
Electric light
Encyclopedia
Electric lights are a convenient and economic form of artificial lighting which provide increased comfort, safety and efficiency. Most electric lighting is powered by centrally-generated electric power, but lighting may also be powered by mobile or standby electric generators or battery systems. Battery
-powered lights, usually called "flashlight
s" or "torches", are used for portability and as backups when the main lights fail. The energy efficiency of electric lighting has increased radically since the first demonstration arc lamp
s and the incandescent light bulb of the 19th century. Modern electric light sources come in a profusion of types and sizes adapted to a myriad of applications.
lighting include:
Different types of lights have vastly differing efficiencies and color of light
. http://www.parliament.the-stationery-office.co.uk/pa/cm200203/cmselect/cmsctech/747/747we81.htm
*Color temperature is defined as the temperature of a black body
emitting a similar spectrum; these spectra are quite different from those of black bodies.
The most efficient source of electric light is the low-pressure sodium lamp. It produces an almost monochromatic orange light, which severely distorts color perception. For this reason, it is generally reserved for outdoor public lighting usages. Low-pressure sodium lights are favoured for public lighting by astronomers, since the light pollution
that they generate can be easily filtered, contrary to broadband or continuous spectra.
There is currently interest in banning some types of filament lamp in some countries, such as Australia planning to ban standard incandescent light bulbs by 2010, because they are inefficient at converting electricity to light. Sri Lanka has already banned importing filament bulbs because of high use of electricity and less light. Less than 3% of the input energy is converted into usable light. Nearly all of the input energy ends up as heat that, in warm climates, must then be removed from the building by ventilation
or air conditioning
, often resulting in more energy consumption. In colder climates where heating and lighting is required during the cold and dark winter months, the heat byproduct has at least some value.
s. The risk of burns or fire is also greater with bare bulbs, leading to their prohibition in some places unless enclosed by the luminaire.
Those designed for 12 V or 24 V operation have compact filaments, useful for good optical control, also they have higher efficiencies (lumens per watt) and better lives than non halogen types. The light output remains almost constant throughout life.
Fluorescents were mostly limited to linear
and a round 'Circline' lamp until the 1980s, with other shapes never gaining much popularity. The compact fluorescent lamp
(CFL) was commercialized in the early 1980s.
Most CFLs have a built-in electrical ballast and fit into a standard screw or bayonet base. Some make use of a separate ballast so that the ballast and tube can be replaced separately.
Typical average lifetime ratings for linear fluorescent tubes are 10,000 and 20,000 hours, compared to 750 hours (110 V) and 1000 hours (240 V) for filament lamps.
Some types of fluorescent lamp ballast have difficulty starting lamps in very cold conditions, so lights used outdoors in cold climates need to be designed for outdoor use to work reliably.
Fluorescents come in a range of different color temperatures. In some countries cool white (CW) is most popular, while in some, warmer whites predominate.
In America, fluorescents most often come in cool white (CW), with some home bulbs being a warm white (WW), which has a pink
ish color. In between there is an "enhanced white" (EW), which is more neutral. There is also a very cold daylight white (DW). Compact fluorescent lamps are usually considered warm white, though many have a yellowish cast like an incandescent. "Warm" and "cool" are entirely relative terms and almost arbitrary
so color temperature
and the color rendering index (CRI) are used as absolute scales of color for fluorescents, and sometimes for other types of lighting.
and output have risen to the point where LEDs are now being used in niche lighting applications.
Indicator LEDs are known for their extremely long life, up to 100,000 hours, but lighting LEDs are operated much less conservatively (due to high LED cost per watt), and consequently have much shorter lives.
Due to the relatively high cost per watt, LED lighting is most useful at very low powers, typically for lamp assemblies of under 10 W. LEDs are currently most useful and cost-effective in low power applications, such as nightlight
s and flashlight
s. Colored LEDs can also be used for accent lighting, such as for glass objects, and even in fake ice cube
s for drink
s at parties. They are also being increasingly used as holiday lighting.
LED efficiencies vary over a very wide range. Some have lower efficiency than filament lamps, and some significantly higher. LED performance in this respect is prone to being misinterpreted, as the inherent directionality of LEDs gives them a much higher light intensity in one direction per given total light output.
Single color LEDs are well developed technology, but white LEDs at time of writing still have some unresolved issues.
