
Economy of Mexico
Encyclopedia
The economy of Mexico
is the 13th largest in the world in nominal terms and the 11th by purchasing power parity, according to the World Bank.
Since the 1994 crisis
, administrations have improved the country's macroeconomic fundamentals
. Mexico was not significantly influenced by the recent 2002 South American crisis
, and maintained positive, although low, rates of growth after a brief period of stagnation in 2001. However, Mexico was one of the Latin American nations most affected by the 2008 recession with its Gross Domestic Product contracting by more than 6%. Moody's
(in March 2000) and Fitch IBCA (in January 2002) issued investment-grade ratings for Mexico's sovereign debt. In spite of its unprecedented macroeconomic stability, which has reduced inflation and interest rates to record lows and has increased per capita income, enormous gaps remain between the urban and the rural population, the northern and southern states, and the rich and the poor. Some of the government's challenges include the upgrade of infrastructure, the modernization of the tax system and labor laws, and the reduction of income inequality.
The economy contains rapidly developing modern industrial and service sectors, with increasing private ownership. Recent administrations have expanded competition in ports, railroads, telecommunications, electricity generation
, natural gas distribution and airports, with the aim of upgrading infrastructure. As an export-oriented economy, more than 90% of Mexican trade is under free trade agreements (FTAs) with more than 40 countries, including the European Union, Japan, Israel, and much of Central
and South America. The most influential FTA is the North American Free Trade Agreement
(NAFTA), which came into effect in 1994, and was signed in 1992 by the governments of the United States, Canada and Mexico. In 2006, trade with Mexico's two northern partners accounted for almost 90% of its exports and 55% of its imports. Recently, the Congress of the Union approved important tax, pension and judicial reforms, and reform to the oil industry is currently being debated. According to the Forbes Global 2000 list of the world's largest companies in 2008, Mexico had 16 companies in the list.
The annual Mexico Investment Summit takes place in Mexico City
covering the development and investment opportunities and challenges across Mexican private equity, venture capital, infrastructure, real estate, agriculture, tourism, energy and natural resources evolving in the country's economy.
brought unprecedented economic growth during the last quarter of the nineteenth century. This growth was accompanied by foreign investment and European immigration, the development of an efficient railroad network and the exploitation of the country's natural resources. Annual economic growth between 1876 and 1910 averaged 3.3%. Political repression and fraud, as well as huge income inequalities exacerbated by the land distribution system based on latifundios
, in which large hacienda
s were owned by a few but worked by millions of underpaid peasants living in precarious conditions, led to the Mexican Revolution
(1910–1917), an armed conflict that drastically transformed Mexico's political, social, cultural, and economical structure during the twentieth century under a premise of social democracy. The war itself, however, left a harsh toll in the economy and population, which decreased over the 11-year period between 1910 and 1921. The reconstruction of the country was to take place in the following decades.
The period from 1930 to 1970 was dubbed by economic historians as the "Mexican Miracle", a period of economic growth spurred by a model of import substitution industrialization (ISI) which protected and promoted the development of national industries. Through the ISI model, the country experienced an economic boom through which industries rapidly expanded their production. Important changes in the economic structure included free land distribution to peasants under the concept of ejido
, the nationalization of the oil and railroad companies, the introduction of social rights into the constitution, the birth of large and influential labor unions, and the upgrading of infrastructure. While population doubled from 1940 to 1970, GDP increased sixfold.
The ISI model had reached its peaked in the late 1960s. During the 1970s, the administrations of Echeverría
and López Portillo
, tried to include social development in their policies, an effort that entailed more public spending. With the discovery of vast oil fields in a time in which oil prices were surging and international interest rates were low -and even negative- the government decided to borrow from international capital markets to invest in the state-owned oil company, which in turn seemed to provide a long-run income source to promote social welfare. In fact, this method produced a remarkable growth in public expenditure, and president López Portillo announced that the time had come to learn to "manage prosperity" as Mexico multiplied its oil production to become the world's fourth largest exporter.
In the period of 1981–1982 the international panorama changed abruptly: oil prices plunged
and interest rates rose. In 1982, president López Portillo, just before ending his administration, suspended payments of foreign debt, devalued the peso
and nationalized the banking system, along with many other industries that were severely affected by the crisis, among them the steel industry. While import substitution had produced an era of industrialization in previous decades, by the 1980s it was evident that that protracted protection had produced an uncompetitive industrial sector with low productivity gains.
President de la Madrid
was the first of a series of presidents that began to implement neoliberal
reforms. After the crisis of 1982, lenders were unwilling to return to Mexico and, in order to keep the current account in balance, the government resorted to currency devaluations, which in turn sparked unprecedented inflation, which reached a historic high in 1987 at 159.7%.
The first step toward the liberalization of trade was Mexico's signature of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade
(GATT) in 1986. During the Salinas administration many state-owned companies were privatized. In 1992, the North American Free Trade Agreement
was signed between the United States, Canada and Mexico, and after the signature of two additional supplements on environments and labor standards, it came into effect on January 1, 1994. Salinas also introduced strict price controls and negotiated smaller minimum wage increments with labor unions with the aim of curbing inflation. While his strategy was successful in reducing inflation, growth averaged only 2.8 percent a year. Moreover, by fixing the exchange rate, the peso became rapidly overvalued while consumer spending increased, causing the current account deficit to reach 7% of GDP in 1994. The deficit was financed through tesobonos a type of public debt instrument that reassured payment in dollars. The Chiapas uprising
, and the assassinations of the ruling party's presidential candidate, Luis Donaldo Colosio
and the Secretary-General of the party and brother of the Assistant-Attorney General
José Francisco Ruiz Massieu
in 1994, sent a disquieting message to investors. Public debt holders rapidly sold their tesobonos, depleting the Central Bank's reserves, while portfolio investments, which had made up 90% of total investment flows, left the country as fast as they had come in. This unsustainable situation eventually forced the entrant Zedillo administration to abandon the fixed exchange rate. The peso sharply devalued and the country entered into an economic crisis in December 1994
. The boom in exports, as well as an international rescue package crafted by American president Bill Clinton
, helped cushion the crisis. In less than 18 months, the economy was growing again, and annual rate growth averaged 5.1 percent between 1995 and 2000.
President Zedillo
and president Fox
continued with trade liberalization and during his administrations several FTAs were signed with Latin American and European countries, Japan and Israel, and both strove to maintain macroeconomic stability. Thus, Mexico became one of the most open countries in the world to trade, and the economy base shifted accordingly. Total trade with the United States and Canada tripled, and total exports and imports almost quadrupled between 1991 and 2003. The nature of foreign investment also changed from portfolio to foreign-direct investment (FDI).
(PPP) was estimated at US $1.463 trillion in 2009, and $874.8 billion
in nominal exchange rates. As such, its standard of living, as measured in GDP in PPP per capita was US $13,200. The World Bank reported in 2009 that the country's Gross National Income
in market exchange rates was the second highest in Latin America, after Brazil
at US $962.076 billion, which lead to the highest income per capita
in the region at $8,960. As such, Mexico is now firmly established as an upper middle-income country. After the slowdown of 2001 the country has recovered and has grown 4.2, 3.0 and 4.8 percent in 2004, 2005 and 2006, even though it is considered to be well below Mexico's potential growth.
The Mexican currency is the peso
(ISO 4217
: MXN; symbol: $). One peso is divided into 100 centavos (cents). MXN replaced MXP in 1993 at a rate of 1000 MXP per 1 MXN. The exchanged rate has remained stable since 1998, oscillating between 9.20 and 11.50 MXN per US$. Interest rates in 2007 were situated at around 7 percent, having reached a historic low in 2002 below 5 percent. Inflation rates are also at historic lows; the inflation rate in Mexico in 2006 was 4.1 percent, and 3 percent by the end of 2007. Unemployment rates are the lowest of all OECD member countries at 3.2 percent. However, underemployment is estimated at 25 percent. Mexico's Human development index
was reported at 0.829, (comprising a life expectancy index of 0.84, an education index of 0.86 and a GDP index of 0.77), ranking 52 in the world within the group of high-development.
.
, or contributions sent by Mexicans living abroad, mostly in the United States, to their families at home in Mexico, are a substantial and growing part of the Mexican economy; they comprised $18 billion in 2005. In 2004, they became the tenth largest source of foreign income after oil, industrial exports, manufactured goods, electronics, heavy industry, automobiles, construction, food, and banking & financial services. Larger than tourism expenditures; and represented 2.1 percent of the nation's Gross Domestic Product. The growth of remittances has been remarkable: they have more than doubled since 1997. Recorded remittance transactions exceeded 41 million in 2003, of which 86 percent were made by electronic transfer.
The Mexican government, cognizant of the economic viability of immigrant workers, began issuing an upgraded version of the Matrícula Consular de Alta Seguridad (MACS, High Security Consular Identification), an identity document issued at Mexican consulates abroad. This document is now accepted as a valid identity card in 32 US states, as well as thousands of police agencies, hundreds of cities and counties, as well as banking institutions.
The main receptors of remittances in 2004 were the states of Michoacán
, Guanajuato
, Jalisco
, Mexico and Puebla
, which jointly captured 45% of total remittances in that year. Several state governments, with the support of the federal government, have implemented programs to use part of the remittances to finance public works. This program, called Dos por Uno (Two for every one) is designed in a way that for each peso contributed by migrants from their remittances, the state and the federal governments will invest two pesos in building infrastructure at their home communities.
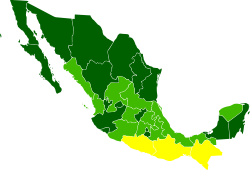 Regional disparities and income inequality continue to be a problem in Mexico. While all constituent states of the federation have a Human Development Index
Regional disparities and income inequality continue to be a problem in Mexico. While all constituent states of the federation have a Human Development Index
(HDI) superior to 0.70 (medium to high development), northern and central states have higher levels of HDI than the southern states. Nuevo León
, Campeche
and the Federal District
have HDI levels similar to European countries, whereas that of Oaxaca
and Chiapas
is similar to that of Syria or Egypt. At the municipal level, disparities are even greater: San Pedro Garza García
in Nuevo León has an HDI similar to that of Germany or New Zealand, whereas, Metlatonoc in Guerrero
, would have an HDI similar to that of Malawi. The majority of the federal entities with high development (superior to 0.80) are located in the northern region (with the exception of Colima
, Jalisco, Aguascalientes
, the Federal District, Querétaro
, as well as the southeastern states of Quintana Roo
and Campeche
). The less developed states (with medium development in terms of HDI, superior to 0.70) are located at the southern Pacific coast (with the exception of Veracruz
).
In terms of share in GDP per sector (in 2004), the largest contributors in agriculture are Jalisco (9.7%), Sinaloa
(7.7%) and Veracruz (7.6%); the greatest contributors in industrial production are the Federal District (15.8%), State of México (11.8%) and Nuevo León (7.9%); the greatest contributors in the service sector are also the Federal District (25.3%), State of México (8.9%) and Nuevo León (7.5%).
Since the 1980s, the economy has slowly become less centralized; the annual rate of GDP growth of the Federal District from 2003–2004 was the smallest of all federal entities at a mere 0.23%, with drastic drops in the agriculture and industrial sectors. Nonetheless, it still accounts for 21.8% of the nation's GDP. The states with the highest GDP growth rates are Quintana Roo (9.04%), Baja California
(8.89%), and San Luis Potosí
(8.18%). In 2000, the federal entities with the highest GDP per capita in Mexico were the Federal District (US $17,696), Campeche (US $13,153) and Nuevo León (US $13,033); the states with the lowest GDP per capita were Chiapas (US $3,302), Oaxaca (US $3,489) and Guerrero (US $4,112).
(PPP) in 2006 was estimated at US $1.134 trillion, and GDP per capita in PPP at US $10,600. The service sector is the largest component of GDP at 70.5%, followed by the industrial sector at 25.7% (2006 est.). Agriculture represents only 3.9% of GDP (2006 est.). Mexican labor force is estimated at 38 million of which 18% is occupied in agriculture, 24% in the industry sector and 58% in the service sector (2003 est.).
