profile has traditionally been dependent upon copper exports. The state-owned firm CODELCO is the world's largest copper-producing company, with recorded copper reserves of 200 years. Chile has made an effort to expand nontraditional exports. The most important non-mineral exports are forestry and wood products, fresh fruit and processed food, fishmeal and seafood, and wine
.
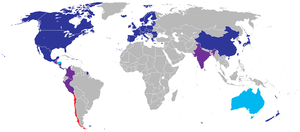 Over the last several years, Chile has signed FTAs with the European Union, South Korea, New Zealand, Singapore, Brunei, China, and Japan. It reached a partial trade agreement with India in 2005 and began negotiations for a full-fledged FTA with India in 2006. Chile conducted trade negotiations in 2007 with Australia, Malaysia, and Thailand, as well as with China to expand an existing agreement beyond just trade in goods. Chile concluded FTA negotiations with Australia and an expanded agreement with China in 2008. The members of the P4 (Chile, Singapore, New Zealand, and Brunei) also plan to conclude a chapter on finance and investment in 2008.
Over the last several years, Chile has signed FTAs with the European Union, South Korea, New Zealand, Singapore, Brunei, China, and Japan. It reached a partial trade agreement with India in 2005 and began negotiations for a full-fledged FTA with India in 2006. Chile conducted trade negotiations in 2007 with Australia, Malaysia, and Thailand, as well as with China to expand an existing agreement beyond just trade in goods. Chile concluded FTA negotiations with Australia and an expanded agreement with China in 2008. The members of the P4 (Chile, Singapore, New Zealand, and Brunei) also plan to conclude a chapter on finance and investment in 2008.
Successive Chilean governments have actively pursued trade-liberalizing agreements. During the 1990s, Chile signed free trade agreements (FTA) with Canada, Mexico, and Central America. Chile also concluded preferential trade agreements with Venezuela, Colombia, and Ecuador. An association agreement with Mercosur-Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay-went into effect in October 1996. Continuing its export-oriented development strategy, Chile completed landmark free trade agreements in 2002 with the European Union and South Korea. Chile, as a member of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) organization, is seeking to boost commercial ties to Asian markets. To that end, it has signed trade agreements in recent years with New Zealand, Singapore, Brunei, India, China, and most recently Japan. In 2007, Chile held trade negotiations with Australia, Thailand, Malaysia, and China. In 2008, Chile hopes to conclude an FTA with Australia, and finalize an expanded agreement (covering trade in services and investment) with China. The P4 (Chile, Singapore, New Zealand, and Brunei) also plan to expand ties through adding a finance and investment chapter to the existing P4 agreement. Chile's trade talks with Malaysia and Thailand are also scheduled to continue in 2008.
After two years of negotiations, the United States and Chile signed an agreement in June 2003 that will lead to completely duty-free bilateral trade within 12 years. The U.S.-Chile FTA entered into force January 1, 2004, following approval by the U.S. and Chilean congresses. The bilateral FTA has inaugurated greatly expanded U.S.-Chilean trade ties, with total bilateral trade jumping by 154% during the FTA's first three years.
Chile unilaterally lowered its across-the-board import tariff for all countries with which it does not have a trade agreement to 6% in 2003. Higher effective tariffs are charged only on imports of wheat, wheat flour, and sugar as a result of a system of import price bands. The price bands were ruled inconsistent with Chile's World Trade Organization
(WTO) obligations in 2002, and the government has introduced legislation to modify them. Under the terms of the U.S.-Chile FTA, the price bands will be completely phased out for U.S. imports of wheat, wheat flour, and sugar within 12 years.
Chile is a strong proponent of pressing ahead on negotiations for a Free Trade Area of the Americas
(FTAA) and is active in the WTO's Doha round of negotiations, principally through its membership in the G-20
and Cairns Group
.
. The percentage of Chileans with household incomes below the poverty line – defined as twice the cost of satisfying a person's minimal nutritional needs – fell from 45.1% in 1987 to 13.7% in 2006, according to government polls. Critics in Chile, however, argue that poverty figures are considerably higher than those officially published. (The government constructs the poverty line based on an outdated 1987 household consumption poll, instead of more recent polls from 1997 or 2007). According to these critics who use data from the 1997 poll, the poverty rate rises to 29%. Using the relative yardstick favoured in many European countries, 27% of Chileans would be poor, according to Juan Carlos Feres of the ECLAC.
Total foreign direct investment
(FDI) was only $3.4 billion in 2006, up 52% from a poor performance in 2005. However, 80% of FDI continues to go to only four sectors: electricity, gas, water and mining. Much of the jump in FDI in 2006 was also the result of acquisitions and mergers, but has done little to create new employment in Chile.
The percent of total income earned by the richest 20% of the Chilean population in 2000 was 61.0% of GDP, while the percent of total income earned by the poorest 20% of the Chilean population was 3.3% of GDP. Chile's Gini Coefficient
in 2003 (53.8) has slightly changed in comparison with the value in 1995 (56.4). In 2005 the 10% poorest among the Chileans received 1.2% of GNP
(2000 = 1.4%), while the 10% richest received 47% of GNP
(2000 = 46%).
Note: 2007 data are provisional, 2008-09 data are preliminary. Source: Central Bank of Chile, accessed on March 28, 2010.
Note: 2007 data are provisional, 2008-09 data are preliminary. GDP subtotal does not include VAT taxes
and import duties (ID); includes imputed bank fees (IB). GDP total = GDP subtotal - IB + VAT + ID. Source: Central Bank of Chile, accessed on March 28, 2010.
Note: Provisional data provided by the Chilean Central Bank's statistics database.
Chile
Chile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
is ranked as an upper-middle income economy by the World Bank
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for capital programmes.The World Bank's official goal is the reduction of poverty...
