
Energy in Victoria
Encyclopedia

Primary energy
Primary energy is an energy form found in nature that has not been subjected to any conversion or transformation process. It is energy contained in raw fuels, and other forms of energy received as input to a system...
source for the generation of electricity
Electricity
Electricity is a general term encompassing a variety of phenomena resulting from the presence and flow of electric charge. These include many easily recognizable phenomena, such as lightning, static electricity, and the flow of electrical current in an electrical wire...
in the State of Victoria
Victoria (Australia)
Victoria is the second most populous state in Australia. Geographically the smallest mainland state, Victoria is bordered by New South Wales, South Australia, and Tasmania on Boundary Islet to the north, west and south respectively....
is brown coal - one of the largest contributors to Australia's total domestic greenhouse gas emissions. Brown coal is used for the generation of approximately 85 percent of Victoria's household, commercial and industrial electricity consumption. The remainder is sourced from natural gas and renewable energy sources - hydro, wind and solar.
History
Electrical power industry
The electric power industry provides the production and delivery of electric energy, often known as power, or electricity, in sufficient quantities to areas that need electricity through a grid connection. The grid distributes electrical energy to customers...
to Melbourne were provided by private companies
Defunct utility companies in Victoria, Australia
The Australian state of Victoria has a number of defunct energy supply and distribution utility companies.-North Melbourne Electric Tramway & Lighting Company:...
, with a number of small power stations such as those at Spencer Street
Spencer Street Power Station, Victoria
Spencer Street Power Station was a Victorian era coal-fired power station which operated on Spencer Street in central Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Opened in 1892, it was closed in 1982 after being deemed an eyesore, and in 2006 demolition commenced....
and Richmond
Richmond Power Station, Victoria
Richmond Power Station is a Victorian era coal fired power station which operated on the banks of the Yarra River in Richmond, Victoria, Australia from its construction in 1891 until its closure in 1976. It was one of the first alternating current electricity generation plants in the state...
operating. These small operations were merged into the State Electricity Commission of Victoria
State Electricity Commission of Victoria
The State Electricity Commission of Victoria was a monopoly electricity generation, transmission and supply utility located in Victoria, Australia...
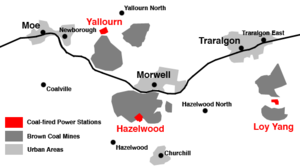
that was formed in 1921, the SECV also building the first of many brown coal fired power stations at Yallourn
Yallourn Power Station, Victoria
Yallourn Power Station was a complex of six brown coal fuelled power stations built progressively from the 1920s to the 1960s. Located in Victoria's Latrobe Valley, the complex was situated beside the Latrobe River, with the company town of Yallourn located to the south west...
in the Latrobe Valley
Latrobe Valley
The Latrobe Valley is an inland geographical region and urban area of Gippsland in the state of Victoria, Australia. It is east of the City Of Melbourne and nestled between the Strzelecki Ranges to the south and the Great Dividing Range to the north – with the highest peak to the north of the...
. The responsibilities of the SECV were privatised between 1995 and 1999. In the urban area, the largest power station is the Newport Power Station located close to the mouth of the Yarra River, the stack of which dominates the skyline of the inner western suburbs.
Coal fueled generators
Initial power generation in Victoria was provided by a number of small companies, with work on a state wide network beginning in the 1920s under the State Electricity Commission of VictoriaState Electricity Commission of Victoria
The State Electricity Commission of Victoria was a monopoly electricity generation, transmission and supply utility located in Victoria, Australia...
. The commission planned capacity upgrades many years in advance, with major base load power plants built at Yallourn
Yallourn Power Station, Victoria
Yallourn Power Station was a complex of six brown coal fuelled power stations built progressively from the 1920s to the 1960s. Located in Victoria's Latrobe Valley, the complex was situated beside the Latrobe River, with the company town of Yallourn located to the south west...
, Hazelwood
Hazelwood Power Station, Victoria
Hazelwood Power Station, in the Latrobe Valley, Victoria, Australia is a brown coal fueled base-load power station built between 1964 and 1971. The power station is of 1,600 megawatt capacity, and supplies up to 25% of Victoria's base load electricity and more than 5% of Australia's total energy...
and Loy Yang
Loy Yang Power Station, Victoria
Loy Yang Power Station is a brown coal fired power station located on the outskirts of the city of Traralgon, in south eastern Victoria, Australia. Loy Yang is a base load supply station, and produces about one third of Victoria's electricity requirements...
.