}
}}
|-
! style="background:#e9e9e9;" | Product
! style="background:#e9e9e9;" | Quantity (Tm)
! style="background:#e9e9e9;" | World Rank1
|- style="background:#f0f0f0;"
||Avocados
| style="text-align:right;"| 1,040,390
| style="text-align:right;"| 1
|-
|Onions and chayote
|align=right|1,130,660
|align=right|1
|- style="background:#f0f0f0;"
||Limes and lemons
| style="text-align:right;"|1,824,890
| style="text-align:right;"|1
|-
|Sunflower seed
|align=right|212,765
|align=right|1
|- style="background:#f0f0f0;"
|| Dry fruits
| style="text-align:right;"| 95,150
| style="text-align:right;"| 2
|-
| Papaya
| align=right|955,694
| align=right|2
|- style="background:#f0f0f0;"
|| Chillies and peppers
| style="text-align:right;"| 1,853,610
| style="text-align:right;"|2
|-
| Whole beans
| align=right| 93 000
| align=right|3
|- style="background:#f0f0f0;"
|| Oranges
| style="text-align:right;"|3,969,810
| style="text-align:right;"|3
|-
| Anise, badian, fennel
| align=right|32 500
| align=right|3
|- style="background:#f0f0f0;"
|| Chicken meat
| style="text-align:right;"|2,245,000
| style="text-align:right;"|3
|-
| Asparagus
| align=right|67,247
| align=right|4
|- style="background:#f0f0f0;"
|| Mangoes
| style="text-align:right;"|1.503.010
| style="text-align:right;"|4
|-
| Corn
| align=right|20,000,000
| align=right|4
|-
| colspan="3" style="background:#e9e9e9; text-align:center;"|1Source:FAO
|}
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
is the 13th largest in the world in nominal terms and the 11th by purchasing power parity, according to the World Bank.
Since the 1994 crisis
1994 economic crisis in Mexico
The 1994 Economic Crisis in Mexico, widely known as the Mexican peso crisis, was caused by the sudden devaluation of the Mexican peso in December 1994....
, administrations have improved the country's macroeconomic fundamentals
Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics dealing with the performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of the whole economy. This includes a national, regional, or global economy...
. Mexico was not significantly influenced by the recent 2002 South American crisis
South American economic crisis of 2002
The South American Economic Crisis is the economic disturbances which have developed in 2002 in the South American countries of Argentina, Brazil and Uruguay....
, and maintained positive, although low, rates of growth after a brief period of stagnation in 2001. However, Mexico was one of the Latin American nations most affected by the 2008 recession with its Gross Domestic Product contracting by more than 6%. Moody's
Moody's
Moody's Corporation is the holding company for Moody's Analytics and Moody's Investors Service, a credit rating agency which performs international financial research and analysis on commercial and government entities. The company also ranks the credit-worthiness of borrowers using a standardized...
(in March 2000) and Fitch IBCA (in January 2002) issued investment-grade ratings for Mexico's sovereign debt. In spite of its unprecedented macroeconomic stability, which has reduced inflation and interest rates to record lows and has increased per capita income, enormous gaps remain between the urban and the rural population, the northern and southern states, and the rich and the poor. Some of the government's challenges include the upgrade of infrastructure, the modernization of the tax system and labor laws, and the reduction of income inequality.
The economy contains rapidly developing modern industrial and service sectors, with increasing private ownership. Recent administrations have expanded competition in ports, railroads, telecommunications, electricity generation
Electricity sector in Mexico
The energy sector in Mexico has certain limitations in terms of private participation and foreign companies are allowed to operate in the country only through specific service contracts. As required by the Constitution, the electricity sector is federally owned, with the Federal Electricity...
, natural gas distribution and airports, with the aim of upgrading infrastructure. As an export-oriented economy, more than 90% of Mexican trade is under free trade agreements (FTAs) with more than 40 countries, including the European Union, Japan, Israel, and much of Central
Central America
Central America is the central geographic region of the Americas. It is the southernmost, isthmian portion of the North American continent, which connects with South America on the southeast. When considered part of the unified continental model, it is considered a subcontinent...
and South America. The most influential FTA is the North American Free Trade Agreement
North American Free Trade Agreement
The North American Free Trade Agreement or NAFTA is an agreement signed by the governments of Canada, Mexico, and the United States, creating a trilateral trade bloc in North America. The agreement came into force on January 1, 1994. It superseded the Canada – United States Free Trade Agreement...
(NAFTA), which came into effect in 1994, and was signed in 1992 by the governments of the United States, Canada and Mexico. In 2006, trade with Mexico's two northern partners accounted for almost 90% of its exports and 55% of its imports. Recently, the Congress of the Union approved important tax, pension and judicial reforms, and reform to the oil industry is currently being debated. According to the Forbes Global 2000 list of the world's largest companies in 2008, Mexico had 16 companies in the list.
The annual Mexico Investment Summit takes place in Mexico City
Mexico City
Mexico City is the Federal District , capital of Mexico and seat of the federal powers of the Mexican Union. It is a federal entity within Mexico which is not part of any one of the 31 Mexican states but belongs to the federation as a whole...
covering the development and investment opportunities and challenges across Mexican private equity, venture capital, infrastructure, real estate, agriculture, tourism, energy and natural resources evolving in the country's economy.
History
Mexican president Porfirio DíazPorfirio Díaz
José de la Cruz Porfirio Díaz Mori was a Mexican-American War volunteer and French intervention hero, an accomplished general and the President of Mexico continuously from 1876 to 1911, with the exception of a brief term in 1876 when he left Juan N...
brought unprecedented economic growth during the last quarter of the nineteenth century. This growth was accompanied by foreign investment and European immigration, the development of an efficient railroad network and the exploitation of the country's natural resources. Annual economic growth between 1876 and 1910 averaged 3.3%. Political repression and fraud, as well as huge income inequalities exacerbated by the land distribution system based on latifundios
Latifundia
Latifundia are pieces of property covering very large land areas. The latifundia of Roman history were great landed estates, specializing in agriculture destined for export: grain, olive oil, or wine...
, in which large hacienda
Hacienda
Hacienda is a Spanish word for an estate. Some haciendas were plantations, mines, or even business factories. Many haciendas combined these productive activities...
s were owned by a few but worked by millions of underpaid peasants living in precarious conditions, led to the Mexican Revolution
Mexican Revolution
The Mexican Revolution was a major armed struggle that started in 1910, with an uprising led by Francisco I. Madero against longtime autocrat Porfirio Díaz. The Revolution was characterized by several socialist, liberal, anarchist, populist, and agrarianist movements. Over time the Revolution...
(1910–1917), an armed conflict that drastically transformed Mexico's political, social, cultural, and economical structure during the twentieth century under a premise of social democracy. The war itself, however, left a harsh toll in the economy and population, which decreased over the 11-year period between 1910 and 1921. The reconstruction of the country was to take place in the following decades.
The period from 1930 to 1970 was dubbed by economic historians as the "Mexican Miracle", a period of economic growth spurred by a model of import substitution industrialization (ISI) which protected and promoted the development of national industries. Through the ISI model, the country experienced an economic boom through which industries rapidly expanded their production. Important changes in the economic structure included free land distribution to peasants under the concept of ejido
Ejido
The ejido system is a process whereby the government promotes the use of communal land shared by the people of the community. This use of community land was a common practice during the time of Aztec rule in Mexico...
, the nationalization of the oil and railroad companies, the introduction of social rights into the constitution, the birth of large and influential labor unions, and the upgrading of infrastructure. While population doubled from 1940 to 1970, GDP increased sixfold.
The ISI model had reached its peaked in the late 1960s. During the 1970s, the administrations of Echeverría
Luis Echeverría
Luis Echeverría Álvarez served as President of Mexico from 1970 to 1976.-Early history:Echeverría joined the faculty of the National Autonomous University of Mexico in 1947 and taught political theory...
and López Portillo
José López Portillo
José López Portillo y Pacheco was the President of Mexico from 1976 to 1982.Born in Mexico City, López Portillo studied Law at the National Autonomous University of Mexico before beginning his political career with the Institutional Revolutionary Party in 1959.He held several positions in the...
, tried to include social development in their policies, an effort that entailed more public spending. With the discovery of vast oil fields in a time in which oil prices were surging and international interest rates were low -and even negative- the government decided to borrow from international capital markets to invest in the state-owned oil company, which in turn seemed to provide a long-run income source to promote social welfare. In fact, this method produced a remarkable growth in public expenditure, and president López Portillo announced that the time had come to learn to "manage prosperity" as Mexico multiplied its oil production to become the world's fourth largest exporter.
| Average annual GDP growth by period | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1900–1929 | 3.4% | |
| 1929–1945 | 4.2% | |
| 1945–1972 | 6.5% | |
| 1972–1981 | 5.5% | |
| 1981–1995 | 1.5% | |
| 1995–2000 | 5.1% | |
| 2000–2011 | 1.6% | |
| Sources: | ||
In the period of 1981–1982 the international panorama changed abruptly: oil prices plunged
1980s oil glut
The 1980s oil glut was a serious surplus of crude oil caused by falling demand following the 1970s Energy Crisis. The world price of oil, which had peaked in 1980 at over US$35 per barrel , fell in 1986 from $27 to below $10...
and interest rates rose. In 1982, president López Portillo, just before ending his administration, suspended payments of foreign debt, devalued the peso
Mexican peso
The peso is the currency of Mexico. Modern peso and dollar currencies have a common origin in the 15th–19th century Spanish dollar, most continuing to use its sign, "$". The Mexican peso is the 12th most traded currency in the world, the third most traded in the Americas, and by far the most...
and nationalized the banking system, along with many other industries that were severely affected by the crisis, among them the steel industry. While import substitution had produced an era of industrialization in previous decades, by the 1980s it was evident that that protracted protection had produced an uncompetitive industrial sector with low productivity gains.
President de la Madrid
Miguel de la Madrid
Miguel de la Madrid Hurtado is a Mexican politician affiliated to the Institutional Revolutionary Party who served as President of Mexico from 1982 to 1988.-Biography:...
was the first of a series of presidents that began to implement neoliberal
Neoliberalism
Neoliberalism is a market-driven approach to economic and social policy based on neoclassical theories of economics that emphasizes the efficiency of private enterprise, liberalized trade and relatively open markets, and therefore seeks to maximize the role of the private sector in determining the...
reforms. After the crisis of 1982, lenders were unwilling to return to Mexico and, in order to keep the current account in balance, the government resorted to currency devaluations, which in turn sparked unprecedented inflation, which reached a historic high in 1987 at 159.7%.
The first step toward the liberalization of trade was Mexico's signature of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade
General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade
The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade was negotiated during the UN Conference on Trade and Employment and was the outcome of the failure of negotiating governments to create the International Trade Organization . GATT was signed in 1947 and lasted until 1993, when it was replaced by the World...
(GATT) in 1986. During the Salinas administration many state-owned companies were privatized. In 1992, the North American Free Trade Agreement
North American Free Trade Agreement
The North American Free Trade Agreement or NAFTA is an agreement signed by the governments of Canada, Mexico, and the United States, creating a trilateral trade bloc in North America. The agreement came into force on January 1, 1994. It superseded the Canada – United States Free Trade Agreement...
was signed between the United States, Canada and Mexico, and after the signature of two additional supplements on environments and labor standards, it came into effect on January 1, 1994. Salinas also introduced strict price controls and negotiated smaller minimum wage increments with labor unions with the aim of curbing inflation. While his strategy was successful in reducing inflation, growth averaged only 2.8 percent a year. Moreover, by fixing the exchange rate, the peso became rapidly overvalued while consumer spending increased, causing the current account deficit to reach 7% of GDP in 1994. The deficit was financed through tesobonos a type of public debt instrument that reassured payment in dollars. The Chiapas uprising
Zapatista Army of National Liberation
The Zapatista Army of National Liberation is a revolutionary leftist group based in Chiapas, the southernmost state of Mexico....
, and the assassinations of the ruling party's presidential candidate, Luis Donaldo Colosio
Luis Donaldo Colosio
Luis Donaldo Colosio Murrieta was a Mexican politician, and PRI presidential candidate, who was assassinated at a campaign rally in Tijuana during the Mexican Presidential campaign of 1994.-Political history:...
and the Secretary-General of the party and brother of the Assistant-Attorney General
Attorney General (Mexico)
The Attorney General of Mexico is the head of the Office of the General Prosecutor and the Federal Public Ministry , an institution belonging to the Federal executive branch that is responsible for the investigation and prosecution of...
José Francisco Ruiz Massieu
José Francisco Ruiz Massieu
José Francisco Ruiz Massieu was a Mexican political figure. He was governor of Guerrero from 1987 to 1993. He then served as the secretary-general of the Institutional Revolutionary Party in 1994...
in 1994, sent a disquieting message to investors. Public debt holders rapidly sold their tesobonos, depleting the Central Bank's reserves, while portfolio investments, which had made up 90% of total investment flows, left the country as fast as they had come in. This unsustainable situation eventually forced the entrant Zedillo administration to abandon the fixed exchange rate. The peso sharply devalued and the country entered into an economic crisis in December 1994
1994 economic crisis in Mexico
The 1994 Economic Crisis in Mexico, widely known as the Mexican peso crisis, was caused by the sudden devaluation of the Mexican peso in December 1994....