, and is one of South America
South America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
's most stable and prosperous nations, leading Latin American nations in human development
Human development (humanity)
Human development in the scope of humanity, specifically international development, is an international and economic development paradigm that is about much more than the rise or fall of national incomes. People are the real wealth of nations...
, competitiveness, income per capita, globalization, economic freedom, and low perception of corruption. However, it has a high economic inequality
Economic inequality
Economic inequality comprises all disparities in the distribution of economic assets and income. The term typically refers to inequality among individuals and groups within a society, but can also refer to inequality among countries. The issue of economic inequality is related to the ideas of...
, as measured by the Gini index.
In May 2010 Chile became the first South American country to join the OECD
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development is an international economic organisation of 34 countries founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade...
. In 2006, Chile became the country with the highest nominal GDP per capita in Latin America. Chile has an inequality-adjusted human development index of 0.634, compared to 0.509 and 0.562 for neighbouring Brazil and Argentina, respectively. 5.3% of the population lives on less than US $2 a day.
The Global Competitiveness Report
Global Competitiveness Report
The Global Competitiveness Report is a yearly report published by the World Economic Forum. The first report was released in 1979. The 2011–2012 report covers 142 major and emerging economies....
for 2009-2010 ranks Chile as being the 30th most competitive country in the world and the first in Latin America, well above from Brazil (56th), Mexico (60th) and Argentina which ranks 85th. The Ease of doing business index
Ease of Doing Business Index
The Ease of Doing Business Index is an index created by the World Bank. Higher rankings indicate better, usually simpler, regulations for businesses and stronger protections of property rights...
created by the World Bank
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for capital programmes.The World Bank's official goal is the reduction of poverty...
lists Chile as 43rd in the world that encompasses better, usually simpler, regulations for businesses and stronger protections of property rights. The privatized national pension system
Chile pension system
The Chile Pension system refers to old-age, disability and survivor pensions for workers in Chile. The pension system was changed by José Piñera, during Augusto Pinochets military government on November 4, 1980 from a PAYGO-system to a fully funded capitalization system run by private sector...
(AFP) has encouraged domestic investment and contributed to an estimated total domestic savings rate of approximately 21% of GDP.
History
After Spanish conquest in the 16th century Chilean economy came to revolve around autarchyc estates called fundos and around the army that was engaged in the Arauco WarArauco War
The Arauco War was a conflict between colonial Spaniards and the Mapuche people in what is now the Araucanía and Biobío regions of modern Chile...
. During early colonial times there were gold exports to Perú from placer deposit
Placer deposit
In geology, a placer deposit or placer is an accumulation of valuable minerals formed by gravity separation during sedimentary processes. The name is from the Spanish word placer, meaning "alluvial sand". Placer mining is an important source of gold, and was the main technique used in the early...
s which soon depleted. Trade restrictions and monopolies established by the Spanish crown are credited for having held back economic development for much of the colonial times. As effect of these restrictions the country incorporated very few new crops and animal breeds after initial conquest. Other sectors that were held back by restrictions were the wine and mining industries. The Bourbon reforms
Bourbon Reforms
The Bourbon Reforms were a set of economic and political legislation introduced by the Spanish Crown under various kings of the House of Bourbon throughout the 18th century. The reforms were intended to stimulate manufacturing and technology in order to modernize Spain...
in the 18th century eased many monopolies and trade restrictions.
In the 1830s Chile consolidated under the ideas of Diego Portales
Diego Portales
Diego José Pedro Víctor Portales Palazuelos was a Chilean statesman and entrepreneur. As a minister of president José Joaquín Prieto Diego Portales played a pivotal role in shaping the state and government politics in the 19th century, delivering with the Constitution of 1833 the framework of the...
as a stable state open to foreign trade. Foreign investment in Chile grew over the 19th century. After the War of the Pacific
War of the Pacific
The War of the Pacific took place in western South America from 1879 through 1883. Chile fought against Bolivia and Peru. Despite cooperation among the three nations in the war against Spain, disputes soon arose over the mineral-rich Peruvian provinces of Tarapaca, Tacna, and Arica, and the...
the Chilean treasury grew by 900%. The League of Nations
League of Nations
The League of Nations was an intergovernmental organization founded as a result of the Paris Peace Conference that ended the First World War. It was the first permanent international organization whose principal mission was to maintain world peace...
labeled Chile the country hardest hit by the Great Depression
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression in the decade preceding World War II. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations, but in most countries it started in about 1929 and lasted until the late 1930s or early 1940s...
because 80% of government revenue came from exports of copper and nitrates, which were in low demand. After the Great Depression Chilean economic policies changed toward import substitution industrialization and the Production Development Corporation
CORFO
Production Development Corporation is a Chilean governmental organization that was founded in 1939, by President Pedro Aguirre Cerda, to promote economic growth in Chile...
was established.
Under the influence of the Chicago Boys
Chicago Boys
The Chicago Boys were a group of young Chilean economists most of whom trained at the University of Chicago under Milton Friedman and Arnold Harberger, or at its affiliate in the economics department at the Catholic University of Chile...
the Pinochet regime made of Chile a leading country in establishing neoliberal policies which are attributed to have lifted the country to become one of the richest in Latin America. Despite a general selling of state property the regime retained the lucrative state owned mining company CODELCO
Codelco
CODELCO is the Chilean state owned copper mining company formed in 1976 from the foreign owned copper companies that were nationalised in 1971. The headquarters are in Santiago and the seven-man board of directors is appointed by the President of the Republic...
which stands for about 30% of government income.
