
Electricity sector of the United States
Encyclopedia
The electricity sector of the United States
includes a large array of stakeholders that provide services through electricity generation
, transmission
, distribution
and marketing for industrial, commercial, public and residential customers. It also includes many public institutions that regulate the sector.
In 1996, there were 3,195 electric utilities in the United States, of which fewer than a 1,000 were engaged in power generation. This leaves a large number of mostly smaller utilities engaged only in power distribution. There were also 65 power marketers. Of all utilities, 2,020 were publicly owned (including 10 Federal utilities), 932 were rural electric cooperatives, and 243 were investor-owned utilities. The electricity transmission network is not owned by individual utilities, but by Independent System Operators or Regional Transmission Organization
s, which are not-for-profit organizations that are obliged to provide indiscriminate access to various suppliers in order to promote competition. They are associated in the North American Electric Reliability Corporation and are typically jointly owned by the utilities in their service area.
The four above-mentioned market segments of the U.S. electricity sector are regulated by different public institutions with some functional overlaps: The federal government sets general policies through the Department of Energy
, environmental policy through the Environmental Protection Agency and consumer protection policy through the Federal Trade Commission
. The safety of nuclear power plants is overseen by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission
. Economic regulation of the distribution segment is a state responsibility, usually carried out through Public Utilities Commission
s; the inter-state transmission segment is regulated by the federal government through the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission
.
Of the electricity generated in the United States in 2006, 70% was produced from fossil fuels (mainly coal and natural gas), almost 20% came from nuclear power, 7% from hydropower and 3% from other forms of renewable energy such as wind and solar energy. The share of renewable energy, in particular wind and solar energy, has increased substantially since 2006 and is expected to increase further.
In 2008 the average electricity tariff in the U.S. was 9.82 Cents/kilowatt-hour (kWh). In 2006-07 electricity tariff
s in the U.S. were higher than in Australia, Canada, France, Sweden and Finland, but lower than in Germany, Italy, Spain and the UK. Residential tariffs vary significantly between states from 6.7 Cents/kWh in West Virginia to 24.1 Cents/kWh in Hawaii. The average residential bill in 2007 was US$ 100/month. Most investments in the U.S. electricity sector are financed by private companies through debt and equity. However, some investments are indirectly financed by taxpayers through various subsidies ranging from tax incentives to subsidies for research and development, feed-in tariff
s for renewable energy and support to low-income households to pay their electric bills.
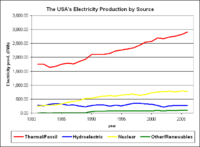
In 2007 the total installed electricity generation capacity in the United States was 1,088 Gigawatts. The main energy sources for electricity generation include:
Actual electricity generation in 2007 was 4,157 Terawatt hours from the following sources:
The share of coal and nuclear in power generation is much higher than their share in installed capacity, because coal and nuclear plants provide base load
and thus are running longer hours than natural gas and petroleum plants which typically provide peak load, or than wind turbines or solar plants that cannot produce electricity continuously.
In 2007 the Department of Energy estimated the planned additional capacity for 2008-12 at 92 GW, most of which to be fueled by natural gas (48 GW) and coal (19GW).
of 2002. and the Energy Policy Act
. As of March 9, 2009, the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission had received applications for permission to construct 26 new nuclear power reactors
. In a joint address to the Congress on February 24, 2009, President Obama called for doubling renewable energy within the next three years.
Renewable energy accounted for more than 10 percent of the domestically-produced energy used in the United States
in the first half of 2008, consisting mainly of large hydropower. According to a report by the Interior Department, U.S. wind power
- including off-shore turbines - could more than meet U.S. electricity needs. The Department of Energy has said wind power could generate 20% of US electricity by 2030.
Several solar thermal power stations, including the new 64 MW Nevada Solar One
, have also been built. The largest of these solar thermal power stations is the SEGS group of plants in the Mojave Desert with a total generating capacity of 354 MW, making the system the largest solar plant of any kind in the world. The largest solar photovoltaic plant in the U.S. is the 14 MW Nellis Solar Power Plant
, located near Las Vegas, Nevada, which is expected to produce more than 30 million kWh/year for Nellis Air Force Base
.
through the Energy Star
program. The Alliance to Save Energy
, an industry group, also promotes energy efficiency.
plays a key role. In addition, the Environmental Protection Agency is in charge of environmental regulation and the Federal Trade Commission
is in charge of consumer protection and the prevention of anti-competitive practices.
Key federal legislation related to the electricity sector includes:
Many state governments have been active in promoting renewable energy. For example, in 2007 25 states and the District of Columbia had established renewable portfolio standard
s (RPS). There is no federal policy on RPS.
Regulation. The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission
is in charge of regulating interstate electricity sales, wholesale electric rates, and licensing hydropower plants. Rates for electricity distribution are regulated by state-level Public Utilities Commissions or Public Services Commissions.
, electricity transmission, electricity distribution
and commercialization. The deregulation of the electricity sector in the U.S. began with the Energy Policy Act of 1992
which removed obstacles for wholesale competition. In practice, however, regulation has been unevenly introduced between states. It began in earnest only from 1996 onwards when the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission
issued orders that required utilities to provide transmission services "on a reasonable and non-discriminatory basis". In some states, such as in California, private utilities were required to sell some of their power plants to prevent concentration of market power.
By 2008 only about a dozen states had deregulated their electricity markets introducing competition for industrial and commercial customers, as well as for residential customers served by private utilities. The Deregulation of the Texas electricity market
in 2002 is one of the best known examples.
and electricity distribution
. The electricity transmission network is not owned by individual utilities, but by not-for-profit organizations that are obliged to provide indiscriminate access to various suppliers in order to promote competition. In 1996, there were 3,195 electric utilities in the United States and 65 power marketers. Of these, 2,020 were publicly owned (including 10 Federal utilities), 932 were rural electric cooperatives, and 243 were investor-owned utilities. Fewer than 1,000 utilities are engaged in power generation.