. The boom in exports, as well as an international rescue package crafted by American president Bill Clinton
Bill Clinton
William Jefferson "Bill" Clinton is an American politician who served as the 42nd President of the United States from 1993 to 2001. Inaugurated at age 46, he was the third-youngest president. He took office at the end of the Cold War, and was the first president of the baby boomer generation...
, helped cushion the crisis. In less than 18 months, the economy was growing again, and annual rate growth averaged 5.1 percent between 1995 and 2000.
President Zedillo
Ernesto Zedillo
Ernesto Zedillo Ponce de León is a Mexican economist and politician. He served as President of Mexico from December 1, 1994 to November 30, 2000, as the last of the uninterrupted seventy year line of Mexican presidents from the Institutional Revolutionary Party...
and president Fox
Vicente Fox
Vicente Fox Quesada is a Mexican former politician who served as President of Mexico from 1 December 2000 to 30 November 2006 and currently serves as co-President of the Centrist Democrat International, an international organization of Christian democratic political parties.Fox was elected...
continued with trade liberalization and during his administrations several FTAs were signed with Latin American and European countries, Japan and Israel, and both strove to maintain macroeconomic stability. Thus, Mexico became one of the most open countries in the world to trade, and the economy base shifted accordingly. Total trade with the United States and Canada tripled, and total exports and imports almost quadrupled between 1991 and 2003. The nature of foreign investment also changed from portfolio to foreign-direct investment (FDI).
Macroeconomic, financial and welfare indicators
| GDP per capita PPP Purchasing power parity In economics, purchasing power parity is a condition between countries where an amount of money has the same purchasing power in different countries. The prices of the goods between the countries would only reflect the exchange rates... |
US $14,900 (2008) |
|---|---|
| GNI per capita PPP Purchasing power parity In economics, purchasing power parity is a condition between countries where an amount of money has the same purchasing power in different countries. The prices of the goods between the countries would only reflect the exchange rates... |
US $11,990 (2006) |
| Inflation (CPI Consumer price index A consumer price index measures changes in the price level of consumer goods and services purchased by households. The CPI, in the United States is defined by the Bureau of Labor Statistics as "a measure of the average change over time in the prices paid by urban consumers for a market basket of... ) |
3% (2007) |
| Gini index | 44.5 |
| Unemployment | 3.7% (2007) |
| HDI Human Development Index The Human Development Index is a composite statistic used to rank countries by level of "human development" and separate "very high human development", "high human development", "medium human development", and "low human development" countries... |
0.750 |
| Labor force | 45.38 million (2007) |
| Pop. in poverty | 13.8% |
Main indicators
Mexico's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in purchasing power parityPurchasing power parity
In economics, purchasing power parity is a condition between countries where an amount of money has the same purchasing power in different countries. The prices of the goods between the countries would only reflect the exchange rates...
(PPP) was estimated at US $1.463 trillion in 2009, and $874.8 billion
1000000000 (number)
1,000,000,000 is the natural number following 999,999,999 and preceding 1,000,000,001.In scientific notation, it is written as 109....
in nominal exchange rates. As such, its standard of living, as measured in GDP in PPP per capita was US $13,200. The World Bank reported in 2009 that the country's Gross National Income
Gross National Income
The GNI consists of: the personal consumption expenditures, the gross private investment, the government consumption expenditures, the net income from assets abroad , and the gross exports of goods and services, after deducting two components: the gross imports of goods and services, and the...
in market exchange rates was the second highest in Latin America, after Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
at US $962.076 billion, which lead to the highest income per capita
Gross National Income
The GNI consists of: the personal consumption expenditures, the gross private investment, the government consumption expenditures, the net income from assets abroad , and the gross exports of goods and services, after deducting two components: the gross imports of goods and services, and the...
in the region at $8,960. As such, Mexico is now firmly established as an upper middle-income country. After the slowdown of 2001 the country has recovered and has grown 4.2, 3.0 and 4.8 percent in 2004, 2005 and 2006, even though it is considered to be well below Mexico's potential growth.
The Mexican currency is the peso
Peso
The word peso was the name of a coin that originated in Spain and became of immense importance internationally...
(ISO 4217
ISO 4217
ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Standards Organization, which delineates currency designators, country codes , and references to minor units in three tables:* Table A.1 – Current currency & funds code list...
: MXN; symbol: $). One peso is divided into 100 centavos (cents). MXN replaced MXP in 1993 at a rate of 1000 MXP per 1 MXN. The exchanged rate has remained stable since 1998, oscillating between 9.20 and 11.50 MXN per US$. Interest rates in 2007 were situated at around 7 percent, having reached a historic low in 2002 below 5 percent. Inflation rates are also at historic lows; the inflation rate in Mexico in 2006 was 4.1 percent, and 3 percent by the end of 2007. Unemployment rates are the lowest of all OECD member countries at 3.2 percent. However, underemployment is estimated at 25 percent. Mexico's Human development index
Human Development Index
The Human Development Index is a composite statistic used to rank countries by level of "human development" and separate "very high human development", "high human development", "medium human development", and "low human development" countries...
was reported at 0.829, (comprising a life expectancy index of 0.84, an education index of 0.86 and a GDP index of 0.77), ranking 52 in the world within the group of high-development.
Poverty
After the 1994–1995 economic crisis, probably the most severe in the country's history, 50% of the population fell into poverty. A rapid growth in exports propitiated by NAFTA and other trade agreements, and the restructuring of the macroeconomic finances initiated during Zedillo's and continued during Fox's administration had significant results in the reduction of the poverty rate: according to the World Bank, poverty was reduced from 24.2% in 2000 to 17.6% in 2004. Most of this reduction was achieved in rural communities whose rate of poverty declined from 42% to 27.9% in the 2000–2004 period, although urban poverty stagnated at 12%. According to the World Bank, in 2004, 17.6% of Mexico's population lived in extreme poverty, while 21% lived in moderated poverty. The CIA Factbook, on the other hand, reported that 13.8% of the population was under the poverty line, as measured in food-based poverty. See Feed the Children VallartaFeed the Children Vallarta
Feed the Children Vallarta is a non-profit tax exempt charitable corporation based in the city of Puerto Vallarta, Jalisco, Mexico. Founded in 1998 as “Desayunos Para Los Niños de Vallarta A.C” or as it soon came to be known simply as “Children of the Dump Vallarta".Since its inception in 1998,...
.
Remittances
RemittancesRemittances
A remittance is a transfer of money by a foreign worker to his or her home country. Note that in 19th century usage a remittance man was someone exiled overseas and sent an allowance on condition that he not return home....
, or contributions sent by Mexicans living abroad, mostly in the United States, to their families at home in Mexico, are a substantial and growing part of the Mexican economy; they comprised $18 billion in 2005. In 2004, they became the tenth largest source of foreign income after oil, industrial exports, manufactured goods, electronics, heavy industry, automobiles, construction, food, and banking & financial services. Larger than tourism expenditures; and represented 2.1 percent of the nation's Gross Domestic Product. The growth of remittances has been remarkable: they have more than doubled since 1997. Recorded remittance transactions exceeded 41 million in 2003, of which 86 percent were made by electronic transfer.
The Mexican government, cognizant of the economic viability of immigrant workers, began issuing an upgraded version of the Matrícula Consular de Alta Seguridad (MACS, High Security Consular Identification), an identity document issued at Mexican consulates abroad. This document is now accepted as a valid identity card in 32 US states, as well as thousands of police agencies, hundreds of cities and counties, as well as banking institutions.
The main receptors of remittances in 2004 were the states of Michoacán
Michoacán
Michoacán officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Michoacán de Ocampo is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 113 municipalities and its capital city is Morelia...
, Guanajuato
Guanajuato
Guanajuato officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Guanajuato is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 46 municipalities and its capital city is Guanajuato....
, Jalisco
Jalisco
Jalisco officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Jalisco is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is located in Western Mexico and divided in 125 municipalities and its capital city is Guadalajara.It is one of the more important states...
, Mexico and Puebla
Puebla
Puebla officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Puebla is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 217 municipalities and its capital city is Puebla....
, which jointly captured 45% of total remittances in that year. Several state governments, with the support of the federal government, have implemented programs to use part of the remittances to finance public works. This program, called Dos por Uno (Two for every one) is designed in a way that for each peso contributed by migrants from their remittances, the state and the federal governments will invest two pesos in building infrastructure at their home communities.
Regional economies

Human Development Index
The Human Development Index is a composite statistic used to rank countries by level of "human development" and separate "very high human development", "high human development", "medium human development", and "low human development" countries...
(HDI) superior to 0.70 (medium to high development), northern and central states have higher levels of HDI than the southern states. Nuevo León
Nuevo León
Nuevo León It is located in Northeastern Mexico. It is bordered by the states of Tamaulipas to the north and east, San Luis Potosí to the south, and Coahuila to the west. To the north, Nuevo León has a 15 kilometer stretch of the U.S.-Mexico border adjacent to the U.S...
, Campeche
Campeche
Campeche is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. Located in Southeast Mexico, it is bordered by the states of Yucatán to the north east, Quintana Roo to the east, and Tabasco to the south west...
and the Federal District
Mexico City
Mexico City is the Federal District , capital of Mexico and seat of the federal powers of the Mexican Union. It is a federal entity within Mexico which is not part of any one of the 31 Mexican states but belongs to the federation as a whole...
have HDI levels similar to European countries, whereas that of Oaxaca
Oaxaca
Oaxaca , , officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Oaxaca is one of the 31 states which, along with the Federal District, comprise the 32 federative entities of Mexico. It is divided into 571 municipalities; of which 418 are governed by the system of customs and traditions...
and Chiapas
Chiapas
Chiapas officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Chiapas is one of the 31 states that, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 118 municipalities and its capital city is Tuxtla Gutierrez. Other important cites in Chiapas include San Cristóbal de las...
is similar to that of Syria or Egypt. At the municipal level, disparities are even greater: San Pedro Garza García
San Pedro Garza García
San Pedro Garza García is a city-municipality of the Mexican state of Nuevo León and is part of Monterrey's Metropolitan Area, based on the suburban North American model...
in Nuevo León has an HDI similar to that of Germany or New Zealand, whereas, Metlatonoc in Guerrero
Guerrero
Guerrero officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Guerrero is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 81 municipalities and its capital city is Chilpancingo....
, would have an HDI similar to that of Malawi. The majority of the federal entities with high development (superior to 0.80) are located in the northern region (with the exception of Colima
Colima
Colima is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, make up the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It shares its name with its capital and main city, Colima....
, Jalisco, Aguascalientes
Aguascalientes
Aguascalientes is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 11 municipalities and its capital city is Aguascalientes....
, the Federal District, Querétaro
Querétaro
Querétaro officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Querétaro de Arteaga is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 18 municipalities and its capital city is Santiago de Querétaro....
, as well as the southeastern states of Quintana Roo
Quintana Roo
Quintana Roo officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Quintana Roo is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 10 municipalities and its capital city is Chetumal....
and Campeche
Campeche
Campeche is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. Located in Southeast Mexico, it is bordered by the states of Yucatán to the north east, Quintana Roo to the east, and Tabasco to the south west...
). The less developed states (with medium development in terms of HDI, superior to 0.70) are located at the southern Pacific coast (with the exception of Veracruz
Veracruz
Veracruz, formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave , is one of the 31 states that, along with the Federal District, comprise the 32 federative entities of Mexico. It is divided in 212 municipalities and its capital city is...
).
In terms of share in GDP per sector (in 2004), the largest contributors in agriculture are Jalisco (9.7%), Sinaloa
Sinaloa
Sinaloa officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Sinaloa is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 18 municipalities and its capital city is Culiacán Rosales....
(7.7%) and Veracruz (7.6%); the greatest contributors in industrial production are the Federal District (15.8%), State of México (11.8%) and Nuevo León (7.9%); the greatest contributors in the service sector are also the Federal District (25.3%), State of México (8.9%) and Nuevo León (7.5%).
Since the 1980s, the economy has slowly become less centralized; the annual rate of GDP growth of the Federal District from 2003–2004 was the smallest of all federal entities at a mere 0.23%, with drastic drops in the agriculture and industrial sectors. Nonetheless, it still accounts for 21.8% of the nation's GDP. The states with the highest GDP growth rates are Quintana Roo (9.04%), Baja California
Baja California
Baja California officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is both the northernmost and westernmost state of Mexico. Before becoming a state in 1953, the area was known as the North...