According to the CIA World Factbook, during the early 1990s, Chile's "reputation as a role model for economic reform" was strengthened when the democratic government of Patricio Aylwin
Patricio Aylwin
Patricio Aylwin Azócar was the first president of Chile after its return to democratic rule in 1990, following the military dictatorship of General Augusto Pinochet.- Early life :...
, who took over from the military in 1990, deepened the economic reform initiated by the military government. Growth in real GDP averaged 8% from 1991–1997, but fell to half that level in 1998 because of tight monetary policies (implemented to keep the current account deficit in check) and because of lower export earnings, the latter which was a product of the Asian financial crisis. Chile's economy has since recovered and has seen growth rates of 5-7% over the past several years.
After a decade of impressive growth rates, Chile began to experience a moderate economic downturn in 1999, brought on by unfavorable global economic conditions related to the Asian financial crisis, which began in 1997. The economy remained sluggish until 2003, when it began to show clear signs of recovery, achieving 4.0% real GDP growth. The Chilean economy finished 2004 with growth of 6.0%. Real GDP growth reached 5.7% in 2005 before falling back to 4.0% in 2006. GDP expanded by 5.1% in 2007.
Agriculture
Agriculture and allied sectors like forestryForestry
Forestry is the interdisciplinary profession embracing the science, art, and craft of creating, managing, using, and conserving forests and associated resources in a sustainable manner to meet desired goals, needs, and values for human benefit. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands...
, logging
Logging
Logging is the cutting, skidding, on-site processing, and loading of trees or logs onto trucks.In forestry, the term logging is sometimes used in a narrow sense concerning the logistics of moving wood from the stump to somewhere outside the forest, usually a sawmill or a lumber yard...
and fishing
Fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch wild fish. Fish are normally caught in the wild. Techniques for catching fish include hand gathering, spearing, netting, angling and trapping....
accounts only for 4.9% of the GDP as of 2007 and employed 13.6% of the country's labor force
Labor force
In economics, a labor force or labour force is a region's combined civilian workforce, including both the employed and unemployed.Normally, the labor force of a country consists of everyone of working age In economics, a labor force or labour force is a region's combined civilian workforce,...
. Some major agriculture products of Chile includes grapes, apples, pears, onions, wheat, corn, oats, peaches, garlic, asparagus, beans, beef, poultry, wool, fish and timber.
Chile’s position in the Southern Hemisphere
Southern Hemisphere
The Southern Hemisphere is the part of Earth that lies south of the equator. The word hemisphere literally means 'half ball' or "half sphere"...
leads to an agricultural season cycle opposite to those of the principal consumer markets, primarily located in the Northern Hemisphere. Chile’s extreme north-south orientation produces 7 different macro-regions distinguished by climate and geographical features, which allows the country itself to stagger harvests and results in extended harvesting seasons. However, the mountainous landscape of Chile
Geography of Chile
Image:Chilenav.gif|thumb|417px|left|Click over the map to obtain a topographic map of the region and its toponymyrect 23 14 119 35 rect 23 35 119 44 rect 23 44 119 54 rect 23 54 119 65 rect 23 65 119 75 rect 23 75 119 85...
limits the extent and intensity of agriculture so that arable land corresponds only to 2.62% of the total territory. Through Chile’s trade agreements, its agricultural products have gained access to a market controlling 77% of the world’s GDP and by approximately 2012, 74% of Chilean agribusiness exports will be duty free.
Chiles principal growing region
Growing region
A growing region is an area suited by climate and soil conditions to the cultivation of a certain type of crop or plant group.Most crops are cultivated not in one place only, but in several distinct regions in diverse parts of the world...
and agricultural heartland is the Central Valley
Chilean Central Valley
The Central Valley , Intermediate Depression or Longitudinal Valley is the depression between the Chilean Costal Range and the Andes Mountains. The central valley should not be confused with Central Chile that encompasses part of the valley...
delimited by the Chilean Coast Range
Chilean Coast Range
The Chilean Coastal Range is a mountain range that runs from north to south along the Pacific coast of South America parallel to the Andean Mountains, extending from Morro de Arica in the north to Taitao Peninsula, where it ends at the Chile Triple Junction, in the south. The range has a strong...
in the west, the Andes
Andes
The Andes is the world's longest continental mountain range. It is a continual range of highlands along the western coast of South America. This range is about long, about to wide , and of an average height of about .Along its length, the Andes is split into several ranges, which are separated...
in the east Aconcagua River
Aconcagua River
For other uses, see Aconcagua .The Aconcagua River is a river in Chile that rises from the joint of two minor tributary rivers at above sea level in the Andes, Juncal river from the east and Blanco river from the south east...
by the north and Bío-Bío River
Bío-Bío River
The Biobío River is the second largest river in Chile. It originates from Icalma and Galletué lakes in the Andes and flows 380 km to the Gulf of Arauco on the Pacific Ocean....
by the south. In the northern half of Chile cultivation is highly dependent on irrigation
Irrigation
Irrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
. South of the Central Valley cultivation is gradually replaced by aquaculture
Aquaculture
Aquaculture, also known as aquafarming, is the farming of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, molluscs and aquatic plants. Aquaculture involves cultivating freshwater and saltwater populations under controlled conditions, and can be contrasted with commercial fishing, which is the...
, silviculture
Silviculture
Silviculture is the practice of controlling the establishment, growth, composition, health, and quality of forests to meet diverse needs and values. The name comes from the Latin silvi- + culture...
, sheep and cattle
Cattle
Cattle are the most common type of large domesticated ungulates. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae, are the most widespread species of the genus Bos, and are most commonly classified collectively as Bos primigenius...
farming.
