
Elections in Spain
Encyclopedia
There are four types of elections in Spain: general elections, elections to the legislatures of the autonomous communities
, local elections and elections to the European Parliament
. General elections and elections to the legislatures of the autonomous communities are called after the mandate of the national or regional legislature expires, usually four years after the last election, although early elections may occur. Elections to local councils (municipal, insular or provincial) and to the European Parliament are held on fixed dates. For most elections party list PR
is used, but the plurality system
is used for the Senate
.
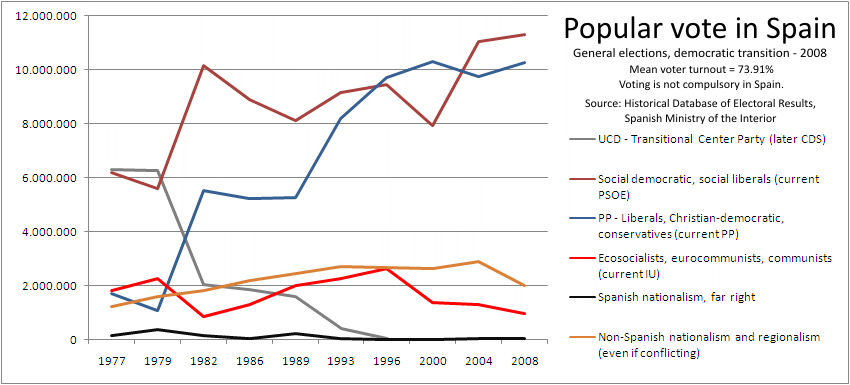 General elections are elections held for the national legislature, which is called in Spain Cortes Generales
General elections are elections held for the national legislature, which is called in Spain Cortes Generales
(literally "General Courts") and consists of two chambers
, the Congress of Deputies
(Congreso de los Diputados) and the Senate
(Senado). The Congress and Senate serve concurrent terms that run for a maximum of four years.
for a maximum four-year term following the d'Hondt method
of proportional representation
. While the constitution
allows limited flexibility in determining this system, it has not changed since the return of democracy.
Seats are allocated as follows: Two seats are given to each of the 50 provinces and one each to Ceuta
and Melilla
, and the remaining 248 are then allocated proportionally to population. In practice, this system overrepresents smaller provinces, and results in very low proportionality in all but the most populous such as Madrid and Barcelona
. Additionally, since there are so many constituencies (52), most are relatively small. This effectively increases the legal 3% threshold
to obtain seats in a constituency, radically decreases proportionality, and favors the two large parties and parties with concentrated regional strength, at the expense of national third parties.
In the provinces, a majoritarian partial block voting
system is used. All peninsular provinces elect four senators each; the insular provinces (Balearic
and Canary
Islands) elect one or three senators per island, and Ceuta and Melilla elect two senators each. Parties nominate three candidates; each voter has three votes (fewer in those constituencies electing fewer senators) and votes for candidates by name, the only instance of personal voting in Spanish national elections. The usual outcome is three senators for the party with the most votes, and one senator for the runner-up, except in very close races.
The autonomous communities receive one senator, plus one for each million inhabitants. They are entitled to determine how they choose their senators but are generally elected by the legislature of the respective community in proportion to its party composition.
are held every four years. Thirteen of the seventeen autonomous parliaments (Aragon
, Asturias
, Balearic Islands
, Canary Islands
, Cantabria
, Castile and León
, Castile-La Mancha
, Extremadura
, La Rioja
, Madrid, Murcia
, Navarre
and Valencia
) take place the same day, the fourth Sunday of May of the year before a leap year
; the last election was held in May 22, 2011
.
The other four communities can place their elections in separate dates: last elections in Andalusia
were in 2008, together with the general election; Euskadi and Galicia had elections in 2009, and Catalonia
in 2010.
s are run by electoral boards which consist of groups of citizens selected by lottery.