(8.89%), and San Luis Potosí
San Luis Potosí
San Luis Potosí officially Estado Libre y Soberano de San Luis Potosí is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 58 municipalities and its capital city is San Luis Potosí....
(8.18%). In 2000, the federal entities with the highest GDP per capita in Mexico were the Federal District (US $17,696), Campeche (US $13,153) and Nuevo León (US $13,033); the states with the lowest GDP per capita were Chiapas (US $3,302), Oaxaca (US $3,489) and Guerrero (US $4,112).
Components of the economy
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in purchasing power parityPurchasing power parity
In economics, purchasing power parity is a condition between countries where an amount of money has the same purchasing power in different countries. The prices of the goods between the countries would only reflect the exchange rates...
(PPP) in 2006 was estimated at US $1.134 trillion, and GDP per capita in PPP at US $10,600. The service sector is the largest component of GDP at 70.5%, followed by the industrial sector at 25.7% (2006 est.). Agriculture represents only 3.9% of GDP (2006 est.). Mexican labor force is estimated at 38 million of which 18% is occupied in agriculture, 24% in the industry sector and 58% in the service sector (2003 est.).
History
| Food and agriculture |
|---|
}}
|-
! style="background:#e9e9e9;" | Product
! style="background:#e9e9e9;" | Quantity (Tm)
! style="background:#e9e9e9;" | World Rank1
|- style="background:#f0f0f0;"
||Avocados
| style="text-align:right;"| 1,040,390
| style="text-align:right;"| 1
|-
|Onions and chayote
|align=right|1,130,660
|align=right|1
|- style="background:#f0f0f0;"
||Limes and lemons
| style="text-align:right;"|1,824,890
| style="text-align:right;"|1
|-
|Sunflower seed
|align=right|212,765
|align=right|1
|- style="background:#f0f0f0;"
|| Dry fruits
| style="text-align:right;"| 95,150
| style="text-align:right;"| 2
|-
| Papaya
| align=right|955,694
| align=right|2
|- style="background:#f0f0f0;"
|| Chillies and peppers
| style="text-align:right;"| 1,853,610
| style="text-align:right;"|2
|-
| Whole beans
| align=right| 93 000
| align=right|3
|- style="background:#f0f0f0;"
|| Oranges
| style="text-align:right;"|3,969,810
| style="text-align:right;"|3
|-
| Anise, badian, fennel
| align=right|32 500
| align=right|3
|- style="background:#f0f0f0;"
|| Chicken meat
| style="text-align:right;"|2,245,000
| style="text-align:right;"|3
|-
| Asparagus
| align=right|67,247
| align=right|4
|- style="background:#f0f0f0;"
|| Mangoes
| style="text-align:right;"|1.503.010
| style="text-align:right;"|4
|-
| Corn
| align=right|20,000,000
| align=right|4
|-
| colspan="3" style="background:#e9e9e9; text-align:center;"|1Source:FAO
|}
After the Mexican Revolution
Mexican Revolution
The Mexican Revolution was a major armed struggle that started in 1910, with an uprising led by Francisco I. Madero against longtime autocrat Porfirio Díaz. The Revolution was characterized by several socialist, liberal, anarchist, populist, and agrarianist movements. Over time the Revolution...
Mexico began an agrarian reform
Agrarian land reform in Mexico
Before the 1910 Mexican Revolution that overthrew Porfirio Díaz, most of the land was owned by a single elite ruling class. Legally there was no slavery or serfdom; however, those with heavy debts, Indian wage workers, or peasants, were essentially debt-slaves to the landowners. A small percentage...
, based on the 27th article of the Mexican Constitution than included transfer of land and/or free land distribution to peasant
Peasant
A peasant is an agricultural worker who generally tend to be poor and homeless-Etymology:The word is derived from 15th century French païsant meaning one from the pays, or countryside, ultimately from the Latin pagus, or outlying administrative district.- Position in society :Peasants typically...
s and small farmers under the concept of the ejido
Ejido
The ejido system is a process whereby the government promotes the use of communal land shared by the people of the community. This use of community land was a common practice during the time of Aztec rule in Mexico...
. This program was further extended during President Cárdenas
Lázaro Cárdenas
Lázaro Cárdenas del Río was President of Mexico from 1934 to 1940.-Early life:Lázaro Cárdenas was born on May 21, 1895 in a lower-middle class family in the village of Jiquilpan, Michoacán. He supported his family from age 16 after the death of his father...
' administration during the 1930s and continued into the 1960s at varying rates. The cooperative agrarian reform, which guaranteed small farmers a means of subsistence livelihood, also caused land fragmentation and lack of capital investment, since commonly held land could not be used as collateral. In an effort to raise rural productivity and living standards, this constitutional article was amended in 1992 to allow for the transfer of property rights of the communal lands to farmers cultivating it. With the ability to rent or sell it, a way was open for the creation of larger farms and the advantages of economies of scale. Large mechanized farms are now operating in some northwestern states (mainly in Sinaloa
Sinaloa
Sinaloa officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Sinaloa is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 18 municipalities and its capital city is Culiacán Rosales....
). However, privatization of ejidos continues to be very slow in the central and southern states where the great majority of peasants produce only for subsistence.
Up until the 1990s, the government encouraged the production of basic crops (mainly corn
Maize
Maize known in many English-speaking countries as corn or mielie/mealie, is a grain domesticated by indigenous peoples in Mesoamerica in prehistoric times. The leafy stalk produces ears which contain seeds called kernels. Though technically a grain, maize kernels are used in cooking as a vegetable...
and beans) by maintaining support prices and controlling imports through the National Company for Popular Subsistence (CONASUPO). With trade liberalization, however, CONASUPO was to be gradually dismantled and two new mechanisms were implemented: Alianza and Procampo. Alianza provides income payments and incentives for mechanization and advanced irrigation systems. Procampo is an income transfer subsidy to farmers. This support program provides 3.5 million farmers who produce basic commodities (mostly corn), and which represent 64% of all farmers, with a fixed income transfer payment per unit of area of cropland. This subsidy increased substantially during president Fox's administration, mainly to white corn producers in order to reduce the amount of imports from the United States. This program has been successful, and in 2004, roughly only 15% of corn imports are white corn –the one used for human consumption and the type that is mostly grown in Mexico– as opposed to 85% of yellow and crashed corn –the one use for feeding livestock, and which is barely produced in Mexico.
Importance of agriculture to Mexico's economy
Agriculture, as a percentage of GDP, has been steadily declining, and now resembles that of developed nations, in that it plays a smaller role in the economy. In 2006, agriculture accounted for only 3.9% of GDP, down from 7% in 1980, and 25% in 1970. Nonetheless, given the historic structure of ejidos, it still employs a considerably high percentage of the work force: 18% in 2003, mostly of which grows basic crops for subsistence, compared to 2–5% in developed nations in which production is highly mechanized.Crops
In spite of being a staple in the Mexican diet, Mexico's comparative advantage in agriculture is not in cornMaize
Maize known in many English-speaking countries as corn or mielie/mealie, is a grain domesticated by indigenous peoples in Mesoamerica in prehistoric times. The leafy stalk produces ears which contain seeds called kernels. Though technically a grain, maize kernels are used in cooking as a vegetable...
, but in horticulture, tropical fruits, and vegetables. Negotiators of NAFTA expected that through liberalization and mechanization of agriculture two-thirds of Mexican corn producers would naturally shift from corn production to horticultural and other labor-intensive crops such as fruits, nuts, vegetables, coffee and sugar cane. While horticultural trade has drastically increased due to NAFTA, it has not absorbed displaced workers from corn production (estimated at around 600,000). Moreover, corn production has remained stable (at 20 million metric tons), arguably, as a result of income support to farmers, or a reluctance to abandon a millenarian tradition in Mexico: not only have peasants grown corn for millennia, corn originated in Mexico. Even today, Mexico is still the fourth largest corn producer in the world.
Potatoes
The area dedicated to potatoes has changed little since 1980 and average yields have almost tripled since 1961. Production reached a record 1.7 million tonnes in 2003. Per capita consumption of potato in Mexico stands at 17 kg a year, very low compared to its maize intake of 400 kg. On average, potato farms in Mexico are larger than those devoted to more basic food crops. Potato production in Mexico is mostly for commercial purposes; the production for household consumption is very small.
Sugar cane
Approximately 160,000 small- and medium-sized farmers grow sugar cane in 15 Mexican states; currently there are 54 sugar mills around the country that produced 4.96 million tons of sugar in the 2009 crop, compared to 5.8 million tons in 2005. Mexico's sugar industry is characterized by high production costs and lack of investment. Mexico produces more sugar than it consumes. Sugar cane is grown on 700,000 farms in Mexico with a yield of 72 metric tons per farm.
Industry
| Industrial production | ||
|---|---|---|
| Main industries | Aircraft, automobile industry, petrochemicals, cement and construction, textiles, food and beverages, mining, consumer durables, tourism | |
| Industrial growth rate | 3.6% (2006) | |
| Labor force | 24% of total labor force | |
| GDP of sector | 25.7% of total GDP | |
The industrial sector as a whole has benefited from trade liberalization; in 2000 it accounted for almost 90% of all export earnings.
Among the most important industrial manufacturers in Mexico is the automotive industry, whose standards of quality are internationally recognized. The automobile sector in Mexico differs from that in other Latin American countries and developing nations in that it does not function as a mere assembly manufacturer. The industry produces technologically complex components and engages in some research and development activities, an example of that is the new Volkswagen Jetta model with up to 70% of parts designed in Mexico. The "Big Three" (General Motors
General Motors
General Motors Company , commonly known as GM, formerly incorporated as General Motors Corporation, is an American multinational automotive corporation headquartered in Detroit, Michigan and the world's second-largest automaker in 2010...
, Ford and Chrysler
Chrysler
Chrysler Group LLC is a multinational automaker headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan, USA. Chrysler was first organized as the Chrysler Corporation in 1925....
) have been operating in Mexico since the 1930s, while Volkswagen
Volkswagen
Volkswagen is a German automobile manufacturer and is the original and biggest-selling marque of the Volkswagen Group, which now also owns the Audi, Bentley, Bugatti, Lamborghini, SEAT, and Škoda marques and the truck manufacturer Scania.Volkswagen means "people's car" in German, where it is...
and Nissan built their plants in the 1960s. Later, Toyota, Honda
Honda
is a Japanese public multinational corporation primarily known as a manufacturer of automobiles and motorcycles.Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, as well as the world's largest manufacturer of internal combustion engines measured by volume, producing more than...
, BMW
BMW
Bayerische Motoren Werke AG is a German automobile, motorcycle and engine manufacturing company founded in 1916. It also owns and produces the Mini marque, and is the parent company of Rolls-Royce Motor Cars. BMW produces motorcycles under BMW Motorrad and Husqvarna brands...
, and Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz is a German manufacturer of automobiles, buses, coaches, and trucks. Mercedes-Benz is a division of its parent company, Daimler AG...
joined in. Given the high requirements of North American components in the industry, many European and Asian parts suppliers have also moved to Mexico: in Puebla
Puebla, Puebla
The city and municipality of Puebla is the capital of the state of Puebla, and one of the five most important colonial cities in Mexico. Being a planned city, it is located to the east of Mexico City and west of Mexico's main port, Veracruz, on the main route between the two.The city was founded...
alone, 70 industrial part-makers cluster around Volkswagen. The relatively small domestic car industry still is represented by DINA Camiones S.A. de C.V.
DINA S.A.
DINA is a Mexican automotive producer of heavy duty and specialty trucks, urban buses, armored military vehicles and intercity coaches...
, a manufacturer of trucks, busses and military vehicles, which through domestic production and purchases of foreign bus manufacturers has become the largest bus manufacturer in the world; Vehizero that builds hybrid trucks and the new car companies Mastretta
Mastretta
Mastrettadesign Tecnoidea SA de CV is a Mexican car maker and design studio established by Mexican industrial designer Daniel Mastretta in Mexico City in 1987. Mastretta under Tecnoidea and Unidiseño brands has previously developed a small number of kit cars, but the 2010 MXT is the first fully...
design that builds the Mastretta MXT
Mastretta MXT
The Mastretta MXT is the first high performance sport automobile produced by the Mexican car maker Mastretta, and is notable for being both completely produced and designed in Mexico, as well as the first fully Mexican made sports car...
sports car and Autobuses King that plans to build 10000 microbuses by 2015, nevertheless new car companies are emerging among them CIMEX that has developed a sport utility truck, the Conin, and it is to be released in September 2010 in Mexico's national auto show, And the new electric car maker Grupo Electrico Motorizado
Some large industries of Mexico include Cemex
Cemex
CEMEX is the world's largest building materials supplier and third largest cement producer. Founded in Mexico in 1906, the company is based in Monterrey, Mexico...