Salmon
Chile is the second largest producer of salmonSalmon
Salmon is the common name for several species of fish in the family Salmonidae. Several other fish in the same family are called trout; the difference is often said to be that salmon migrate and trout are resident, but this distinction does not strictly hold true...
in the world. As of August 2007, Chile’s share of worldwide salmon industry sales was 38.2%, rising from just 10% in 1990. The average growth rate of the industry for the 20 years between 1984 and 2004 was 42% per year. The presence of large foreign firms in the salmon industry has brought what probably most contributes to Chile’s burgeoning salmon production, technology. Technology transfer has allowed Chile to build its global competitiveness and innovation and has led to the expansion of production as well as to an increase in average firm size in the industry.
Forestry
The Chilean forestry industry grew to comprise 13% of the country’s total exports in 2005, making it one of the largest export sectors for Chile. Radiata Pine and EucalyptusEucalyptus
Eucalyptus is a diverse genus of flowering trees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Members of the genus dominate the tree flora of Australia...
comprise the vast majority of Chile's forestry exports. Within the forestry sector, the largest contributor to total production is pulp
Pulp (paper)
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibres from wood, fibre crops or waste paper. Wood pulp is the most common raw material in papermaking.-History:...
, followed by wood-based panels and lumber
Lumber
Lumber or timber is wood in any of its stages from felling through readiness for use as structural material for construction, or wood pulp for paper production....
. Due to popular and increasing demands for Chile’s forestry products, the government is currently focusing on increasing the already vast acreage of Chile’s Pine and Eucalyptus plantations as well as opening new industrial plants.
Mining

Finance
Chile's financial sector has grown quickly in recent years, with a banking reform law approved in 1997 that broadened the scope of permissible foreign activity for Chilean banks. The Chilean Government implemented a further liberalization of capital markets in 2001, and there is further pending legislation proposing further liberalization. Over the last ten years, Chileans have enjoyed the introduction of new financial tools such as home equity loans, currency futures and options, factoring, leasing, and debit cards. The introduction of these new products has also been accompanied by an increased use of traditional instruments such as loans and credit cards. Chile's private pension system, with assets worth roughly $70 billion at the end of 2006, has been an important source of investment capital for the capital market. However, by 2009, it has been reported that $21 billion had been lost from the pension system to the global financial crisis.Tourism
Tourism in Chile has experienced sustained growth over the last decades. ChileChile
Chile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
received about 2.25 million foreign visitors in 2006, up to 2.50 million in 2007
The percentages of foreign tourists arrivals by land, air and sea were, respectively, 55.3%, 40.5% and 4.2% for that year. The two main gateways for international tourists visiting Chile are Comodoro Arturo Merino Benítez International Airport
Comodoro Arturo Merino Benítez International Airport
Comodoro Arturo Merino Benítez International Airport , also known as Pudahuel Airport and Santiago International Airport, located in Pudahuel, north-west of downtown Santiago, is Chile's largest aviation facility and the busiest international air passenger gateway to the country...
and Paso Los Libertadores
Paso Libertadores
The Paso Internacional Los Libertadores, also called Cristo Redentor, is a mountain pass in the Andes between Argentina and Chile. It is the main transport route out of Chilean capital city Santiago into Mendoza city in Argentina and so carries quite heavy traffic.From the Argentine side the...
.
Chile a great diversity of natural landscapes, from the Mars-like landscapes of the hyperarid Atacama Desert
Atacama Desert
The Atacama Desert is a plateau in South America, covering a strip of land on the Pacific coast, west of the Andes mountains. It is, according to NASA, National Geographic and many other publications, the driest desert in the world...
to the glacier-fed fjords of the Chilean Patagonia
Patagonia
Patagonia is a region located in Argentina and Chile, integrating the southernmost section of the Andes mountains to the southwest towards the Pacific ocean and from the east of the cordillera to the valleys it follows south through Colorado River towards Carmen de Patagones in the Atlantic Ocean...
, passing by the winelands backdropped by the Andes
Andes
The Andes is the world's longest continental mountain range. It is a continual range of highlands along the western coast of South America. This range is about long, about to wide , and of an average height of about .Along its length, the Andes is split into several ranges, which are separated...
of the Central Valley
Chilean Central Valley
The Central Valley , Intermediate Depression or Longitudinal Valley is the depression between the Chilean Costal Range and the Andes Mountains. The central valley should not be confused with Central Chile that encompasses part of the valley...
and the old-growth forests of the Lakes District. Easter Island
Easter Island
Easter Island is a Polynesian island in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian triangle. A special territory of Chile that was annexed in 1888, Easter Island is famous for its 887 extant monumental statues, called moai, created by the early Rapanui people...
and Juan Fernández Archipelago, including Robinson Crusoe Island
Robinson Crusoe Island
Robinson Crusoe Island , formerly known as Más a Tierra , or Aguas Buenas, is the largest island of the Chilean Juan Fernández archipelago, situated 674 kilometres west of South America in the South Pacific Ocean...
, are also major attractions.
Many of the most visited attractions in Chile are protected areas. The extensive Chilean protected areas
Protected areas of Chile
The protected areas of Chile are areas that have natural beauty or significant historical value protected by the government of Chile. These protected areas cover over , which is 19% of the territory of Chile...
system includes 32 national parks, 48 natural reserves and 15 natural monuments.
Economic policies

Chile's independent Central Bank
Central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, or monetary authority is a public institution that usually issues the currency, regulates the money supply, and controls the interest rates in a country. Central banks often also oversee the commercial banking system of their respective countries...
pursues an inflation target of between 2% and 4%. Inflation has not exceeded 5% since 1998. Chile registered an inflation rate of 3.2% in 2006. The Chilean peso's rapid appreciation against the U.S. dollar in recent years has helped dampen inflation. Most wage settlements and loans are indexed, reducing inflation's volatility. Under the compulsory private pension system, most formal sector employees pay 10% of their salaries into privately managed funds.