The format of the ballot paper is designed by the Spanish state, however, the law allows political parties to produce and distribute their own ballot papers, either by mailing them to voters or by other means such as street distribution, provided that they comply with the official model. The government then covers the cost of all printed ballot papers. These must then be marked by voters, either in the polling station or outside the polling station and placed inside sealed envelopes which are then placed inside ballot box
es in the polling station. Following the close of polls, the ballots are then counted in each individual polling station in the presence of representatives of the political parties and candidates. The ballots are then immediately destroyed, with the exception of those considered invalid or challenged by the candidates' representatives, which are retained for further scrutiny. The result is that full recounts are impossible.
Autonomous communities of Spain
An autonomous community In other languages of Spain:*Catalan/Valencian .*Galician .*Basque . The second article of the constitution recognizes the rights of "nationalities and regions" to self-government and declares the "indissoluble unity of the Spanish nation".Political power in Spain is...
, local elections and elections to the European Parliament
European Parliament
The European Parliament is the directly elected parliamentary institution of the European Union . Together with the Council of the European Union and the Commission, it exercises the legislative function of the EU and it has been described as one of the most powerful legislatures in the world...
. General elections and elections to the legislatures of the autonomous communities are called after the mandate of the national or regional legislature expires, usually four years after the last election, although early elections may occur. Elections to local councils (municipal, insular or provincial) and to the European Parliament are held on fixed dates. For most elections party list PR
Party-list proportional representation
Party-list proportional representation systems are a family of voting systems emphasizing proportional representation in elections in which multiple candidates are elected...
is used, but the plurality system
Plurality-at-large voting
Plurality-at-large voting is a non-proportional voting system for electing several representatives from a single multimember electoral district using a series of check boxes and tallying votes similar to a plurality election...
is used for the Senate
Spanish Senate
The Senate of Spain is the upper house of Spain's parliament, the . It is made up of 264 members: 208 elected by popular vote, and 56 appointed by the regional legislatures. All senators serve four-year terms, though regional legislatures may recall their appointees at any time.The last election...
.
General elections

Cortes Generales
The Cortes Generales is the legislature of Spain. It is a bicameral parliament, composed of the Congress of Deputies and the Senate . The Cortes has power to enact any law and to amend the constitution...
(literally "General Courts") and consists of two chambers
Bicameralism
In the government, bicameralism is the practice of having two legislative or parliamentary chambers. Thus, a bicameral parliament or bicameral legislature is a legislature which consists of two chambers or houses....
, the Congress of Deputies
Spanish Congress of Deputies
The Spanish Congress of Deputies is the lower house of the Cortes Generales, Spain's legislative branch. It has 350 members, elected by popular vote on block lists by proportional representation in constituencies matching the Spanish provinces using the D'Hondt method. Deputies serve four-year terms...
(Congreso de los Diputados) and the Senate
Spanish Senate
The Senate of Spain is the upper house of Spain's parliament, the . It is made up of 264 members: 208 elected by popular vote, and 56 appointed by the regional legislatures. All senators serve four-year terms, though regional legislatures may recall their appointees at any time.The last election...
(Senado). The Congress and Senate serve concurrent terms that run for a maximum of four years.
Congress of Deputies
The Congress has 350 members, elected from each provinceProvinces of Spain
Spain and its autonomous communities are divided into fifty provinces .In other languages of Spain:*Catalan/Valencian , sing. província.*Galician , sing. provincia.*Basque |Galicia]] — are not also the capitals of provinces...
for a maximum four-year term following the d'Hondt method
D'Hondt method
The d'Hondt method is a highest averages method for allocating seats in party-list proportional representation. The method described is named after Belgian mathematician Victor D'Hondt who described it in 1878...
of proportional representation
Proportional representation
Proportional representation is a concept in voting systems used to elect an assembly or council. PR means that the number of seats won by a party or group of candidates is proportionate to the number of votes received. For example, under a PR voting system if 30% of voters support a particular...
. While the constitution
Spanish Constitution of 1978
-Structure of the State:The Constitution recognizes the existence of nationalities and regions . Preliminary Title As a result, Spain is now composed entirely of 17 Autonomous Communities and two autonomous cities with varying degrees of autonomy, to the extent that, even though the Constitution...
allows limited flexibility in determining this system, it has not changed since the return of democracy.
