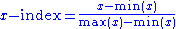Human Development Index
Encyclopedia
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a composite statistic used to rank countries by level of "human development
" and separate "very high human development", "high human development", "medium human development", and "low human development" countries. The Human Development Index (HDI) is a comparative measure of life expectancy, literacy, education and standards of living for countries worldwide. It is a standard means of measuring well-being, especially child welfare. It is used to distinguish whether the country is a developed, a developing or an under-developed country, and also to measure the impact of economic policies on quality of life. There are also HDI for states, cities, villages, etc. by local organizations or companies.
(UNDP). These were devised and launched by Pakistani economist Mahbub ul Haq
in 1990 and had the explicit purpose "to shift the focus of development economics from national income accounting to people centered policies". To produce the Human Development Reports, Mahbub ul Haq brought together a group of well-known development economists including: Paul Streeten
, Frances Stewart
, Gustav Ranis
, Keith Griffin
, Sudhir Anand and Meghnad Desai. But it was Nobel laureate Amartya Sen
’s work on capabilities and functionings that provided the underlying conceptual framework. Haq was sure that a simple composite measure of human development was needed in order to convince the public, academics, and policy-makers that they can and should evaluate development not only by economic advances but also improvements in human well-being. Sen initially opposed this idea, but he went on to help Haq develop the Human Development Index (HDI). Sen was worried that it was difficult to capture the full complexity of human capabilities in a single index but Haq persuaded him that only a single number would shift the attention of policy-makers from concentration on economic to human well-being.
Other organizations and companies also make HD Indices with differing formulae and results (see below).
Published on 4 November 2010 (and updated on 10 June 2011), starting with the 2011 Human Development Report the HDI combines three dimensions:
The HDI combined three dimensions up until its 2011 report:
1. Life Expectancy Index (LEI)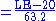
2. Education Index
(EI)
2.1 Mean Years of Schooling Index (MYSI)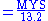
2.2 Expected Years of Schooling Index (EYSI)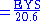
3. Income Index (II)
Finally, the HDI is the geometric mean
of the previous three normalized indices:

LE: Life expectancy at birth
MYS: Mean years of schooling (Years that a 25-year-old person or older has spent in schools)
EYS: Expected years of schooling (Years that a 5-year-old child will spend with his education in his whole life)
GNIpc: Gross national income at purchasing power parity per capita
 This is the methodology used by the UNDP up until its 2011 report.
This is the methodology used by the UNDP up until its 2011 report.
The formula defining the HDI is promulgated by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)
In general, to transform a raw variable
, say , into a unit-free index
, into a unit-free index
between 0 and 1 (which allows different indices to be added together), the following formula
is used:
where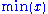 and
and 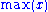 are the lowest and highest values
are the lowest and highest values
the variable can attain, respectively.
can attain, respectively.
The Human Development Index (HDI) then represents the uniformly weighted sum with ⅓ contributed by each of the following factor indices:
Other organizations/companies may include Democracy Index
, Population, etc. which produces different number of HDI.
):
Note: The green arrows , red arrows , and blue dashes represent changes in rank when compared to the new 2011 data HDI for 2010 - published in the 2011 report (p. 131).
Note: The green arrows , red arrows , and blue dashes represent changes in rank when compared to the 2011 HDI list, for countries listed in both rankings.
Countries in the top quartile of HDI ("Very high human development" group) with a missing IHDI include: New Zealand
, Liechtenstein
, Japan
, Hong Kong
, Singapore
, United Arab Emirates
, Andorra
, Brunei
, Malta
, Qatar
, Bahrain
, Chile
, Argentina
and Barbados
.
, Marshall Islands
, Monaco
, Nauru
, San Marino
, Somalia
and Tuvalu
.
Note: The green arrows , red arrows , and blue dashes represent changes in rank when compared to the 2009 HDI published in the 2010 report.
Note: The green arrows , red arrows , and blue dashes represent changes in rank when compared to the 2010 HDI list, for countries listed in both rankings.
Countries in the top quartile of HDI ("Very high human development" group) with a missing IHDI include: New Zealand
, Liechtenstein
, Japan
, Hong Kong
, Singapore
, Andorra
, United Arab Emirates
, Malta
, Brunei
, Qatar
, Bahrain
and Barbados
.
lodged a formal protest at its lack of inclusion. The UNDP explained that Cuba had been excluded due to the lack of an "internationally reported figure for Cuba’s Gross National Income adjusted for Purchasing Power Parity". All other indicators for Cuba were available, and reported by the UNDP, but the lack of one indicator meant that no ranking could be attributed to the country.
Africa
Americas
Asia
Europe
Oceania
by UNDP was released on October 5, 2009, and covers the period up to 2007. It was titled "Overcoming barriers: Human mobility and development". The top countries by HDI were grouped in a new category called "Very High Human Development". The report refers to these countries as developed countries. They are:
Africa
Asia
Europe
Oceania
(PPP), implying substantial adjustments for many countries, resulting in changes in HDI values and, in many cases, HDI ranks.
Africa
Europe
Oceania
, Brazil
, on November 27, 2007. Its focus was on "Fighting climate change: Human solidarity in a divided world." Most of the data used for the report are derived largely from 2005 or earlier, thus indicating an HDI for 2005. Not all UN member states
choose to or are able to provide the necessary statistics.
The report showed a small increase in world HDI in comparison with last year's report. This rise was fueled by a general improvement in the developing world, especially of the least developed countries
group. This marked improvement at the bottom was offset with a decrease in HDI of high income countries.
A HDI below 0.5 is considered to represent "low development". All 22 countries in that category are located in Africa
. The highest-scoring Sub-Saharan countries, Gabon
and South Africa
, are ranked 119th and 121st, respectively. Nine countries departed from this category this year and joined the "medium development" group.
A HDI of 0.8 or more is considered to represent "high development". This includes all developed countries, such as those in North America
, Western Europe
, Oceania
, and Eastern Asia, as well as some developing countries in Eastern Europe
, Central and South America, Southeast Asia
, the Caribbean
, and the oil-rich Arabian Peninsula
. Seven countries were promoted to this category this year, leaving the "medium development" group: Albania
, Belarus
, Brazil
, Libya
, Macedonia
, Russia
and Saudi Arabia
.
On the following table, green arrows represent an increase in ranking over the previous study, while red arrows represent a decrease in ranking. They are followed by the number of spaces they moved. Blue dashes represent a nation that did not move in the rankings since the previous study.
have been ranked the highest nine times, Canada
eight times, followed by Japan
which has been ranked highest three times. Iceland
has been ranked highest twice.
Economist
Bryan Caplan
has criticised the way HDI scores are produced; each of the three components are bounded between zero and one. As a result of that, rich countries effectively cannot improve their rating (and thus their ranking relative to other countries) in certain categories, even though there is a lot of scope for economic growth and longevity left. "This effectively means that a country of immortals with infinite per-capita GDP would get a score of .666 (lower than South Africa and Tajikistan) if its population were illiterate and never went to school." He argues, "Scandinavia comes out on top according to the HDI because the HDI is basically a measure of how Scandinavian your country is."
Economists Hendrik Wolff, Howard Chong and Maximilian Auffhammer
discuss the HDI from the perspective of data error in the underlying health, education and income statistics used to construct the HDI. They identify three sources of data error which are due to (i) data updating, (ii) formula revisions and (iii) thresholds to classify a country’s development status and find that 11%, 21% and 34% of all countries can be interpreted as currently misclassified in the development bins due to the three sources of data error, respectively. The authors suggest that the United Nations should discontinue the practice of classifying countries into development bins because the cut-off values seem arbitrary, can provide incentives for strategic behavior in reporting official statistics, and have the potential to misguide politicians, investors, charity donators and the public at large which use the HDI. In 2010 the UNDP reacted to the criticism and updated the thresholds to classify nations as low, medium and high human development countries. In a comment to The Economist
in early January 2011, the Human Development Report Office responded to a January 6, 2011 article in The Economist
which discusses the Wolff et al. paper. The Human Development Report Office states that they undertook a systematic revision of the methods used for the calculation of the HDI and that the new methodology directly addresses the critique by Wolff et al. in that it generates a system for continuous updating of the human development categories whenever formula or data revisions take place.
