
Electromagnetic lock
Encyclopedia
An electromagnetic lock, magnetic lock, or maglock is a locking device
that consists of an electromagnet
and an armature plate. By attaching the electromagnet to the door frame and the armature plate to the door, a current
passing through the electromagnet attracts the armature plate, holding the door shut. Unlike an electric strike
a magnetic lock has no interconnecting parts and is therefore not suitable for high security applications because it is possible to bypass the lock by disrupting the power supply. Nevertheless, the strength of today's magnetic locks compares well with that of conventional door locks and they cost less than conventional light bulb
s to operate. Power supplies incorporating a trickle-charged lead-acid battery pack can be used to retain security for short-term power outages.
 The electromagnetic lock was patented on May 2, 1989, by Arthur, Richard and David Geringer of Security Door Controls, an access control hardware manufacturing firm. The device outlined in their designs was the same in principle as the modern magnetic lock consisting of an electromagnet and an armature plate. The patent did not make any reference to the manufacturing methods of the electromagnet and detailed several variations on the design, including one that used a spring-loaded armature plate to bring the armature plate closer to the electromagnet. The patent expired on May 2, 2009.
The electromagnetic lock was patented on May 2, 1989, by Arthur, Richard and David Geringer of Security Door Controls, an access control hardware manufacturing firm. The device outlined in their designs was the same in principle as the modern magnetic lock consisting of an electromagnet and an armature plate. The patent did not make any reference to the manufacturing methods of the electromagnet and detailed several variations on the design, including one that used a spring-loaded armature plate to bring the armature plate closer to the electromagnet. The patent expired on May 2, 2009.
This device was a shear magnetic lock as opposed to the original (and now ubiquitous) 'direct pull' electromagnetic lock and was an improvement on a 1984 patent cited in the same document.
. Essentially it consists of an electromagnet
attracting a conductor with a force large enough to prevent the door from being opened. In a more detailed examination, the device makes use of the fact that a current through one or more loops of wire (known as a solenoid
) produces a magnetic field. This works in free space, but if the solenoid is wrapped around a ferromagnetic core such as soft iron
the effect of the field is greatly amplified. This is because the internal magnetic domains of the material align with each other to greatly enhance the magnetic flux density.
, it can be shown that the magnetic flux density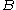 induced by a solenoid of effective length
induced by a solenoid of effective length 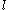 with a current
with a current  through
through 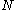 loops is given by the equation:
loops is given by the equation:
 dsf
dsf
The force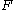 between the electromagnet and the armature plate with surface area
between the electromagnet and the armature plate with surface area 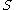 exposed to the electromagnet is given by the equation:
exposed to the electromagnet is given by the equation:
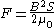
In both equations,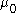 represents the permeability of free space and
represents the permeability of free space and 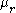 the relative permeability of the core.
the relative permeability of the core.
Although the actual performance of a magnetic lock may differ substantially due to various losses (such as flux leakage between the electromagnet and the conductor), the equations give a good insight into what is necessary to produce a strong magnetic lock. For example, the force of the lock is proportional to the square of the relative permeability of the magnetic core. Given the relative permeability of a material can vary from around 250 for cobalt
to around 5000 for soft iron
and 7000 for silicon
-iron
, the choice of magnetic core can therefore have an important impact upon the strength of a magnetic lock. Also relevant is the choice of current, number of loops and effective length of the electromagnet.
is an important consideration.
The standard size electromagnetic lock is used as a gate lock.
The magnetic lock is suitable for both in-swing and out-swing doors.
Brackets (L bracket, LZ bracket, U bracket) are used to adjust the space between the door and lock.
The principle behind the electromagnetic lock is to use electromagnetism to maintain the lock after energizing. The electromagnetism exploits the advantage of a solenoid
. The holding force should be a collinear load and the lock and armature plate should be face-to-face in the correct position to achieve optimal operation.
Generally, the specification of the electromagnet locks is dual voltages 12/24 V DC.
Single voltage output can be required for 12 V DC or 24 V DC applications.
The figure presents the relationship between voltage and holding force.
When the current is fixed, voltage is proportional to power consumption.
Fail-Safe
– to achieve human safety: The lock will be released when the power shuts down.