, the worlds largest construction company and the third largest cement producer the alcohol beverage industries, including world-renowned players like Grupo Modelo
Grupo Modelo
Grupo Modelo is a large brewery in Mexico, It has 63% of the Mexican beer market, and exports beer to the United Kingdom, United States and Canada . Its export brands include Corona, Modelo, and Pacífico...
; conglomerates like FEMSA, which apart from being the largest single producer of alcoholic beverages and owning multiple commercial interests such OXXO
OXXO
OXXO is a primarily-franchised chain of convenience stores from Mexico, with over 7,000 stores across Latin America. It is the largest chain of this kind of store in Mexico. It is wholly owned by the beverage company FEMSA...
convenience store chain, is also the second-largest Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola is a carbonated soft drink sold in stores, restaurants, and vending machines in more than 200 countries. It is produced by The Coca-Cola Company of Atlanta, Georgia, and is often referred to simply as Coke...
bottler in the world; Gruma
Gruma
Gruma is the largest manufacturer of corn flour and tortillas in the world. Its brand names include Mission , Maseca, and Guerrero. Founded in 1949 as "Molinos Azteca, S.A.", the company is now based in Monterrey, Mexico and has subsidiaries in the United States, China, England, Central America,...
, the largest producer of corn flour and tortillas in the world; and Grupo Bimbo
Grupo Bimbo
Grupo Bimbo is the largest Mexican food company and the largest bakery in the world with brands in Americas, Europe, and China.-History:Grupo Bimbo was established in Mexico in 1945 by Lorenzo Servitje, Jose T. Mata, Jaime Sendra, and Jaime Jorba...
, Telmex
Telmex
Telmex is a telecommunications company headquartered in Mexico City that provides telecommunication products and services in Mexico, Argentina, Colombia, Brazil and other countries in Latin America. In addition to traditional fixed-line telephone service, Telmex also offers Internet access, data,...
, Televisa
Televisa
Televisa is a Mexican multimedia conglomerate, the largest mass media company in Latin America and in the Spanish-speaking world. It is a major international entertainment business, with much of its programming airing in the United States on Univision, with which it has an exclusive contract...
, among many others. In 2005, according to the World Bank, high-tech industrial production represented 19.6% of total exports.
Maquiladora
Maquiladora
A maquiladora or maquila is a concept often referred to as an operation that involves manufacturing in a country that is not the client's and as such has an interesting duty or tariff treatment...
s (Mexican factories which take in imported raw materials and produce goods for domestic consumption and export on behalf of foreign companies) have become the landmark of trade in Mexico. This sector has benefited from NAFTA, in that real income in the maquiladora sector has increased 15.5% since 1994, though from the non-maquiladora sector has grown much faster. Contrary to popular belief, this should be no surprise since maquiladora's products could enter the US duty free since the 1960s industry agreement. Other sectors now benefit from the free trade agreement, and the share of exports from non-border states has increased in the last 5 years while the share of exports from maquiladora-border states has decreased.
Currently Mexico is focusing in developing an aerospace industry and the assembly of helicopter and regional jet aircraft fuselages is taking place. Foreign firms such as MD Helicopters
MD Helicopters
MD Helicopters, Inc. is an aerospace company that produces helicopters primarily for commercial use. Coverage here includes the company's tenure as McDonnell Douglas Helicopter Systems, a subsidiary of McDonnell Douglas.-Background:...
, Bell, Cessna and Bombardier
Bombardier Aerospace
Bombardier Aerospace is a division of Bombardier Inc. and is the third-largest airplane manufacturer in the world. It is headquartered in Dorval, Quebec, Canada.- History :...
build helicopter, aircraft and regional jets fuselages in Mexico. Although the Mexican aircraft industry is mostly foreign, as is its car industry, Mexican firms have been founded such as Aeromarmi, which builds light propeller airplanes, and Hydra Technologies, which builds Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
Unmanned aerial vehicle
An unmanned aerial vehicle , also known as a unmanned aircraft system , remotely piloted aircraft or unmanned aircraft, is a machine which functions either by the remote control of a navigator or pilot or autonomously, that is, as a self-directing entity...
s such as the S4 Ehécatl, other important companies are Frisa Aerospace that manufactures jet engine parts for the new Mitsubishi Regional jet and Kuo Aerospace that builds parts for aircraft landing gear
As compared with the United States or countries in Western Europe a larger sector of Mexico's industrial economy is food manufacturing which includes several world class companies but the regional industry is undeveloped. There are national brands that have become international and local Mom and Pop producers but little manufacturing in between.
Electronics
The electronics industry of Mexico has grown enormously within the last decade. Mexico has the sixth largest electronics industry in the world after ChinaChina
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
, United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
, South Korea
South Korea
The Republic of Korea , , is a sovereign state in East Asia, located on the southern portion of the Korean Peninsula. It is neighbored by the People's Republic of China to the west, Japan to the east, North Korea to the north, and the East China Sea and Republic of China to the south...
, and Taiwan
Taiwan
Taiwan , also known, especially in the past, as Formosa , is the largest island of the same-named island group of East Asia in the western Pacific Ocean and located off the southeastern coast of mainland China. The island forms over 99% of the current territory of the Republic of China following...
. Mexico is the second largest exporter of electronics to the United Sates where it exported $71.4 billion worth of electronics in 2011. The Mexican electronics industry is dominated by the manufacture and OEM design of televisions, displays, computers, mobile phones, circuit boards, semiconductors, electronic appliances, communications equipment and LCD modules. The Mexican electronics industry grew 20% between 2010 and 2011, up from it's constant growth rate of 17% between 2003 and 2009. Currently electronics represent 30% of Mexico's none petroleum based exports.
Televisions
The design and manufacture of flat panel plasma, LCD and LED televisions is the single largest sector of the Mexican electronics industry, representing 25% of Mexico's electronics export revenue. In 2007 Mexico surpassed South Korea and China as the largest manufacturer of televisions, with Sony
Sony
, commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues....
, Toshiba
Toshiba
is a multinational electronics and electrical equipment corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. It is a diversified manufacturer and marketer of electrical products, spanning information & communications equipment and systems, Internet-based solutions and services, electronic components and...
, Samsung
Samsung
The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea...
, Sharp
Sharp Corporation
is a Japanese multinational corporation that designs and manufactures electronic products. Headquartered in Abeno-ku, Osaka, Japan, Sharp employs more than 55,580 people worldwide as of June 2011. The company was founded in September 1912 and takes its name from one of its founder's first...
(through Semex
Semex
Semex full name Sharp Electrónica Mexico S.A. de C.V. is the semi-independent Mexican division of Japanese Sharp electronics corporation. It is responsible for the manufacture of all Sharp printed ciruitboards, LED, LCD, and plasma panels, modules and televisions in North and South America and is...
), LG
LG
LG may refer to:*LG Corp., a South Korean electronics and petrochemicals conglomerate*LG Electronics, an affiliate of the South Korean LG Group which produces electronic products* Lawrence Graham, a London headquartered firm of business lawyers...
, Lanix
Lanix
Lanix is a Mexican electronics company based in Hermosillo, Sonora, Mexico. It is Mexico's largest domestically owned electronics company, and sells a wide array of both consumer and professional electronics...
, Phillips
Phillips
-Places:In the United States:*Phillips, California, unincorporated community in El Dorado County*Phillips, Maine, town in Franklin County*Phillips, Nebraska, village in Hamilton County*Phillips, Minneapolis, Minnesota, community in the city of Minneapolis...
, Elcoteq
Elcoteq
Elcoteq SE is a Finnish contract manufacturer, EMS, and ODM company headquartered in Luxembourg. The company filed for bankruptcy protection in Luxembourg on October 6 2011....
, Tatung
Tatung Company
Tatung Company , also known as Tatung, is a multinational corporation established in 1918 and headquartered in Zhongshan, Taipei, Taiwan. Tatung also maintains a regional headquarters in Long Beach, California for the U.S...
, Panasonic
Panasonic
Panasonic is an international brand name for Japanese electric products manufacturer Panasonic Corporation, which was formerly known as Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd...
, and Vizio
Vizio
Vizio is a privately held producer of consumer electronics, based in Irvine, California, USA. It was founded in October 2002 as V Inc. Vizio's major partner in the consumer electronics arena is AmTran Technology, a Taiwan-based OEM/ODM that manufactures more than half of the televisions sold...
manufacturing CRT, LCD, LED and Plasma televisions in Mexico. Due to Mexico's position as the largest manufacturer of television it is known as the television capital of the world in the electronics industry.
Mobile Phones
Since 2008 Mexico has been the third largest manufacturer of mobile phones after China and South Korea with companies such as Lanix
Lanix
Lanix is a Mexican electronics company based in Hermosillo, Sonora, Mexico. It is Mexico's largest domestically owned electronics company, and sells a wide array of both consumer and professional electronics...
, Sony Ericsson
Sony Ericsson
Sony Ericsson Mobile Communications AB is a joint venture established on October 1, 2001 by the Japanese consumer electronics company Sony Corporation and the Swedish telecommunications company Ericsson to manufacture mobile phones....
, Motorola
Motorola
Motorola, Inc. was an American multinational telecommunications company based in Schaumburg, Illinois, which was eventually divided into two independent public companies, Motorola Mobility and Motorola Solutions on January 4, 2011, after losing $4.3 billion from 2007 to 2009...
, Samsung
Samsung
The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea...
, LG
LG
LG may refer to:*LG Corp., a South Korean electronics and petrochemicals conglomerate*LG Electronics, an affiliate of the South Korean LG Group which produces electronic products* Lawrence Graham, a London headquartered firm of business lawyers...
, Nokia
Nokia
Nokia Corporation is a Finnish multinational communications corporation that is headquartered in Keilaniemi, Espoo, a city neighbouring Finland's capital Helsinki...
, Sharp
Sharp Corporation
is a Japanese multinational corporation that designs and manufactures electronic products. Headquartered in Abeno-ku, Osaka, Japan, Sharp employs more than 55,580 people worldwide as of June 2011. The company was founded in September 1912 and takes its name from one of its founder's first...
, Zonda
Zonda Telecom
Zonda Telecom is a Mexican Telecommunications company founded in Guadalajara, Jalisco, in 1968 as a Television manufacturer.This company has several manufacturing plants in the Guadalajara Metropolitan Area, which manufacture its own products as well as manufacture electronic products for other...
, Foxconn
Foxconn
The Foxconn Technology Group is a multinational business group anchored by the Hon Hai Precision Industry Co., Ltd. , a Taiwan-registered corporation headquartered in Tucheng, Taiwan...
BlackBerry
BlackBerry
BlackBerry is a line of mobile email and smartphone devices developed and designed by Canadian company Research In Motion since 1999.BlackBerry devices are smartphones, designed to function as personal digital assistants, portable media players, internet browsers, gaming devices, and much more...
, manufacturing mobile phones in the country.
Computers
Mexico is the third largest manufacturer of computers in the world with both domestic companies such as Lanix
Lanix
Lanix is a Mexican electronics company based in Hermosillo, Sonora, Mexico. It is Mexico's largest domestically owned electronics company, and sells a wide array of both consumer and professional electronics...
, Texa
Texa
Texa is a small island directly south of Islay, in the Inner Hebrides, Scotland. It reaches a height of at its highest point, Ceann Garbh. It is part of the parish of Kildalton on Islay. The distilleries of Laphroaig and Lagavulin are nearby on the Islay coast, as well as Port Ellen...
, Meebox
Meebox
Meebox, also rendered as Meeb[ ]x, is a Mexican company specializing in the design and manufacturer of computers and other consumer electronics. Meebox has operations in Latin America and the United States. It was the first Mexican company to manufacture a full functioned tablet computer and is one...
and foreign companies such as Dell
Dell
Dell, Inc. is an American multinational information technology corporation based in 1 Dell Way, Round Rock, Texas, United States, that develops, sells and supports computers and related products and services. Bearing the name of its founder, Michael Dell, the company is one of the largest...
, Sony
Sony
, commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues....
, HP, Acer Compaq
Compaq
Compaq Computer Corporation is a personal computer company founded in 1982. Once the largest supplier of personal computing systems in the world, Compaq existed as an independent corporation until 2002, when it was acquired for US$25 billion by Hewlett-Packard....