(producing mainly nuclear and hydropower), the Bonneville Power Administration
(in the Pacific Northwest
) and the Power Marketing Administration
of the Department of Energy
(hydropower), municipal utilities and utility cooperative
s.
The largest private electric producers in the United States include:
power grids in North America, the Eastern Interconnection
and the Western Interconnection
. Besides this there are two minor power grids in the U.S., the Alaska Interconnection and the Texas Interconnection
. Despite bearing separate designations, the Eastern, Western and Texas Interconnections are tied together at various points creating effectively a single grid for the contiguous U.S., Canada and parts of Mexico. The transmission grids are operated by transmission system operator
s (TSOs), not-for profit companies that are typically owned by the utilities in their respective service area, where they coordinate, control and monitor the operation of the electrical power system. TSOs are obliged to provide non-discriminatory transmission access to electricity generators and customers. TSOs can by of two types:Independent System Operators (ISOs) and Regional Transmission Organization
s (RTOs). The former operate within a single state and the latter cover wider areas crossing state borders.
In 2009 there were four RTOs in the U.S.:
There are also three ISOs:
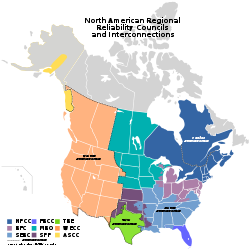 RTOs are similar, but not identical to the nine Regional Reliability Councils associated in the North American Electric Reliability Corporation, a non-profit entity that is in charge of improving the reliability and security of the bulk power system in the U.S., Canada and the northern part of Baja California in Mexico. The members of the Regional Reliability Councils include private, public and cooperative utilities, power marketers and final customers. The Regional Reliability Councils are:
RTOs are similar, but not identical to the nine Regional Reliability Councils associated in the North American Electric Reliability Corporation, a non-profit entity that is in charge of improving the reliability and security of the bulk power system in the U.S., Canada and the northern part of Baja California in Mexico. The members of the Regional Reliability Councils include private, public and cooperative utilities, power marketers and final customers. The Regional Reliability Councils are:
The FERC distinguishes between 10 power markets in the U.S., including the seven for which RTOs have been established, well as:
ISOs and RTOs were established in the 1990s when states and regions established wholesale competition for electricity.
In 2006-07 commercial electricity tariff
s in the U.S. (9.28 cents/kWh) were higher than in Australia (7.1 cents/kWh), Canada (6.18 cents/kWh) that relies mainly on hydropower or in France (8.54 cents/kWh) that relies heavily on nuclear power, but lower than in Germany (13.16 cents/kWh), Italy (15.74 cents/kWh) or the UK (11.16 cents/kWh) that all rely to a larger degree on fossil fuels, all compared at purchasing power parity
.
Residential tariffs vary significantly between states from 6.7 cents/kWh in West Virginia to 24.1 cents/kWh in Hawaii. An important factor that influences tariff levels is the mix of energy sources used in power generation. For example, access to cheap federal power from hydropower plants contributes to low electricity tariffs in some states.
Average residential electricity consumption in the U.S. was 936 kWh/month per in 2007, and the average bill was US$ 100/month. Average residential consumption varies considerably between states from 530 kWh/month in Maine to 1344 kWh/month in Tennessee. Factors that influence residential energy consumption are climate, tariffs and efforts to promote energy conservation.
Tax incentives include federal and state tax deduction
s and tax break
s. Tax incentives can be directed at consumers, such as for the purchase of energy-efficient appliances or for solar energy systems, small wind systems, geothermal heat pump
s, and residential fuel cell
and microturbine systems. Tax incentives can also be directed at electricity producers, in particular for renewable energy.
The Low Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP) received federal funding of $5.1 billion in Fiscal Year 2009. It is funded mainly by the federal government through the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Administration for Children and Families, and is administered by states and territories. While some of its funding is for fuel for heating, some is also used to cover electricity bills for both heating and cooling.
In April, 2009, 11 U.S. state legislatures were considering adopting an feed-in tariff
s as a complement to their renewable electricity mandates.
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
includes a large array of stakeholders that provide services through electricity generation
Electricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric energy from other forms of energy.The fundamental principles of electricity generation were discovered during the 1820s and early 1830s by the British scientist Michael Faraday...
, transmission
Electric power transmission
Electric-power transmission is the bulk transfer of electrical energy, from generating power plants to Electrical substations located near demand centers...
, distribution
Electric power distribution
File:Electricity grid simple- North America.svg|thumb|380px|right|Simplified diagram of AC electricity distribution from generation stations to consumers...
and marketing for industrial, commercial, public and residential customers. It also includes many public institutions that regulate the sector.
In 1996, there were 3,195 electric utilities in the United States, of which fewer than a 1,000 were engaged in power generation. This leaves a large number of mostly smaller utilities engaged only in power distribution. There were also 65 power marketers. Of all utilities, 2,020 were publicly owned (including 10 Federal utilities), 932 were rural electric cooperatives, and 243 were investor-owned utilities. The electricity transmission network is not owned by individual utilities, but by Independent System Operators or Regional Transmission Organization
Regional Transmission Organization
A regional transmission organization in the United States is an organization that is responsible for moving electricity over large interstate areas. Like a transmission system operator , an RTO coordinates, controls and monitors an electricity transmission grid that is larger with much higher...
s, which are not-for-profit organizations that are obliged to provide indiscriminate access to various suppliers in order to promote competition. They are associated in the North American Electric Reliability Corporation and are typically jointly owned by the utilities in their service area.
The four above-mentioned market segments of the U.S. electricity sector are regulated by different public institutions with some functional overlaps: The federal government sets general policies through the Department of Energy
United States Department of Energy
The United States Department of Energy is a Cabinet-level department of the United States government concerned with the United States' policies regarding energy and safety in handling nuclear material...
