
Energy in Germany
Encyclopedia
| Germany Germany Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate... : Electricity sector |
|---|
|-
!align="center" bgcolor="lightblue" colspan="3"|Data
|-
!align="left" valign="top"|Electricity coverage
|valign="top"| n/a(total), n/a(rural);
|-
!align="left" valign="top"|Continuity of supply
|valign="top"| 0,2815 hrs (16,89 min) interruption per subscriber per year
|-
!align="left" valign="top"|Installed capacity
|valign="top"| n/a GW
|-
!align="left" valign="top"|Share of fossil energy consumed
|valign="top"| 62 %
|-
!align="left" valign="top"|Share of renewable energy
Renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat, which are renewable . About 16% of global final energy consumption comes from renewables, with 10% coming from traditional biomass, which is mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from...
consumed
|valign="top"| 12 % (including large hydropower)
|-
!align="left" valign="top"|GHG
Greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone...
emissions from electricity generation (2003)
|valign="top"| n/a Mt CO2
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
|-
!align="left" valign="top"|Average electricity use (2005)
|valign="top"| n/a kW·h per capita
|-
!align="left" valign="top"|Average industrial tariff (US$/kW·h, 2006)
|valign="top"| medium: n/a
|}
Energy in Germany describes energy
World energy resources and consumption
]World energy consumption in 2010: over 5% growthEnergy markets have combined crisis recovery and strong industry dynamism. Energy consumption in the G20 soared by more than 5% in 2010, after the slight decrease of 2009. This strong increase is the result of two converging trends...
and electricity
Electricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric energy from other forms of energy.The fundamental principles of electricity generation were discovered during the 1820s and early 1830s by the British scientist Michael Faraday...
production, consumption and import in Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
. Energy policy of Germany will describe the politics of Germany
Politics of Germany
The Federal Republic of Germany is a federal parliamentary republic, based on representative democracy. The Chancellor is the head of government, while the President of Germany is the head of state, which is a ceremonial role but with substantial reserve powers.Executive power is vested in the...
related to energy more in detail. Electricity sector in Germany
Electricity sector in Germany
The electricity sector in Germany included in the year 2009 fossil fuelled power 61 %, nuclear power 23 % and renewable energy 18 %. Germany has defined a phase-out policy of nuclear power by 2022...
is the main article of electricity in Germany. The energy sector in Germany is one of the biggest in the world with state-of-the-art clean energy industry.
The German economy
Economy of Germany
Germany is the largest national economy in Europe, the fourth-largest by nominal GDP in the world, and fifth by GDP in 2008. Since the age of industrialisation, the country has been a driver, innovator, and beneficiary of an ever more globalised economy...
is large and developed
Developed country
A developed country is a country that has a high level of development according to some criteria. Which criteria, and which countries are classified as being developed, is a contentious issue...
, ranking fifth in the world by GDP (PPP). Because of this, Germany consumed the fifth most energy per capita in the world in 2004.
In 2002, Germany was Europe's largest consumer of electricity; electricity consumption that year totaled 512.9 billion kilowatt-hours.
Energy policy
Germany will close all its nuclear reactorsNuclear power in Germany
Nuclear power in Germany accounted for 23% of national electricity consumption, before the permanent shutdown of 8 plants in March 2011. German nuclear power began with research reactors in the 1950s and 1960s with the first commercial plant coming online in 1969...
latest in the end of 2022. Vote result was 513 Yes, 79 No and 8 Empty. The seven oldest reactors were permanently closed after the Fukushima
Fukushima
may refer to:*Fukushima City – the capital city of Fukushima Prefecture, Japan*Fukushima Prefecture – a Japanese prefecture*Two nuclear power plants located in Fukushima Prefecture:**Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant...
accident.
Government policy emphasizes conservation and the development of renewable sources, such as solar, wind
Wind power
Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into a useful form of energy, such as using wind turbines to make electricity, windmills for mechanical power, windpumps for water pumping or drainage, or sails to propel ships....
, biomass
Biomass
Biomass, as a renewable energy source, is biological material from living, or recently living organisms. As an energy source, biomass can either be used directly, or converted into other energy products such as biofuel....
, water, and geothermal
Geothermal power
Geothermal energy is thermal energy generated and stored in the Earth. Thermal energy is the energy that determines the temperature of matter. Earth's geothermal energy originates from the original formation of the planet and from radioactive decay of minerals...
power. As a result of energy saving measures, energy efficiency
Energy conversion efficiency
Energy conversion efficiency is the ratio between the useful output of an energy conversion machine and the input, in energy terms. The useful output may be electric power, mechanical work, or heat.-Overview:...
(the amount of energy required to produce a unit of gross domestic product) has been improving since the beginning of the 1970s. The government has set the goal of meeting half the country's energy demands from alternative energy by 2050. Germany is the fourth largest producer of nuclear power in the world, but in 2000 the government and the German nuclear power industry
Nuclear power in Germany
Nuclear power in Germany accounted for 23% of national electricity consumption, before the permanent shutdown of 8 plants in March 2011. German nuclear power began with research reactors in the 1950s and 1960s with the first commercial plant coming online in 1969...
agreed to phase out all nuclear power plant
Nuclear power plant
A nuclear power plant is a thermal power station in which the heat source is one or more nuclear reactors. As in a conventional thermal power station the heat is used to generate steam which drives a steam turbine connected to a generator which produces electricity.Nuclear power plants are usually...
s by 2021. In September 2010, however, Merkel’s government reached a late-night deal which would see the country’s 17 nuclear plants run, on average, 12 years longer than planned, with some remaining in production until well into the 2030s. Then, following Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster
Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster
The is a series of equipment failures, nuclear meltdowns, and releases of radioactive materials at the Fukushima I Nuclear Power Plant, following the Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami on 11 March 2011. The plant comprises six separate boiling water reactors originally designed by General Electric ,...