LED technology is useful for lighting designers because of its low power consumption, low heat generation, instantaneous on/off control, and in the case of single color LEDs, continuity of color throughout the life of the diode and relatively low cost of manufacture.
In the last few years, software has been developed to merge lighting and video by enabling lighting designers to stream video content to their LED fixtures, creating low resolution video walls.
For general domestic lighting, total cost of ownership of LED lighting is still much higher than for other well established lighting types.
s in open air, supplied by a current-limiting ballast
. The electric arc
is struck by touching the rods then separating them. The ensuing arc heats the carbon tips to white heat. These lamps have higher efficiency than filament lamps, but the carbon rods are short lived and require constant adjustment in use. The lamps produce significant ultra-violet output, they require ventilation when used indoors, and due to their intensity they need protecting from direct sight.
Carbon arc lamps operate at high powers, and had high efficiency compared to other pre-1920s light sources. They also are a point source of light. These properties made them ideally suited to search lights, follow spots and film projector lights.
Their need for ongoing attendance and adjustment, and frequent rod replacement made them ill suited to general lighting, though they were used for high power lighting in the years when nothing else with comparable output power existed. Carbon arcs fell out of use even for niche applications during and after World War 2.
s separated by a gas. Gases used include, neon
, argon
, xenon
, sodium
, metal halide, and mercury
.
The core operating principle is much the same as the carbon arc lamp, but the term 'arc lamp' is normally used to refer to carbon arc lamps, with more modern types of gas discharge lamp normally called 'discharge lamps'.
With some discharge lamps, very high voltage is used to strike the arc. This requires an electrical circuit called an igniter, which is part of the ballast circuitry. After the arc is struck, the internal resistance of the lamp drops to a low level, and the ballast limits the current to the operating current. Without a ballast, excess current would flow, causing rapid destruction of the lamp.
Some lamp types contain a little neon, which permits striking at normal running voltage, with no external igniter circuitry. Low pressure sodium lamps
operate this way.
The simplest ballasts are just an inductor, and are chosen where cost is the deciding factor, such as street lighting. More advanced electronic ballasts may be designed to maintain constant light output over the life of the lamp, may drive the lamp with a square wave to maintain completely flicker-free output, and shut down in the event of certain faults. These more complex ballasts are chosen in the film industry for example.
Lamps are also sensitive to switching cycles. The rapid heating of a lamp filament or electrodes when a lamp is turned on is the most stressful event on the lamp. Most test cycles have the lamps on for 3 hours and then off for 20 minutes. (Some standard had to be used since it is unknown how the lamp will be used by consumers.) This switching cycle repeats until the lamps fail and the data is recorded. If switching is increased to only 1 hour on, the lamp life is usually reduced because the number of times the lamp has been turned on has increased. Rooms with frequent switching (bathroom, bedrooms, etc.) can expect much shorter lamp life than what is printed on the box.
) is sufficient for cities to be easily visible at night from the air, and from space. This wasted light is the source of light pollution
that burdens astronomers
and others.
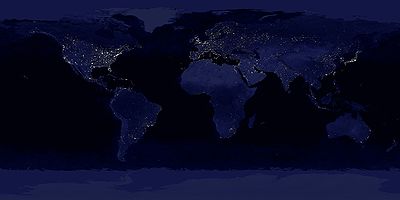
Human-made lights highlight particularly developed or populated areas of the Earth's surface, including the seaboards of Europe, the eastern United States, and Japan.
Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
-powered lights, usually called "flashlight
Flashlight
A flashlight is a hand-held electric-powered light source. Usually the light source is a small incandescent lightbulb or light-emitting diode...
s" or "torches", are used for portability and as backups when the main lights fail. The energy efficiency of electric lighting has increased radically since the first demonstration arc lamp
Arc lamp
"Arc lamp" or "arc light" is the general term for a class of lamps that produce light by an electric arc . The lamp consists of two electrodes, first made from carbon but typically made today of tungsten, which are separated by a gas...
s and the incandescent light bulb of the 19th century. Modern electric light sources come in a profusion of types and sizes adapted to a myriad of applications.
