
Electro-optic modulator
Encyclopedia
Electro-optic modulator (EOM) is an optical device in which a signal-controlled element displaying electro-optic effect
is used to modulate a beam of light
. The modulation
may be imposed on the phase
, frequency
, amplitude
, or polarization of the modulated beam. Modulation bandwidths extending into the gigahertz range are possible with the use of laser
-controlled modulators.
Generally a nonlinear optical
material (organic polymers have the fastest response rates, and thus are best for this application) with an incident static or low frequency optical field
will see a modulation of its refractive index
.
Certain materials change their optical properties when subjected to an electric field. This is caused by forces that distort the positions, orientations, or shape of the molecules constituting the material. The electro-optic effect
is the change in the refractive index resulting from applications of a dc or low-frequency electric field.
, whose refractive index is a function of the strength of the local electric field
. That means that if lithium niobate is exposed to an electric field, light will travel more slowly through it. But the phase of the light leaving the crystal is directly proportional to the length of time it took that light to pass through it. Therefore, the phase of the laser light exiting an EOM can be controlled by changing the electric field in the crystal.
Note that the electric field can be created by placing a parallel plate capacitor
across the crystal. Since the field inside a parallel plate capacitor depends linearly on the potential, the index of refraction depends linearly on the field (for crystals where Pockels effect
dominates), and the phase depends linearly on the index of refraction, the phase modulation must depend linearly on the potential applied to the EOM.
The voltage required for inducing a phase change of π is called the half-wave voltage (Vπ). For a Pockels cell, it is usually hundreds or even thousands of volts, so that a high-voltage amplifier is required. Suitable electronic circuits can switch such large voltages within a few nanoseconds, allowing the use of EOMs as fast optical switches.
Liquid crystal devices are electro-optical phase modulators if no polarizers are used.
. A beam splitter divides the laser light into two paths, one of which has a phase modulator as described above. The beams are then recombined. Changing the electric field on the phase modulating path will then determine whether the two beams interfere constructively or destructively at the output, and thereby control the amplitude or intensity of the exiting light. This device is called a Mach-Zehnder modulator.
A very common application of EOMs is for creating sideband
s in a monochromatic laser beam. To see how this works, first imagine that the strength of a laser beam with frequency
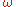 entering the EOM is given by
entering the EOM is given by
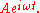
Now suppose we apply a sinusoidally varying potential voltage to the EOM with frequency and small amplitude
and small amplitude 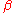 . This adds a time dependent phase to the above expression,
. This adds a time dependent phase to the above expression,
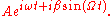
Since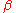 is small, we can use the Taylor expansion for the exponential
is small, we can use the Taylor expansion for the exponential
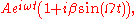
to which we apply a simple identity for sine
,
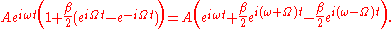
This expression we interpret to mean that we have the original carrier frequency
plus two small sidebands, one at and another at
and another at  . Notice however that we only used the first term in the Taylor expansion - in truth there are an infinite number of sidebands. There is a useful identity involving Bessel functions
. Notice however that we only used the first term in the Taylor expansion - in truth there are an infinite number of sidebands. There is a useful identity involving Bessel functions
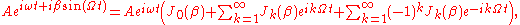
which gives the amplitudes of all the sidebands. Notice that if one modulates the amplitude instead of the phase, one gets only the first set of sidebands,
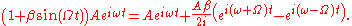
Electro-optic effect
An electro-optic effect is a change in the optical properties of a material in response to an electric field that varies slowly compared with the frequency of light...
is used to modulate a beam of light
Light beam
A light beam or beam of light is a narrow projection of light energy radiating from a source into a beam. Sunlight is a natural example of a light beam when filtered through various mediums...
. The modulation
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
may be imposed on the phase
Phase (waves)
Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
, frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
, amplitude
Amplitude
Amplitude is the magnitude of change in the oscillating variable with each oscillation within an oscillating system. For example, sound waves in air are oscillations in atmospheric pressure and their amplitudes are proportional to the change in pressure during one oscillation...
, or polarization of the modulated beam. Modulation bandwidths extending into the gigahertz range are possible with the use of laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
-controlled modulators.
Generally a nonlinear optical
Nonlinear optics
Nonlinear optics is the branch of optics that describes the behavior of light in nonlinear media, that is, media in which the dielectric polarization P responds nonlinearly to the electric field E of the light...
material (organic polymers have the fastest response rates, and thus are best for this application) with an incident static or low frequency optical field
Optical field
The optical field is a term used in physics and vector calculus to designate the electric field shown as E in the electromagnetic wave equation which can be derived from Maxwell's Equations...
will see a modulation of its refractive index
Refractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
.
Certain materials change their optical properties when subjected to an electric field. This is caused by forces that distort the positions, orientations, or shape of the molecules constituting the material. The electro-optic effect
Electro-optic effect
An electro-optic effect is a change in the optical properties of a material in response to an electric field that varies slowly compared with the frequency of light...
is the change in the refractive index resulting from applications of a dc or low-frequency electric field.
Phase modulation
The simplest kind of EOM consists of a crystal, such as Lithium niobateLithium niobate
Lithium niobate is a compound of niobium, lithium, and oxygen. Its single crystals are an important material for optical waveguides, mobile phones, optical modulators and various other linear and non-linear optical applications.-Properties:...