, environmental policy through the Environmental Protection Agency and consumer protection policy through the Federal Trade Commission
Federal Trade Commission
The Federal Trade Commission is an independent agency of the United States government, established in 1914 by the Federal Trade Commission Act...
. The safety of nuclear power plants is overseen by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission
Nuclear Regulatory Commission
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission is an independent agency of the United States government that was established by the Energy Reorganization Act of 1974 from the United States Atomic Energy Commission, and was first opened January 19, 1975...
. Economic regulation of the distribution segment is a state responsibility, usually carried out through Public Utilities Commission
Public Utilities Commission
A Utilities commission, Utility Regulatory Commission , Public Utilities Commission or Public Service Commission is a governing body that regulates the rates and services of a public utility...
s; the inter-state transmission segment is regulated by the federal government through the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission
Federal Energy Regulatory Commission
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission is the United States federal agency with jurisdiction over interstate electricity sales, wholesale electric rates, hydroelectric licensing, natural gas pricing, and oil pipeline rates...
.
Of the electricity generated in the United States in 2006, 70% was produced from fossil fuels (mainly coal and natural gas), almost 20% came from nuclear power, 7% from hydropower and 3% from other forms of renewable energy such as wind and solar energy. The share of renewable energy, in particular wind and solar energy, has increased substantially since 2006 and is expected to increase further.
In 2008 the average electricity tariff in the U.S. was 9.82 Cents/kilowatt-hour (kWh). In 2006-07 electricity tariff
Electricity tariff
Electricity pricing varies widely from country to country, and may vary signicantly from locality to locality within a particular country. There are many reasons that account for these differences in price...
s in the U.S. were higher than in Australia, Canada, France, Sweden and Finland, but lower than in Germany, Italy, Spain and the UK. Residential tariffs vary significantly between states from 6.7 Cents/kWh in West Virginia to 24.1 Cents/kWh in Hawaii. The average residential bill in 2007 was US$ 100/month. Most investments in the U.S. electricity sector are financed by private companies through debt and equity. However, some investments are indirectly financed by taxpayers through various subsidies ranging from tax incentives to subsidies for research and development, feed-in tariff
Feed-in Tariff
A feed-in tariff is a policy mechanism designed to accelerate investment in renewable energy technologies. It achieves this by offering long-term contracts to renewable energy producers, typically based on the cost of generation of each technology...
s for renewable energy and support to low-income households to pay their electric bills.
Electricity consumption
| Electricity consumption per person in the United States (kWh/person) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Use | Production | Import | Import % | Fossil | Nuclear Nuclear power Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity... |
Nuc. Nuclear power Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity... % |
Other RE Renewable energy Renewable energy is energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat, which are renewable . About 16% of global final energy consumption comes from renewables, with 10% coming from traditional biomass, which is mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from... |
Bio Biomass Biomass, as a renewable energy source, is biological material from living, or recently living organisms. As an energy source, biomass can either be used directly, or converted into other energy products such as biofuel.... +waste |
Wind | Non RE Renewable energy Renewable energy is energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat, which are renewable . About 16% of global final energy consumption comes from renewables, with 10% coming from traditional biomass, which is mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from... use* |
RE Renewable energy Renewable energy is energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat, which are renewable . About 16% of global final energy consumption comes from renewables, with 10% coming from traditional biomass, which is mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from... %* |
|
| 2004 | 14,240 | 14,201 | 38 | 0.3 % | 10,074 | 2,767 | 19.4 % | 1,117 | 244 | 12,879 | 9.6 % | |
| 2005 | 14,532 | 14,449 | 83 | 0.6 % | 10,375 | 2,733 | 18.8 % | 1,101 | 240 | 13,191 | 9.2 % | |
| 2006 | 14,608 | 14,504 | 103 | 0.7 % | 10,449 | 2,766 | 18.9 % | 1,054 | 236 | 13,318 | 8.8 % | |
| 2008 | 14,378 | 14,270 | 108 | 0.8 % | 10,162 | 2,746 | 19.1 % | 1,139 | 224 | 13,015 | 9.5 % | |
| 2009 | 13,642 | 13,531 | 111 | 0.8 % | 9,424 | 2,699 | 19.8 % | 957* | 219 | 232 | 12,234 | 10.3 % |
| * Other RE Renewable energy Renewable energy is energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat, which are renewable . About 16% of global final energy consumption comes from renewables, with 10% coming from traditional biomass, which is mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from... is waterpower, solar and geothermal electricity Geothermal electricity Geothermal electricity is electricity generated from geothermal energy.Technologies in use include dry steam power plants, flash steam power plants and binary cycle power plants... and wind power Wind power Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into a useful form of energy, such as using wind turbines to make electricity, windmills for mechanical power, windpumps for water pumping or drainage, or sails to propel ships.... until 2008 * Non RE use = use – production of renewable electricity * RE % = (production of RE / use) * 100 % Note: European Union Renewable energy in the European Union The countries of the European Union are currently the number two global leaders in the development and application of renewable energy. Promoting the use of renewable energy sources is important both to the reduction of the EU's dependence on foreign energy imports, and in meeting targets to combat... calculates the share of renewable energies in gross electrical consumption. |
||||||||||||
Electricity generation

| Gross production of electricity by power source in the United States (TWh) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Production | Import | Coal Coal power in the United States Coal power in the United States accounts for 46% of the country's electricity production. Utilities buy more than 90 percent of the coal mined in the United States.... |
Gas | Nuclear | Hydro | Oil | Other | |
| 2004 | 4,148 | 34 | 2,090 | 732 | 813 | 271 | 139 | 103 |