Types
Types of electricElectricity
Electricity is a general term encompassing a variety of phenomena resulting from the presence and flow of electric charge. These include many easily recognizable phenomena, such as lightning, static electricity, and the flow of electrical current in an electrical wire...
lighting include:
- incandescent light bulbIncandescent light bulbThe incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe makes light by heating a metal filament wire to a high temperature until it glows. The hot filament is protected from air by a glass bulb that is filled with inert gas or evacuated. In a halogen lamp, a chemical process...
s - arc lampArc lamp"Arc lamp" or "arc light" is the general term for a class of lamps that produce light by an electric arc . The lamp consists of two electrodes, first made from carbon but typically made today of tungsten, which are separated by a gas...
s - gas discharge lamps, e.g., fluorescent lights and compact fluorescent lampCompact fluorescent lampA compact fluorescent lamp , also called compact fluorescent light, energy-saving light, and compact fluorescent tube, is a fluorescent lamp designed to replace an incandescent lamp; some types fit into light fixtures formerly used for incandescent lamps...
s, neon lampNeon lampA neon lamp is a miniature gas discharge lamp that typically contains neon gas at a low pressure in a glass capsule. Only a thin region adjacent to the electrodes glows in these lamps, which distinguishes them from the much longer and brighter neon tubes used for signage...
s, flood lampsMetal halide lampMetal-halide lamps, a member of the high-intensity discharge family of lamps, produce high light output for their size, making them a compact, powerful, and efficient light source. By adding rare earth metal salts to the mercury vapor lamp, improved luminous efficacy and light color is obtained...
, modern photographic flashes - laserLaserA laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
s - light-emitting diodeLight-emitting diodeA light-emitting diode is a semiconductor light source. LEDs are used as indicator lamps in many devices and are increasingly used for other lighting...
s, including OLEDOrganic light-emitting diodeAn OLED is a light-emitting diode in which the emissive electroluminescent layer is a film of organic compounds which emit light in response to an electric current. This layer of organic semiconductor material is situated between two electrodes...
s - sulfur lampSulfur lampThe sulfur lamp is a highly efficient full-spectrum electrodeless lighting system whose light is generated by sulfur plasma that has been excited by microwave radiation. The technology was developed in the early 1990s, but, although it appeared initially to be very promising, sulfur lighting was...
s
Different types of lights have vastly differing efficiencies and color of light
Color temperature
Color temperature is a characteristic of visible light that has important applications in lighting, photography, videography, publishing, manufacturing, astrophysics, and other fields. The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal black-body radiator that radiates light of...
. http://www.parliament.the-stationery-office.co.uk/pa/cm200203/cmselect/cmsctech/747/747we81.htm
| Name | Optical spectrum | Nominal efficiency (lm Lumen (unit) The lumen is the SI derived unit of luminous flux, a measure of the total "amount" of visible light emitted by a source. Luminous flux differs from power in that luminous flux measurements reflect the varying sensitivity of the human eye to different wavelengths of light, while radiant flux... /W Watt The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:... ) |
Lifetime (MTBF) (hours) |
Color temperature Color temperature Color temperature is a characteristic of visible light that has important applications in lighting, photography, videography, publishing, manufacturing, astrophysics, and other fields. The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal black-body radiator that radiates light of... (kelvin Kelvin The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all... s) |
Color Color Color or colour is the visual perceptual property corresponding in humans to the categories called red, green, blue and others. Color derives from the spectrum of light interacting in the eye with the spectral sensitivities of the light receptors... |
Color rendering index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incandescent light bulb Incandescent light bulb The incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe makes light by heating a metal filament wire to a high temperature until it glows. The hot filament is protected from air by a glass bulb that is filled with inert gas or evacuated. In a halogen lamp, a chemical process... |
Continuous Continuous spectrum The spectrum of a linear operator is commonly divided into three parts: point spectrum, continuous spectrum, and residual spectrum.If H is a topological vector space and A:H \to H is a linear map, the spectrum of A is the set of complex numbers \lambda such that A - \lambda I : H \to H is not... |