At present, most of electricity in Victoria is generated by burning brown coal in thermal power stations in the Latrobe Valley
Latrobe Valley
The Latrobe Valley is an inland geographical region and urban area of Gippsland in the state of Victoria, Australia. It is east of the City Of Melbourne and nestled between the Strzelecki Ranges to the south and the Great Dividing Range to the north – with the highest peak to the north of the...
.
The major electricity consumers in Victoria are the aluminium smelters
Aluminium smelting
Aluminium smelting is the process of extracting aluminium from its oxide alumina, generally by the Hall-Héroult process. Alumina is extracted from the ore Bauxite by means of the Bayer process at an alumina refinery....
at Portland
Portland aluminium smelter
The Portland aluminium smelter is located atPortland, Victoria, Australia.The smelter has a production capacity of 345,000 tonnes of aluminium per yearThe smelter is a joint venture owned by...
and Point Henry
Point Henry smelter
The Point Henry aluminium smelter is located near Geelong, Victoria in the suburb of Moolap. The smelter has a production capacity of 185,000 tonnes of aluminium a year. It is operated by Alcoa World Alumina and Chemicals Australia, a joint venture between Alcoa and Alumina Limited...
in Geelong.

New South Wales
New South Wales is a state of :Australia, located in the east of the country. It is bordered by Queensland, Victoria and South Australia to the north, south and west respectively. To the east, the state is bordered by the Tasman Sea, which forms part of the Pacific Ocean. New South Wales...
for its fuel needs.
It was not until the 1920s that the Latrobe Valley
Latrobe Valley
The Latrobe Valley is an inland geographical region and urban area of Gippsland in the state of Victoria, Australia. It is east of the City Of Melbourne and nestled between the Strzelecki Ranges to the south and the Great Dividing Range to the north – with the highest peak to the north of the...
coalfields were fully exploited for power generation, when the State Electricity Commission of Victoria
State Electricity Commission of Victoria
The State Electricity Commission of Victoria was a monopoly electricity generation, transmission and supply utility located in Victoria, Australia...
built the Yallourn Power Station
Yallourn Power Station, Victoria
Yallourn Power Station was a complex of six brown coal fuelled power stations built progressively from the 1920s to the 1960s. Located in Victoria's Latrobe Valley, the complex was situated beside the Latrobe River, with the company town of Yallourn located to the south west...
and associated open cut mine. Since then two more open cut mines have opened in the valley, feeding power station
Power station
A power station is an industrial facility for the generation of electric energy....
s at Hazelwood
Hazelwood Power Station, Victoria
Hazelwood Power Station, in the Latrobe Valley, Victoria, Australia is a brown coal fueled base-load power station built between 1964 and 1971. The power station is of 1,600 megawatt capacity, and supplies up to 25% of Victoria's base load electricity and more than 5% of Australia's total energy...
and Loy Yang
Loy Yang Power Station, Victoria
Loy Yang Power Station is a brown coal fired power station located on the outskirts of the city of Traralgon, in south eastern Victoria, Australia. Loy Yang is a base load supply station, and produces about one third of Victoria's electricity requirements...
.
Additional brown coal reserves were at Altona
Altona, Victoria
Altona is a suburb in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 13 km south-west from Melbourne's central business district. Its Local Government Area is the City of Hobsons Bay. At the 2006 Census, Altona had a population of 9685....
, and Anglesea
Anglesea, Victoria
Anglesea is a town in Victoria, Australia. It is located on the Great Ocean Road in the Surf Coast Shire local government area. At the 2006 census, Anglesea had a population of 2,290....
, and black coal in the Strzelecki Ranges
Strzelecki Ranges
Strzelecki Ranges, also known as Strzelecki Hills is a low mountain range in the Gippsland region of south-eastern Australia between the Latrobe Valley to the north and Bass Strait to the south...
in South Gippsland
South Gippsland
South Gippsland, a region of Gippsland in Victoria, Australia, is a well-watered region consisting of low, rolling hills descending to the coast in the south and the Latrobe Valley in the north. Low granite hills continue into Wilsons Promontory, the southernmost point of Victoria and mainland...
. Both the Altona and Strzelecki Ranges coalfields were small in size, and required underground mining. Both were wound up in the early 20th century. The Anglesea coalfield has been mined for Alcoa's Anglesea Power Station
Anglesea Power Station, Victoria (Australia)
Anglesea Power Station is located at Anglesea, in Victoria, Australia within the floristically rich Anglesea Heath area. It is brown coal powered with one steam turbine with a capacity of 150MW of electricity, supplying almost 40% of the electricity used by the nearby Point Henry aluminium...
since the 1960s.