| 2008 | 4,344 | 33 | 2,133 | 911 | 838 | 282 | 58 | 122 |
| 2008 | 49.1 % | 21.0 % | 19.3 % | 6.5 % | 1.3 % | 2.8 % | ||
| Other may include wind power Wind power Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into a useful form of energy, such as using wind turbines to make electricity, windmills for mechanical power, windpumps for water pumping or drainage, or sails to propel ships.... , solar power Solar power Solar energy, radiant light and heat from the sun, has been harnessed by humans since ancient times using a range of ever-evolving technologies. Solar radiation, along with secondary solar-powered resources such as wind and wave power, hydroelectricity and biomass, account for most of the available... , geothermal power Geothermal power Geothermal energy is thermal energy generated and stored in the Earth. Thermal energy is the energy that determines the temperature of matter. Earth's geothermal energy originates from the original formation of the planet and from radioactive decay of minerals... , wood Wood Wood is a hard, fibrous tissue found in many trees. It has been used for hundreds of thousands of years for both fuel and as a construction material. It is an organic material, a natural composite of cellulose fibers embedded in a matrix of lignin which resists compression... , biogas Biogas Biogas typically refers to a gas produced by the biological breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen. Organic waste such as dead plant and animal material, animal dung, and kitchen waste can be converted into a gaseous fuel called biogas... and wastes. |
||||||||
In 2007 the total installed electricity generation capacity in the United States was 1,088 Gigawatts. The main energy sources for electricity generation include:
- Thermal/Fossil 857 GW
- Nuclear 106 GW
- Hydropower 78 GW
- Wind 17 MW (25 MW in 2008)
Actual electricity generation in 2007 was 4,157 Terawatt hours from the following sources:
- Thermal/Fossil 2,977 TWh
- Nuclear 806 TWh
- Hydropower 248 TWh
- Other renewables 105 TWh (including landfill gasLandfill gasLandfill gas is a complex mix of different gases created by the action of microorganisms within a landfill.-Production:Landfill gas production results from chemical reactions and microbes acting upon the waste as the putrescible materials begins to break down in the landfill...
, geothermal energy, solar and wind)
The share of coal and nuclear in power generation is much higher than their share in installed capacity, because coal and nuclear plants provide base load
Base load power plant
Baseload is the minimum amount of power that a utility or distribution company must make available to its customers, or the amount of power required to meet minimum demands based on reasonable expectations of customer requirements...
and thus are running longer hours than natural gas and petroleum plants which typically provide peak load, or than wind turbines or solar plants that cannot produce electricity continuously.
| Power Source | Units in Operation | Total Nameplate Capacity (MW) | % of total Capacity | Annual Production (billion kWh) | % of annual production |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wind Power Wind power Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into a useful form of energy, such as using wind turbines to make electricity, windmills for mechanical power, windpumps for water pumping or drainage, or sails to propel ships.... |
|||||
| Solar Energy | |||||
| Petroleum Coke Petroleum coke Petroleum coke is a carbonaceous solid derived from oil refinery coker units or other cracking processes. Other coke has traditionally been derived from coal.... Fueled Boiler Boiler A boiler is a closed vessel in which water or other fluid is heated. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications.-Materials:... |
|||||
| Oil Fired Oil An oil is any substance that is liquid at ambient temperatures and does not mix with water but may mix with other oils and organic solvents. This general definition includes vegetable oils, volatile essential oils, petrochemical oils, and synthetic oils.... Boiler Boiler A boiler is a closed vessel in which water or other fluid is heated. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications.-Materials:... |
|||||
| Nuclear Power Nuclear power Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity... |
|||||
| Natural Gas Natural gas Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural... Fueled Boiler Boiler A boiler is a closed vessel in which water or other fluid is heated. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications.-Materials:... |
|||||
| Diesel Generators Diesel engine A diesel engine is an internal combustion engine that uses the heat of compression to initiate ignition to burn the fuel, which is injected into the combustion chamber... |
|||||
| Incinerators | |||||
| Hydroelectric | |||||
| Geothermal | |||||
| Fuel Oil Fuel oil Fuel oil is a fraction obtained from petroleum distillation, either as a distillate or a residue. Broadly speaking, fuel oil is any liquid petroleum product that is burned in a furnace or boiler for the generation of heat or used in an engine for the generation of power, except oils having a flash... |
|||||
| Combustion Turbine Generators Gas turbine A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of internal combustion engine. It has an upstream rotating compressor coupled to a downstream turbine, and a combustion chamber in-between.... |
|||||
| Combined Cycle Natural Gas | |||||
| Coal Fired Boilers Coal Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure... |
|||||
| Biomass Biomass Biomass, as a renewable energy source, is biological material from living, or recently living organisms. As an energy source, biomass can either be used directly, or converted into other energy products such as biofuel.... |
|||||
Coal and Gas
Fossil fuels - mainly coal and natural gas - remain the backbone of electricity generation in the U.S., accounting for 69% of installed generation capacity in 2006.In 2007 the Department of Energy estimated the planned additional capacity for 2008-12 at 92 GW, most of which to be fueled by natural gas (48 GW) and coal (19GW).
Nuclear power
As of 2007 in the United States, there are 104 commercial nuclear reactors in the US, generating approximately 20% of the nation's total electric energy consumption. For many years, no new nuclear plants have been built in the US. However, since 2005 there has been a renewed interest in nuclear power in the US. This has been facilitated in part by the federal government with the Nuclear Power 2010 ProgramNuclear Power 2010 Program
The "Nuclear Power 2010 Program" was unveiled by the U.S. Secretary of Energy Spencer Abraham on February 14, 2002 as one means towards addressing the expected need for new power plants...
of 2002. and the Energy Policy Act
Energy Policy Act of 2005
The Energy Policy Act of 2005 is a bill passed by the United States Congress on July 29, 2005, and signed into law by President George W. Bush on August 8, 2005, at Sandia National Laboratories in Albuquerque, New Mexico...