, the government changed its mind again and decided to proceed with the plan to close all nuclear plants in the country by 2022.
After becoming Chancellor of Germany, Angela Merkel
Angela Merkel
Angela Dorothea Merkel is the current Chancellor of Germany . Merkel, elected to the Bundestag from Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, has been the chairwoman of the Christian Democratic Union since 2000, and chairwoman of the CDU-CSU parliamentary coalition from 2002 to 2005.From 2005 to 2009 she led a...
expressed concern for overreliance on Russian energy
Russia in the European energy sector
Russia has a significant role in the European energy sector as the largest exporter of oil and natural gas to the European Union. In 2007, the European Union imported from Russia 185 million tonnes of crude oil, which accounted for 32.6% of total oil import, and 100.7 million tonnes of...
, but she received little support from others in Berlin.
Overview
| Energy in Germany | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capita | Prim. energy | Production | Import | Electricity | CO2-emission | |
| Million | TWh | TWh | TWh | TWh | Mt | |
| 2004 | 82.5 | 4,048 | 1,582 | 2,509 | 580 | 849 |
| 2007 | 82.3 | 3,853 | 1,594 | 2,344 | 591 | 798 |
| 2008 | 82.1 | 3,899 | 1,560 | 2,453 | 587 | 804 |
| 2009 | 81.9 | 3,705 | 1,478 | 2,360 | 555 | 750 |
| Change 2004-2009 | -0.8 % | -8.5 % | -6.6 % | -5.9 % | -4.3 % | -11.6 % |
| Mtoe = 11.63 TWh, Prim. energy includes energy losses that are 2/3 for nuclear power | ||||||
Sustainable energy
On September 2010 the German government announced a new aggressive energy policy with the following targets:- Reducing CO2Carbon dioxideCarbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
emissions 40% below 1990 levels by 2020 and 80% below 1990 levels by 2050 - Increasing the relative share of renewable energy in gross energy consumption to 18% by 2020, 30% by 2030 and 60% by 2050
- Increasing the relative share of renewable energy in gross electrical consumption to 35% by 2020 and 80% by 2050
- Increasing the national energy efficiency by cutting electrical consumption 50% below 2008 levels by 2050
Electricity
The main source of electricity still remains coal. The recent plan to build 26 new coal plants is controversial in light of Germany's commitment to curbing emissions. LigniteLignite
Lignite, often referred to as brown coal, or Rosebud coal by Northern Pacific Railroad,is a soft brown fuel with characteristics that put it somewhere between coal and peat...
is extracted in the extreme western and eastern parts of the country, mainly in Nordrhein-Westfalen, Sachsen and Brandenburg
Brandenburg
Brandenburg is one of the sixteen federal-states of Germany. It lies in the east of the country and is one of the new federal states that were re-created in 1990 upon the reunification of the former West Germany and East Germany. The capital is Potsdam...
. Considerable amounts are burned in coal plants near to the mining areas, to produce electricity. Transporting lignite over far distances is not economically feasible, therefore the plants are located practically next to the extraction sites. Bituminous coal
Bituminous coal
Bituminous coal or black coal is a relatively soft coal containing a tarlike substance called bitumen. It is of higher quality than lignite coal but of poorer quality than Anthracite...
is mined in Nordrhein-Westfalen and Saarland. Most power plants burning bituminous coal operate on imported material, therefore the plants are located not only near to the mining sites, but throughout the country. Germany is the world’s largest operators of non-hydro renewables capacity in the world, including the world’s second largest operator of wind generation.
Consumption
]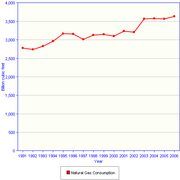
- Oil 34.6%
- Bituminous coal 11.1%
- Lignite 11.4%
- Natural gas 21.7%
- Nuclear power 11.0%
- Hydro- and wind power 1.5%
- Others 9.0%
Renewable energy is far more present in the domestically produced energy, since Germany imports about two thirds of its energy.
Germany is the fifth largest consumer of oil in the world. Russia, Norway, and the United Kingdom are the largest exporters of oil to Germany, in that order.
Germany is the third largest consumer of natural gas in the world. Because of its location at the center of Europe,
Germany is the fourth largest consumer of coal in the world. Germany has the largest market of electricity in Europe.
Energy efficiency in Germany
The energy efficiency bottom-up index for the whole economy (ODEX) in Germany decreased by 18 % between 1991–2006, which is equivalent to an energy efficiency improvement by 1.2 % per annum on average based on the ODEX, which calculates technical efficiency improvements. Since the beginning of the new century, however, the efficiency improvement measured by the ODEX slowed down. Whereas between 1991 and 2001, a continuous decrease by 1.5 %/y could be observed, the decrease in the period 2001-2006 only amounted to 0.5%, which is below the EU-27 level.External links
- Germany Energy Profile from the Energy Information Administration
- International Energy Agency: Electricity/Heat in Germany in 2005
- Statistical Energy Yearbook, 2010