Seats are allocated as follows: Two seats are given to each of the 50 provinces and one each to Ceuta
Ceuta
Ceuta is an autonomous city of Spain and an exclave located on the north coast of North Africa surrounded by Morocco. Separated from the Iberian peninsula by the Strait of Gibraltar, Ceuta lies on the border of the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. Ceuta along with the other Spanish...
and Melilla
Melilla
Melilla is a autonomous city of Spain and an exclave on the north coast of Morocco. Melilla, along with the Spanish exclave Ceuta, is one of the two Spanish territories located in mainland Africa...
, and the remaining 248 are then allocated proportionally to population. In practice, this system overrepresents smaller provinces, and results in very low proportionality in all but the most populous such as Madrid and Barcelona
Barcelona (province)
Barcelona is a province of eastern Spain, in the center of the autonomous community of Catalonia.-Overview:It is bordered by the provinces of Tarragona, Lleida, and Girona, and by the Mediterranean Sea....
. Additionally, since there are so many constituencies (52), most are relatively small. This effectively increases the legal 3% threshold
Election threshold
In party-list proportional representation systems, an election threshold is a clause that stipulates that a party must receive a minimum percentage of votes, either nationally or within a particular district, to obtain any seats in the parliament...
to obtain seats in a constituency, radically decreases proportionality, and favors the two large parties and parties with concentrated regional strength, at the expense of national third parties.
Senate
The system for electing the Senate was first used in 1979, though with regard to the provinces the system is unchanged since 1977. Senators are elected directly from the provinces and indirectly from the autonomous communities; currently, there are 264 senators, 208 directly elected and 56 indirectly elected.In the provinces, a majoritarian partial block voting
Plurality-at-large voting
Plurality-at-large voting is a non-proportional voting system for electing several representatives from a single multimember electoral district using a series of check boxes and tallying votes similar to a plurality election...
system is used. All peninsular provinces elect four senators each; the insular provinces (Balearic
Balearic Islands
The Balearic Islands are an archipelago of Spain in the western Mediterranean Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula.The four largest islands are: Majorca, Minorca, Ibiza and Formentera. The archipelago forms an autonomous community and a province of Spain with Palma as the capital...
and Canary
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands , also known as the Canaries , is a Spanish archipelago located just off the northwest coast of mainland Africa, 100 km west of the border between Morocco and the Western Sahara. The Canaries are a Spanish autonomous community and an outermost region of the European Union...
Islands) elect one or three senators per island, and Ceuta and Melilla elect two senators each. Parties nominate three candidates; each voter has three votes (fewer in those constituencies electing fewer senators) and votes for candidates by name, the only instance of personal voting in Spanish national elections. The usual outcome is three senators for the party with the most votes, and one senator for the runner-up, except in very close races.
The autonomous communities receive one senator, plus one for each million inhabitants. They are entitled to determine how they choose their senators but are generally elected by the legislature of the respective community in proportion to its party composition.