, Samsung
Samsung
The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea...
and Lenovo manufacturing various types of computers across the country.
OEM and ODM manufacturing
Mexico is also home to a large number of OEM and ODM manufactures both foreign and domestic. Among them include Foxconn
Foxconn
The Foxconn Technology Group is a multinational business group anchored by the Hon Hai Precision Industry Co., Ltd. , a Taiwan-registered corporation headquartered in Tucheng, Taiwan...
, Jabil, Elcoteq
Elcoteq
Elcoteq SE is a Finnish contract manufacturer, EMS, and ODM company headquartered in Luxembourg. The company filed for bankruptcy protection in Luxembourg on October 6 2011....
, Falco
Falco Electronics
Falco Electronics is a multinational Mexican electronics corporation founded in 1991, in Merida, Yucatán, México.-Products and Services:Falco's main business activities are the design and manufacture of power magnetics, semiconductors and circuitboards...
, Compal
Compal Electronics
Compal Electronics is a Taiwanese original design manufacturer , handling the production of notebook computers, monitors, and televisions for a variety of clients around the world, including Acer Inc., Dell, Toshiba, Hewlett-Packard, and Fujitsu Siemens Computers...
, Lanix
Lanix
Lanix is a Mexican electronics company based in Hermosillo, Sonora, Mexico. It is Mexico's largest domestically owned electronics company, and sells a wide array of both consumer and professional electronics...
and Flextronics
Flextronics
Flextronics International Ltd. is an electronics manufacturing services provider that offers services to original equipment manufacturers . It also provides supporting supply chain services, including packaging and transportation throughout the world, as well as design and after-sales...
. These companies assemble finished electronics or design and manufacture electronic components on behalf of larger companies such as Sony
Sony
, commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues....
or Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American public multinational corporation headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA that develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of products and services predominantly related to computing through its various product divisions...
using locally sourced components, for example the ODM, Flextronics
Flextronics
Flextronics International Ltd. is an electronics manufacturing services provider that offers services to original equipment manufacturers . It also provides supporting supply chain services, including packaging and transportation throughout the world, as well as design and after-sales...
manufactures Xbox video games systems in Guadalajara
Guadalajara
Guadalajara may refer to:In Mexico:*Guadalajara, Jalisco, the capital of the state of Jalisco and second largest city in Mexico**Guadalajara Metropolitan Area*University of Guadalajara, a public university in Guadalajara, Jalisco...
, Mexico for Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American public multinational corporation headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA that develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of products and services predominantly related to computing through its various product divisions...
using components such as power systems and printed circuit boards from a local company, Falco Electronics
Falco Electronics
Falco Electronics is a multinational Mexican electronics corporation founded in 1991, in Merida, Yucatán, México.-Products and Services:Falco's main business activities are the design and manufacture of power magnetics, semiconductors and circuitboards...
which acts as the OEM.
Engineering and Design
Joint Production
While many foreign companies like Phillips
Phillips
-Places:In the United States:*Phillips, California, unincorporated community in El Dorado County*Phillips, Maine, town in Franklin County*Phillips, Nebraska, village in Hamilton County*Phillips, Minneapolis, Minnesota, community in the city of Minneapolis...
, Vizio
Vizio
Vizio is a privately held producer of consumer electronics, based in Irvine, California, USA. It was founded in October 2002 as V Inc. Vizio's major partner in the consumer electronics arena is AmTran Technology, a Taiwan-based OEM/ODM that manufactures more than half of the televisions sold...
and LG
LG
LG may refer to:*LG Corp., a South Korean electronics and petrochemicals conglomerate*LG Electronics, an affiliate of the South Korean LG Group which produces electronic products* Lawrence Graham, a London headquartered firm of business lawyers...
simply install wholly owned factories in Mexico a number of foreign companies have set up semi-independent joint venture companies with Mexican businesses to manufacture and design components in Mexico. These companies are independently operated from their foreign parent companies and are registered in Mexico. These local companies function under Mexican law and retain a sizable portion of the revenue. These companies typically function dually as in-company OEM development and design facilities and manufacturing centers and usually produce most components needed to manufacture the finished products. An example would by Sharp which has formed Semex
Semex
Semex full name Sharp Electrónica Mexico S.A. de C.V. is the semi-independent Mexican division of Japanese Sharp electronics corporation. It is responsible for the manufacture of all Sharp printed ciruitboards, LED, LCD, and plasma panels, modules and televisions in North and South America and is...
. Semex was founded as a joint venture between Sharp
Sharp Corporation
is a Japanese multinational corporation that designs and manufactures electronic products. Headquartered in Abeno-ku, Osaka, Japan, Sharp employs more than 55,580 people worldwide as of June 2011. The company was founded in September 1912 and takes its name from one of its founder's first...
and Mexican investors which acts as an autonomous independent company which Sharp only maintains partial control over. The company manufactures whole products such televisions and designs individual components on behalf of Sharp such as LCD modules and in return Semex
Semex
Semex full name Sharp Electrónica Mexico S.A. de C.V. is the semi-independent Mexican division of Japanese Sharp electronics corporation. It is responsible for the manufacture of all Sharp printed ciruitboards, LED, LCD, and plasma panels, modules and televisions in North and South America and is...
is granted access to Sharp capital, technology, research capacity and branding. Notable foreign companies which have set up joint venture entities in Mexico include Samsung which formed Samex, a local designer and manufacturer of finished televisions, white goods and individual electronic components like printed circuit boards, LCD panels and semiconductors, Toshiba
Toshiba
is a multinational electronics and electrical equipment corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. It is a diversified manufacturer and marketer of electrical products, spanning information & communications equipment and systems, Internet-based solutions and services, electronic components and...
, who formed Toshiba de México, S.A. de C.V., an administratively autonomous subsidiary which produces electronics parts, televisions and heavy industrial equipment.
Some of these subsidiaries have grown to expand into multiple branches effectively becoming autonomous conglomerates within their own parent companies. Sony
Sony
, commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues....
for example started operations in Mexico in 1976 with a group of Mexican investors, and founded the joint venture, Sony de Mexico which produces LED panels, LCD modules, automotive electronics, appliances and printed circuit boards amongst other products for its Japanese parent company, Sony KG
Sony
, commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues....
. Sony de Mexico has research facilities in Monterrey
Monterrey
Monterrey , is the capital city of the northeastern state of Nuevo León in the country of Mexico. The city is anchor to the third-largest metropolitan area in Mexico and is ranked as the ninth-largest city in the nation. Monterrey serves as a commercial center in the north of the country and is the...
and Mexico City
Mexico City
Mexico City is the Federal District , capital of Mexico and seat of the federal powers of the Mexican Union. It is a federal entity within Mexico which is not part of any one of the 31 Mexican states but belongs to the federation as a whole...
, designs many of the Sony products manufactured in Mexico and has now expanded to create its own finance, music and entertainment subsidiaries which are Mexican registered and independent of their Japanese parent corporation.
Domestic Industry
Although much of Mexico's electronics industry is driven by foreign companies, Mexico also has a sizeable domestic electronics industry and a number of electronics companies including Mabe
Mabe Mexico
Mabe is a global company which designs, produces, and distributes appliances to more than 70 countries around the world. The company was incorporated in 1946 in Mexico City. Mabe was initially dedicated to manufacture kitchen furniture. In the 1950s, Mabe began manufacturing various appliances...
, a major appliance manufacturer and OEM which has been functioning since the nineteen fifties and has expanded into the global market, Meebox
Meebox
Meebox, also rendered as Meeb[ ]x, is a Mexican company specializing in the design and manufacturer of computers and other consumer electronics. Meebox has operations in Latin America and the United States. It was the first Mexican company to manufacture a full functioned tablet computer and is one...
, a designer and manufacturer desktop and tablet computers, solar power panels and electronics components, Texa, which manufactures computers laptops and servers, Falco
Falco Electronics
Falco Electronics is a multinational Mexican electronics corporation founded in 1991, in Merida, Yucatán, México.-Products and Services:Falco's main business activities are the design and manufacture of power magnetics, semiconductors and circuitboards...
, a major international manufacturer of electronic components such as printed circuitboards, power systems, semiconductors, gate drives and which has production facilities in Mexico, India and China, and Lanix
Lanix
Lanix is a Mexican electronics company based in Hermosillo, Sonora, Mexico. It is Mexico's largest domestically owned electronics company, and sells a wide array of both consumer and professional electronics...
, Mexico's largest electronics company which manufactures products such as computers, laptops, smartphones, LED
LED display
An LED display is a flat panel display, which uses light-emitting diodes as a video display. An LED panel is a small display, or a component of a larger display. They are typically used outdoors in store signs and billboards, and in recent years have also become commonly used in destination signs...
and LCD displays, flash memory
Flash memory
Flash memory is a non-volatile computer storage chip that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. It was developed from EEPROM and must be erased in fairly large blocks before these can be rewritten with new data...
, tablets, servers
Server (computing)
In the context of client-server architecture, a server is a computer program running to serve the requests of other programs, the "clients". Thus, the "server" performs some computational task on behalf of "clients"...
, hard drives, RAM
Ram
-Animals:*Ram, an uncastrated male sheep*Ram cichlid, a species of freshwater fish endemic to Colombia and Venezuela-Military:*Battering ram*Ramming, a military tactic in which one vehicle runs into another...
, optical disk drives, and printed circuitboards
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
and employes over 11,000 people in Mexico and Chile and distributes its products throughout Latin America. Another area being currently developed in Mexico is Robotics, Mexico's new Mexone robot has been designed with the idea that in future years develop a commercial application for such advanced robots
Energy and mineral resources
Mineral resources are the "nation's property" (i.e. public property) by constitution. As such, the energy sector is administered by the government with varying degrees of private investment. Mexico is the sixth-largest oil producer in the world, with 3700000 oilbbl/d. PemexPemex
Petróleos Mexicanos or Pemex is a Mexican state-owned petroleum company. As of 2010, with a total asset worth of $415.75 billion, it is the second non-publicly listed largest company in the world by total market value, and Latin America's second largest enterprise by annual revenue as of 2009...
, the public company in charge of administering research, exploration and sales of oil, is the largest company (oil or otherwise) in Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
, and the second largest in Latin America after Brazil's Petrobras
Petrobras
Petróleo Brasileiro or Petrobras is a semi-public Brazilian multinational energy corporation headquartered in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. It is the largest company in Latin America by market capitalization and revenue, and the largest company headquartered in the Southern Hemisphere by market...
.
Nonetheless, the company is heavily taxed, a significant source of revenue for the government, of almost 62 per cent of the company's sales. Without enough money to continue investing in finding new sources or upgrading infrastructure, and being protected constitutionally from private and foreign investment, some have predicted the company may face institutional collapse. While the oil industry is still relevant for the government's budget, its importance in GDP and exports has steadily fallen since the 1980s. In 1980 oil exports accounted for 61.6% of total exports; by 2000 it was only 7.3%.
Services
The tertiary sector was estimated to account for 70.5% of the country's GDP, and employs 58% of the active population. This section includes transportation, commerce, warehousing, restaurant and hotels, arts and entertainment, health, education, financial and banking services, telecommunications as well as public administration and defense. Mexico's service sector is strong, and in 2001 replaced BrazilBrazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
's as the largest service sector in Latin America in dollar terms.
Tourism
Tourism is one of the most important industries in Mexico. It is the fourth largest source of foreign exchange for the country. Mexico is the eighth most visited country in the world (with over 20 million tourists a year).Banking system
According to the IMF
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
the Mexican banking system is strong, in which private banks are profitable and well-capitalized. The financial and banking sector is increasingly dominated by foreign companies or mergers of foreign and Mexican companies with the notable exception of Banorte
Banorte
Banorte is a major bank in Mexico, based in Monterrey. Banorte is ranked in the 84th place out of 100 in the 2007 Great Place to Work List for Mexico.-History:...
. The acquisition of Banamex, one of the oldest surviving financial institutions in Mexico, by Citigroup
Citigroup
Citigroup Inc. or Citi is an American multinational financial services corporation headquartered in Manhattan, New York City, New York, United States. Citigroup was formed from one of the world's largest mergers in history by combining the banking giant Citicorp and financial conglomerate...
was the largest US-Mexico corporate merger, at US $12.5 billion. In spite of that, the largest financial institution in Mexico is Bancomer associated to the Spanish BBVA.