Fail-Secure – to achieve property safety: The lock remains closed when the power is shut down.
An electromagnet lock is used for Fail-Safe applications, and the lock should satisfy the specifications in fire regulations to be safe in emergency situations.
Lock (device)
A lock is a mechanical or electronic fastening device that is released by a physical object or secret information , or combination of more than one of these....
that consists of an electromagnet
Electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by the flow of electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off...
and an armature plate. By attaching the electromagnet to the door frame and the armature plate to the door, a current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
passing through the electromagnet attracts the armature plate, holding the door shut. Unlike an electric strike
Electric strike
An electric strike is an access control device used for doors. It replaces the fixed strike faceplate often used with a latchbar . Like a fixed strike, it normally presents a ramped surface to the locking latch allowing the door to close and latch just like a fixed strike would...
a magnetic lock has no interconnecting parts and is therefore not suitable for high security applications because it is possible to bypass the lock by disrupting the power supply. Nevertheless, the strength of today's magnetic locks compares well with that of conventional door locks and they cost less than conventional light bulb
Incandescent light bulb
The incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe makes light by heating a metal filament wire to a high temperature until it glows. The hot filament is protected from air by a glass bulb that is filled with inert gas or evacuated. In a halogen lamp, a chemical process...
s to operate. Power supplies incorporating a trickle-charged lead-acid battery pack can be used to retain security for short-term power outages.

This device was a shear magnetic lock as opposed to the original (and now ubiquitous) 'direct pull' electromagnetic lock and was an improvement on a 1984 patent cited in the same document.
Operation
The magnetic lock relies upon some of the basic concepts of electromagnetismElectromagnetism
Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three are the strong interaction, the weak interaction and gravitation...
. Essentially it consists of an electromagnet
Electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by the flow of electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off...
attracting a conductor with a force large enough to prevent the door from being opened. In a more detailed examination, the device makes use of the fact that a current through one or more loops of wire (known as a solenoid
Solenoid
A solenoid is a coil wound into a tightly packed helix. In physics, the term solenoid refers to a long, thin loop of wire, often wrapped around a metallic core, which produces a magnetic field when an electric current is passed through it. Solenoids are important because they can create...
) produces a magnetic field. This works in free space, but if the solenoid is wrapped around a ferromagnetic core such as soft iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
the effect of the field is greatly amplified. This is because the internal magnetic domains of the material align with each other to greatly enhance the magnetic flux density.
Equations
Using the Biot-Savart lawBiot-Savart law
The Biot–Savart law is an equation in electromagnetism that describes the magnetic field B generated by an electric current. The vector field B depends on the magnitude, direction, length, and proximity of the electric current, and also on a fundamental constant called the magnetic constant...
, it can be shown that the magnetic flux density
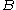 induced by a solenoid of effective length
induced by a solenoid of effective length 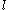 with a current
with a current  through
through 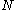 loops is given by the equation:
loops is given by the equation: dsf
dsfThe force
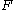 between the electromagnet and the armature plate with surface area
between the electromagnet and the armature plate with surface area 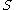 exposed to the electromagnet is given by the equation:
exposed to the electromagnet is given by the equation: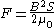
In both equations,
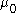 represents the permeability of free space and
represents the permeability of free space and 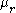 the relative permeability of the core.
the relative permeability of the core.Although the actual performance of a magnetic lock may differ substantially due to various losses (such as flux leakage between the electromagnet and the conductor), the equations give a good insight into what is necessary to produce a strong magnetic lock. For example, the force of the lock is proportional to the square of the relative permeability of the magnetic core. Given the relative permeability of a material can vary from around 250 for cobalt
Cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element with symbol Co and atomic number 27. It is found naturally only in chemically combined form. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal....
to around 5000 for soft iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
and 7000 for silicon
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
-iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
, the choice of magnetic core can therefore have an important impact upon the strength of a magnetic lock. Also relevant is the choice of current, number of loops and effective length of the electromagnet.
Technical comparison
Magnetic locks possess a number of advantages over conventional locks and electric strikes. For example, their durability and quick operation can make them valuable in a high-traffic office environment where electronic authentication is necessary.Advantages
- Easy to install: Magnetic locks are generally easier to install than other locks since there are no interconnecting parts.