. As of March 9, 2009, the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission had received applications for permission to construct 26 new nuclear power reactors
Renewable energy
The development of renewable energy and energy efficiency marks "a new era of energy exploration" in the United States, according to President Barack ObamaBarack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.Born in...
. In a joint address to the Congress on February 24, 2009, President Obama called for doubling renewable energy within the next three years.
Renewable energy accounted for more than 10 percent of the domestically-produced energy used in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
in the first half of 2008, consisting mainly of large hydropower. According to a report by the Interior Department, U.S. wind power
Wind power in the United States
As of the third quarter of 2011, the cumulative installed capacity of wind power in the United States was 43,461 megawatts , making it second in the world, behind China. In 2010 wind power accounted for 2.3% of the electricity generated in the United States...
- including off-shore turbines - could more than meet U.S. electricity needs. The Department of Energy has said wind power could generate 20% of US electricity by 2030.
Several solar thermal power stations, including the new 64 MW Nevada Solar One
Nevada Solar One
Nevada Solar One is a concentrated solar power plant, with a nominal capacity of 64 MW and maximum capacity of 75 MW spread over an area of 400 Acres. The projected CO2 emissions avoided is equivalent to taking approximately 20,000 cars off the road annually. The project required an investment of...
, have also been built. The largest of these solar thermal power stations is the SEGS group of plants in the Mojave Desert with a total generating capacity of 354 MW, making the system the largest solar plant of any kind in the world. The largest solar photovoltaic plant in the U.S. is the 14 MW Nellis Solar Power Plant
Nellis Solar Power Plant
The Nellis Solar Power Plant is located within Nellis Air Force Base in Clark County, Nevada, on the northeast side of Las Vegas. The Nellis solar energy system will generate in excess of 25 million kilowatt-hours of electricity annually and supply more than 25 percent of the power used...
, located near Las Vegas, Nevada, which is expected to produce more than 30 million kWh/year for Nellis Air Force Base
Nellis Air Force Base
Nellis Air Force Base is a United States Air Force Base, located approximately northeast of Las Vegas, Nevada. It is under the jurisdiction of Air Combat Command .-Overview:...
.
Energy efficiency and conservation
The federal government promotes energy efficiencyEfficient energy use
Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the goal of efforts to reduce the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a home allows a building to use less heating and cooling energy to achieve and maintain a comfortable temperature...
through the Energy Star
Energy Star
Energy Star is an international standard for energy efficient consumer products originated in the United States of America. It was first created as a United States government program during the early 1990s, but Australia, Canada, Japan, New Zealand, Taiwan and the European Union have also adopted...
program. The Alliance to Save Energy
Alliance to Save Energy
The Alliance to Save Energy is a coalition consisting largely of industrial, technological, and energy corporations. The Alliance states that its mission is to "support energy efficiency as a cost-effective energy resource under existing market conditions and advocate energy-efficiency policies...
, an industry group, also promotes energy efficiency.
Policy and regulation
Policy. Policy for the electricity sector in the United States is set by the executive and legislative bodies of the federal government and state governments. Within the executive branch of the federal government the Department of EnergyUnited States Department of Energy
The United States Department of Energy is a Cabinet-level department of the United States government concerned with the United States' policies regarding energy and safety in handling nuclear material...
plays a key role. In addition, the Environmental Protection Agency is in charge of environmental regulation and the Federal Trade Commission
Federal Trade Commission
The Federal Trade Commission is an independent agency of the United States government, established in 1914 by the Federal Trade Commission Act...
is in charge of consumer protection and the prevention of anti-competitive practices.
Key federal legislation related to the electricity sector includes:
- the Federal Power ActFederal Power ActThe Federal Power Act is a law appearing in Chapter 12 of Title 16 of the United States Code, entitled "Federal Regulation and Development of Power". Enacted as the Federal Water Power Act on June 10, 1920, and amended many times since, its original purpose was to more effectively coordinate the...
of 1935 that promoted hydropower and increased the role of the federal government in the sector, - the National Energy ActNational Energy ActThe National Energy Act of 1978 was a legislative response by the U.S. Congress to the 1973 energy crisis. It includes the following statutes:* Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act * Energy Tax Act * National Energy Conservation Policy Act...
of 1978, including the Public Utility Regulatory Policies ActPublic Utility Regulatory Policies ActThe Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act is a law, passed in 1978 by the United States Congress as part of the National Energy Act. It is meant to promote greater use of domestic renewable energy...
(PURPA), which required utilities to provide residential consumers with energy conservation audits and other services to encourage slower growth of electricity demand, and was intended to promote renewable energy with the result of promoting mainly co-generation; - the Energy Policy Act of 1992Energy Policy Act of 1992The Energy Policy Act is a United States government act.It was passed by Congress and addressed energy efficiency, energy conservation and energy management , natural gas imports and exports , alternative fuels and requiring certain fleets to acquire alternative fuel vehicles, which are capable of...
which provided further incentives for energy efficiency and removed obstacles to wholesale competition; and - the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007The Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 is an Act of Congress concerning the energy policy of the United States...
which phased out incandescent light bulbIncandescent light bulbThe incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe makes light by heating a metal filament wire to a high temperature until it glows. The hot filament is protected from air by a glass bulb that is filled with inert gas or evacuated. In a halogen lamp, a chemical process...
s.
Many state governments have been active in promoting renewable energy. For example, in 2007 25 states and the District of Columbia had established renewable portfolio standard
Renewable Portfolio Standard
A Renewable Portfolio Standard is a regulation that requires the increased production of energy from renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, biomass, and geothermal...
s (RPS). There is no federal policy on RPS.
Regulation. The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission
Federal Energy Regulatory Commission
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission is the United States federal agency with jurisdiction over interstate electricity sales, wholesale electric rates, hydroelectric licensing, natural gas pricing, and oil pipeline rates...
is in charge of regulating interstate electricity sales, wholesale electric rates, and licensing hydropower plants. Rates for electricity distribution are regulated by state-level Public Utilities Commissions or Public Services Commissions.