12-17 | 1000-20000 | 2700 | Warm white (yellowish) | 100 |
| Halogen lamp Halogen lamp A halogen lamp, also known as a tungsten halogen lamp, is an incandescent lamp with a tungsten filament contained within an inert gas and a small amount of a halogen such as iodine or bromine. The chemical halogen cycle redeposits evaporated tungsten back on to the filament, extending the life of... |
Continuous | 16-23 | 3000-6000 | 3200 | Warm white (yellowish) | 100 |
| Fluorescent lamp Fluorescent lamp A fluorescent lamp or fluorescent tube is a gas-discharge lamp that uses electricity to excite mercury vapor. The excited mercury atoms produce short-wave ultraviolet light that then causes a phosphor to fluoresce, producing visible light. A fluorescent lamp converts electrical power into useful... |
Mercury Mercury (element) Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum... line + Phosphor Phosphor A phosphor, most generally, is a substance that exhibits the phenomenon of luminescence. Somewhat confusingly, this includes both phosphorescent materials, which show a slow decay in brightness , and fluorescent materials, where the emission decay takes place over tens of nanoseconds... |
52-100 | 8000-20000 | 2700-5000* | White (with a tinge of green) | 15-85 |
| Metal halide lamp Metal halide lamp Metal-halide lamps, a member of the high-intensity discharge family of lamps, produce high light output for their size, making them a compact, powerful, and efficient light source. By adding rare earth metal salts to the mercury vapor lamp, improved luminous efficacy and light color is obtained... |
Quasi-continuous | 50-115 | 6000-20000 | 3000-4500 | Cold white | 65-93 |
| Sulfur lamp Sulfur lamp The sulfur lamp is a highly efficient full-spectrum electrodeless lighting system whose light is generated by sulfur plasma that has been excited by microwave radiation. The technology was developed in the early 1990s, but, although it appeared initially to be very promising, sulfur lighting was... |
Continuous | 80-110 | 15000-20000 | 6000 | Pale green | 79 |
| High pressure sodium Sodium vapor lamp A sodium vapor lamp is a gas discharge lamp that uses sodium in an excited state to produce light. There are two varieties of such lamps: low pressure and high pressure... |
Broadband | 55-140 | 10000-40000 | 1800-2200* | Pinkish orange | 0-70 |
| Low pressure sodium Sodium vapor lamp A sodium vapor lamp is a gas discharge lamp that uses sodium in an excited state to produce light. There are two varieties of such lamps: low pressure and high pressure... |
Narrow line | 100-200 | 18000-20000 | 1800* | Yellow, virtually no color rendering | 0 |
*Color temperature is defined as the temperature of a black body
Black body
A black body is an idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation. Because of this perfect absorptivity at all wavelengths, a black body is also the best possible emitter of thermal radiation, which it radiates incandescently in a characteristic, continuous spectrum...
emitting a similar spectrum; these spectra are quite different from those of black bodies.
The most efficient source of electric light is the low-pressure sodium lamp. It produces an almost monochromatic orange light, which severely distorts color perception. For this reason, it is generally reserved for outdoor public lighting usages. Low-pressure sodium lights are favoured for public lighting by astronomers, since the light pollution
Light pollution
Light pollution, also known as photopollution or luminous pollution, is excessive or obtrusive artificial light.The International Dark-Sky Association defines light pollution as:...
that they generate can be easily filtered, contrary to broadband or continuous spectra.
Incandescent light bulb
Incandescent light bulb as we know it today, with a coiled filament of tungsten, was commercialized in the 1920s developed from the carbon filament lamp introduced in about 1880. As well as bulbs for normal illumination, there is a very wide range, including low voltage, low-power types often used as components in equipment, but now largely displaced by LEDsThere is currently interest in banning some types of filament lamp in some countries, such as Australia planning to ban standard incandescent light bulbs by 2010, because they are inefficient at converting electricity to light. Sri Lanka has already banned importing filament bulbs because of high use of electricity and less light. Less than 3% of the input energy is converted into usable light. Nearly all of the input energy ends up as heat that, in warm climates, must then be removed from the building by ventilation
Ventilation (architecture)
Ventilating is the process of "changing" or replacing air in any space to provide high indoor air quality...
or air conditioning
Air conditioning
An air conditioner is a home appliance, system, or mechanism designed to dehumidify and extract heat from an area. The cooling is done using a simple refrigeration cycle...
, often resulting in more energy consumption. In colder climates where heating and lighting is required during the cold and dark winter months, the heat byproduct has at least some value.