As of 2006, Chile invested only 0.6% of its annual GDP in research and development (R&D). Even then, two-thirds of that was government spending. Beyond its general economic and political stability, the government has also encouraged the use of Chile as an "investment platform" for multinational corporations planning to operate in the region, but this will have limited value given the developing business climate in Chile itself. Chile's approach to foreign direct investment is codified in the country's Foreign Investment Law, which gives foreign investors the same treatment as Chileans. Registration is reported to be simple and transparent, and foreign investors are guaranteed access to the official foreign exchange market to repatriate their profits and capital.
Faced with an international economic downturn the government announced a $4 billion economic stimulus plan to spur employment and growth, and despite the global financial crisis, aimed for an expansion of between 2 percent and 3 percent of GDP for 2009. Nonetheless, economic analysts disagreed with government estimates and predicted economic growth at a median of 1.5 percent. According to the CIA World FactBook, the GDP contracted an estimated -1.7% in 2009.
The Chilean Government has formed a Council on Innovation and Competition, which is tasked with identifying new sectors and industries to promote. It is hoped that this, combined with some tax reforms to encourage domestic and foreign investment in research and development
Research and development
The phrase research and development , according to the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, refers to "creative work undertaken on a systematic basis in order to increase the stock of knowledge, including knowledge of man, culture and society, and the use of this stock of...
, will bring in additional FDI to new parts of the economy.
Chile maintains one of the best credit ratings (S&P A+) in Latin America. There are three main ways for Chilean firms to raise funds abroad: bank loans, issuance of bonds, and the selling of stocks on U.S. markets through American Depository Receipts (ADRs). Nearly all of the funds raised through these means go to finance domestic Chilean investment. The government is required by law to run a fiscal surplus of at least 1% of GDP. In 2006, the Government of Chile ran a surplus of $11.3 billion, equal to almost 8% of GDP. The Government of Chile continues to pay down its foreign debt, with public debt only 3.9% of GDP at the end of 2006.
Foreign trade
2006 was a record year for Chilean trade. Total trade registered a 31% increase over 2005. During 2006, exports of goods and services totaled US $58 billion, an increase of 41%. This figure was somewhat distorted by the skyrocketing price of copper. In 2006, copper exports reached a historical high of US $33.3 billion. Imports totaled US $35 billion, an increase of 17% compared to the previous year. Chile thus recorded a positive trade balance of US $23 billion in 2006.The main destinations for Chilean exports were the Americas (US $39 billion), Asia (US $27.8 billion) and Europe (US $22.2 billion). Seen as shares of Chile's export markets, 42% of exports went to the Americas, 30% to Asia and 24% to Europe. Within Chile's diversified network of trade relationships, its most important partner remained the United States. Total trade with the U.S. was US $14.8 billion in 2006. Since the U.S.-Chile Free Trade Agreement went into effect on January 1, 2004, U.S.-Chilean trade has increased by 154%. Internal Government of Chile figures show that even when factoring out inflation and the recent high price of copper, bilateral trade between the U.S. and Chile has grown over 60% since then.
Total trade with Europe also grew in 2006, expanding by 42%. The Netherlands and Italy were Chile's main European trading partners. Total trade with Asia also grew significantly at nearly 31%. Trade with Korea and Japan grew significantly, but China remained Chile's most important trading partner in Asia. Chile's total trade with China reached U.S. $8.8 billion in 2006, representing nearly 66% of the value of its trade relationship with Asia.
The growth of exports in 2006 was mainly caused by a strong increase in sales to the United States, the Netherlands, and Japan. These three markets alone accounted for an additional US $5.5 billion worth of Chilean exports. Chilean exports to the United States totaled US $9.3 billion, representing a 37.7% increase compared to 2005 (US $6.7 billion). Exports to the European Union were US $15.4 billion, a 63.7% increased compared to 2005 (US $9.4 billion). Exports to Asia increased from US $15.2 billion in 2005 to US $19.7 billion in 2006, a 29.9% increase.
During 2006, Chile imported US $26 billion from the Americas, representing 54% of total imports, followed by Asia at 22%, and Europe at 16%. Mercosur members were the main suppliers of imports to Chile at US $9.1 billion, followed by the United States with US $5.5 billion and the European Union with US $5.2 billion. From Asia, China was the most important exporter to Chile, with goods valued at US $3.6 billion. Year-on-year growth in imports was especially strong from a number of countries-Ecuador (123.9%), Thailand (72.1%), Korea (52.6%), and China (36.9%).
Chile's overall trade profile has traditionally been dependent upon copper exports. The state-owned firm CODELCO is the world's largest copper-producing company, with recorded copper reserves of 200 years. Chile has made an effort to expand nontraditional exports. The most important non-mineral exports are forestry and wood products, fresh fruit and processed food, fishmeal and seafood, and wine
Chilean wine
Chilean wine is wine made in the South American country of Chile. The region has a long viticultural history for a New World wine region dating to the 16th century when the Spanish conquistadors brought Vitis vinifera vines with them as they colonized the region. In the mid-19th century, French...
.
Trade agreements

Successive Chilean governments have actively pursued trade-liberalizing agreements. During the 1990s, Chile signed free trade agreements (FTA) with Canada, Mexico, and Central America. Chile also concluded preferential trade agreements with Venezuela, Colombia, and Ecuador. An association agreement with Mercosur-Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay-went into effect in October 1996. Continuing its export-oriented development strategy, Chile completed landmark free trade agreements in 2002 with the European Union and South Korea. Chile, as a member of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) organization, is seeking to boost commercial ties to Asian markets. To that end, it has signed trade agreements in recent years with New Zealand, Singapore, Brunei, India, China, and most recently Japan. In 2007, Chile held trade negotiations with Australia, Thailand, Malaysia, and China. In 2008, Chile hopes to conclude an FTA with Australia, and finalize an expanded agreement (covering trade in services and investment) with China. The P4 (Chile, Singapore, New Zealand, and Brunei) also plan to expand ties through adding a finance and investment chapter to the existing P4 agreement. Chile's trade talks with Malaysia and Thailand are also scheduled to continue in 2008.