Deregulation and competition
Deregulation of the electricity sector consists in the introduction of competition and the unbundling of vertically integrated utilities in separate entities in charge of electricity generationElectricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric energy from other forms of energy.The fundamental principles of electricity generation were discovered during the 1820s and early 1830s by the British scientist Michael Faraday...
, electricity transmission, electricity distribution
Electricity distribution
File:Electricity grid simple- North America.svg|thumb|380px|right|Simplified diagram of AC electricity distribution from generation stations to consumers...
and commercialization. The deregulation of the electricity sector in the U.S. began with the Energy Policy Act of 1992
Energy Policy Act of 1992
The Energy Policy Act is a United States government act.It was passed by Congress and addressed energy efficiency, energy conservation and energy management , natural gas imports and exports , alternative fuels and requiring certain fleets to acquire alternative fuel vehicles, which are capable of...
which removed obstacles for wholesale competition. In practice, however, regulation has been unevenly introduced between states. It began in earnest only from 1996 onwards when the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission
Federal Energy Regulatory Commission
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission is the United States federal agency with jurisdiction over interstate electricity sales, wholesale electric rates, hydroelectric licensing, natural gas pricing, and oil pipeline rates...
issued orders that required utilities to provide transmission services "on a reasonable and non-discriminatory basis". In some states, such as in California, private utilities were required to sell some of their power plants to prevent concentration of market power.
By 2008 only about a dozen states had deregulated their electricity markets introducing competition for industrial and commercial customers, as well as for residential customers served by private utilities. The Deregulation of the Texas electricity market
Deregulation of the Texas Electricity Market
Electricity deregulation in Texas was the result of the coming into force of Texas Senate Bill 7 on January 1, 2002. According to the law, deregulation is to be phased in over several years....
in 2002 is one of the best known examples.
Service provision
Electric utilities in the U.S. can be both in charge of electricity generationElectricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric energy from other forms of energy.The fundamental principles of electricity generation were discovered during the 1820s and early 1830s by the British scientist Michael Faraday...
and electricity distribution
Electricity distribution
File:Electricity grid simple- North America.svg|thumb|380px|right|Simplified diagram of AC electricity distribution from generation stations to consumers...
. The electricity transmission network is not owned by individual utilities, but by not-for-profit organizations that are obliged to provide indiscriminate access to various suppliers in order to promote competition. In 1996, there were 3,195 electric utilities in the United States and 65 power marketers. Of these, 2,020 were publicly owned (including 10 Federal utilities), 932 were rural electric cooperatives, and 243 were investor-owned utilities. Fewer than 1,000 utilities are engaged in power generation.
Generation
About 80% of the electricity in the U.S. is generated by private ("investor-owned") utilities. The remaining electricity is produced by federal agencies such as the Tennessee Valley AuthorityTennessee Valley Authority
The Tennessee Valley Authority is a federally owned corporation in the United States created by congressional charter in May 1933 to provide navigation, flood control, electricity generation, fertilizer manufacturing, and economic development in the Tennessee Valley, a region particularly affected...
(producing mainly nuclear and hydropower), the Bonneville Power Administration
Bonneville Power Administration
The Bonneville Power Administration is an American federal agency based in the Pacific Northwest. BPA was created by an act of Congress in 1937 to market electric power from the Bonneville Dam located on the Columbia River and to construct facilities necessary to transmit that power...
(in the Pacific Northwest
Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest is a region in northwestern North America, bounded by the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains on the east. Definitions of the region vary and there is no commonly agreed upon boundary, even among Pacific Northwesterners. A common concept of the...
) and the Power Marketing Administration
Power Marketing Administration
A Power Marketing Administration is a United States federal agency within the Department of Energy with the responsibility for marketing hydropower, primarily from multiple-purpose water projects operated by the Bureau of Reclamation, the Army Corps of Engineers, and the International Boundary and...
of the Department of Energy
United States Department of Energy
The United States Department of Energy is a Cabinet-level department of the United States government concerned with the United States' policies regarding energy and safety in handling nuclear material...
(hydropower), municipal utilities and utility cooperative
Utility cooperative
A utility cooperative is a type of cooperative that is tasked with the delivery of a public utility such as electricity, water or telecommunications to its members...
s.
The largest private electric producers in the United States include:
- AES CorporationAES CorporationAES Corporation is a Fortune 500 company that generates and distributes electrical power. The company was founded on January 28, 1981, as Applied Energy Services by Roger Sant from the US Federal Energy Administration and Dennis Bakke from the Office of Management and Budget. AES Corporation is...
- Southern CompanySouthern CompanySouthern Company is a public utility holding company of primarily electric utilities in the southern United States. It is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia with executive offices also located in Birmingham, Alabama. The company is currently the 16th largest utility company in the world and the...
, 42 GW - American Electric PowerAmerican Electric PowerAmerican Electric Power is a major investor-owner electric utility in various parts of the United States. AEP ranks among the nation's largest generators of electricity, owning nearly 38,000 megawatts of generating capacity in the U.S...
, 38 GW - Duke EnergyDuke EnergyDuke Energy , headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina, is an energy company with assets in the United States, Canada and Latin America.-Overview:...
, 36 GW - LuminantLuminantLuminant is a Texas-based electric utility. It is a wholly owned subsidiary of Energy Future Holdings Corporation. Luminant's operations include electricity generation and wholesaling, mining, construction, and development...
, 18 GW - Reliant EnergyReliant EnergyRRI Energy, Inc. , based in Houston, Texas, United States, was an energy company that provided electricity to wholesale customers in the United States. The company was one of the largest independent power producers in the nation with more than 14,000 megawatts of power generation capacity across...