Halogen lamp
Halogen lamps are usually much smaller than standard incandescents, because for successful operation a bulb temperature over 200 °C is generally necessary. For this reason, most have a bulb of fused silica (quartz), but sometimes aluminosilicate glass. This is often sealed inside an additional layer of glass. The outer glass is a safety precaution, reducing UV emission and because halogen bulbs can occasionally explode during operation. One reason is if the quartz bulb has oily residue from fingerprintFingerprint
A fingerprint in its narrow sense is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. In a wider use of the term, fingerprints are the traces of an impression from the friction ridges of any part of a human hand. A print from the foot can also leave an impression of friction ridges...
s. The risk of burns or fire is also greater with bare bulbs, leading to their prohibition in some places unless enclosed by the luminaire.
Those designed for 12 V or 24 V operation have compact filaments, useful for good optical control, also they have higher efficiencies (lumens per watt) and better lives than non halogen types. The light output remains almost constant throughout life.
Fluorescent lamp
Fluorescent lamps have much higher efficiency than filament lamps. For the same amount of light generated, they typically use around one-quarter to one-third the power of an incandescent.Fluorescents were mostly limited to linear
Linear
In mathematics, a linear map or function f is a function which satisfies the following two properties:* Additivity : f = f + f...
and a round 'Circline' lamp until the 1980s, with other shapes never gaining much popularity. The compact fluorescent lamp
Compact fluorescent lamp
A compact fluorescent lamp , also called compact fluorescent light, energy-saving light, and compact fluorescent tube, is a fluorescent lamp designed to replace an incandescent lamp; some types fit into light fixtures formerly used for incandescent lamps...
(CFL) was commercialized in the early 1980s.
Most CFLs have a built-in electrical ballast and fit into a standard screw or bayonet base. Some make use of a separate ballast so that the ballast and tube can be replaced separately.
Typical average lifetime ratings for linear fluorescent tubes are 10,000 and 20,000 hours, compared to 750 hours (110 V) and 1000 hours (240 V) for filament lamps.
Some types of fluorescent lamp ballast have difficulty starting lamps in very cold conditions, so lights used outdoors in cold climates need to be designed for outdoor use to work reliably.
Fluorescents come in a range of different color temperatures. In some countries cool white (CW) is most popular, while in some, warmer whites predominate.
In America, fluorescents most often come in cool white (CW), with some home bulbs being a warm white (WW), which has a pink
Pink
Pink is a mixture of red and white. Commonly used for Valentine's Day and Easter, pink is sometimes referred to as "the color of love." The use of the word for the color known today as pink was first recorded in the late 17th century....
ish color. In between there is an "enhanced white" (EW), which is more neutral. There is also a very cold daylight white (DW). Compact fluorescent lamps are usually considered warm white, though many have a yellowish cast like an incandescent. "Warm" and "cool" are entirely relative terms and almost arbitrary
Arbitrary
Arbitrariness is a term given to choices and actions subject to individual will, judgment or preference, based solely upon an individual's opinion or discretion.Arbitrary decisions are not necessarily the same as random decisions...
so color temperature
Color temperature
Color temperature is a characteristic of visible light that has important applications in lighting, photography, videography, publishing, manufacturing, astrophysics, and other fields. The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal black-body radiator that radiates light of...
and the color rendering index (CRI) are used as absolute scales of color for fluorescents, and sometimes for other types of lighting.
LED lamp
Solid state LEDs have been popular as indicator lights since the 1970s. In recent years, efficacyLuminous efficacy
Luminous efficacy is a measure of how well a light source produces visible light. It is the ratio of luminous flux to power. Depending on context, the power can be either the radiant flux of the source's output, or it can be the total electric power consumed by the source.Which sense of the term is...
and output have risen to the point where LEDs are now being used in niche lighting applications.
Indicator LEDs are known for their extremely long life, up to 100,000 hours, but lighting LEDs are operated much less conservatively (due to high LED cost per watt), and consequently have much shorter lives.