The following are common criticisms directed at the HDI: that it is a redundant measure that adds little to the value of the individual measures composing it; that it is a means to provide legitimacy to arbitrary weightings of a few aspects of social development; that it is a number producing a relative ranking which is useless for inter-temporal comparisons, and difficult to compare a country's progress or regression since the HDI for a country in a given year depends on the levels of, say, life expectancy or GDP per capita of other countries in that year. However, each year, UN member states are listed and ranked according to the computed HDI. If high, the rank in the list can be easily used as a means of national aggrandizement; alternatively, if low, it can be used to highlight national insufficiencies. Using the HDI as an absolute index of social welfare, some authors have used panel HDI data to measure the impact of economic policies on quality of life
.
Ratan Lal Basu
criticises the HDI concept from a completely different angle. According to him the Amartya Sen
-Mahbub ul Haq
concept of HDI considers that provision of material amenities alone would bring about Human Development, but Basu opines that Human Development in the true sense should embrace both material and moral development. According to him human development based on HDI alone, is similar to dairy farm economics to improve dairy farm output. To quote: ‘So human development effort should not end up in amelioration of material deprivations alone: it must undertake to bring about spiritual and moral development to assist the biped to become truly human.’ For example, a high suicide rate would bring the index down.
A few authors have proposed alternative indices to address some of the index's shortcomings. However, of those proposed alternatives to the HDI, few have produced alternatives covering so many countries, and that no development index (other than, perhaps, Gross Domestic Product per capita) has been used so extensively—or effectively, in discussions and developmental planning as the HDI.
However, there has been one lament about the HDI that has resulted in an alternative index: David Hastings, of the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific
published a report geographically extending the HDI to 230+ economies, whereas the UNDP HDI for 2009 enumerates 182 economies and coverage for the 2010 HDI dropped to 169 countries.
The income component of HDI is problematic, because there is effectively little difference given to a very high, high, and medium income countries. For example, even with a GNI per capita of $20,000, the income index is only 19% below that of a country with a per capita GNI of $45,000, despite the 150% difference. This is attributed to the logarithmic formula used to calculate the income index. Because of this property, the highest income countries have their income index (33% of total HDI) understated versus every other country that is not very high income, and so on. The problem is worsened with inequality adjusted income, where the income index is adjusted for inequality. Effectively, this means that countries with much lower inequality adjusted incomes may have a higher income index. For example, Country A has a GNI per capita of $45,000 (index=.864), while B is at $15,000 (.695). The former has an inequality factor of .75, while the latter has an inequality factor of .95. In pure income amounts, Country A is still much better off ($33,750 vs $12,350). However, because the index itself is adjusted, Country B ends up having a higher inequality adjusted income index; Country B:(.95*.695)=.66, Country A: (.75*.864)=.648. Thus, while the normal HDI measure does not take into account large differences in income between groups of countries, the inequality adjusted form allows for much poorer countries (adjusted for inequality) to have a higher index. Therefore, it cannot be said that the income component of HDI or IHDI is a proxy for standard of living. This is in addition to the fact that GNI is not a direct proxy for household income.
Lists:
Human development (humanity)
Human development in the scope of humanity, specifically international development, is an international and economic development paradigm that is about much more than the rise or fall of national incomes. People are the real wealth of nations...
" and separate "very high human development", "high human development", "medium human development", and "low human development" countries. The Human Development Index (HDI) is a comparative measure of life expectancy, literacy, education and standards of living for countries worldwide. It is a standard means of measuring well-being, especially child welfare. It is used to distinguish whether the country is a developed, a developing or an under-developed country, and also to measure the impact of economic policies on quality of life. There are also HDI for states, cities, villages, etc. by local organizations or companies.
Origins
The origins of the HDI are found in the annual Human Development Reports of the United Nations Development ProgrammeUnited Nations Development Programme
The United Nations Development Programme is the United Nations' global development network. It advocates for change and connects countries to knowledge, experience and resources to help people build a better life. UNDP operates in 177 countries, working with nations on their own solutions to...
(UNDP). These were devised and launched by Pakistani economist Mahbub ul Haq
Mahbub ul Haq
Mahbub ul Haq was an Pakistani economist who is known to be the pioneer of Human development theory and the founder of the Human Development Report...
in 1990 and had the explicit purpose "to shift the focus of development economics from national income accounting to people centered policies". To produce the Human Development Reports, Mahbub ul Haq brought together a group of well-known development economists including: Paul Streeten
Paul Streeten
Paul Streeten is an economics professor. He was a professor at Boston University, USA until his retirement. He has been a distinguished academic working on development economics since the 1950s.-Biography:...
, Frances Stewart
Frances Stewart
Frances Julia Stewart is Professor of Development Economics and Director of the Centre for Research on Inequality, Human Security and Ethnicity , University of Oxford. A pre-eminent development economist, she was named one of fifty outstanding technological leaders for 2003 by Scientific American...
, Gustav Ranis
Gustav Ranis
Gustav Ranis is a leading development economist. Ranis is the Frank Altschul Professor Emeritus of International Economics, Yale University.-Career:...
, Keith Griffin
Keith Griffin (economist)
Keith B. Griffin is an economist, notable for his pioneering work on the economics of poverty reduction over more than forty years.From 1979 to 1988 he was President of Magdalen College, Oxford and he remains an honorary fellow there.-Selected publications:...
, Sudhir Anand and Meghnad Desai. But it was Nobel laureate Amartya Sen
Amartya Sen
Amartya Sen, CH is an Indian economist who was awarded the 1998 Nobel Prize in Economic Sciences for his contributions to welfare economics and social choice theory, and for his interest in the problems of society's poorest members...
’s work on capabilities and functionings that provided the underlying conceptual framework. Haq was sure that a simple composite measure of human development was needed in order to convince the public, academics, and policy-makers that they can and should evaluate development not only by economic advances but also improvements in human well-being. Sen initially opposed this idea, but he went on to help Haq develop the Human Development Index (HDI). Sen was worried that it was difficult to capture the full complexity of human capabilities in a single index but Haq persuaded him that only a single number would shift the attention of policy-makers from concentration on economic to human well-being.
Other organizations and companies also make HD Indices with differing formulae and results (see below).
Dimensions and calculation
Published on 4 November 2010 (and updated on 10 June 2011), starting with the 2011 Human Development Report the HDI combines three dimensions:
- A long and healthy life: Life expectancy at birth
- Education index: Mean years of schooling and Expected years of schooling
- A decent standard of living: GNIGross National IncomeThe GNI consists of: the personal consumption expenditures, the gross private investment, the government consumption expenditures, the net income from assets abroad , and the gross exports of goods and services, after deducting two components: the gross imports of goods and services, and the...
per capita (PPP US$)
The HDI combined three dimensions up until its 2011 report:
- Life expectancyLife expectancyLife expectancy is the expected number of years of life remaining at a given age. It is denoted by ex, which means the average number of subsequent years of life for someone now aged x, according to a particular mortality experience...
at birth, as an index of population health and longevity - Knowledge and education, as measured by the adult literacyLiteracyLiteracy has traditionally been described as the ability to read for knowledge, write coherently and think critically about printed material.Literacy represents the lifelong, intellectual process of gaining meaning from print...
rate (with two-thirds weighting) and the combined primary, secondary, and tertiary gross enrollment ratio (with one-third weighting). - Standard of livingStandard of livingStandard of living is generally measured by standards such as real income per person and poverty rate. Other measures such as access and quality of health care, income growth inequality and educational standards are also used. Examples are access to certain goods , or measures of health such as...