In 2001-02, the Latrobe Valley produced 98.5% of Australia’s total brown coal production of 66.7 Mt.
Brown coal has 3 times the climate change
Climate change
Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions or the distribution of events around that average...
and global warming
Global warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
causing GHG emissions per KWh of electricity produced as natural gas. Hazelwood is commonly regarded as the most greenhouse gas polluting power station in Australia. If as is expected after the release of the report of the Garnaut Climate Change Review
Garnaut Climate Change Review
The Garnaut Climate Change Review was a study by Professor Ross Garnaut, commissioned by then Opposition Leader, Kevin Rudd and by the Australian State and Territory Governments on 30 April 2007...
a cap and trade emissions trading scheme is adopted to reduce the effects of global warming on Australia
Effects of global warming on Australia
Predictions measuring the effects of global warming on Australia assert that climate change will negatively impact the continent's environment, economy, and communities...
, electricity produced by burning brown coal will be expected to increase significantly in price.
Coal mines in Victoria currently operating:
| Mine | Location | Owner | Lat & Long | Type of Coal | Tons Mined PA | Major Buyers | Major Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yallourn | Yallourn Yallourn, Victoria Yallourn, Victoria was a company town in Victoria, Australia built between the 1920s and 1950s to house employees of the State Electricity Commission of Victoria, who operated the nearby Yallourn Power Station complex. However, expansion of the adjacent open-cut brown coal mine led to the closure... |
TRUenergy TRUenergy TRUenergy is an energy company headquartered in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.Founded in 1995 as a retailer and generator of electricity, and a retailer of natural gas, the company is formed from the combination of retail and generation assets purchased by Hong Kong-based CLP from Singapore Power... |
? | Lignite | ? | Yallourn Power Station Yallourn Power Station, Victoria Yallourn Power Station was a complex of six brown coal fuelled power stations built progressively from the 1920s to the 1960s. Located in Victoria's Latrobe Valley, the complex was situated beside the Latrobe River, with the company town of Yallourn located to the south west... |
Open Cut |
| Morwell | Morwell Morwell, Victoria -Transport:The main form of transport in Morwell is the automobile. The Princes Freeway now bypasses the town to the south while the old Princes Highway which once passed through east-west through its centre is now Princes Drive and Commercial Road. The highway connects Morwell with other... |
International Power International Power International Power PLC is an international electricity generator formed in 2000 by the demerger of National Power. It is headquartered at Senator House, 85 Queen Victoria Street in the City of London... |
? | Lignite | ? | Hazelwood Power Station Hazelwood Power Station, Victoria Hazelwood Power Station, in the Latrobe Valley, Victoria, Australia is a brown coal fueled base-load power station built between 1964 and 1971. The power station is of 1,600 megawatt capacity, and supplies up to 25% of Victoria's base load electricity and more than 5% of Australia's total energy... , Energy Brix |
Open Cut |
| Anglesea | Anglesea Anglesea, Victoria Anglesea is a town in Victoria, Australia. It is located on the Great Ocean Road in the Surf Coast Shire local government area. At the 2006 census, Anglesea had a population of 2,290.... |
Alcoa | ? | Lignite | ? | Anglesea Power Station Anglesea Power Station, Victoria (Australia) Anglesea Power Station is located at Anglesea, in Victoria, Australia within the floristically rich Anglesea Heath area. It is brown coal powered with one steam turbine with a capacity of 150MW of electricity, supplying almost 40% of the electricity used by the nearby Point Henry aluminium... |
Open Cut |
| Loy Lang | Traralgon Traralgon, Victoria Traralgon is a regional city located in the Latrobe Valley in the Gippsland region of Victoria, Australia. Traralgon is a city within the City of Latrobe.... |
Loy Yang Power | ? | Lignite | ? | Loy Yang Power Station Loy Yang Power Station, Victoria Loy Yang Power Station is a brown coal fired power station located on the outskirts of the city of Traralgon, in south eastern Victoria, Australia. Loy Yang is a base load supply station, and produces about one third of Victoria's electricity requirements... |
Open Cut |
Hydro

The Rubicon Hydroelectric Scheme
Rubicon Hydroelectric Scheme
The Rubicon Hydroelectric Scheme is located on the Rubicon and Royston Rivers, north east of Melbourne, 40 km south-west of Alexandra, Victoria, Australia. The scheme commenced in 1922, and was the first state-owned hydroelectric scheme to generate electricity in mainland Australia, and among...