, whose refractive index is a function of the strength of the local electric field
Electric field
In physics, an electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field depicts the force exerted on other electrically charged objects by the electrically charged particle the field is surrounding...
. That means that if lithium niobate is exposed to an electric field, light will travel more slowly through it. But the phase of the light leaving the crystal is directly proportional to the length of time it took that light to pass through it. Therefore, the phase of the laser light exiting an EOM can be controlled by changing the electric field in the crystal.
Note that the electric field can be created by placing a parallel plate capacitor
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
across the crystal. Since the field inside a parallel plate capacitor depends linearly on the potential, the index of refraction depends linearly on the field (for crystals where Pockels effect
Pockels effect
The Pockels effect , or Pockels electro-optic effect, produces birefringence in an optical medium induced by a constant or varying electric field. It is distinguished from the Kerr effect by the fact that the birefringence is proportional to the electric field, whereas in the Kerr effect it is...
dominates), and the phase depends linearly on the index of refraction, the phase modulation must depend linearly on the potential applied to the EOM.
The voltage required for inducing a phase change of π is called the half-wave voltage (Vπ). For a Pockels cell, it is usually hundreds or even thousands of volts, so that a high-voltage amplifier is required. Suitable electronic circuits can switch such large voltages within a few nanoseconds, allowing the use of EOMs as fast optical switches.
Liquid crystal devices are electro-optical phase modulators if no polarizers are used.
Amplitude modulation
A phase modulating EOM can also be used as an amplitude modulator by using a Mach-Zehnder interferometerMach-Zehnder interferometer
The Mach–Zehnder interferometer is a device used to determine the relative phase shift between two collimated beams from a coherent light source. The interferometer has been used, amongst other things, to measure small phase shifts in one of the two beams caused by a small sample or the change in...
. A beam splitter divides the laser light into two paths, one of which has a phase modulator as described above. The beams are then recombined. Changing the electric field on the phase modulating path will then determine whether the two beams interfere constructively or destructively at the output, and thereby control the amplitude or intensity of the exiting light. This device is called a Mach-Zehnder modulator.
A very common application of EOMs is for creating sideband
Sideband
In radio communications, a sideband is a band of frequencies higher than or lower than the carrier frequency, containing power as a result of the modulation process. The sidebands consist of all the Fourier components of the modulated signal except the carrier...
s in a monochromatic laser beam. To see how this works, first imagine that the strength of a laser beam with frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
 entering the EOM is given by
entering the EOM is given by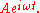
Now suppose we apply a sinusoidally varying potential voltage to the EOM with frequency
 and small amplitude
and small amplitude 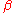 . This adds a time dependent phase to the above expression,
. This adds a time dependent phase to the above expression,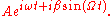
Since
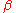 is small, we can use the Taylor expansion for the exponential
is small, we can use the Taylor expansion for the exponential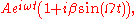
to which we apply a simple identity for sine
Sine
In mathematics, the sine function is a function of an angle. In a right triangle, sine gives the ratio of the length of the side opposite to an angle to the length of the hypotenuse.Sine is usually listed first amongst the trigonometric functions....
,
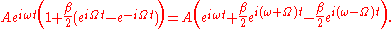
This expression we interpret to mean that we have the original carrier frequency
Carrier wave
In telecommunications, a carrier wave or carrier is a waveform that is modulated with an input signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave is usually a much higher frequency than the input signal...
plus two small sidebands, one at
 and another at
and another at  . Notice however that we only used the first term in the Taylor expansion - in truth there are an infinite number of sidebands. There is a useful identity involving Bessel functions
. Notice however that we only used the first term in the Taylor expansion - in truth there are an infinite number of sidebands. There is a useful identity involving Bessel functions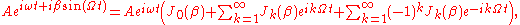
which gives the amplitudes of all the sidebands. Notice that if one modulates the amplitude instead of the phase, one gets only the first set of sidebands,
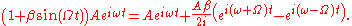
Polarization modulation
Depending on the type and orientation of the nonlinear crystal, and on the direction of the applied electric field, the phase delay can depend on the polarization direction. A Pockels cell can thus be seen as a voltage-controlled waveplate, and it can be used for modulating the polarization state. For a linear input polarization (often oriented at 45° to the crystal axes), the output polarization will in general be elliptical, rather than simply a linear polarization state with a rotated direction.See also
- Pockels effectPockels effectThe Pockels effect , or Pockels electro-optic effect, produces birefringence in an optical medium induced by a constant or varying electric field. It is distinguished from the Kerr effect by the fact that the birefringence is proportional to the electric field, whereas in the Kerr effect it is...
- Acousto-optic modulatorAcousto-optic modulatorAn acousto-optic modulator , also called a Bragg cell, uses the acousto-optic effect to diffract and shift the frequency of light using sound waves . They are used in lasers for Q-switching, telecommunications for signal modulation, and in spectroscopy for frequency control. A piezoelectric...
- Phase modulationPhase modulationPhase modulation is a form of modulation that represents information as variations in the instantaneous phase of a carrier wave.Unlike its more popular counterpart, frequency modulation , PM is not very widely used for radio transmissions...
- Dielectric wireless receiverDielectric wireless receiverDielectric wireless receiver is a type of radiofrequency receiver front-end featuring a complete absence of electronic circuitry and metal interconnects. It offers immunity against damage from intense electromagnetic radiation, produced by EMP and HPM sources...