, as indicated by the natural logarithmNatural logarithmThe natural logarithm is the logarithm to the base e, where e is an irrational and transcendental constant approximately equal to 2.718281828...
of gross domestic productGross domestic productGross domestic product refers to the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period. GDP per capita is often considered an indicator of a country's standard of living....
per capitaPer capitaPer capita is a Latin prepositional phrase: per and capita . The phrase thus means "by heads" or "for each head", i.e. per individual or per person...
at purchasing power parity.
New methodology for 2011 data onwards
In its 2010 Human Development Report the UNDP began using a new method of calculating the HDI. The following three indices are used:1. Life Expectancy Index (LEI)
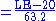
2. Education Index
Education Index
This article contains information based on the pre-2010 Human Development Reports. The HDI and its education component have changed in 2010.The United Nations publishes a Human Development Index every year, which consists of the Education index, GDP Index and Life Expectancy Index...
(EI)

2.1 Mean Years of Schooling Index (MYSI)
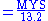
2.2 Expected Years of Schooling Index (EYSI)
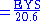
3. Income Index (II)

Finally, the HDI is the geometric mean
Geometric mean
The geometric mean, in mathematics, is a type of mean or average, which indicates the central tendency or typical value of a set of numbers. It is similar to the arithmetic mean, except that the numbers are multiplied and then the nth root of the resulting product is taken.For instance, the...
of the previous three normalized indices:

LE: Life expectancy at birth
MYS: Mean years of schooling (Years that a 25-year-old person or older has spent in schools)
EYS: Expected years of schooling (Years that a 5-year-old child will spend with his education in his whole life)
GNIpc: Gross national income at purchasing power parity per capita
Methodology used until 2011

The formula defining the HDI is promulgated by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)
In general, to transform a raw variable
Variable (mathematics)
In mathematics, a variable is a value that may change within the scope of a given problem or set of operations. In contrast, a constant is a value that remains unchanged, though often unknown or undetermined. The concepts of constants and variables are fundamental to many areas of mathematics and...
, say
 , into a unit-free index
, into a unit-free indexIndex (economics)
In economics and finance, an index is a statistical measure of changes in a representative group of individual data points. These data may be derived from any number of sources, including company performance, prices, productivity, and employment. Economic indices track economic health from...
between 0 and 1 (which allows different indices to be added together), the following formula
Formula
In mathematics, a formula is an entity constructed using the symbols and formation rules of a given logical language....
is used:
where
 and
and 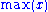 are the lowest and highest values
are the lowest and highest valuesMaxima and minima
In mathematics, the maximum and minimum of a function, known collectively as extrema , are the largest and smallest value that the function takes at a point either within a given neighborhood or on the function domain in its entirety .More generally, the...
the variable
 can attain, respectively.
can attain, respectively.The Human Development Index (HDI) then represents the uniformly weighted sum with ⅓ contributed by each of the following factor indices:
- Life Expectancy Index =
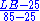
- Education IndexEducation IndexThis article contains information based on the pre-2010 Human Development Reports. The HDI and its education component have changed in 2010.The United Nations publishes a Human Development Index every year, which consists of the Education index, GDP Index and Life Expectancy Index...
=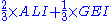
- Adult Literacy Index (ALI) =

- Gross Enrollment Index (GEI) =
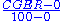
- Adult Literacy Index (ALI) =
- GDP =
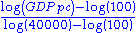
Other organizations/companies may include Democracy Index
Democracy Index
The Democracy Index is an index compiled by the Economist Intelligence Unit that claims to measure the state of democracy in 167 countries, of which 166 are sovereign states and 165 are UN member states...
, Population, etc. which produces different number of HDI.
2011 report
The 2011 Human Development Report was released on 2 November 2011, and calculated HDI values based on estimates for 2011. Below is the list of the "Very High Human Development" countries (equal to the top quartileQuartile
In descriptive statistics, the quartiles of a set of values are the three points that divide the data set into four equal groups, each representing a fourth of the population being sampled...
):
Note: The green arrows , red arrows , and blue dashes represent changes in rank when compared to the new 2011 data HDI for 2010 - published in the 2011 report (p. 131).
 Norway 0.943
Norway 0.943
 Australia 0.929
Australia 0.929
 Netherlands 0.910
Netherlands 0.910
 United States 0.910
United States 0.910
 New Zealand 0.908
New Zealand 0.908
 Canada 0.908
Canada 0.908
 Republic of Ireland 0.908
Republic of Ireland 0.908
 Liechtenstein 0.905
Liechtenstein 0.905
 Germany 0.905
Germany 0.905
 Sweden 0.904
Sweden 0.904
 Switzerland 0.903
Switzerland 0.903
 Japan 0.901
Japan 0.901
 Hong Kong 0.898 ( 1)
Hong Kong 0.898 ( 1)
 Iceland 0.898 ( -1)
Iceland 0.898 ( -1)
 South Korea 0.897
South Korea 0.897
 Denmark 0.895
Denmark 0.895
 Israel 0.888
Israel 0.888
 Belgium 0.886
Belgium 0.886
 Austria 0.885
Austria 0.885
 Early Modern France 0.884
Early Modern France 0.884
 Slovenia 0.884
Slovenia 0.884
 Finland 0.882
Finland 0.882
 Spain 0.878
Spain 0.878
 Italy 0.874
Italy 0.874
 Luxembourg 0.867
Luxembourg 0.867
 Singapore 0.866
Singapore 0.866
 Czech Republic 0.865
Czech Republic 0.865
 United Kingdom 0.863
United Kingdom 0.863
 Greece 0.861
Greece 0.861
 United Arab Emirates 0.846
United Arab Emirates 0.846
 Cyprus 0.840
Cyprus 0.840
 Andorra 0.838
Andorra 0.838
 Brunei 0.838
Brunei 0.838
 Estonia 0.835
Estonia 0.835
 Slovakia 0.834
Slovakia 0.834
 Malta 0.832
Malta 0.832
 Qatar 0.831
Qatar 0.831
 Hungary 0.816
Hungary 0.816
 Poland 0.813
Poland 0.813
 Lithuania 0.810 ( 1)
Lithuania 0.810 ( 1)
 Portugal 0.809 ( -1)
Portugal 0.809 ( -1)
 Bahrain 0.806
Bahrain 0.806
 Latvia 0.805
Latvia 0.805
 Chile 0.805
Chile 0.805
 Argentina 0.797 ( 1)
Argentina 0.797 ( 1)
 Independent State of Croatia 0.796 ( -1)
Independent State of Croatia 0.796 ( -1)
 Barbados 0.793
Barbados 0.793
Non-UN members (not calculated by UNDP)
0.882 (Ranked 22nd among countries if included)..Inequality-adjusted HDI
Below is a list of countries in the top quartile by Inequality-adjusted Human Development Index (IHDI).Note: The green arrows , red arrows , and blue dashes represent changes in rank when compared to the 2011 HDI list, for countries listed in both rankings.