List of general elections in Spain
| Political position Political spectrum A political spectrum is a way of modeling different political positions by placing them upon one or more geometric axes symbolizing independent political dimensions.... of the government |
| Election | Result | Government | |Prime Minister Prime Minister of Spain The President of the Government of Spain , sometimes known in English as the Prime Minister of Spain, is the head of Government of Spain. The current office is established under the Constitution of 1978... |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1977 Spanish general election, 1977 The Spanish general election of 1977 took place on 15 June 1977. It was the first election since the death of Francisco Franco.Voting was on the basis of universal suffrage in a secret ballot. The elections were held using closed list proportional representation in 52 electoral districts... |
Hung parliament Hung parliament In a two-party parliamentary system of government, a hung parliament occurs when neither major political party has an absolute majority of seats in the parliament . It is also less commonly known as a balanced parliament or a legislature under no overall control... , UCD short by 10 MP's |
UCD minority government Minority government A minority government or a minority cabinet is a cabinet of a parliamentary system formed when a political party or coalition of parties does not have a majority of overall seats in the parliament but is sworn into government to break a Hung Parliament election result. It is also known as a... |
Adolfo Suárez Adolfo Suárez Adolfo Suárez y González, 1st Duke of Suárez, Grandee of Spain, KOGF is a Spanish lawyer and politician. Suárez was Spain's first democratically elected prime minister after the dictatorship of Francisco Franco, and the key figure in the country's transition to democracy.-Parents:He is a son of... |
|
| 1979 Spanish general election, 1979 General elections were held in Spain on 1 March 1979.-References:* *... |
Hung parliament, UCD short by 8 MP's | UCD government with support from People's Alliance, Andalusian Party and Aragonese Party Aragonese Party The Aragonese Party is a political party which advocates the interests of Aragon within Spain. The party was founded in 1978 under the name Aragonese Regionalist Party, but changed its name in 1990, keeping the initials PAR.... |
Adolfo Suárez Adolfo Suárez Adolfo Suárez y González, 1st Duke of Suárez, Grandee of Spain, KOGF is a Spanish lawyer and politician. Suárez was Spain's first democratically elected prime minister after the dictatorship of Francisco Franco, and the key figure in the country's transition to democracy.-Parents:He is a son of... (resigned) Leopoldo Calvo-Sotelo |
|
| 1982 Spanish general election, 1982 General elections were held in Spain on 28 October 1982.PSOE and PSC presented two different lists of candidates: with the PSOE contesting most of Spain and the PSC only standing in Catalonia... |
PSOE Spanish Socialist Workers' Party The Spanish Socialist Workers' Party is a social-democratic political party in Spain. Its political position is Centre-left. The PSOE is the former ruling party of Spain, until beaten in the elections of November 2011 and the second oldest, exceeded only by the Partido Carlista, founded in... landslide victory Landslide victory In politics, a landslide victory is the victory of a candidate or political party by an overwhelming margin in an election... and absolute majority of 54 |
PSOE majority government Majority government A majority government is when the governing party has an absolute majority of seats in the legislature or parliament in a parliamentary system. This is as opposed to a minority government, where even the largest party wins only a plurality of seats and thus must constantly bargain for support from... |
Felipe González Felipe González Felipe González Márquez is a Spanish socialist politician. He was the General Secretary of the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party from 1974 to 1997. To date, he remains the longest-serving Prime Minister of Spain, after having served four successive mandates from 1982 to 1996.-Early life:Felipe was... |
|
| 1986 Spanish general election, 1986 General elections were held in Spain on 23 June 1986. In this election, the Communist Party of Spain merged with other minor left parties to form the coalition Izquierda Unida; in Catalonia they ran as the Catalan Left Union. Similarly, the People's Alliance merged with two other conservative... |
PSOE Spanish Socialist Workers' Party The Spanish Socialist Workers' Party is a social-democratic political party in Spain. Its political position is Centre-left. The PSOE is the former ruling party of Spain, until beaten in the elections of November 2011 and the second oldest, exceeded only by the Partido Carlista, founded in... absolute majority of 22 |
PSOE majority government | Felipe González Felipe González Felipe González Márquez is a Spanish socialist politician. He was the General Secretary of the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party from 1974 to 1997. To date, he remains the longest-serving Prime Minister of Spain, after having served four successive mandates from 1982 to 1996.-Early life:Felipe was... |
|
| 1989 Spanish general election, 1989 -Results:-External links:**... |