After two years of negotiations, the United States and Chile signed an agreement in June 2003 that will lead to completely duty-free bilateral trade within 12 years. The U.S.-Chile FTA entered into force January 1, 2004, following approval by the U.S. and Chilean congresses. The bilateral FTA has inaugurated greatly expanded U.S.-Chilean trade ties, with total bilateral trade jumping by 154% during the FTA's first three years.
Chile unilaterally lowered its across-the-board import tariff for all countries with which it does not have a trade agreement to 6% in 2003. Higher effective tariffs are charged only on imports of wheat, wheat flour, and sugar as a result of a system of import price bands. The price bands were ruled inconsistent with Chile's World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization is an organization that intends to supervise and liberalize international trade. The organization officially commenced on January 1, 1995 under the Marrakech Agreement, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade , which commenced in 1948...
(WTO) obligations in 2002, and the government has introduced legislation to modify them. Under the terms of the U.S.-Chile FTA, the price bands will be completely phased out for U.S. imports of wheat, wheat flour, and sugar within 12 years.
Chile is a strong proponent of pressing ahead on negotiations for a Free Trade Area of the Americas
Free Trade Area of the Americas
The Free Trade Area of the Americas , , ) was a proposed agreement to eliminate or reduce the trade barriers among all countries in the Americas but Cuba. In the last round of negotiations, trade ministers from 34 countries met in Miami, United States, in November 2003 to discuss the proposal...
(FTAA) and is active in the WTO's Doha round of negotiations, principally through its membership in the G-20
G20 developing nations
The G20 is a bloc of developing nations established on 20 August 2003. Distinct and separate from the G-20 major economies, the group emerged at the 5th Ministerial WTO conference, held in Cancún, Mexico, from 10 September to 14 September 2003...
and Cairns Group
Cairns Group
The Cairns Group is an interest group of 19 agricultural exporting countries, composed of Argentina, Australia, Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Guatemala, Indonesia, Malaysia, New Zealand, Pakistan, Paraguay, Peru, the Philippines, South Africa, Thailand, and Uruguay.-History...
.
Issues
Unemployment hovered at 8%-10% after the start of the economic slowdown in 1999, above the 7% average for the 1990s. Unemployment finally dipped to 7.8% in 2006, and continued to fall in 2007, averaging 6.8% monthly (up to August). Wages have risen faster than inflation as a result of higher productivity, boosting national living standardsStandard of living
Standard of living is generally measured by standards such as real income per person and poverty rate. Other measures such as access and quality of health care, income growth inequality and educational standards are also used. Examples are access to certain goods , or measures of health such as...
. The percentage of Chileans with household incomes below the poverty line – defined as twice the cost of satisfying a person's minimal nutritional needs – fell from 45.1% in 1987 to 13.7% in 2006, according to government polls. Critics in Chile, however, argue that poverty figures are considerably higher than those officially published. (The government constructs the poverty line based on an outdated 1987 household consumption poll, instead of more recent polls from 1997 or 2007). According to these critics who use data from the 1997 poll, the poverty rate rises to 29%. Using the relative yardstick favoured in many European countries, 27% of Chileans would be poor, according to Juan Carlos Feres of the ECLAC.
Total foreign direct investment
Foreign direct investment
Foreign direct investment or foreign investment refers to the net inflows of investment to acquire a lasting management interest in an enterprise operating in an economy other than that of the investor.. It is the sum of equity capital,other long-term capital, and short-term capital as shown in...
(FDI) was only $3.4 billion in 2006, up 52% from a poor performance in 2005. However, 80% of FDI continues to go to only four sectors: electricity, gas, water and mining. Much of the jump in FDI in 2006 was also the result of acquisitions and mergers, but has done little to create new employment in Chile.
The percent of total income earned by the richest 20% of the Chilean population in 2000 was 61.0% of GDP, while the percent of total income earned by the poorest 20% of the Chilean population was 3.3% of GDP. Chile's Gini Coefficient
Gini coefficient
The Gini coefficient is a measure of statistical dispersion developed by the Italian statistician and sociologist Corrado Gini and published in his 1912 paper "Variability and Mutability" ....
in 2003 (53.8) has slightly changed in comparison with the value in 1995 (56.4). In 2005 the 10% poorest among the Chileans received 1.2% of GNP
GNP
Gross National Product is the market value of all products and services produced in one year by labor and property supplied by the residents of a country...
(2000 = 1.4%), while the 10% richest received 47% of GNP
GNP
Gross National Product is the market value of all products and services produced in one year by labor and property supplied by the residents of a country...
(2000 = 46%).