 Norway 0.890
Norway 0.890
 Australia 0.856
Australia 0.856
 Sweden 0.851 ( 5)
Sweden 0.851 ( 5)
 Netherlands 0.846 ( 1)
Netherlands 0.846 ( 1)
 Iceland 0.845 ( 5)
Iceland 0.845 ( 5)
 Republic of Ireland 0.843
Republic of Ireland 0.843
 Germany 0.842
Germany 0.842
 Denmark 0.842 ( 4)
Denmark 0.842 ( 4)
 Switzerland 0.840
Switzerland 0.840
 Slovenia 0.837 ( 7)
Slovenia 0.837 ( 7)
 Finland 0.833 ( 7)
Finland 0.833 ( 7)
 Canada 0.829 ( 7)
Canada 0.829 ( 7)
 Czech Republic 0.821 ( 9)
Czech Republic 0.821 ( 9)
 Austria 0.820 ( 1)
Austria 0.820 ( 1)
 Belgium 0.819 ( 1)
Belgium 0.819 ( 1)
 Early Modern France 0.804
Early Modern France 0.804
 Spain 0.799 ( 2)
Spain 0.799 ( 2)
 Luxembourg 0.799 ( 3)
Luxembourg 0.799 ( 3)
 United Kingdom 0.791 ( 4)
United Kingdom 0.791 ( 4)
 Slovakia 0.787 ( 7)
Slovakia 0.787 ( 7)
 Israel 0.779 ( 8)
Israel 0.779 ( 8)
 Italy 0.779 ( 2)
Italy 0.779 ( 2)
 United States 0.771 ( 19)
United States 0.771 ( 19)
 Estonia 0.769 ( 2)
Estonia 0.769 ( 2)
 Hungary 0.759 ( 3)
Hungary 0.759 ( 3)
 Greece 0.756 ( 2)
Greece 0.756 ( 2)
 Cyprus 0.755 ( 2)
Cyprus 0.755 ( 2)
 South Korea 0.749 ( 17)
South Korea 0.749 ( 17)
 Poland 0.734
Poland 0.734
 Lithuania 0.730
Lithuania 0.730
 Portugal 0.726
Portugal 0.726
 Kingdom of Montenegro 0.718 ( 7)
Kingdom of Montenegro 0.718 ( 7)
 Latvia 0.717 ( 1)
Latvia 0.717 ( 1)
 Serbia 0.694 ( 9)
Serbia 0.694 ( 9)
 Belarus 0.693 ( 10)
Belarus 0.693 ( 10)
Countries in the top quartile of HDI ("Very high human development" group) with a missing IHDI include: New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
, Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein
The Principality of Liechtenstein is a doubly landlocked alpine country in Central Europe, bordered by Switzerland to the west and south and by Austria to the east. Its area is just over , and it has an estimated population of 35,000. Its capital is Vaduz. The biggest town is Schaan...
, Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
, Hong Kong
Hong Kong
Hong Kong is one of two Special Administrative Regions of the People's Republic of China , the other being Macau. A city-state situated on China's south coast and enclosed by the Pearl River Delta and South China Sea, it is renowned for its expansive skyline and deep natural harbour...
, Singapore
Singapore
Singapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
, United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates, abbreviated as the UAE, or shortened to "the Emirates", is a state situated in the southeast of the Arabian Peninsula in Western Asia on the Persian Gulf, bordering Oman, and Saudi Arabia, and sharing sea borders with Iraq, Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, and Iran.The UAE is a...
, Andorra
Andorra
Andorra , officially the Principality of Andorra , also called the Principality of the Valleys of Andorra, , is a small landlocked country in southwestern Europe, located in the eastern Pyrenees mountains and bordered by Spain and France. It is the sixth smallest nation in Europe having an area of...
, Brunei
Brunei
Brunei , officially the State of Brunei Darussalam or the Nation of Brunei, the Abode of Peace , is a sovereign state located on the north coast of the island of Borneo, in Southeast Asia...
, Malta
Malta
Malta , officially known as the Republic of Malta , is a Southern European country consisting of an archipelago situated in the centre of the Mediterranean, south of Sicily, east of Tunisia and north of Libya, with Gibraltar to the west and Alexandria to the east.Malta covers just over in...
, Qatar
Qatar
Qatar , also known as the State of Qatar or locally Dawlat Qaṭar, is a sovereign Arab state, located in the Middle East, occupying the small Qatar Peninsula on the northeasterly coast of the much larger Arabian Peninsula. Its sole land border is with Saudi Arabia to the south, with the rest of its...
, Bahrain
Bahrain
' , officially the Kingdom of Bahrain , is a small island state near the western shores of the Persian Gulf. It is ruled by the Al Khalifa royal family. The population in 2010 stood at 1,214,705, including 235,108 non-nationals. Formerly an emirate, Bahrain was declared a kingdom in 2002.Bahrain is...
, Chile
Chile
Chile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
, Argentina
Argentina
Argentina , officially the Argentine Republic , is the second largest country in South America by land area, after Brazil. It is constituted as a federation of 23 provinces and an autonomous city, Buenos Aires...
and Barbados
Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles. It is in length and as much as in width, amounting to . It is situated in the western area of the North Atlantic and 100 kilometres east of the Windward Islands and the Caribbean Sea; therein, it is about east of the islands of Saint...
.
Countries not included
Some countries were not included for various reasons, mainly the unavailability of certain crucial data. The following United Nations Member States were not included in the 2011 report: North KoreaNorth Korea
The Democratic People’s Republic of Korea , , is a country in East Asia, occupying the northern half of the Korean Peninsula. Its capital and largest city is Pyongyang. The Korean Demilitarized Zone serves as the buffer zone between North Korea and South Korea...
, Marshall Islands
Marshall Islands
The Republic of the Marshall Islands , , is a Micronesian nation of atolls and islands in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, just west of the International Date Line and just north of the Equator. As of July 2011 the population was 67,182...
, Monaco
Monaco
Monaco , officially the Principality of Monaco , is a sovereign city state on the French Riviera. It is bordered on three sides by its neighbour, France, and its centre is about from Italy. Its area is with a population of 35,986 as of 2011 and is the most densely populated country in the...
, Nauru
Nauru
Nauru , officially the Republic of Nauru and formerly known as Pleasant Island, is an island country in Micronesia in the South Pacific. Its nearest neighbour is Banaba Island in Kiribati, to the east. Nauru is the world's smallest republic, covering just...
, San Marino
San Marino
San Marino, officially the Republic of San Marino , is a state situated on the Italian Peninsula on the eastern side of the Apennine Mountains. It is an enclave surrounded by Italy. Its size is just over with an estimated population of over 30,000. Its capital is the City of San Marino...
, Somalia
Somalia
Somalia , officially the Somali Republic and formerly known as the Somali Democratic Republic under Socialist rule, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. Since the outbreak of the Somali Civil War in 1991 there has been no central government control over most of the country's territory...
and Tuvalu
Tuvalu
Tuvalu , formerly known as the Ellice Islands, is a Polynesian island nation located in the Pacific Ocean, midway between Hawaii and Australia. Its nearest neighbours are Kiribati, Nauru, Samoa and Fiji. It comprises four reef islands and five true atolls...
.
2010 report
The 2010 Human Development Report by the United Nations Development Program was released on November 4, 2010, and calculates HDI values based on estimates for 2010. Below is the list of the "Very High Human Development" countries:Note: The green arrows , red arrows , and blue dashes represent changes in rank when compared to the 2009 HDI published in the 2010 report.
 Norway 0.938
Norway 0.938
 Australia 0.937
Australia 0.937
 New Zealand 0.907
New Zealand 0.907
 United States 0.902
United States 0.902
 Republic of Ireland 0.895
Republic of Ireland 0.895
 Liechtenstein 0.891
Liechtenstein 0.891
 Netherlands 0.890
Netherlands 0.890
 Canada 0.888
Canada 0.888
 Sweden 0.885
Sweden 0.885
 Germany 0.885
Germany 0.885
 Japan 0.884
Japan 0.884
 South Korea 0.877
South Korea 0.877
 Switzerland 0.874
Switzerland 0.874
 Early Modern France 0.872 ( 2)
Early Modern France 0.872 ( 2)
 Israel 0.872 ( 1)
Israel 0.872 ( 1)
 Finland 0.871 ( 1)
Finland 0.871 ( 1)
 Iceland 0.869
Iceland 0.869
 Belgium 0.867
Belgium 0.867
 Denmark 0.866
Denmark 0.866
 Spain 0.863
Spain 0.863
 Hong Kong 0.862
Hong Kong 0.862
 Greece 0.855
Greece 0.855
 Italy 0.854
Italy 0.854
 Luxembourg 0.852
Luxembourg 0.852
 Austria 0.851
Austria 0.851
 United Kingdom 0.849
United Kingdom 0.849
 Singapore 0.846
Singapore 0.846
 Czech Republic 0.841
Czech Republic 0.841
 Slovenia 0.828
Slovenia 0.828
 Andorra 0.824
Andorra 0.824
 Slovakia 0.818
Slovakia 0.818
 United Arab Emirates 0.815 ( 1)
United Arab Emirates 0.815 ( 1)
 Malta 0.815 ( 1)
Malta 0.815 ( 1)
 Estonia 0.812
Estonia 0.812
 Cyprus 0.810
Cyprus 0.810
 Hungary 0.805 ( 1)
Hungary 0.805 ( 1)
 Brunei 0.805 ( 1)
Brunei 0.805 ( 1)
 Qatar 0.803
Qatar 0.803
 Bahrain 0.801
Bahrain 0.801
 Portugal 0.795 ( 1)
Portugal 0.795 ( 1)
 Poland 0.795 ( 1)
Poland 0.795 ( 1)
 Barbados 0.788
Barbados 0.788
Inequality-adjusted HDI
The 2010 Human Development Report was the first to calculate an Inequality-adjusted Human Development Index (IHDI), which factors in inequalities in the three basic dimensions of human development (income, life expectancy, and education). Below is a list of countries in the top quartile by IHDI:Note: The green arrows , red arrows , and blue dashes represent changes in rank when compared to the 2010 HDI list, for countries listed in both rankings.