PSOE Spanish Socialist Workers' Party The Spanish Socialist Workers' Party is a social-democratic political party in Spain. Its political position is Centre-left. The PSOE is the former ruling party of Spain, until beaten in the elections of November 2011 and the second oldest, exceeded only by the Partido Carlista, founded in... victory, with exactly one half of the seats |
PSOE government with support from Canarian Coalition Canarian Coalition The Canarian Coalition , abbreviated to CC, is a Canarian nationalist and liberal political party in the Canary Islands of Spain. The party aim is for greater autonomy for the islands, but short of independence. The party has governed the Canary Islands since 1993... |
Felipe González Felipe González Felipe González Márquez is a Spanish socialist politician. He was the General Secretary of the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party from 1974 to 1997. To date, he remains the longest-serving Prime Minister of Spain, after having served four successive mandates from 1982 to 1996.-Early life:Felipe was... |
|
| 1993 Spanish general election, 1993 -Results:-External links:*... |
Hung parliament, PSOE Spanish Socialist Workers' Party The Spanish Socialist Workers' Party is a social-democratic political party in Spain. Its political position is Centre-left. The PSOE is the former ruling party of Spain, until beaten in the elections of November 2011 and the second oldest, exceeded only by the Partido Carlista, founded in... short by 17 MP's |
PSOE government with support from Convergence and Union and the Basque Nationalist Party Basque Nationalist Party The Basque National Party is the largest and oldest Basque nationalist party. It is currently the largest political party in the Basque Autonomous Community also with a minor presence in Navarre and a marginal one in the French Basque Country... |
Felipe González Felipe González Felipe González Márquez is a Spanish socialist politician. He was the General Secretary of the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party from 1974 to 1997. To date, he remains the longest-serving Prime Minister of Spain, after having served four successive mandates from 1982 to 1996.-Early life:Felipe was... |
|
| 1996 Spanish general election, 1996 General elections were held in Spain on March 3, 1996. The Prime Minister Felipe González of Spanish Socialist Workers' Party lost the elections to Partido Popular and their leader José María Aznar.... |
Hung parliament, PP People's Party (Spain) The People's Party is a conservative political party in Spain.The People's Party was a re-foundation in 1989 of the People's Alliance , a party led and founded by Manuel Fraga Iribarne, a former Minister of Tourism during Francisco Franco's dictatorship... short by 20 MP's |
PP government with support from Convergence and Union, the Basque Nationalist Party Basque Nationalist Party The Basque National Party is the largest and oldest Basque nationalist party. It is currently the largest political party in the Basque Autonomous Community also with a minor presence in Navarre and a marginal one in the French Basque Country... and Canarian Coalition Canarian Coalition The Canarian Coalition , abbreviated to CC, is a Canarian nationalist and liberal political party in the Canary Islands of Spain. The party aim is for greater autonomy for the islands, but short of independence. The party has governed the Canary Islands since 1993... |
José María Aznar José María Aznar José María Alfredo Aznar López served as the Prime Minister of Spain from 1996 to 2004. He is on the board of directors of News Corporation.-Early life:... |
|
| 2000 Spanish general election, 2000 Legislative elections were held in Spain on 12 March 2000. The incumbent People's Party of Prime Minister José María Aznar was elected to a second term in office, converting its plurality of seats in the Congress of Deputies into a majority, and increasing its lead over the opposition Spanish... |
PP People's Party (Spain) The People's Party is a conservative political party in Spain.The People's Party was a re-foundation in 1989 of the People's Alliance , a party led and founded by Manuel Fraga Iribarne, a former Minister of Tourism during Francisco Franco's dictatorship... absolute majority of 16 |
PP majority government Majority government A majority government is when the governing party has an absolute majority of seats in the legislature or parliament in a parliamentary system. This is as opposed to a minority government, where even the largest party wins only a plurality of seats and thus must constantly bargain for support from... |
José María Aznar José María Aznar José María Alfredo Aznar López served as the Prime Minister of Spain from 1996 to 2004. He is on the board of directors of News Corporation.-Early life:... |
|
| 2004 | Hung parliament, PSOE Spanish Socialist Workers' Party The Spanish Socialist Workers' Party is a social-democratic political party in Spain. Its political position is Centre-left. The PSOE is the former ruling party of Spain, until beaten in the elections of November 2011 and the second oldest, exceeded only by the Partido Carlista, founded in... short by 12 MP's |