Due to the relatively high cost per watt, LED lighting is most useful at very low powers, typically for lamp assemblies of under 10 W. LEDs are currently most useful and cost-effective in low power applications, such as nightlight
Nightlight
A nightlight is a small light fixture, often electrical, placed for comfort or convenience in dark areas or areas that become dark at certain times, such as in an emergency...
s and flashlight
Flashlight
A flashlight is a hand-held electric-powered light source. Usually the light source is a small incandescent lightbulb or light-emitting diode...
s. Colored LEDs can also be used for accent lighting, such as for glass objects, and even in fake ice cube
Ice cube
Ice cubes are small, roughly cube-shaped pieces of ice, conventionally used to cool beverages. Ice cubes are often preferred over crushed ice because they melt more slowly; they are standard in mixed drinks that call for ice, in which case the drink is said to be "on the rocks."Ice cubes are...
s for drink
Drink
A drink, or beverage, is a liquid which is specifically prepared for human consumption. In addition to fulfilling a basic human need, beverages form part of the culture of human society.-Water:...
s at parties. They are also being increasingly used as holiday lighting.
LED efficiencies vary over a very wide range. Some have lower efficiency than filament lamps, and some significantly higher. LED performance in this respect is prone to being misinterpreted, as the inherent directionality of LEDs gives them a much higher light intensity in one direction per given total light output.
Single color LEDs are well developed technology, but white LEDs at time of writing still have some unresolved issues.
- CRI is not particularly good, resulting in less than accurate color rendition.
- The light distribution from the phosphor does not fully match the distribution of light from the LED die, so color temperature varies at differing angles.
- Phosphor performance degrades over time, resulting in change of color temperature and falling output. With some LEDs degradation can be quite fast.
- Limited heat tolerance means that the amount of power packable into a lamp assembly is a fraction of the power usable in a similarly sized incandescent lamp.
LED technology is useful for lighting designers because of its low power consumption, low heat generation, instantaneous on/off control, and in the case of single color LEDs, continuity of color throughout the life of the diode and relatively low cost of manufacture.
In the last few years, software has been developed to merge lighting and video by enabling lighting designers to stream video content to their LED fixtures, creating low resolution video walls.
For general domestic lighting, total cost of ownership of LED lighting is still much higher than for other well established lighting types.
Carbon arc lamp
Carbon arc lamps consist of two carbon rod electrodeElectrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit...
s in open air, supplied by a current-limiting ballast
Electrical ballast
An electrical ballast is a device intended to limit the amount of current in an electric circuit. A familiar and widely used example is the inductive ballast used in fluorescent lamps, to limit the current through the tube, which would otherwise rise to destructive levels due to the tube's...
. The electric arc
Electric arc
An electric arc is an electrical breakdown of a gas which produces an ongoing plasma discharge, resulting from a current flowing through normally nonconductive media such as air. A synonym is arc discharge. An arc discharge is characterized by a lower voltage than a glow discharge, and relies on...
is struck by touching the rods then separating them. The ensuing arc heats the carbon tips to white heat. These lamps have higher efficiency than filament lamps, but the carbon rods are short lived and require constant adjustment in use. The lamps produce significant ultra-violet output, they require ventilation when used indoors, and due to their intensity they need protecting from direct sight.
Carbon arc lamps operate at high powers, and had high efficiency compared to other pre-1920s light sources. They also are a point source of light. These properties made them ideally suited to search lights, follow spots and film projector lights.
Their need for ongoing attendance and adjustment, and frequent rod replacement made them ill suited to general lighting, though they were used for high power lighting in the years when nothing else with comparable output power existed. Carbon arcs fell out of use even for niche applications during and after World War 2.
Discharge lamp
A discharge lamp has a glass or silica envelope containing two metal electrodeElectrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit...
s separated by a gas. Gases used include, neon
Neon
Neon is the chemical element that has the symbol Ne and an atomic number of 10. Although a very common element in the universe, it is rare on Earth. A colorless, inert noble gas under standard conditions, neon gives a distinct reddish-orange glow when used in either low-voltage neon glow lamps or...
, argon
Argon
Argon is a chemical element represented by the symbol Ar. Argon has atomic number 18 and is the third element in group 18 of the periodic table . Argon is the third most common gas in the Earth's atmosphere, at 0.93%, making it more common than carbon dioxide...
, xenon
Xenon
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. The element name is pronounced or . A colorless, heavy, odorless noble gas, xenon occurs in the Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts...
, sodium
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal and is a member of the alkali metals; its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists in numerous minerals, most commonly as sodium chloride...
, metal halide, and mercury
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum...
.
The core operating principle is much the same as the carbon arc lamp, but the term 'arc lamp' is normally used to refer to carbon arc lamps, with more modern types of gas discharge lamp normally called 'discharge lamps'.