 Norway 0.876
Norway 0.876
 Australia 0.864
Australia 0.864
 Sweden 0.824 ( 4)
Sweden 0.824 ( 4)
 Netherlands 0.818 ( 1)
Netherlands 0.818 ( 1)
 Germany 0.814 ( 3)
Germany 0.814 ( 3)
 Switzerland 0.813 ( 4)
Switzerland 0.813 ( 4)
 Republic of Ireland 0.813 ( 3)
Republic of Ireland 0.813 ( 3)
 Canada 0.812 ( 2)
Canada 0.812 ( 2)
 Iceland 0.811 ( 5)
Iceland 0.811 ( 5)
 Denmark 0.810 ( 6)
Denmark 0.810 ( 6)
 Finland 0.806 ( 2)
Finland 0.806 ( 2)
 United States 0.799 ( 9)
United States 0.799 ( 9)
 Belgium 0.794 ( 2)
Belgium 0.794 ( 2)
 Early Modern France 0.792 ( 3)
Early Modern France 0.792 ( 3)
 Czech Republic 0.790 ( 8)
Czech Republic 0.790 ( 8)
 Austria 0.787 ( 5)
Austria 0.787 ( 5)
 Spain 0.779
Spain 0.779
 Luxembourg 0.775 ( 2)
Luxembourg 0.775 ( 2)
 Slovenia 0.771 ( 5)
Slovenia 0.771 ( 5)
 Greece 0.768 ( 2)
Greece 0.768 ( 2)
 United Kingdom 0.766 ( 1)
United Kingdom 0.766 ( 1)
 Slovakia 0.764 ( 3)
Slovakia 0.764 ( 3)
 Israel 0.763 ( 11)
Israel 0.763 ( 11)
 Italy 0.752 ( 5)
Italy 0.752 ( 5)
 Hungary 0.736 ( 3)
Hungary 0.736 ( 3)
 Estonia 0.733
Estonia 0.733
 South Korea 0.731 ( 18)
South Korea 0.731 ( 18)
 Cyprus 0.716 ( 1)
Cyprus 0.716 ( 1)
 Poland 0.709 ( 1)
Poland 0.709 ( 1)
 Portugal 0.700 ( 1)
Portugal 0.700 ( 1)
 Lithuania 0.693 ( 1)
Lithuania 0.693 ( 1)
 Kingdom of Montenegro 0.693 ( 4)
Kingdom of Montenegro 0.693 ( 4)
 Latvia 0.684 ( 2)
Latvia 0.684 ( 2)
 Kingdom of Romania 0.675 ( 3)
Kingdom of Romania 0.675 ( 3)
 The Bahamas 0.671 ( 4)
The Bahamas 0.671 ( 4)
Countries in the top quartile of HDI ("Very high human development" group) with a missing IHDI include: New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
, Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein
The Principality of Liechtenstein is a doubly landlocked alpine country in Central Europe, bordered by Switzerland to the west and south and by Austria to the east. Its area is just over , and it has an estimated population of 35,000. Its capital is Vaduz. The biggest town is Schaan...
, Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
, Hong Kong
Hong Kong
Hong Kong is one of two Special Administrative Regions of the People's Republic of China , the other being Macau. A city-state situated on China's south coast and enclosed by the Pearl River Delta and South China Sea, it is renowned for its expansive skyline and deep natural harbour...
, Singapore
Singapore
Singapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
, Andorra
Andorra
Andorra , officially the Principality of Andorra , also called the Principality of the Valleys of Andorra, , is a small landlocked country in southwestern Europe, located in the eastern Pyrenees mountains and bordered by Spain and France. It is the sixth smallest nation in Europe having an area of...
, United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates, abbreviated as the UAE, or shortened to "the Emirates", is a state situated in the southeast of the Arabian Peninsula in Western Asia on the Persian Gulf, bordering Oman, and Saudi Arabia, and sharing sea borders with Iraq, Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, and Iran.The UAE is a...
, Malta
Malta
Malta , officially known as the Republic of Malta , is a Southern European country consisting of an archipelago situated in the centre of the Mediterranean, south of Sicily, east of Tunisia and north of Libya, with Gibraltar to the west and Alexandria to the east.Malta covers just over in...
, Brunei
Brunei
Brunei , officially the State of Brunei Darussalam or the Nation of Brunei, the Abode of Peace , is a sovereign state located on the north coast of the island of Borneo, in Southeast Asia...
, Qatar
Qatar
Qatar , also known as the State of Qatar or locally Dawlat Qaṭar, is a sovereign Arab state, located in the Middle East, occupying the small Qatar Peninsula on the northeasterly coast of the much larger Arabian Peninsula. Its sole land border is with Saudi Arabia to the south, with the rest of its...
, Bahrain
Bahrain
' , officially the Kingdom of Bahrain , is a small island state near the western shores of the Persian Gulf. It is ruled by the Al Khalifa royal family. The population in 2010 stood at 1,214,705, including 235,108 non-nationals. Formerly an emirate, Bahrain was declared a kingdom in 2002.Bahrain is...
and Barbados
Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles. It is in length and as much as in width, amounting to . It is situated in the western area of the North Atlantic and 100 kilometres east of the Windward Islands and the Caribbean Sea; therein, it is about east of the islands of Saint...
.
Countries not included
Some countries were not included for various reasons, mainly the unavailability of certain crucial data. The following United Nations Member States were not included in the 2010 report. CubaCuba
The Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
lodged a formal protest at its lack of inclusion. The UNDP explained that Cuba had been excluded due to the lack of an "internationally reported figure for Cuba’s Gross National Income adjusted for Purchasing Power Parity". All other indicators for Cuba were available, and reported by the UNDP, but the lack of one indicator meant that no ranking could be attributed to the country.
Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
Americas
Americas
The Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily...
Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
Oceania
Oceania
Oceania is a region centered on the islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean. Conceptions of what constitutes Oceania range from the coral atolls and volcanic islands of the South Pacific to the entire insular region between Asia and the Americas, including Australasia and the Malay Archipelago...