was completed by the State Electricity Commission of Victoria in 1924, and was an important component of the state electrical grid at the time. It was later followed by the Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme
Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme
The Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme is the largest hydro-electric scheme in Victoria and the second largest in mainland Australia after the Snowy Mountains Scheme...
that was constructed between 1938 and 1961, the Eildon Power Station in 1956, Victoria's involvement in the Snowy Mountains Scheme
Snowy Mountains Scheme
The Snowy Mountains scheme is a hydroelectricity and irrigation complex in south-east Australia. It consists of sixteen major dams; seven power stations; a pumping station; and 225 kilometres of tunnels, pipelines and aqueducts and was constructed between 1949 and 1974. The Chief engineer was Sir...
that was built from the 1950s to 1970s, and the Dartmouth Power Station in 1981.
Solar
Small-scale personal, commercial and community roof-mounted systems are becoming more prevalent, and a large-scale solar energy project located in Mildura is under construction.Wind


Trials of wind power
Wind power
Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into a useful form of energy, such as using wind turbines to make electricity, windmills for mechanical power, windpumps for water pumping or drainage, or sails to propel ships....
in Victoria commenced in 1987, when the State Electricity Commission of Victoria erected a 60 kW capacity Westwind
Westwind
Westwind may refer to:* IAI Westwind, a business jet* Westwind an IAI Westwind used as the Honduras Presidential Plane.* Call sign for West Wind Aviation - aviation company based in Saskatoon...
wind generator
Wind generator
A wind generator is a device that generates electrical power from wind energy.Wind generators have traditionally been wind turbines, i.e. a propeller attached to an electric generator attached to appropriate electronics to attach it to the electrical grid or to charge batteries.Recently, however, a...
at Breamlea
Breamlea, Victoria
Breamlea, Victoria, Australia, is a secluded seaside hamlet located 28 km south of Geelong on the south coast of Australia halfway between Barwon Heads and Torquay on the Bellarine Peninsula. At the 2006 census, Breamlea and the surrounding area had a population of 244.-Geography:Breamlea is...
, Victoria
Victoria (Australia)
Victoria is the second most populous state in Australia. Geographically the smallest mainland state, Victoria is bordered by New South Wales, South Australia, and Tasmania on Boundary Islet to the north, west and south respectively....
as a demonstration project. The generator was sold to a private group in 1994 with the privatisation of the SECV.
It was not until the early 2000s that the commercial use of wind power for electricity commenced. Wind farms at Codrington
Codrington Wind Farm, Victoria
Codrington Wind Farm is a wind farm on the coast of south-western Victoria, Australia near Yambuk.Completed in June 2001, the 18.2 MW installation of 14 wind turbines generates 51 GWh annually, for a capital cost of 30 million Australian dollars by...
, Challicum Hills
Challicum Hills Wind Farm, Victoria (Australia)
Challicum Hills Wind Farm is a wind farm encompassed by 35 NEG NM 64 wind turbines, with a total generating capacity of 52.5 MW of electricity. The wind farm is near Ararat in western Victoria, Australia. The power station was commissioned in August 2003 and is in a long term PPA with Origin...
and Portland
Portland Wind Project
The Portland wind farm is one of Australia's largest wind farms. Located on the coast of south-western Victoria near the city of Portland, it consists of four separate sites, of which three have been completed...
were all built by private companies with State Government funding assistance.
Briquettes
Due to the low energy value of raw brown coal, long distance transport of the fuel was not economic. As a result, the State Electricity Commission of Victoria used German technology to produce hard briquetteBriquette
A briquette is a block of flammable matter used as fuel to start and maintain a fire. Common types of briquettes are charcoal briquettes and biomass briquettes.-Constituents of charcoal briquettes:...
s from Latrobe Valley brown coal. The initial plant was established in the 1920s at Yallourn
Yallourn, Victoria
Yallourn, Victoria was a company town in Victoria, Australia built between the 1920s and 1950s to house employees of the State Electricity Commission of Victoria, who operated the nearby Yallourn Power Station complex. However, expansion of the adjacent open-cut brown coal mine led to the closure...
, with a second opening at Morwell
Morwell, Victoria
-Transport:The main form of transport in Morwell is the automobile. The Princes Freeway now bypasses the town to the south while the old Princes Highway which once passed through east-west through its centre is now Princes Drive and Commercial Road. The highway connects Morwell with other...
in the 1940s. These plants crushed, dried and pressed brown coal to extract the water, and form a hard fast-burning block that was easy to transport.