- Quick to operate: Magnetic locks unlock instantly when the power is cut, allowing for quick operation in comparison to other locks.
- Sturdy: Magnetic locks may also suffer less damage from multiple blows than do conventional locks. If a magnetic lock is forced open with a crowbar, it will often do little or no damage to the door or lock.
Disadvantages
- Requires continuous power: To remain locked, the magnetic lock requires a constant power source. The power drain of the lock is typically around 3 wattWattThe watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
s, far less than that of a conventional lightbulb (around 60 watts), but it may cause security concerns as the device will become unlocked if the power source is disrupted. By comparison, electric strikeElectric strikeAn electric strike is an access control device used for doors. It replaces the fixed strike faceplate often used with a latchbar . Like a fixed strike, it normally presents a ramped surface to the locking latch allowing the door to close and latch just like a fixed strike would...
s can be designed to remain locked should the power source be disrupted. Nevertheless, this behaviour may actually be preferable in terms of fire safetyFire safetyFire safety refers to precautions that are taken to prevent or reduce the likelihood of a fire that may result in death, injury, or property damage, alert those in a structure to the presence of a fire in the event one occurs, better enable those threatened by a fire to survive, or to reduce the...
.
Installation
The magnetic lock should always be installed on the inside (secure side) of the door. Installation is as simple as installing the header of the door frame for out-swinging doors or using a Z-bracket for in-swinging doors. It is important to make sure the armature plate and the electromagnet align as closely as possible to ensure efficient operation. Magnetic locks are almost always part of a complete electronic security system. Such a system may simply consist of an attached keycard reader or may be more complex, involving connection to a central computer that monitors the building's security. Whatever the choice of locking system, fire safetyFire safety
Fire safety refers to precautions that are taken to prevent or reduce the likelihood of a fire that may result in death, injury, or property damage, alert those in a structure to the presence of a fire in the event one occurs, better enable those threatened by a fire to survive, or to reduce the...
is an important consideration.
Holding force
A magnetic lock has a metal plate surrounded by a coil of wire that can be magnetized. The number of coils determines the holding force which characterizes the lock:- Micro Size: 300 lbf (1,334.5 N) holding force.
- Mini Size: 600 lbf (2,668.9 N) holding force
- Midi Size: 800 lbf (3,558.6 N) holding force
- Standard Size: 1200 lbf (5,337.9 N) holding force.
The standard size electromagnetic lock is used as a gate lock.
Principle
Most installations are surface mounts. For safety, magnetic lock, cables, and wires should be inserted in the door or be a flush mount.The magnetic lock is suitable for both in-swing and out-swing doors.
Brackets (L bracket, LZ bracket, U bracket) are used to adjust the space between the door and lock.
The principle behind the electromagnetic lock is to use electromagnetism to maintain the lock after energizing. The electromagnetism exploits the advantage of a solenoid
Solenoid
A solenoid is a coil wound into a tightly packed helix. In physics, the term solenoid refers to a long, thin loop of wire, often wrapped around a metallic core, which produces a magnetic field when an electric current is passed through it. Solenoids are important because they can create...
. The holding force should be a collinear load and the lock and armature plate should be face-to-face in the correct position to achieve optimal operation.
Voltage
The power for an electromagnet lock is DC (Direct Current), around 6 W. The current is around 0.5 A when the power is 12 V DC.Generally, the specification of the electromagnet locks is dual voltages 12/24 V DC.
Single voltage output can be required for 12 V DC or 24 V DC applications.
The figure presents the relationship between voltage and holding force.
When the current is fixed, voltage is proportional to power consumption.
Application modes
For safety purposes an electric lock has two modes:Fail-Safe
Fail-safe
A fail-safe or fail-secure device is one that, in the event of failure, responds in a way that will cause no harm, or at least a minimum of harm, to other devices or danger to personnel....
– to achieve human safety: The lock will be released when the power shuts down.
Fail-Secure – to achieve property safety: The lock remains closed when the power is shut down.
An electromagnet lock is used for Fail-Safe applications, and the lock should satisfy the specifications in fire regulations to be safe in emergency situations.