, 14 GW - Pacific Gas and Electric CompanyPacific Gas and Electric CompanyThe Pacific Gas and Electric Company , commonly known as PG&E, is the utility that provides natural gas and electricity to most of the northern two-thirds of California, from Bakersfield almost to the Oregon border...
- Allegheny EnergyAllegheny EnergyAllegheny Energy is an electric utility headquartered in Greensburg, Pennsylvania. It owns and operates electric generation facilities and delivers electric services to customers in Pennsylvania, West Virginia, Maryland, and Virginia...
Transmission
There are two major alternating current (AC)Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
power grids in North America, the Eastern Interconnection
Eastern Interconnection
The Eastern Interconnection is one of the two major alternating current power grids in North America. The other major interconnection is the Western Interconnection...
and the Western Interconnection
Western Interconnection
The Western Interconnection is one of the two major alternating current power grids in North America. The other major wide area synchronous grid is the Eastern Interconnection...
. Besides this there are two minor power grids in the U.S., the Alaska Interconnection and the Texas Interconnection
Texas Interconnection
The Texas Interconnection is one of the three minor alternating current power grids in North America. The other two minor interconnections are the Québec Interconnection and the Alaska Interconnection...
. Despite bearing separate designations, the Eastern, Western and Texas Interconnections are tied together at various points creating effectively a single grid for the contiguous U.S., Canada and parts of Mexico. The transmission grids are operated by transmission system operator
Transmission system operator
File:Electricity grid simple- North America.svg|thumb|380px|right|Simplified diagram of AC electricity distribution from generation stations to consumersrect 2 243 235 438 Power stationrect 276 317 412 556 Transformer...
s (TSOs), not-for profit companies that are typically owned by the utilities in their respective service area, where they coordinate, control and monitor the operation of the electrical power system. TSOs are obliged to provide non-discriminatory transmission access to electricity generators and customers. TSOs can by of two types:Independent System Operators (ISOs) and Regional Transmission Organization
Regional Transmission Organization
A regional transmission organization in the United States is an organization that is responsible for moving electricity over large interstate areas. Like a transmission system operator , an RTO coordinates, controls and monitors an electricity transmission grid that is larger with much higher...
s (RTOs). The former operate within a single state and the latter cover wider areas crossing state borders.
In 2009 there were four RTOs in the U.S.:
- ISO New EnglandISO New EnglandISO New England Inc. is an independent, non-profit Regional Transmission Organization , serving Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island and Vermont....
(ISO-NE, which is an RTO despite its name); - Midwest Independent Transmission System OperatorMidwest Independent Transmission System OperatorThe Midwest Independent Transmission System Operator, Inc. is an Independent System Operator and the Regional Transmission Organization that provides open-access transmission service and monitors the high voltage transmission system throughout the Midwest United States and Manitoba, Canada...
; - PJM InterconnectionPJM InterconnectionPJM Interconnection LLC is a Regional Transmission Organization which is part of the Eastern Interconnection grid operating an electric transmission system serving all or parts of Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Maryland, Michigan, New Jersey, North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Tennessee,...
in the Mid-Atlantic region; and - Southwest Power PoolSouthwest Power PoolThe Southwest Power Pool is the oldest North American Reliability Organization still in operation. SPP's story began in the early days of WWII, when America was furiously ramping up production of weapons and military supplies. After entering the War, the USA had an immediate and crucial need to...
(SPP) covering Oklahoma, Kansas and parts of Arkansas, Missouri, Texas and New Mexico.
There are also three ISOs:
- California Independent System Operator (California ISO);
- New York Independent System Operator (NYISO);
- Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT, an ISO).

- Eastern InterconnectionEastern InterconnectionThe Eastern Interconnection is one of the two major alternating current power grids in North America. The other major interconnection is the Western Interconnection...
- Florida Reliability Coordinating CouncilFlorida Reliability Coordinating CouncilThe Florida Reliability Coordinating Council is one of 8 Regional Entities delegated authority to insure reliability by North American Electric Reliability Corporation in North American and was formed on September 16, 1996. The area served by FRCC was previously served by SERC Reliability...
(FRCC) - Midwest Reliability OrganizationMidwest Reliability OrganizationThe Midwest Reliability Organization began operations on January 1, 2005, as the successor to the Mid-continent Area Power Pool , which was formed in 1965. MRO is one of nine regional electric reliability councils under North American Electric Reliability Corporation authority...
(MRO) - Northeast Power Coordinating CouncilNortheast Power Coordinating CouncilThe Northeast Power Coordinating Council was formed January 19, 1966, as a successor to the Canada–United States Eastern Interconnection . NPCC is one of nine regional electric reliability councils under North American Electric Reliability Corporation authority. NERC and the regional...
(NPCC) - ReliabilityFirst CorporationReliabilityfirstReliabilityFirst Corporation is one of the eight Federal Energy Regulatory Commission approved Regional Reliability Organizations responsible for ensuring the reliability of the North American bulk power system, pursuant to the Energy Policy Act of 2005...
(RFC) - SERC Reliability CorporationSERC Reliability CorporationThe SERC Reliability Corporation is one of nine regional electric reliability councils under North American Electric Reliability Corporation authority. NERC and the regional reliability councils were formed following the Northeast Blackout of 1965. SERC was formed on April 29, 2005, as the...
(SERC) - Southwest Power PoolSouthwest Power PoolThe Southwest Power Pool is the oldest North American Reliability Organization still in operation. SPP's story began in the early days of WWII, when America was furiously ramping up production of weapons and military supplies. After entering the War, the USA had an immediate and crucial need to...
(SPP)
- Florida Reliability Coordinating Council
- Western InterconnectionWestern InterconnectionThe Western Interconnection is one of the two major alternating current power grids in North America. The other major wide area synchronous grid is the Eastern Interconnection...