Non-UN members (not calculated by UNDP)
0.868 (Ranked 18th among countries if included).2009 report
The 2009 Human Development ReportHuman Development Report
The Human Development Report is an annual milestone publication by the Human Development Report Office of the United Nations Development Programme .-History:...
by UNDP was released on October 5, 2009, and covers the period up to 2007. It was titled "Overcoming barriers: Human mobility and development". The top countries by HDI were grouped in a new category called "Very High Human Development". The report refers to these countries as developed countries. They are:
 Norway 0.971 ( 1)
Norway 0.971 ( 1) Australia 0.970 ( 2)
Australia 0.970 ( 2) Iceland 0.969 ( 2)
Iceland 0.969 ( 2) Canada 0.966 ( 1)
Canada 0.966 ( 1) Republic of Ireland 0.965
Republic of Ireland 0.965  Netherlands 0.964
Netherlands 0.964  Sweden 0.963
Sweden 0.963  Early Modern France 0.961 ( 3)
Early Modern France 0.961 ( 3) Switzerland 0.960 ( 1)
Switzerland 0.960 ( 1) Japan 0.960 ( 2)
Japan 0.960 ( 2) Luxembourg 0.960 ( 2)
Luxembourg 0.960 ( 2) Finland 0.959
Finland 0.959  United States 0.956 ( 2)
United States 0.956 ( 2)
-
 Austria 0.955
Austria 0.955  Spain 0.955 ( 1)
Spain 0.955 ( 1) Denmark 0.955 ( 2)
Denmark 0.955 ( 2) Belgium 0.953
Belgium 0.953  Italy 0.951 ( 1)
Italy 0.951 ( 1) Liechtenstein 0.951 ( 1)
Liechtenstein 0.951 ( 1) New Zealand 0.950
New Zealand 0.950  United Kingdom 0.947
United Kingdom 0.947  Germany 0.947
Germany 0.947  Singapore 0.944 ( 1)
Singapore 0.944 ( 1) Hong Kong 0.944 ( 1)
Hong Kong 0.944 ( 1) Greece 0.942
Greece 0.942  South Korea 0.937
South Korea 0.937
-
 Israel 0.935 ( 1)
Israel 0.935 ( 1)  Andorra 0.934 ( 1)
Andorra 0.934 ( 1) Slovenia 0.929
Slovenia 0.929  Brunei 0.920
Brunei 0.920  Kuwait 0.916
Kuwait 0.916  Cyprus 0.914
Cyprus 0.914  Qatar 0.910 ( 1)
Qatar 0.910 ( 1) Portugal 0.909 ( 1)
Portugal 0.909 ( 1) United Arab Emirates 0.903 ( 2)
United Arab Emirates 0.903 ( 2) Czech Republic 0.903
Czech Republic 0.903  Barbados 0.903 ( 2)
Barbados 0.903 ( 2) Malta 0.902 ( 3)
Malta 0.902 ( 3)
Countries not included
Some countries were not included for various reasons, such as being a non-UN member or unable or unwilling to provide the necessary data at the time of publication. Besides the states with limited recognition, the following states were also not included.Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
Oceania
Oceania
Oceania is a region centered on the islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean. Conceptions of what constitutes Oceania range from the coral atolls and volcanic islands of the South Pacific to the entire insular region between Asia and the Americas, including Australasia and the Malay Archipelago...
2008 statistical update
A new index was released on December 18, 2008. This so-called "statistical update" covered the period up to 2006 and was published without an accompanying Human Development Report. The update is relevant due to newly released estimates of purchasing power paritiesPurchasing power parity
In economics, purchasing power parity is a condition between countries where an amount of money has the same purchasing power in different countries. The prices of the goods between the countries would only reflect the exchange rates...
(PPP), implying substantial adjustments for many countries, resulting in changes in HDI values and, in many cases, HDI ranks.
- 0.968
- 0.968
- 0.967 ( 1)
- 0.965 ( 1)
- 0.960
- 0.958 ( 3)
- 0.958 ( 1)
- 0.956
- 0.956 ( 9)
- 0.955 ( 3)
- 0.954 ( 1)
- 0.954 ( 1)
- 0.952 ( 1)
- 0.951 ( 1)
- 0.950 ( 3)
- 0.949 ( 3)
- 0.948 ( 1)
- 0.947 ( 6)
- 0.945 ( 1)
- 0.944 ( 1)
- 0.942 ( 4)
- 0.942 ( 1)
- 0.940 ( 1)
- 0.930 ( 1)
- 0.928 ( 1)
- 0.923 ( 1)
- 0.919 ( 3)
- 0.918 ( 3)
- 0.912 ( 4)
- 0.912 ( 2)
- 0.903 ( 8)
- 0.902 ( 9)
- 0.900 ( 4)
Countries not included
Some countries were not included for various reasons, such as being a non-UN member, unable, or unwilling to provide the necessary data at the time of publication. Besides the states with limited recognition, the following states were also not included.Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
Oceania
Oceania
Oceania is a region centered on the islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean. Conceptions of what constitutes Oceania range from the coral atolls and volcanic islands of the South Pacific to the entire insular region between Asia and the Americas, including Australasia and the Malay Archipelago...
2007/2008 report
The Human Development Report for 2007/2008 was launched in BrasiliaBrasília
Brasília is the capital city of Brazil. The name is commonly spelled Brasilia in English. The city and its District are located in the Central-West region of the country, along a plateau known as Planalto Central. It has a population of about 2,557,000 as of the 2008 IBGE estimate, making it the...
, Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
, on November 27, 2007. Its focus was on "Fighting climate change: Human solidarity in a divided world." Most of the data used for the report are derived largely from 2005 or earlier, thus indicating an HDI for 2005. Not all UN member states
United Nations member states
There are 193 United Nations member states, and each of them is a member of the United Nations General Assembly.The criteria for admission of new members are set out in the United Nations Charter, Chapter II, Article 4, as follows:...
choose to or are able to provide the necessary statistics.
The report showed a small increase in world HDI in comparison with last year's report. This rise was fueled by a general improvement in the developing world, especially of the least developed countries
Least Developed Countries
Least developed country is the name given to a country which, according to the United Nations, exhibits the lowest indicators of socioeconomic development, with the lowest Human Development Index ratings of all countries in the world...
group. This marked improvement at the bottom was offset with a decrease in HDI of high income countries.
A HDI below 0.5 is considered to represent "low development". All 22 countries in that category are located in Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
. The highest-scoring Sub-Saharan countries, Gabon
Gabon
Gabon , officially the Gabonese Republic is a state in west central Africa sharing borders with Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, and with the Republic of the Congo curving around the east and south. The Gulf of Guinea, an arm of the Atlantic Ocean is to the west...
and South Africa
South Africa
The Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
, are ranked 119th and 121st, respectively. Nine countries departed from this category this year and joined the "medium development" group.
A HDI of 0.8 or more is considered to represent "high development". This includes all developed countries, such as those in North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
, Western Europe
Western Europe
Western Europe is a loose term for the collection of countries in the western most region of the European continents, though this definition is context-dependent and carries cultural and political connotations. One definition describes Western Europe as a geographic entity—the region lying in the...
, Oceania
Oceania
Oceania is a region centered on the islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean. Conceptions of what constitutes Oceania range from the coral atolls and volcanic islands of the South Pacific to the entire insular region between Asia and the Americas, including Australasia and the Malay Archipelago...
, and Eastern Asia, as well as some developing countries in Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
, Central and South America, Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
, the Caribbean
Caribbean
The Caribbean is a crescent-shaped group of islands more than 2,000 miles long separating the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea, to the west and south, from the Atlantic Ocean, to the east and north...
, and the oil-rich Arabian Peninsula
Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula is a land mass situated north-east of Africa. Also known as Arabia or the Arabian subcontinent, it is the world's largest peninsula and covers 3,237,500 km2...
. Seven countries were promoted to this category this year, leaving the "medium development" group: Albania
Albania
Albania , officially known as the Republic of Albania , is a country in Southeastern Europe, in the Balkans region. It is bordered by Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, the Republic of Macedonia to the east and Greece to the south and southeast. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea...
, Belarus
Belarus
Belarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,...
, Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
, Libya
Libya
Libya is an African country in the Maghreb region of North Africa bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, and Algeria and Tunisia to the west....
, Macedonia
Republic of Macedonia
Macedonia , officially the Republic of Macedonia , is a country located in the central Balkan peninsula in Southeast Europe. It is one of the successor states of the former Yugoslavia, from which it declared independence in 1991...
, Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
and Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia , commonly known in British English as Saudi Arabia and in Arabic as as-Sa‘ūdiyyah , is the largest state in Western Asia by land area, constituting the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and the second-largest in the Arab World...
.
On the following table, green arrows represent an increase in ranking over the previous study, while red arrows represent a decrease in ranking. They are followed by the number of spaces they moved. Blue dashes represent a nation that did not move in the rankings since the previous study.
- 0.968 ( 1)
- 0.968 ( 1)
- 0.962
- 0.961 ( 2)
- 0.959 ( 1)
- 0.956 ( 1)
- 0.955 ( 2)
- 0.953 ( 1)
- 0.953 ( 1)
- 0.952 ( 6)
- 0.952
- 0.951 ( 4)
- 0.949 ( 6)
- 0.949 ( 1)
- 0.948 ( 1)
- 0.946 ( 4)
- 0.946 ( 1)
- 0.944 ( 6)
- 0.943 ( 1)
- 0.941 ( 3)
- 0.937 ( 1)
- 0.935 ( 1)
- 0.932
- 0.926
- 0.922
- 0.921
- 0.917
- 0.903 ( 1)
- 0.897 ( 1)
- 0.894 ( 4)
Past top countries
The list below displays the top-ranked country from each year of the Human Development Index. NorwayNorway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
have been ranked the highest nine times, Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
eight times, followed by Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
which has been ranked highest three times. Iceland
Iceland
Iceland , described as the Republic of Iceland, is a Nordic and European island country in the North Atlantic Ocean, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Iceland also refers to the main island of the country, which contains almost all the population and almost all the land area. The country has a population...
has been ranked highest twice.
In each original report
The year represents when the report was published. In parentheses is the year for which the index was calculated.- 2011 (2011)–
- 2010 (2010)–
- 2009 (2007)–
- 2008 (2006)–
 Iceland
Iceland - 2007 (2005)–
 Iceland
Iceland - 2006 (2004)–
 Norway
Norway - 2005 (2003)–
 Norway
Norway - 2004 (2002)–
 Norway
Norway - 2003 (2001)–
 Norway
Norway - 2002 (2000)–
 Norway
Norway - 2001 (1999)–
 Norway
Norway - 2000 (1998)–
 Canada
Canada - 1999 (1997)–
 Canada
Canada - 1998 (1995)–
 Canada
Canada - 1997 (1994)–
 Canada
Canada - 1996 (1993)–
 Canada
Canada - 1995 (1992)–
 Canada
Canada - 1994 (????)–
 Canada
Canada - 1993 (????)–
 Japan
Japan - 1992 (1990)–
 Canada
Canada - 1991 (1990)–
 Japan
Japan - 1990 (????)–
 Japan
Japan
Future HDI projections
In April 2010, the Human Development Report Office provided the 2010-2030 HDI projections (quoted in September 2010, by the United Nations Development Programme, in the Human Development Research paper 2010/40, pp. 40–42). These projections were reached by re-calculating the HDI, using (for components of the HDI) projections of the components conducted by agencies that provide the UNDP with data for the HDI.Criticisms
The Human Development Index has been criticised on a number of grounds, including failure to include any ecological considerations, focusing exclusively on national performance and ranking (although many national Human Development Reports, looking at subnational performance, have been published by UNDP and others—so this last claim is untrue), not paying much attention to development from a global perspective and based on grounds of measurement error of the underlying statistics and formula changes by the UNDP which can lead to severe misclassifications of countries in the categories of being a 'low', 'medium', 'high' or 'very high' human development country. Other authors claimed that the Human Development Reports "have lost touch with their original vision and the index fails to capture the essence of the world it seeks to portray". The index has also been criticized as "redundant" and a "reinvention of the wheel", measuring aspects of development that have already been exhaustively studied. The index has further been criticised for having an inappropriate treatment of income, lacking year-to-year comparability, and assessing development differently in different groups of countries.Economist
Economist
An economist is a professional in the social science discipline of economics. The individual may also study, develop, and apply theories and concepts from economics and write about economic policy...
Bryan Caplan
Bryan Caplan
Bryan Caplan is an American economist, a Professor of Economics at George Mason University, Research Fellow at the Mercatus Center, adjunct scholar of the Cato Institute, and blogger for Econlog. He is best known for his work in public choice theory and for his libertarian ideology.-Personal...
has criticised the way HDI scores are produced; each of the three components are bounded between zero and one. As a result of that, rich countries effectively cannot improve their rating (and thus their ranking relative to other countries) in certain categories, even though there is a lot of scope for economic growth and longevity left. "This effectively means that a country of immortals with infinite per-capita GDP would get a score of .666 (lower than South Africa and Tajikistan) if its population were illiterate and never went to school." He argues, "Scandinavia comes out on top according to the HDI because the HDI is basically a measure of how Scandinavian your country is."
Economists Hendrik Wolff, Howard Chong and Maximilian Auffhammer
Maximilian Auffhammer
Maximilian Auffhammer is a UC-Berkeley based environmental economist who has produced some important forecasts of Chinese carbon dioxide releases....
discuss the HDI from the perspective of data error in the underlying health, education and income statistics used to construct the HDI. They identify three sources of data error which are due to (i) data updating, (ii) formula revisions and (iii) thresholds to classify a country’s development status and find that 11%, 21% and 34% of all countries can be interpreted as currently misclassified in the development bins due to the three sources of data error, respectively. The authors suggest that the United Nations should discontinue the practice of classifying countries into development bins because the cut-off values seem arbitrary, can provide incentives for strategic behavior in reporting official statistics, and have the potential to misguide politicians, investors, charity donators and the public at large which use the HDI. In 2010 the UNDP reacted to the criticism and updated the thresholds to classify nations as low, medium and high human development countries. In a comment to The Economist
The Economist
The Economist is an English-language weekly news and international affairs publication owned by The Economist Newspaper Ltd. and edited in offices in the City of Westminster, London, England. Continuous publication began under founder James Wilson in September 1843...
in early January 2011, the Human Development Report Office responded to a January 6, 2011 article in The Economist
The Economist
The Economist is an English-language weekly news and international affairs publication owned by The Economist Newspaper Ltd. and edited in offices in the City of Westminster, London, England. Continuous publication began under founder James Wilson in September 1843...
which discusses the Wolff et al. paper. The Human Development Report Office states that they undertook a systematic revision of the methods used for the calculation of the HDI and that the new methodology directly addresses the critique by Wolff et al. in that it generates a system for continuous updating of the human development categories whenever formula or data revisions take place.
The following are common criticisms directed at the HDI: that it is a redundant measure that adds little to the value of the individual measures composing it; that it is a means to provide legitimacy to arbitrary weightings of a few aspects of social development; that it is a number producing a relative ranking which is useless for inter-temporal comparisons, and difficult to compare a country's progress or regression since the HDI for a country in a given year depends on the levels of, say, life expectancy or GDP per capita of other countries in that year. However, each year, UN member states are listed and ranked according to the computed HDI. If high, the rank in the list can be easily used as a means of national aggrandizement; alternatively, if low, it can be used to highlight national insufficiencies. Using the HDI as an absolute index of social welfare, some authors have used panel HDI data to measure the impact of economic policies on quality of life
Quality of life
The term quality of life is used to evaluate the general well-being of individuals and societies. The term is used in a wide range of contexts, including the fields of international development, healthcare, and politics. Quality of life should not be confused with the concept of standard of...
.
Ratan Lal Basu
Ratan Lal Basu
Ratan Lal Basu is an economist and English fiction author from Kolkata, India.-Childhood and parents:...
criticises the HDI concept from a completely different angle. According to him the Amartya Sen
Amartya Sen
Amartya Sen, CH is an Indian economist who was awarded the 1998 Nobel Prize in Economic Sciences for his contributions to welfare economics and social choice theory, and for his interest in the problems of society's poorest members...