With some discharge lamps, very high voltage is used to strike the arc. This requires an electrical circuit called an igniter, which is part of the ballast circuitry. After the arc is struck, the internal resistance of the lamp drops to a low level, and the ballast limits the current to the operating current. Without a ballast, excess current would flow, causing rapid destruction of the lamp.
Some lamp types contain a little neon, which permits striking at normal running voltage, with no external igniter circuitry. Low pressure sodium lamps
Sodium vapor lamp
A sodium vapor lamp is a gas discharge lamp that uses sodium in an excited state to produce light. There are two varieties of such lamps: low pressure and high pressure...
operate this way.
The simplest ballasts are just an inductor, and are chosen where cost is the deciding factor, such as street lighting. More advanced electronic ballasts may be designed to maintain constant light output over the life of the lamp, may drive the lamp with a square wave to maintain completely flicker-free output, and shut down in the event of certain faults. These more complex ballasts are chosen in the film industry for example.
Lamp life expectancy
Life expectancy is defined as the number of hours of operation for a lamp until 50% of them fail. This means that it is possible for some lamps to fail after a short amount of time and for some to last significantly longer than the rated lamp life. This is an average (median) life expectancy. Production tolerances as low as 1% can create a variance of 25% in lamp life. For LEDs, lamp life is when 50% of lamps have lumen output drop to 70% or less.Lamps are also sensitive to switching cycles. The rapid heating of a lamp filament or electrodes when a lamp is turned on is the most stressful event on the lamp. Most test cycles have the lamps on for 3 hours and then off for 20 minutes. (Some standard had to be used since it is unknown how the lamp will be used by consumers.) This switching cycle repeats until the lamps fail and the data is recorded. If switching is increased to only 1 hour on, the lamp life is usually reduced because the number of times the lamp has been turned on has increased. Rooms with frequent switching (bathroom, bedrooms, etc.) can expect much shorter lamp life than what is printed on the box.
Vendors
- GEGêGê are the people who spoke Ge languages of the northern South American Caribbean coast and Brazil. In Brazil the Gê were found in Rio de Janeiro, Minas Gerais, Bahia, Piaui, Mato Grosso, Goias, Tocantins, Maranhão, and as far south as Paraguay....
Lighting - OsramOsramOsram, founded 1919, is part of the industry sector of Siemens AG and one of the two leading lighting manufacturers in the world. The name is derived from osmium and Wolfram , as both these elements were commonly used for lighting filaments at the time the company was founded...
- PhilipsPhilipsKoninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. , more commonly known as Philips, is a multinational Dutch electronics company....
Lighting
Public lighting
The total amount of artificial light (especially from street lightStreet light
A street light, lamppost, street lamp, light standard, or lamp standard is a raised source of light on the edge of a road or walkway, which is turned on or lit at a certain time every night. Modern lamps may also have light-sensitive photocells to turn them on at dusk, off at dawn, or activate...
) is sufficient for cities to be easily visible at night from the air, and from space. This wasted light is the source of light pollution
Light pollution
Light pollution, also known as photopollution or luminous pollution, is excessive or obtrusive artificial light.The International Dark-Sky Association defines light pollution as:...
that burdens astronomers
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
and others.

Human-made lights highlight particularly developed or populated areas of the Earth's surface, including the seaboards of Europe, the eastern United States, and Japan.
See also
- DaylightingDaylightingDaylighting is the practice of placing windows or other openings and reflective surfaces so that during the day natural light provides effective internal lighting. Particular attention is given to daylighting while designing a building when the aim is to maximize visual comfort or to reduce energy...
- List of light sources
- Henry Woodward (inventor)Henry Woodward (inventor)Henry Woodward was a Canadian inventor and a major pioneer in the development of the incandescent lamp.-Work on the incandescent light bulb:On July 24, 1874, Woodward and his partner, Mathew Evans, a hotel keeper, patented an electric light bulb. Woodward was a medical student at the time. Their...
- Solar lampSolar lampA solar lamp is a portable light fixture composed of a LED lamp, a photovoltaic solar panel, and a rechargeable battery.Outdoor lamps are used for lawn and garden decorations. Indoor solar lamps are also used for general illumination .Solar lights are used for decoration, and come in a wide variety...