- Western Electricity Coordinating CouncilWestern Electricity Coordinating CouncilThe Western Electricity Coordinating Council was formed on April 18, 2002, from the merger of the Western Systems Coordinating Council which itself was formed on August 14, 1967, the Southwest Regional Transmission Association , and Western Regional Transmission Association...
(WECC)
- Western Electricity Coordinating Council
- Texas InterconnectionTexas InterconnectionThe Texas Interconnection is one of the three minor alternating current power grids in North America. The other two minor interconnections are the Québec Interconnection and the Alaska Interconnection...
- Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT)
The FERC distinguishes between 10 power markets in the U.S., including the seven for which RTOs have been established, well as:
- Northwest
- Southwest (covering Arizona, most of New Mexico and Colorado)
- Southeast
ISOs and RTOs were established in the 1990s when states and regions established wholesale competition for electricity.
Distribution
About 75% of electricity sales to final customers are undertaken by private utilities, with the remainder being sold by municipal utilities and cooperatives.Tariffs and affordability
In 2008 the average electricity tariff in the U.S. was 9.82 cents/kWh, up from 6.9 cents/kWh in 1995. Residential tariffs were somewhat higher at 11.36 cents/kWh, while commercial tariffs stood at 10.28 cents/kWh and industrial tariffs at 7.01 cents/kWh. The cost of supplying high-voltage power to high-volume industrial customers is lower than the cost of providing low-voltage (110 V) power to residential and commercial customers.In 2006-07 commercial electricity tariff
Electricity tariff
Electricity pricing varies widely from country to country, and may vary signicantly from locality to locality within a particular country. There are many reasons that account for these differences in price...
s in the U.S. (9.28 cents/kWh) were higher than in Australia (7.1 cents/kWh), Canada (6.18 cents/kWh) that relies mainly on hydropower or in France (8.54 cents/kWh) that relies heavily on nuclear power, but lower than in Germany (13.16 cents/kWh), Italy (15.74 cents/kWh) or the UK (11.16 cents/kWh) that all rely to a larger degree on fossil fuels, all compared at purchasing power parity
Purchasing power parity
In economics, purchasing power parity is a condition between countries where an amount of money has the same purchasing power in different countries. The prices of the goods between the countries would only reflect the exchange rates...
.
Residential tariffs vary significantly between states from 6.7 cents/kWh in West Virginia to 24.1 cents/kWh in Hawaii. An important factor that influences tariff levels is the mix of energy sources used in power generation. For example, access to cheap federal power from hydropower plants contributes to low electricity tariffs in some states.
Average residential electricity consumption in the U.S. was 936 kWh/month per in 2007, and the average bill was US$ 100/month. Average residential consumption varies considerably between states from 530 kWh/month in Maine to 1344 kWh/month in Tennessee. Factors that influence residential energy consumption are climate, tariffs and efforts to promote energy conservation.
Revenues
Total revenue from the sale of electricity in 2008 was US$344bn, including US$148bn from residential customers, US$129bn from commercial customers and US$66bn from industrial customers. Many large industries self-generate electricity and their electricity consumption thus is not included in these figures.Financing
Most investments in the U.S. electricity sector are financed by private companies through debt and equity. However, some investments are indirectly financed by taxpayers through various subsidies.Subsidies and tax incentives
There is a large array of subsidies in the U.S. electricity sector ranging from various forms of tax incentives to subsidies for research and development, feed-in tariffs for renewable energy and support to low-income households to pay their electric bills. Some subsidies are available throughout the U.S., while others are only available in some states.Tax incentives include federal and state tax deduction
Tax deduction
Income tax systems generally allow a tax deduction, i.e., a reduction of the income subject to tax, for various items, especially expenses incurred to produce income. Often these deductions are subject to limitations or conditions...
s and tax break
Tax break
Tax break is a slang term referring to any item which reduces tax, including any tax exemption, tax deduction, or tax credit. Tax break is also a pejorative term used in the United States to refer to purportedly favorable tax treatment of any class of persons, as in "individuals get a tax break...
s. Tax incentives can be directed at consumers, such as for the purchase of energy-efficient appliances or for solar energy systems, small wind systems, geothermal heat pump
Heat pump
A heat pump is a machine or device that effectively "moves" thermal energy from one location called the "source," which is at a lower temperature, to another location called the "sink" or "heat sink", which is at a higher temperature. An air conditioner is a particular type of heat pump, but the...
s, and residential fuel cell
Fuel cell
A fuel cell is a device that converts the chemical energy from a fuel into electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen or another oxidizing agent. Hydrogen is the most common fuel, but hydrocarbons such as natural gas and alcohols like methanol are sometimes used...
and microturbine systems. Tax incentives can also be directed at electricity producers, in particular for renewable energy.
The Low Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP) received federal funding of $5.1 billion in Fiscal Year 2009. It is funded mainly by the federal government through the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Administration for Children and Families, and is administered by states and territories. While some of its funding is for fuel for heating, some is also used to cover electricity bills for both heating and cooling.
In April, 2009, 11 U.S. state legislatures were considering adopting an feed-in tariff
Feed-in Tariff
A feed-in tariff is a policy mechanism designed to accelerate investment in renewable energy technologies. It achieves this by offering long-term contracts to renewable energy producers, typically based on the cost of generation of each technology...
s as a complement to their renewable electricity mandates.
See also
- Energy in the United States
- California electricity crisisCalifornia electricity crisisThe California electricity crisis, also known as the Western U.S. Energy Crisis of 2000 and 2001 was a situation in which California had a shortage of electricity caused by market manipulations and illegal shutdowns of pipelines by Texas energy consortiums...
(2001) - Northeast Blackout of 2003Northeast Blackout of 2003The Northeast blackout of 2003 was a widespread power outage that occurred throughout parts of the Northeastern and Midwestern United States and Ontario, Canada on Thursday, August 14, 2003, just before 4:10 p.m....