-Mahbub ul Haq
Mahbub ul Haq
Mahbub ul Haq was an Pakistani economist who is known to be the pioneer of Human development theory and the founder of the Human Development Report...
concept of HDI considers that provision of material amenities alone would bring about Human Development, but Basu opines that Human Development in the true sense should embrace both material and moral development. According to him human development based on HDI alone, is similar to dairy farm economics to improve dairy farm output. To quote: ‘So human development effort should not end up in amelioration of material deprivations alone: it must undertake to bring about spiritual and moral development to assist the biped to become truly human.’ For example, a high suicide rate would bring the index down.
A few authors have proposed alternative indices to address some of the index's shortcomings. However, of those proposed alternatives to the HDI, few have produced alternatives covering so many countries, and that no development index (other than, perhaps, Gross Domestic Product per capita) has been used so extensively—or effectively, in discussions and developmental planning as the HDI.
However, there has been one lament about the HDI that has resulted in an alternative index: David Hastings, of the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific
United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific
The Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific , located in Bangkok, Thailand, is the regional arm of the United Nations Secretariat for the Asian and Pacific region. It was established in 1947 to encourage economic cooperation among its member states...
published a report geographically extending the HDI to 230+ economies, whereas the UNDP HDI for 2009 enumerates 182 economies and coverage for the 2010 HDI dropped to 169 countries.
The income component of HDI is problematic, because there is effectively little difference given to a very high, high, and medium income countries. For example, even with a GNI per capita of $20,000, the income index is only 19% below that of a country with a per capita GNI of $45,000, despite the 150% difference. This is attributed to the logarithmic formula used to calculate the income index. Because of this property, the highest income countries have their income index (33% of total HDI) understated versus every other country that is not very high income, and so on. The problem is worsened with inequality adjusted income, where the income index is adjusted for inequality. Effectively, this means that countries with much lower inequality adjusted incomes may have a higher income index. For example, Country A has a GNI per capita of $45,000 (index=.864), while B is at $15,000 (.695). The former has an inequality factor of .75, while the latter has an inequality factor of .95. In pure income amounts, Country A is still much better off ($33,750 vs $12,350). However, because the index itself is adjusted, Country B ends up having a higher inequality adjusted income index; Country B:(.95*.695)=.66, Country A: (.75*.864)=.648. Thus, while the normal HDI measure does not take into account large differences in income between groups of countries, the inequality adjusted form allows for much poorer countries (adjusted for inequality) to have a higher index. Therefore, it cannot be said that the income component of HDI or IHDI is a proxy for standard of living. This is in addition to the fact that GNI is not a direct proxy for household income.
See also
- Education IndexEducation IndexThis article contains information based on the pre-2010 Human Development Reports. The HDI and its education component have changed in 2010.The United Nations publishes a Human Development Index every year, which consists of the Education index, GDP Index and Life Expectancy Index...
- Democracy IndexDemocracy IndexThe Democracy Index is an index compiled by the Economist Intelligence Unit that claims to measure the state of democracy in 167 countries, of which 166 are sovereign states and 165 are UN member states...
- Freedom HouseFreedom HouseFreedom House is an international non-governmental organization based in Washington, D.C. that conducts research and advocacy on democracy, political freedom and human rights...
- Gini coefficientGini coefficientThe Gini coefficient is a measure of statistical dispersion developed by the Italian statistician and sociologist Corrado Gini and published in his 1912 paper "Variability and Mutability" ....
- Gender Parity IndexGender Parity IndexThe Gender Parity Index is a socioeconomic index usually designed to measure the relative access to education of males and females. In its simplest form, it is calculated as the quotient of the number of females by the number of males enrolled in a given stage of education...
- Gender-related Development IndexGender-related Development IndexThe Gender-related Development Index and the Gender Empowerment Measure were introduced in 1995 in the Human Development Report written by the United Nations Development Program. The aim of these measurements was to add a gender-sensitive dimension to the HDI. The first measurement that they...
- Gender Empowerment MeasureGender Empowerment MeasureThe United Nation's Development Programme's attempt to measure the extent of gender equality across the globe's countries, based on estimates of women's relative economic income, high-paying positions, and access to professional and parliamentary positions....
- Genuine Progress IndicatorGenuine Progress IndicatorThe genuine progress indicator is an alternative metric system which is an addition to the national system of accounts that has been suggested to replace, or supplement, gross domestic product as a metric of economic growth...
- Global Peace IndexGlobal Peace IndexThe Global Peace Index is an attempt to measure the relative position of nations' and regions' peacefulness. It is the product of Institute for Economics and Peace and developed in consultation with an international panel of peace experts from peace institutes and think tanks with data collected...
- Legatum Prosperity IndexLegatum Prosperity IndexThe Legatum Prosperity Index is an annual ranking developed by the Legatum Institute of 110 countries. The ranking is based according to a variety of factors including wealth, economic growth, personal wellbeing, and quality of life. Norway topped the lists of the the last two reports, those of...
- Living Planet IndexLiving Planet IndexThe Living Planet Index is an indicator of the state of global biological diversity, based on trends in vertebrate populations of species from around the world....
- Gross national happinessGross national happinessThe assessment of gross national happiness was designed in an attempt to define an indicator that measures quality of life or social progress in more holistic and psychological terms than only the economic indicator of gross domestic product .-Origins and meaning:The term...
- Happy Planet IndexHappy Planet IndexThe Happy Planet Index is an index of human well-being and environmental impact that was introduced by the New Economics Foundation in July 2006. The index is designed to challenge well-established indices of countries’ development, such as Gross Domestic Product and the Human Development Index...
- Physical quality-of-life indexPhysical quality-of-life indexThe Physical Quality of Life Index is an attempt to measure the quality of life or well-being of a country. The value is the average of three statistics: basic literacy rate, infant mortality, and life expectancy at age one, all equally weighted on a 0 to 100 scale.It was developed for the...
- Human development (humanity)Human development (humanity)Human development in the scope of humanity, specifically international development, is an international and economic development paradigm that is about much more than the rise or fall of national incomes. People are the real wealth of nations...
- American Human Development Report
- Child Development IndexChild Development IndexThe Child Development Index is an index combining performance measures specific to children - education, health and nutrition - to produce a score on a scale of 0 to 100. A zero score would be the best...
- Satisfaction with Life IndexSatisfaction with Life IndexThe Satisfaction with Life Index was created by Adrian G. White, an Analytic Social Psychologist at the University of Leicester, using data from a metastudy. It is an attempt to show life satisfaction in different nations....
- Genuine progress indicatorGenuine Progress IndicatorThe genuine progress indicator is an alternative metric system which is an addition to the national system of accounts that has been suggested to replace, or supplement, gross domestic product as a metric of economic growth...
- Multidimensional Poverty IndexMultidimensional Poverty IndexThe Multidimensional Poverty Index ' was developed in 2010 by Oxford Poverty & Human Development Initiative and the United Nations Development Programme.-History:...
Lists:
- List of countries by Human Development Index
- List of countries by inequality-adjusted HDI
- List of African countries by Human Development Index
- List of Australian states and territories by HDI
- List of Argentine provinces by Human Development Index
- List of Brazilian states by Human Development Index
- List of Chilean regions by Human Development Index
- List of Chinese administrative divisions by Human Development Index
- List of European countries by Human Development Index
- List of Indian states by Human Development Index
- List of Latin American countries by Human Development Index
- List of Mexican states by Human Development Index
- List of Pakistani Districts by Human Development Index
- List of Philippine provinces by Human Development Index
- List of Russian federal subjects by HDI
- List of South African provinces by HDI
- List of US states by HDI
- List of Venezuelan states by Human Development Index
External links
- Human Development Report
- 2011 Human Development Index Update
- Human Development Interactive Map
- Human Development Tools and Rankings
- An independent HDI covering 232 countries, formulated along lines of the traditional (pre-2010) approach.
- List of countries by HDI at NationMaster.com
- America Is # ... 15? by Dalton Conley, The Nation, March 4, 2009