The process of institution building in the financial sector in Mexico has evolved hand in hand with the efforts of financial liberalization and of inserting the economy more fully into world markets. Over the recent years, there has been a wave of acquisitions by foreign institutions such as US-based Citigroup, Spain’s BBVA and the UK’s HSBC. Their presence, along with a better regulatory framework, has allowed Mexico’s banking system to recover from the 1994–95 peso devaluation. Lending to the public and private sector is increasing and so is activity in the areas of insurance, leasing and mortgages. However, bank credit accounts for only 22% of GDP, which is significantly low compared to 70% in Chile. Credit to the Agricultural sector has fallen 45.5% in six years (2001 to 2007), and now represents about 1% of total bank loans. Other important institutions include savings and loans, credit unions, government development banks, “non-bank banks”, bonded warehouse
Bonded warehouse
A Bonded warehouse is a building or other secured area in which dutiable goods may be stored, manipulated, or undergo manufacturing operations without payment of duty. It may be managed by the state or by private enterprise. In the latter case a customs bond must be posted with the government...
s, bonding companies and foreign-exchange firms.
A wave of acquisitions has left Mexico’s financial sector in foreign hands. Their foreign-run affiliates compete with independent financial firms operating as commercial banks, brokerage and securities houses, insurance companies, retirement-fund administrators, mutual funds, and leasing companies. Other important institutions include savings and loans, credit unions, government development banks, “non-bank banks”, bonded warehouses, bonding companies and foreign-exchange firms.
Securities market
Mexico has a single securities market, the Mexican Stock Exchange (Bolsa Mexicana de Valores
Bolsa Mexicana de Valores
The Mexican Stock Exchange is Mexico's only stock exchange. It is situated on Paseo de la Reforma, a prestigious avenue in central Mexico City...
, known as the Bolsa). The market has grown steadily, with its main indices increasing by more than 150% in 2003–05. It is Latin America's second largest exchange, after Brazil's. Still, the Bolsa remains relatively small when compared to other North American exchanges. The New York Stock Exchange is about 100 times larger; the Toronto Stock Exchange is six times larger.
The Indice de Precios y Cotizaciones
Indice de Precios y Cotizaciones
The Indice de Precios y Cotizaciones is an index of 35 stocks that trade on the Bolsa Mexicana de Valores.The companies of Carlos Slim represent 43% of this index.-Components:2003#Alfa#América Móvil#América Telecom#Apasco#Carso Telekom...
(IPC, the general equities index) is the benchmark stock index on the Bolsa. In 2005 the IPC surged 37.8%, to 17,802.71 from 12,917.88, backed by a stronger Mexican economy and lower interest rates. It continued its steep rise through the beginning of 2006, reaching 19,272.63 points at end-March 2006. The stockmarket also posted a record low vacancy rate, according to the central bank. Local stockmarket capitalisation totalled US$236bn at end-2005, up from US$170bn at end-2004. As of March 2006 there were 135 listed companies, down from 153 a year earlier. Only a handful of the listed companies are foreign. Most are from Mexico City
Mexico City
Mexico City is the Federal District , capital of Mexico and seat of the federal powers of the Mexican Union. It is a federal entity within Mexico which is not part of any one of the 31 Mexican states but belongs to the federation as a whole...
or Monterrey
Monterrey
Monterrey , is the capital city of the northeastern state of Nuevo León in the country of Mexico. The city is anchor to the third-largest metropolitan area in Mexico and is ranked as the ninth-largest city in the nation. Monterrey serves as a commercial center in the north of the country and is the...
; companies from these two cities compose 67% of the total listed companies.
The IPC consists of a sample of 35 shares weighted according to their market capitalisation. Heavy hitters are America Telecom, the holding company that manages Latin America’s largest mobile company, América Móvil
América Móvil
América Móvil is a Mexican telecommunication company headquartered in Mexico City, Mexico. It is the fourth largest mobile network operator in terms of equity subscribers, one of the largest corporations in Latin America, and the world. America Movil is a Fortune 500 company...
; Telefonos de Mexico
Telmex
Telmex is a telecommunications company headquartered in Mexico City that provides telecommunication products and services in Mexico, Argentina, Colombia, Brazil and other countries in Latin America. In addition to traditional fixed-line telephone service, Telmex also offers Internet access, data,...
, Mexico’s largest telephone company; Grupo Bimbo
Grupo Bimbo
Grupo Bimbo is the largest Mexican food company and the largest bakery in the world with brands in Americas, Europe, and China.-History:Grupo Bimbo was established in Mexico in 1945 by Lorenzo Servitje, Jose T. Mata, Jaime Sendra, and Jaime Jorba...
, world's biggest baker; and Wal-Mart de México
Walmex
Wal-Mart de Mexico , is a Mexican public corporation, which is 31% owned by the American retail multinational corporation Wal-Mart Stores, Inc. It has been traded in the Mexican Stock Exchange since 1977 ....
, a subsidiary of the US retail giant. The makeup of the IPC is adjusted every six months, with selection aimed at including the most liquid shares in terms of value, volume and number of trades.
Mexico’s stockmarket is closely linked to developments in the US. Thus, volatility in the New York and Nasdaq stock exchanges, as well as interest-rate changes and economic expectations in the US, can steer the performance of Mexican equities. This is both because of Mexico’s economic dependence on the US and the high volume of trading in Mexican equities through American Depositary Receipts (ADRs). Currently, the decline in the value of the dollar is making non-US markets, including Mexico's, more attractive.
Despite the recent gains, investors remain wary of making placements in second-tier initial public offerings (IPOs). Purchasers of new issues were disappointed after prices fell in numerous medium-sized companies that made offerings in 1996 and 1997. IPO activity in Mexico remains tepid and the market for second-tier IPOs is barely visible. There were three IPOs in 2005.
Government policies and the Central Bank
| Financial indicators |
|---|
}}
|-
! style="text-align:left; background:#f0f0f0; vertical-align:top;"|Currency exchange rate
| style="background:#f0f0f0; vertical-align:top;"| 12.74 MXN per 1 USD (03/03/2010)
|-
! style="text-align:left; vertical-align:top;"|Reserves
|valign="top"| US $134.534 billion (2011)
|-
! style="text-align:left; background:#f0f0f0; vertical-align:top;"|Government budget
| style="background:#f0f0f0; vertical-align:top;"| US $196.5 billion (revenues)
|-
! style="text-align:left; vertical-align:top;"|Public debt
|valign="top"| 20.7% of GDP (2006)
|-
! style="text-align:left; background:#f0f0f0; vertical-align:top;"|External debt
| style="background:#f0f0f0; vertical-align:top;"| US $178.3 billion (2006)
|-
! style="text-align:left; vertical-align:top;"|Bank funding rate
|valign="top"| 5.25% (5/15/2009)
|-
| style="text-align:center; background:lightblue;" colspan="2"|
|}
Banco de México is Mexico's central bank
Central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, or monetary authority is a public institution that usually issues the currency, regulates the money supply, and controls the interest rates in a country. Central banks often also oversee the commercial banking system of their respective countries...
, an internally autonomous public institution whose governor is appointed by the president
President of Mexico
The President of the United Mexican States is the head of state and government of Mexico. Under the Constitution, the president is also the Supreme Commander of the Mexican armed forces...
and approved by the legislature to which it is fully responsible. Banco de México's functions are outlined in the 28th article of the constitution
Constitution of Mexico
The Political Constitution of the United Mexican States is the current constitution of Mexico. It was drafted in Santiago de Querétaro, in the State of Querétaro, by a constitutional convention, during the Mexican Revolution. It was approved by the Constitutional Congress on February 5, 1917...
and further expanded in the Monetary Law of the United Mexican States. Banco de México's main objective is to achieve stability in the purchasing power of the national currency. It is also the lender of last resort.
Currency policy
Mexico has a floating exchange rateFloating exchange rate
A floating exchange rate or fluctuating exchange rate is a type of exchange rate regime wherein a currency's value is allowed to fluctuate according to the foreign exchange market. A currency that uses a floating exchange rate is known as a floating currency....
regime.
The floating exchange originated with reforms initiated after the December 1994 peso crash which had followed an unsustainable adherence to a short band. Under the new system, Banco de México now makes no commitment to the level of the peso exchange rate, although it does employ an automatic mechanism to accumulate foreign reserves. It also possesses tools aimed at smoothing out volatility. The Exchange Rate Commission sets policy; it is made up of six members—three each from the Ministry of Finance and Public Credit (Secretaría de Hacienda y Crédito Publico—SHCP) and the central bank, with the SHCP holding the deciding vote.
In August 1996, Banco de México initiated a mechanism to acquire foreign reserves when the peso is strong, without giving the market signals about a target range for the exchange rate. The resulting high levels of reserves, mostly from petroleum revenues, have helped to improve the terms and conditions on debt Mexico places on foreign markets. However, there is concern that the government relies too heavily on oil income in order to build a healthy base of reserves. According to the central bank, international reserves stood at US $75.8 billion in 2007. In May 2003, Banco de México launched a program that sells U.S. dollars via a monthly auction, with the goal of maintaining a stable, but moderate, level of reserves.
From April 1, 1998 through April 1, 2008 the Peso traded around a range varying from $8.46 MXN per $1.00 USD on April 21, 1998 to $11.69 MXN per $1.00 USD on May 11, 2004, a 10 year peak depreciation of 38.18% between the two reference date extremes before recovering.
After the onset of the US credit crisis that accelerated in October 2008, the Peso had an exchange rate during October 1, 2008 through April 1, 2009 fluctuating from lowest to highest between $10.96 MXN per $1.00 USD on October 1, 2008 to $15.42 MXN per $1.00 USD on March 9, 2009, a peak depreciation ytd of 28.92% during those six months between the two reference date extremes before recovering.
From the $11.69 rate during 2004's low to the $15.42 rate during 2009's low, the peso depreciated 31.91% in that span covering the US recession coinciding Iraq War of 2003 and 2004 to the US & Global Credit Crisis of 2008.
Some experts including analysts at Goldman Sachs who coined the term BRIC in reference to the growing economics of Brazil, Russia, India, and China for marketing purposes believe that Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
is going to be the 5th or 6th biggest economy in the world by the year 2050, behind China
People's Republic of China
China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
, United States, India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, Brazil, and possibly Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
.
Monetary system
Mexico’s monetary policy was revised following the 1994–95 financial crisis, when officials decided that maintaining general price stability was the best way to contribute to the sustained growth of employment and economic activity. As a result, Banco de México has as its primary objective maintaining stability in the purchasing power of the peso. It sets an inflation target, which requires it to establish corresponding quantitative targets for the growth of the monetary base and for the expansion of net domestic credit.The central bank also monitors the evolution of several economic indicators, such as the exchange rate, differences between observed and projected inflation, the results of surveys on the public and specialists’ inflation expectations, revisions on collective employment contracts, producer prices, and the balances of the current and capital accounts.
A debate continues over whether Mexico should switch to a US-style interest rate-targeting system. Government officials in favor of a change say that the new system would give them more control over interest rates, which are becoming more important as consumer credit levels rise.
Until 2008(???), Mexico used a unique system, amongst the OECD countries, to control inflation in a mechanism known as the corto (lit. "shortage") a mechanism that allowed the central bank to influence market interest rates by leaving the banking system short of its daily demand for money by a predetermined amount. If the central bank wanted to push interest rates higher, it increased the corto. If it wished to lower interest rates, it decreased the corto. Source: BANXICO: in April 2004, the Central Bank began setting a referential overnight interest rate as its monetary policy.
Trade
| International trade |
|---|
}}
|-
! style="text-align:left; background:#f0f0f0; vertical-align:top;"|Exports
| style="background:#f0f0f0; vertical-align:top;"| US $248.8 billion f.o.b. (2006)
|-
! style="text-align:left; vertical-align:top;"|Imports
|valign="top"| US $253.1 billion f.o.b. (2006)
|-
! style="text-align:left; background:#f0f0f0; vertical-align:top;"|Current account
| style="background:#f0f0f0; vertical-align:top;"| US $400.1 million (2006)
|-
! style="text-align:left; vertical-align:top;"|Export partners
|valign="top"| US 90.9%, Canada 2.2%, Spain 1.4%, Germany 1.3%, Colombia 0.9% (2006)
|-
! style="text-align:left; background:#f0f0f0; vertical-align:top;"|Import partners
| style="background:#f0f0f0; vertical-align:top;"| US 53.4%, China 8%, Japan 5.9% (2005)
|-
| style="text-align:center; background:lightblue;" colspan="2"|
|}
Mexico is an export oriented economy. It is an important trade power as measured by the value of merchandise traded, and the country with the greatest number of free trade agreements. In 2005, Mexico was the world's fifteenth largest merchandise exporter and twelfth largest merchandise importer with a 12% annual percentage increase in overall trade. In fact, from 1991 to 2005 Mexican trade increased fivefold. Mexico is the biggest exporter and importer in Latin America; in 2005, Mexico alone exported US $213.7 billion, roughly equivalent to the sum of the exports of Brazil, Argentina, Venezuela, Uruguay, and Paraguay. By 2009 Mexico ranked once again number 15 on World's leading exporters with US $230 billion (And amongst the top ten excluding Intra-EU countries). However, Mexican trade is fully integrated with that of its North American partners: close to 90% of Mexican exports and 50% of its imports are traded with the United States and Canada. Nonetheless, NAFTA has not produced trade diversion. While trade with the United States increased 183% from 1993–2002, and that with Canada 165%, other trade agreements have shown even more impressive results: trade with Chile increased 285%, with Costa Rica 528% and Honduras 420%. Trade with the European Union increased 105% over the same time period.