GDP composition
Main macroeconomic aggregates of GDP.| Sector | 2003-09 (%) | 2009 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Private consumption Consumption (economics) Consumption is a common concept in economics, and gives rise to derived concepts such as consumer debt. Generally, consumption is defined in part by comparison to production. But the precise definition can vary because different schools of economists define production quite differently... |
58.3 | 59.8 |
| Government consumption Government spending Government spending includes all government consumption, investment but excludes transfer payments made by a state. Government acquisition of goods and services for current use to directly satisfy individual or collective needs of the members of the community is classed as government final... |
11.6 | 13.4 |
| Changes in inventories | 0.4 | -2.4 |
| Gross fixed capital formation Gross fixed capital formation Gross fixed capital formation is a macroeconomic concept used in official national accounts such as the UNSNA, NIPAs and the European System of Accounts . The concept dates back to the NBER studies of Simon Kuznets of capital formation in the 1930s, and standard measures for it were adopted in the... |
20.8 | 21.4 |
| (Exports) | (42.1) | (38.1) |
| (Imports) | (33.1) | (30.4) |
| Exports - Imports | 8.9 | 7.8 |
| GDP | 100.00 | 100.00 |
Note: 2007 data are provisional, 2008-09 data are preliminary. Source: Central Bank of Chile, accessed on March 28, 2010.
GDP by sector
Gross domestic product by sector of the economy.| Sector | 2003-09 (%) | 2009 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture Agriculture in Chile Agriculture in Chile encompasses a wide range of different activities due its particular geography, climate and geology and human factors. Historically agriculture is one of the bases of Chile's economy, now agriculture and allied sectors like forestry, logging and fishing accounts only for 4.9% of... and forestry Forestry Forestry is the interdisciplinary profession embracing the science, art, and craft of creating, managing, using, and conserving forests and associated resources in a sustainable manner to meet desired goals, needs, and values for human benefit. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands... |
3.1 | 2.6 |
| Fishing Fishing in Chile Fishing in Chile is a major industry with a total catch of 4,442,877 tons of fishes in 2006. Due to the Humboldt Current the Chilean Sea is considered among the most productive marine ecosystems in the world as well as the largest upwelling system. Artisan fishing is practised all over Chile's... |
1.0 | 0.8 |
| Mining Mining in Chile HOWDY PARTNER!:D.. The sector in Chile is one of the pillars of Chilean economy and copper exports alone stands for more than one third of government income. Most mining in Chile is concentrated to the Norte Grande region spanning most of the Atacama Desert...
|
17.4 15.6 1.8 |
16.4 14.4 2.0 |
| Manufacturing industry Manufacturing Manufacturing is the use of machines, tools and labor to produce goods for use or sale. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech, but is most commonly applied to industrial production, in which raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale... Drink A drink, or beverage, is a liquid which is specifically prepared for human consumption. In addition to fulfilling a basic human need, beverages form part of the culture of human society.-Water:... and tobacco Tobacco Tobacco is an agricultural product processed from the leaves of plants in the genus Nicotiana. It can be consumed, used as a pesticide and, in the form of nicotine tartrate, used in some medicines... Textile A textile or cloth is a flexible woven material consisting of a network of natural or artificial fibres often referred to as thread or yarn. Yarn is produced by spinning raw fibres of wool, flax, cotton, or other material to produce long strands... , clothing Clothing Clothing refers to any covering for the human body that is worn. The wearing of clothing is exclusively a human characteristic and is a feature of nearly all human societies... and leather Leather Leather is a durable and flexible material created via the tanning of putrescible animal rawhide and skin, primarily cattlehide. It can be produced through different manufacturing processes, ranging from cottage industry to heavy industry.-Forms:... Wood Wood is a hard, fibrous tissue found in many trees. It has been used for hundreds of thousands of years for both fuel and as a construction material. It is an organic material, a natural composite of cellulose fibers embedded in a matrix of lignin which resists compression... and furniture Furniture Furniture is the mass noun for the movable objects intended to support various human activities such as seating and sleeping in beds, to hold objects at a convenient height for work using horizontal surfaces above the ground, or to store things... Paper Paper is a thin material mainly used for writing upon, printing upon, drawing or for packaging. It is produced by pressing together moist fibers, typically cellulose pulp derived from wood, rags or grasses, and drying them into flexible sheets.... and printing Printing Printing is a process for reproducing text and image, typically with ink on paper using a printing press. It is often carried out as a large-scale industrial process, and is an essential part of publishing and transaction printing.... Petroleum Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling... , rubber Rubber Natural rubber, also called India rubber or caoutchouc, is an elastomer that was originally derived from latex, a milky colloid produced by some plants. The plants would be ‘tapped’, that is, an incision made into the bark of the tree and the sticky, milk colored latex sap collected and refined... and plastic Plastic A plastic material is any of a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic organic solids used in the manufacture of industrial products. Plastics are typically polymers of high molecular mass, and may contain other substances to improve performance and/or reduce production costs... |
14.8 4.6 0.6 0.9 1.4 3.8 1.4 2.1 |
12.7 4.7 0.3 0.5 1.1 2.9 1.0 2.2 |
| Electricity Electricity Electricity is a general term encompassing a variety of phenomena resulting from the presence and flow of electric charge. These include many easily recognizable phenomena, such as lightning, static electricity, and the flow of electrical current in an electrical wire... , gas Gas Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons... and water Water Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a... |
3.3 | 5.0 |
| Construction Construction In the fields of architecture and civil engineering, construction is a process that consists of the building or assembling of infrastructure. Far from being a single activity, large scale construction is a feat of human multitasking... |
7.1 | 8.0 |
| Retail Retail Retail consists of the sale of physical goods or merchandise from a fixed location, such as a department store, boutique or kiosk, or by mail, in small or individual lots for direct consumption by the purchaser. Retailing may include subordinated services, such as delivery. Purchasers may be... , restaurants and hotels |
9.4 | 9.4 |
| Transportation | 6.3 | 5.8 |
| Communications | 2.2 | 2.3 |
| Financial services Financial services Financial services refer to services provided by the finance industry. The finance industry encompasses a broad range of organizations that deal with the management of money. Among these organizations are credit unions, banks, credit card companies, insurance companies, consumer finance companies,... |
15.1 | 15.9 |
| Real estate Real estate In general use, esp. North American, 'real estate' is taken to mean "Property consisting of land and the buildings on it, along with its natural resources such as crops, minerals, or water; immovable property of this nature; an interest vested in this; an item of real property; buildings or... |
5.2 | 5.1 |
| Personal services (health, education, and so on.) | 10.9 | 11.8 |
| Public administration Public administration Public Administration houses the implementation of government policy and an academic discipline that studies this implementation and that prepares civil servants for this work. As a "field of inquiry with a diverse scope" its "fundamental goal..... |
4.2 | 4.5 |
| GDP subtotal | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| GDP rest | 5.3 | 5.6 |
| GDP total millions of current Chilean pesos billions of current U.S. dollars |
100.0 — — |
100.0 91,591,252 163.670 |
Note: 2007 data are provisional, 2008-09 data are preliminary. GDP subtotal does not include VAT taxes
Value added tax
A value added tax or value-added tax is a form of consumption tax. From the perspective of the buyer, it is a tax on the purchase price. From that of the seller, it is a tax only on the "value added" to a product, material or service, from an accounting point of view, by this stage of its...