PSOE government with support from United Left United Left (Spain) The United Left is a political coalition that was organized in 1986 bringing together several political organisations opposed to Spain joining NATO. It was formed by a number of groups of leftists, greens, left-wing socialists and republicans, but was dominated by the Communist Party of Spain... and Republican Left of Catalonia |
José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero is a member of the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party . He was elected for two terms as Prime Minister of Spain, in the 2004 and 2008 general elections. On 2 April 2011 he announced he will not stand for re-election in 2012... |
|
| 2008 Spanish general election, 2008 Legislative elections for the Spanish Cortes Generales were held on March 9, 2008. The elections were for 350 seats in the Congress of Deputies, and the 208 directly elected seats in the upper house, the Senate, determining the Prime Minister of Spain... |
Hung parliament, PSOE Spanish Socialist Workers' Party The Spanish Socialist Workers' Party is a social-democratic political party in Spain. Its political position is Centre-left. The PSOE is the former ruling party of Spain, until beaten in the elections of November 2011 and the second oldest, exceeded only by the Partido Carlista, founded in... short by 7 MP's |
PSOE minority government Minority government A minority government or a minority cabinet is a cabinet of a parliamentary system formed when a political party or coalition of parties does not have a majority of overall seats in the parliament but is sworn into government to break a Hung Parliament election result. It is also known as a... |
José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero is a member of the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party . He was elected for two terms as Prime Minister of Spain, in the 2004 and 2008 general elections. On 2 April 2011 he announced he will not stand for re-election in 2012... |
|
| 2011 | PP People's Party (Spain) The People's Party is a conservative political party in Spain.The People's Party was a re-foundation in 1989 of the People's Alliance , a party led and founded by Manuel Fraga Iribarne, a former Minister of Tourism during Francisco Franco's dictatorship... absolute majority of 22 |
PP majority government Majority government A majority government is when the governing party has an absolute majority of seats in the legislature or parliament in a parliamentary system. This is as opposed to a minority government, where even the largest party wins only a plurality of seats and thus must constantly bargain for support from... |
Mariano Rajoy Mariano Rajoy Mariano Rajoy Brey is a Spanish People's Party politician and is the Prime Minister-elect since 20 November 2011. He will be sworn into office in mid-December 2011.... |
Elections to legislatures of the autonomous communities
Elections to the unicameral parliaments of the autonomous communities of SpainAutonomous communities of Spain
An autonomous community In other languages of Spain:*Catalan/Valencian .*Galician .*Basque . The second article of the constitution recognizes the rights of "nationalities and regions" to self-government and declares the "indissoluble unity of the Spanish nation".Political power in Spain is...
are held every four years. Thirteen of the seventeen autonomous parliaments (Aragon
Aragon
Aragon is a modern autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. Located in northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces : Huesca, Zaragoza, and Teruel. Its capital is Zaragoza...
, Asturias
Asturias
The Principality of Asturias is an autonomous community of the Kingdom of Spain, coextensive with the former Kingdom of Asturias in the Middle Ages...
, Balearic Islands
Balearic Islands
The Balearic Islands are an archipelago of Spain in the western Mediterranean Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula.The four largest islands are: Majorca, Minorca, Ibiza and Formentera. The archipelago forms an autonomous community and a province of Spain with Palma as the capital...
, Canary Islands
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands , also known as the Canaries , is a Spanish archipelago located just off the northwest coast of mainland Africa, 100 km west of the border between Morocco and the Western Sahara. The Canaries are a Spanish autonomous community and an outermost region of the European Union...
, Cantabria
Cantabria
Cantabria is a Spanish historical region and autonomous community with Santander as its capital city. It is bordered on the east by the Basque Autonomous Community , on the south by Castile and León , on the west by the Principality of Asturias, and on the north by the Cantabrian Sea.Cantabria...
, Castile and León
Castile and León
Castile and León is an autonomous community in north-western Spain. It was so constituted in 1983 and it comprises the historical regions of León and Old Castile...
, Castile-La Mancha
Castile-La Mancha
Castile-La Mancha is an autonomous community of Spain. Castile-La Mancha is bordered by Castile and León, Madrid, Aragon, Valencia, Murcia, Andalusia, and Extremadura. It is one of the most sparsely populated of Spain's autonomous communities...
, Extremadura
Extremadura
Extremadura is an autonomous community of western Spain whose capital city is Mérida. Its component provinces are Cáceres and Badajoz. It is bordered by Portugal to the west...