The SECV encouraged the use of briquettes in both industrial and domestic cooking and heating, as a replacement for imported black coal. Briquettes were also used in a number of peak load thermal power stations that were located away from the Latrobe Valley. Briquette usage in Victoria today has dropped since the introduction of natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
to the state, but the Morwell Energy Brix factory remains today.
Gas
Supply of town gas to Melbourne was initially provided by private companies such as the Melbourne Metropolitan Gas Company from the 1850s, with gasworksGasworks
A gasworks or gas house is a factory for the manufacture of gas. The use of natural gas has made many redundant in the developed world, however they are often still used for storage.- Early gasworks :...
being scattered throughout the suburbs. The Gas and Fuel Corporation of Victoria
Gas and fuel corporation of victoria
The Gas and Fuel Corporation of Victoria was a government-owned monopoly supplier of household gas in Victoria, Australia.In 1951, the Victorian government took over two of the three main gas utilities in Melbourne - the Metropolitan Gas Company and the Brighton Gas Company...
was formed in 1951 to manage gas supply state wide, and to build a centralised gasworks at Morwell
Morwell, Victoria
-Transport:The main form of transport in Morwell is the automobile. The Princes Freeway now bypasses the town to the south while the old Princes Highway which once passed through east-west through its centre is now Princes Drive and Commercial Road. The highway connects Morwell with other...
. The discovery of natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
in Bass Strait
Bass Strait
Bass Strait is a sea strait separating Tasmania from the south of the Australian mainland, specifically the state of Victoria.-Extent:The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of the Bass Strait as follows:...
in the 1960s saw gas supplies converted to the new fuel by the 1970s. The Gas and Fuel Corporation was privatised in the late 1990s.
Town gas production in Victoria started in the 1850 to supply gas for lighting, heating, and cooking. It was originally the domain of many private companies, who all operated their own small gasworks
Gasworks
A gasworks or gas house is a factory for the manufacture of gas. The use of natural gas has made many redundant in the developed world, however they are often still used for storage.- Early gasworks :...
which converted black coal into gas. The Gas and Fuel Corporation of Victoria
Gas and fuel corporation of victoria
The Gas and Fuel Corporation of Victoria was a government-owned monopoly supplier of household gas in Victoria, Australia.In 1951, the Victorian government took over two of the three main gas utilities in Melbourne - the Metropolitan Gas Company and the Brighton Gas Company...
was formed in 1950, and built a centralised brown coal gasification plant at Morwell. The plant opened in 1956 and used the German Lurgi process to produce gas that was transferred to Melbourne
Melbourne
Melbourne is the capital and most populous city in the state of Victoria, and the second most populous city in Australia. The Melbourne City Centre is the hub of the greater metropolitan area and the Census statistical division—of which "Melbourne" is the common name. As of June 2009, the greater...
via a high pressure gas pipeline.
The production of town gas was changed in the late 1950s when Syngas
Syngas
Syngas is the name given to a gas mixture that contains varying amounts of carbon monoxide and hydrogen. Examples of production methods include steam reforming of natural gas or liquid hydrocarbons to produce hydrogen, the gasification of coal, biomass, and in some types of waste-to-energy...
production was developed, a process that converted waste gases from oil refineries
Oil refinery
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is processed and refined into more useful petroleum products, such as gasoline, diesel fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, kerosene, and liquefied petroleum gas...
to a useful energy product. The final blow to gas production was in 1965 when natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
was discovered in Bass Strait
Bass Strait
Bass Strait is a sea strait separating Tasmania from the south of the Australian mainland, specifically the state of Victoria.-Extent:The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of the Bass Strait as follows:...
, with the majority of Victoria changed over by the 1970s.
The search for natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
in Bass Strait
Bass Strait
Bass Strait is a sea strait separating Tasmania from the south of the Australian mainland, specifically the state of Victoria.-Extent:The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of the Bass Strait as follows:...
off Gippsland
Gippsland
Gippsland is a large rural region in Victoria, Australia. It begins immediately east of the suburbs of Melbourne and stretches to the New South Wales border, lying between the Great Dividing Range to the north and Bass Strait to the south...
commenced in the mid 1960s by Esso Australia
Esso Australia
Esso Australia is an Australian affiliate of ExxonMobil, the US based oil giant. Esso operates a number of oil and gas platforms in Bass Strait, south east of Melbourne, Australia, as well as a gas processing facility at Longford and Long Island Point in Hastings....
and BHP
BHP Billiton
BHP Billiton is a global mining, oil and gas company headquartered in Melbourne, Australia and with a major management office in London, United Kingdom...
