
Einstein ring
Encyclopedia

Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
an Einstein ring is the deformation of the light from a source (such as a galaxy
Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
or star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
) into a ring through gravitational lens
Gravitational lens
A gravitational lens refers to a distribution of matter between a distant source and an observer, that is capable of bending the light from the source, as it travels towards the observer...
ing of the source's light by an object with an extremely large mass (such as another galaxy, or a black hole
Black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime from which nothing, not even light, can escape. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass will deform spacetime to form a black hole. Around a black hole there is a mathematically defined surface called an event horizon that...
). This occurs when the source, lens and observer are all aligned. The first complete Einstein ring, designated B1938+666, was discovered by collaboration between astronomers at the University of Manchester
University of Manchester
The University of Manchester is a public research university located in Manchester, United Kingdom. It is a "red brick" university and a member of the Russell Group of research-intensive British universities and the N8 Group...
and NASA's
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
Hubble Space Telescope
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was carried into orbit by a Space Shuttle in 1990 and remains in operation. A 2.4 meter aperture telescope in low Earth orbit, Hubble's four main instruments observe in the near ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared...
in 1998.
Introduction
Gravitational lensing is predicted by Albert EinsteinAlbert Einstein
Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist who developed the theory of general relativity, effecting a revolution in physics. For this achievement, Einstein is often regarded as the father of modern physics and one of the most prolific intellects in human history...
's theory of general relativity
General relativity
General relativity or the general theory of relativity is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1916. It is the current description of gravitation in modern physics...
. Instead of light from a source traveling in a straight line (in three dimensions), it is bent by the presence of a massive body, which distorts spacetime
Spacetime
In physics, spacetime is any mathematical model that combines space and time into a single continuum. Spacetime is usually interpreted with space as being three-dimensional and time playing the role of a fourth dimension that is of a different sort from the spatial dimensions...
. An Einstein Ring is a special case of gravitational lensing, caused by the exact alignment of the source, lens and observer. This results in a symmetry around the lens, causing a ring-like structure.
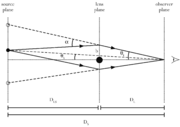
Einstein radius
The Einstein radius is the radius of an Einstein ring, and is a characteristic angle for gravitational lensing in general, as typical distances between images in gravitational lensing are of the order of the Einstein radius.- Derivation :...
. In radians, it is

where
-
 is the gravitational constantGravitational constantThe gravitational constant, denoted G, is an empirical physical constant involved in the calculation of the gravitational attraction between objects with mass. It appears in Newton's law of universal gravitation and in Einstein's theory of general relativity. It is also known as the universal...
is the gravitational constantGravitational constantThe gravitational constant, denoted G, is an empirical physical constant involved in the calculation of the gravitational attraction between objects with mass. It appears in Newton's law of universal gravitation and in Einstein's theory of general relativity. It is also known as the universal...
, -
 is the mass of the lens,
is the mass of the lens, -
 is the speed of lightSpeed of lightThe speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
is the speed of lightSpeed of lightThe speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
, -
 is the angular diameter distance to the lens,
is the angular diameter distance to the lens, -
 is the angular diameter distance to the source, and
is the angular diameter distance to the source, and -
 is the angular diameter distance between the lens and the source.
is the angular diameter distance between the lens and the source.
Note that, over cosmological distances
 in general.
in general.History
The bending of light by a gravitational body was predicted by Einstein in 1912, a few years before the publication of General Relativity in 1916 (see Renn et al. 1997). The ring effect was first mentioned in academic literatureAcademic journal
An academic journal is a peer-reviewed periodical in which scholarship relating to a particular academic discipline is published. Academic journals serve as forums for the introduction and presentation for scrutiny of new research, and the critique of existing research...
by Orest Chwolson in 1924. Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist who developed the theory of general relativity, effecting a revolution in physics. For this achievement, Einstein is often regarded as the father of modern physics and one of the most prolific intellects in human history...
remarked upon this effect in 1936 in a paper prompted by a letter by a Czech engineer, R W Mandl http://www.slac.stanford.edu/pubs/beamline/31/1/31-1-maurer.pdf, but stated
In this statement, β is the Einstein Radius currently denoted by
 (see above). However, Einstein was only considering the chance of observing Einstein rings produced by stars, which is low; however, the chance of observing those produced by larger lenses such as galaxies or black holes is higher since the angular size of an Einstein ring increases with the mass of the lens.
(see above). However, Einstein was only considering the chance of observing Einstein rings produced by stars, which is low; however, the chance of observing those produced by larger lenses such as galaxies or black holes is higher since the angular size of an Einstein ring increases with the mass of the lens.Known Einstein rings
Hundreds of gravitational lenses are currently known. About half a dozen of them are partial Einstein rings with diameters up to an arcsecond, although as either the mass distribution of the lenses is not perfectly axially symmetrical, or the source, lens and observer are not perfectly aligned, we have yet to see a perfect Einstein ring. Most rings have been discovered in the radio range.| Name | Location (RA Right ascension Right ascension is the astronomical term for one of the two coordinates of a point on the celestial sphere when using the equatorial coordinate system. The other coordinate is the declination.-Explanation:... , dec Declination In astronomy, declination is one of the two coordinates of the equatorial coordinate system, the other being either right ascension or hour angle. Declination in astronomy is comparable to geographic latitude, but projected onto the celestial sphere. Declination is measured in degrees north and... ) |
Radius | Arc size | Optical/radio Radio frequency Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals... |
Discovery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOR J0332-3557 | 03h:32m:59s:94, -35°57'51".7, J2000 | 1".48 | Partial, 260° | Radio | Cabanac (2005) |
| SDSSJ0946+1006 SDSSJ0946+1006 SDSSJ0946+1006 is an unusual gravitational lens system consisting of three galaxies at distances of respectively three, six, and eleven billion light years from Earth... |
09h 46m 56.s68, +10° 06' 52."6 J2000 | Optical | Gavazzi (2008) | ||
| MG1131 + 0456 |
Extra rings

Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was carried into orbit by a Space Shuttle in 1990 and remains in operation. A 2.4 meter aperture telescope in low Earth orbit, Hubble's four main instruments observe in the near ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared...
, a double ring has been found by Raphael Gavazzi of the STScI and Tommaso Treu of the University of California, Santa Barbara
University of California, Santa Barbara
The University of California, Santa Barbara, commonly known as UCSB or UC Santa Barbara, is a public research university and one of the 10 general campuses of the University of California system. The main campus is located on a site in Goleta, California, from Santa Barbara and northwest of Los...
. This arises from the light from three galaxies at distances of 3, 6 and 11 billion light years. Such rings help in understanding the distribution of dark matter
Dark matter
In astronomy and cosmology, dark matter is matter that neither emits nor scatters light or other electromagnetic radiation, and so cannot be directly detected via optical or radio astronomy...
, dark energy
Dark energy
In physical cosmology, astronomy and celestial mechanics, dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy that permeates all of space and tends to accelerate the expansion of the universe. Dark energy is the most accepted theory to explain recent observations that the universe appears to be expanding...
, the nature of distant galaxies, and the curvature of the universe. The odds of finding such a double ring are 1 in 10,000. Sampling 50 suitable double rings would provide astronomers with a more accurate measurement of the dark matter content of the universe and the equation of state of the dark energy to within 10 percent precision.
A simulation
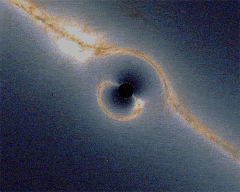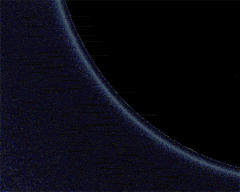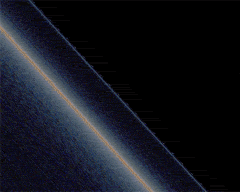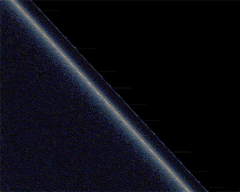
Schwarzschild metric
In Einstein's theory of general relativity, the Schwarzschild solution describes the gravitational field outside a spherical, uncharged, non-rotating mass such as a star, planet, or black hole. It is also a good approximation to the gravitational field of a slowly rotating body like the Earth or...
in front of the Milky Way
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
. The first Einstein ring corresponds to the most distorted region of the picture and is clearly depicted by the galactic disc
Disc (galaxy)
A disc is a component of disc galaxies, such as spiral galaxies, or lenticular galaxies.The galactic disc is the plane in which the spirals, bars and discs of disc galaxies exist. Galaxy discs tend to have more gas and dust, and younger stars than galactic bulges, or galactic haloes.The galactic...
. The zoom then reveals a series of 4 extra rings, increasingly thinner and closer to the black hole shadow. They are easily seen through the multiple images of the galactic disk. Odd rings correspond to points which are behind the black hole (from the observer point of view) and correspond here to the bright yellow region of the galactic disc (close to the galactic center), whereas even rings correspond to images of regions which are behind the observer, which appear bluer since the corresponding part of the galactic disk is dimmer here.