, La Rioja
La Rioja (Spain)
La Rioja is an autonomous community and a province of northern Spain. Its capital is Logroño. Other cities and towns in the province include Calahorra, Arnedo, Alfaro, Haro, Santo Domingo de la Calzada, and Nájera.-History:...
, Madrid, Murcia
Region of Murcia
The Region of Murcia is an autonomous community of Spain located in the southeast of the country, between Andalusia and Valencian Community, on the Mediterranean coast....
, Navarre
Navarre
Navarre , officially the Chartered Community of Navarre is an autonomous community in northern Spain, bordering the Basque Country, La Rioja, and Aragon in Spain and Aquitaine in France...
and Valencia
Valencian Community
The Valencian Community is an autonomous community of Spain located in central and south-eastern Iberian Peninsula. Its capital and largest city is Valencia...
) take place the same day, the fourth Sunday of May of the year before a leap year
Leap year
A leap year is a year containing one extra day in order to keep the calendar year synchronized with the astronomical or seasonal year...
; the last election was held in May 22, 2011
Spanish local and regional elections, 2011
Local and regional elections were held on 22 May 2011 in Spain. Local elections are held at once across all of Spain, while regional elections were held in 13 of Spain's 17 autonomous communities; Andalusia, Catalonia, Galicia, and the Basque Country have different electoral cycles.The days before...
.
The other four communities can place their elections in separate dates: last elections in Andalusia
Andalusia
Andalusia is the most populous and the second largest in area of the autonomous communities of Spain. The Andalusian autonomous community is officially recognised as a nationality of Spain. The territory is divided into eight provinces: Huelva, Seville, Cádiz, Córdoba, Málaga, Jaén, Granada and...
were in 2008, together with the general election; Euskadi and Galicia had elections in 2009, and Catalonia
Catalonia
Catalonia is an autonomous community in northeastern Spain, with the official status of a "nationality" of Spain. Catalonia comprises four provinces: Barcelona, Girona, Lleida, and Tarragona. Its capital and largest city is Barcelona. Catalonia covers an area of 32,114 km² and has an...
in 2010.
Local elections
Elections in the municipalities take place in all the country in the same day as the 13 regional elections, in May of the year before a leap year. Last time was May 22, 2011.Electoral procedures
The laws regulating the conduct and administration of elections are laid out in detail in the 1985 electoral law. (Ley Orgánica del Régimen Electoral General.) Under this law, the elections are supervised by the Electoral Commission (Junta Electoral), a permanent body composed of eight Supreme Court judges and five political scientists or sociologists appointed by the Congress of Deputies. The Electoral commission is supported in its work by the Interior Ministry. On election day, polling stationPolling station
A polling place or polling station is where voters cast their ballots in elections.Since elections generally take place over a one- or two-day span on a periodic basis, often annual or longer, polling places are often located in facilities used for other purposes, such as schools, churches, sports...
s are run by electoral boards which consist of groups of citizens selected by lottery.
The format of the ballot paper is designed by the Spanish state, however, the law allows political parties to produce and distribute their own ballot papers, either by mailing them to voters or by other means such as street distribution, provided that they comply with the official model. The government then covers the cost of all printed ballot papers. These must then be marked by voters, either in the polling station or outside the polling station and placed inside sealed envelopes which are then placed inside ballot box
Ballot box
A ballot box is a temporarily sealed container, usually square box though sometimes a tamper resistant bag, with a narrow slot in the top sufficient to accept a ballot paper in an election but which prevents anyone from accessing the votes cast until the close of the voting period...
es in the polling station. Following the close of polls, the ballots are then counted in each individual polling station in the presence of representatives of the political parties and candidates. The ballots are then immediately destroyed, with the exception of those considered invalid or challenged by the candidates' representatives, which are retained for further scrutiny. The result is that full recounts are impossible.
External links
- General Directorate of Domestic Politics, archived results back to 1976
- Adam Carr's Election Archive
- Parties and elections
- NSD: European Election Database - Spain publishes regional level election data; allows for comparisons of election results, 199-2008