and import duties (ID); includes imputed bank fees (IB). GDP total = GDP subtotal - IB + VAT + ID. Source: Central Bank of Chile, accessed on March 28, 2010.
Top exports
Chile's top exports in 2008.| Export | % |
|---|---|
| Mining Mining in Chile HOWDY PARTNER!:D.. The sector in Chile is one of the pillars of Chilean economy and copper exports alone stands for more than one third of government income. Most mining in Chile is concentrated to the Norte Grande region spanning most of the Atacama Desert...
|
49.46 42.49 4.36 |
| Agriculture Agriculture Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the... , forestry Forestry Forestry is the interdisciplinary profession embracing the science, art, and craft of creating, managing, using, and conserving forests and associated resources in a sustainable manner to meet desired goals, needs, and values for human benefit. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands... and fishing Fishing Fishing is the activity of trying to catch wild fish. Fish are normally caught in the wild. Techniques for catching fish include hand gathering, spearing, netting, angling and trapping.... Fruit In broad terms, a fruit is a structure of a plant that contains its seeds.The term has different meanings dependent on context. In non-technical usage, such as food preparation, fruit normally means the fleshy seed-associated structures of certain plants that are sweet and edible in the raw state,... Grape A grape is a non-climacteric fruit, specifically a berry, that grows on the perennial and deciduous woody vines of the genus Vitis. Grapes can be eaten raw or they can be used for making jam, juice, jelly, vinegar, wine, grape seed extracts, raisins, molasses and grape seed oil. Grapes are also... |
5.04 4.33 1.63 |
| Industrial Industry Industry refers to the production of an economic good or service within an economy.-Industrial sectors:There are four key industrial economic sectors: the primary sector, largely raw material extraction industries such as mining and farming; the secondary sector, involving refining, construction,... Salmon Salmon is the common name for several species of fish in the family Salmonidae. Several other fish in the same family are called trout; the difference is often said to be that salmon migrate and trout are resident, but this distinction does not strictly hold true... and trout Trout Trout is the name for a number of species of freshwater and saltwater fish belonging to the Salmoninae subfamily of the family Salmonidae. Salmon belong to the same family as trout. Most salmon species spend almost all their lives in salt water... Chilean wine Chilean wine is wine made in the South American country of Chile. The region has a long viticultural history for a New World wine region dating to the 16th century when the Spanish conquistadors brought Vitis vinifera vines with them as they colonized the region. In the mid-19th century, French... Forestry Forestry is the interdisciplinary profession embracing the science, art, and craft of creating, managing, using, and conserving forests and associated resources in a sustainable manner to meet desired goals, needs, and values for human benefit. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands... and wood furniture Furniture Furniture is the mass noun for the movable objects intended to support various human activities such as seating and sleeping in beds, to hold objects at a convenient height for work using horizontal surfaces above the ground, or to store things... Cellulose Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to over ten thousand β linked D-glucose units.... , paper Paper Paper is a thin material mainly used for writing upon, printing upon, drawing or for packaging. It is produced by pressing together moist fibers, typically cellulose pulp derived from wood, rags or grasses, and drying them into flexible sheets.... and others |
27.45 9.03 3.01 1.78 2.78 4.27 4.94 2.15 |
| Other | 4.11 |
| Goods total | 86.07 |
| Transport Transport Transport or transportation is the movement of people, cattle, animals and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, rail, road, water, cable, pipeline, and space. The field can be divided into infrastructure, vehicles, and operations... Ship transport Ship transport is watercraft carrying people or goods . Sea transport has been the largest carrier of freight throughout recorded history. Although the importance of sea travel for passengers has decreased due to aviation, it is effective for short trips and pleasure cruises... Aviation Aviation is the design, development, production, operation, and use of aircraft, especially heavier-than-air aircraft. Aviation is derived from avis, the Latin word for bird.-History:... |
8.26 5.22 2.62 |
| Travel Travel Travel is the movement of people or objects between relatively distant geographical locations. 'Travel' can also include relatively short stays between successive movements.-Etymology:... |
2.28 |
| Other |
3.39 |
| Services total | 13.93 |
| Total exports billions of US dollars United States dollar The United States dollar , also referred to as the American dollar, is the official currency of the United States of America. It is divided into 100 smaller units called cents or pennies.... FOB FOB (shipping) FOB is an initialism which pertains to the shipping of goods. Depending on specific usage, it may stand for Free On Board or Freight On Board. FOB specifies which party pays for which shipment and loading costs, and/or where responsibility for the goods is transferred... |
100.00 77.210 |
Note: Provisional data provided by the Chilean Central Bank's statistics database.