. The floating rig Glomar III was used for exploration drilling, which begun on 27 December 1964. After two months gas was struck, and by June 1965 it was confirmed a major gas field had been found. Known as the Barracouta field, discovery of the Marlin field followed in March 1966. Both of these fields use offshore drilling rigs
Oil platform
An oil platform, also referred to as an offshore platform or, somewhat incorrectly, oil rig, is a lаrge structure with facilities to drill wells, to extract and process oil and natural gas, and to temporarily store product until it can be brought to shore for refining and marketing...
as a production base. By 1969 the production plant and distribution network were complete, allowing natural gas to be sold to consumers.
Additional gas reserves were discovered offshore from the Otway Ranges in recent years. BHP Billiton
BHP Billiton
BHP Billiton is a global mining, oil and gas company headquartered in Melbourne, Australia and with a major management office in London, United Kingdom...
discovered the Minerva gas field 1993, with production commencing in 2004. The Santos Ltd.
Santos Ltd.
Santos Ltd. is a large Australian oil and gas exploration company. Its name is an acronym for South Australia Northern Territory Oil Search.-Operations:...
operated Casino field was discovered in 2002, and started production in 2006. In 2002 Woodside Petroleum
Woodside Petroleum
Woodside Petroleum Limited is an Australian petroleum exploration and production company. It is a public company listed on the Australian Securities Exchange and has its headquarters in Perth, Western Australia.-History:...
prepared to develop their Geographe and Thylacine gas fields. These newer gas fields use undersea wellhead
Wellhead
A wellhead is a general term used to describe the component at the surface of an oil or gas well that provides the structural and pressure-containing interface for the drilling and production equipment....
s connected to the shore and production facilities with pipelines, minimising the visual impact on the coastline.
Today approximately 1.5 million domestic customers in Victoria are supplied with gas via over 25,000 kilometres of mains. Industrial and commercial consumers account for nearly 50 per cent of gas sales. In the 2005/2006 fiscal year, the average gas production in Victoria was over 700 Mcuft per day and represented 18% of the total national gas sales, with demand growing at 2% a year.
Oil
Oil was first discovered in the Gippsland Basin under Bass StraitBass Strait
Bass Strait is a sea strait separating Tasmania from the south of the Australian mainland, specifically the state of Victoria.-Extent:The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of the Bass Strait as follows:...
by Esso Australia
Esso Australia
Esso Australia is an Australian affiliate of ExxonMobil, the US based oil giant. Esso operates a number of oil and gas platforms in Bass Strait, south east of Melbourne, Australia, as well as a gas processing facility at Longford and Long Island Point in Hastings....
and BHP
BHP Billiton
BHP Billiton is a global mining, oil and gas company headquartered in Melbourne, Australia and with a major management office in London, United Kingdom...
in March 1966 in what is now the Marlin field. By early 1968, the Halibut and Kingfish oil fields were discovered nearby. Production from the fields was estimated at up to 300000 barrels (47,696.2 m³) per day, with recoverable reserves in the Gippsland Basin in the region of 4 Goilbbl.
In 1985, oil production from the Gippsland Basin peaked to an annual average of 450000 barrels (71,544.3 m³) per day. In 2005-2006, the average daily oil production declined to 83000 oilbbl/d, but despite the decline Victoria still produces almost 19.5% of crude oil in Australia.
See also
- Energy policy of AustraliaEnergy policy of AustraliaEnergy policy of Australia describes the energy policy in the politics of Australia. Energy in Australia describes energy and electricity production, consumption and export/import in Australia...
- Renewable energy in AustraliaRenewable energy in AustraliaRenewable energy in Australia represents 5.2% of total energy consumption, but only 1.7% of total production, the difference being the result of significant non-renewable energy exports. In the five years to 2009 renewable energy consumption grew by 3.5%, faster than other energy sources. Of all...
- Solar power in AustraliaSolar power in AustraliaAustralia has an estimated 300 MW of installed photovoltaic power , contributing an estimated 0.1 to 0.2% of total electricity production despite the hot and sunny climate that would make it ideal for utilisation...
- Wind power in AustraliaWind power in AustraliaWind power in Australia is a proven and reliable technology that can be and is readily deployed. As of October 2010, there were 52 wind farms in Australia, most of which had turbines of from 1.5 to 3 megawatts...