Free trade agreements
Mexico joined the General Agreement on Tariffs and TradeGeneral Agreement on Tariffs and Trade
The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade was negotiated during the UN Conference on Trade and Employment and was the outcome of the failure of negotiating governments to create the International Trade Organization . GATT was signed in 1947 and lasted until 1993, when it was replaced by the World...
(GATT) in 1986, and today is an active and constructive participant of the World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization is an organization that intends to supervise and liberalize international trade. The organization officially commenced on January 1, 1995 under the Marrakech Agreement, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade , which commenced in 1948...
. Fox's administration promoted the establishment of a Free Trade Area of the Americas
Free Trade Area of the Americas
The Free Trade Area of the Americas , , ) was a proposed agreement to eliminate or reduce the trade barriers among all countries in the Americas but Cuba. In the last round of negotiations, trade ministers from 34 countries met in Miami, United States, in November 2003 to discuss the proposal...
; Puebla
Puebla, Puebla
The city and municipality of Puebla is the capital of the state of Puebla, and one of the five most important colonial cities in Mexico. Being a planned city, it is located to the east of Mexico City and west of Mexico's main port, Veracruz, on the main route between the two.The city was founded...
served as temporary headquarters for the negotiations, and several other cities are now candidates for its permanent headquarters if the agreement is reached and implemented.
Mexico has signed 12 free trade agreements with 44 countries:
- the North American Free Trade AgreementNorth American Free Trade AgreementThe North American Free Trade Agreement or NAFTA is an agreement signed by the governments of Canada, Mexico, and the United States, creating a trilateral trade bloc in North America. The agreement came into force on January 1, 1994. It superseded the Canada – United States Free Trade Agreement...
(NAFTA) (1994) with the United States and Canada; - Grupo de los tresG3 Free Trade AgreementThe G-3 is a free trade agreement between Colombia, Mexico, and Venezuela that came into effect on January 1, 1995, which created an extended market of 149 million consumers with a combined GDP of US$486.5 billion. The agreement states a ten percent tariff reduction over ten years for the trade...
, Group of the three [countries], or G-3 (1995) with ColombiaColombiaColombia, officially the Republic of Colombia , is a unitary constitutional republic comprising thirty-two departments. The country is located in northwestern South America, bordered to the east by Venezuela and Brazil; to the south by Ecuador and Peru; to the north by the Caribbean Sea; to the...
and VenezuelaVenezuelaVenezuela , officially called the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela , is a tropical country on the northern coast of South America. It borders Colombia to the west, Guyana to the east, and Brazil to the south...
; the latter decided to terminate the agreement in 2006; Mexico announced its intention to invite EcuadorEcuadorEcuador , officially the Republic of Ecuador is a representative democratic republic in South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and by the Pacific Ocean to the west. It is one of only two countries in South America, along with Chile, that do not have a border...
, Peru or PanamaPanamaPanama , officially the Republic of Panama , is the southernmost country of Central America. Situated on the isthmus connecting North and South America, it is bordered by Costa Rica to the northwest, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. The...
as a replacement; - Free Trade Agreement with Costa RicaCosta RicaCosta Rica , officially the Republic of Costa Rica is a multilingual, multiethnic and multicultural country in Central America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, Panama to the southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the west and the Caribbean Sea to the east....
(1995); - Free Trade Agreement with BoliviaBoliviaBolivia officially known as Plurinational State of Bolivia , is a landlocked country in central South America. It is the poorest country in South America...
(1995); - Free Trade Agreement with NicaraguaNicaraguaNicaragua is the largest country in the Central American American isthmus, bordered by Honduras to the north and Costa Rica to the south. The country is situated between 11 and 14 degrees north of the Equator in the Northern Hemisphere, which places it entirely within the tropics. The Pacific Ocean...
(1998);
- Free Trade Agreement with ChileChileChile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
(1999); - Free Trade Agreement with the European UnionEuropean UnionThe European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
(2000); - Free Trade Agreement with IsraelIsraelThe State of Israel is a parliamentary republic located in the Middle East, along the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea...
(2000); - TN Free Trade Agreement (2001), with GuatemalaGuatemalaGuatemala is a country in Central America bordered by Mexico to the north and west, the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, Belize to the northeast, the Caribbean to the east, and Honduras and El Salvador to the southeast...
, El Salvador and HondurasHondurasHonduras is a republic in Central America. It was previously known as Spanish Honduras to differentiate it from British Honduras, which became the modern-day state of Belize...
; - Free Trade Agreement with the European Free Trade AssociationEuropean Free Trade AssociationThe European Free Trade Association or EFTA is a free trade organisation between four European countries that operates parallel to, and is linked to, the European Union . EFTA was established on 3 May 1960 as a trade bloc-alternative for European states who were either unable to, or chose not to,...
(EFTA), integrated by IcelandIcelandIceland , described as the Republic of Iceland, is a Nordic and European island country in the North Atlantic Ocean, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Iceland also refers to the main island of the country, which contains almost all the population and almost all the land area. The country has a population...
, Norway, LiechtensteinLiechtensteinThe Principality of Liechtenstein is a doubly landlocked alpine country in Central Europe, bordered by Switzerland to the west and south and by Austria to the east. Its area is just over , and it has an estimated population of 35,000. Its capital is Vaduz. The biggest town is Schaan...
and SwitzerlandSwitzerlandSwitzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
(2001); - Free Trade Agreement with UruguayUruguayUruguay ,officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay,sometimes the Eastern Republic of Uruguay; ) is a country in the southeastern part of South America. It is home to some 3.5 million people, of whom 1.8 million live in the capital Montevideo and its metropolitan area...
(2004); and - Free Trade Agreement with Japan (2005)
Mexico has shown interest in becoming an associate member of Mercosur
Mercosur
Mercosur or Mercosul is an economic and political agreement among Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay. Founded in 1991 by the Treaty of Asunción, which was later amended and updated by the 1994 Treaty of Ouro Preto. Its purpose is to promote free trade and the fluid movement of goods, people,...
. The Mexican government has also started negotiations with South Korea, Singapore and Peru, and also wishes to start negotiations with Australia for a trade agreement between the two countries.
NAFTA

The NAAEC agreement was a response to environmentalists' concerns that companies would relocate to Mexico or the United States would lower its standards if the three countries did not achieve a unanimous regulation on the environment. The NAAEC, in an aim to be more than a set of environmental regulations, established the North American Commission for Environmental Cooperation (NACEC), a mechanism for addressing trade and environmental issues, the North American Development Bank (NADBank) for assisting and financing investments in pollution reduction and the Border Environmental Cooperation Commission (BECC). The NADBank and the BECC have provided economic benefits to Mexico by financing 36 projects, mostly in the water sector. By complementing NAFTA with the NAAEC, it has been labeled the "greenest" trade agreement.
The NAALC supplement to NAFTA aimed to create a foundation for cooperation among the three members for the resolution of labor problems, as well as to promote greater cooperation among trade unions and social organizations in all three countries, in order to fight for the improvement of labor conditions. Though most economists agree that it is difficult to assess the direct impact of the NAALC, it is agreed that there has been a convergence of labor standards in North America. Given its limitations, however, NAALC has not produced (and in fact was not intended to achieve) convergence in employment, productivity and salary trend in North America.
The agreement fell short in liberalizing movement of people across the three countries. In a limited way, however, immigration of skilled Mexican and Canadian workers to the United States was permitted under the TN status
TN status
TN status is a special non-immigrant status in the United States unique to citizens of Canada and Mexico. Professions identified in the Canada - United States Free Trade Agreement which began in 1988 are permitted TN Visas for legal work in the United States and Canada, creating freedom of labor...
. NAFTA allows for a wide list of professions, most of which require at least a Bachelor's degree, for which a Mexican or a Canadian citizen can request TN status and temporarily immigrate to the United States. Unlike the visas available to other countries, TN status requires no sponsorship, but simply a job offer letter.
The overall benefits of NAFTA have been quantified by several economists, whose findings have been reported in several publications like the World Bank
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for capital programmes.The World Bank's official goal is the reduction of poverty...
's Lessons from NAFTA for LA and the Caribbean, NAFTA's Impact on North America, and NAFTA revisited by the Institute for International Economics. They assess that NAFTA has been positive for Mexico, whose poverty rates have fallen, and real income salaries have risen even after accounting for the 1994–1995 Economic Crisis. Nonetheless, they also state that it has not been enough, or fast enough, to produce an economic convergence nor to reduce the poverty rates substantially or to promote higher rates of growth. Beside this the textile industry gain hype with this agreement and the textile industry in Mexico gained open access to the American market, promoting exports to the United States. The value of Mexican cotton and apparel exports to the U.S. grew from $ 3 billion in 1995 to $ 8.4 billion in 2002, a record high of $ 9.4 billion in 2000. At the same time, the share of Mexico’s cotton textile market the U.S. has increased from 8 percent in 1995 to 13 percent in 2002. Some have suggested that in order to fully benefit from the agreement Mexico should invest in education and promote innovation as well as in infrastructure and agriculture.
Contrary to popular belief, the maquiladora
Maquiladora
A maquiladora or maquila is a concept often referred to as an operation that involves manufacturing in a country that is not the client's and as such has an interesting duty or tariff treatment...
program was in place far before NAFTA, in some sense dating all the way back to 1965. A maquiladora manufacturer operates by importing raw materials into Mexico either tariff free (NAFTA) or at a reduced rate on a temporary basis (18 months) and then using Mexico's relatively less expensive labor costs to produce finished goods for export. Prior to NAFTA maquiladora companies importing raw materials from anywhere in the world were given preferencial tariff rates by the Mexican government so long as the finished good was for export. The US, prior to NAFTA, allowed Maquiladora manufactured goods to be imported into the US with the tariff rate only being applied to the value of non US raw materials used to produce the good, thus reducing the tariff relative to other countries. NAFTA has eliminated all tariffs on goods between the two countries, but for the maquiladora industry significantly increased the tariff rates for goods sourced outside of NAFTA.
Given the overall size of trade between Mexico and the United States, there are remarkably few trade disputes, involving relatively small dollar amounts. These disputes are generally settled in WTO or NAFTA panels or through negotiations between the two countries. The most significant areas of friction involve trucking, sugar, high fructose corn syrup
High fructose corn syrup
High-fructose corn syrup — also called glucose-fructose syrup in the UK, glucose/fructose in Canada, and high-fructose maize syrup in other countries — comprises any of a group of corn syrups that has undergone enzymatic processing to convert some of its glucose into fructose to produce...
, and a number of other agricultural products.
Mexican trade facilitation and competitiveness
A research brief published by the World BankWorld Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for capital programmes.The World Bank's official goal is the reduction of poverty...
as part of its Trade Costs and Facilitation Project suggests that Mexico has the potential to substantially increase trade flows and economic growth through trade facilitation
Trade facilitation
Trade facilitation looks at how procedures and controls governing the movement of goods across national borders can be improved to reduce associated cost burdens and maximise efficiency while safeguarding legitimate regulatory objectives...
reform. The study examines the potential impacts of trade facilitation reforms in four areas: port efficiency, customs administration, information technology, and regulatory environment (including standards).
The study projects overall increments from domestic reforms to be on the order of $31.8 billion, equivalent to 22.4 percent of total Mexican manufacturing exports for 2000–03. On the imports side, the corresponding figures are $17.1 billion and 11.2 percent, respectively. Increases in exports, including textiles, would result primarily from improvements in port efficiency and the regulatory environment. Exports of transport equipment would be expected to increase by the greatest increment from improvements in port efficiency, whereas exports of food and machinery would largely be the result of improvements in the regulatory environment. On the imports side, Mexican improvements in port efficiency would appear to be the most important factor, although for imports of transport equipment, improvements in service sector infrastructure would also be of relative importance.

