
Enhanced Graphics Adapter
Encyclopedia

IBM PC
The IBM Personal Computer, commonly known as the IBM PC, is the original version and progenitor of the IBM PC compatible hardware platform. It is IBM model number 5150, and was introduced on August 12, 1981...
computer display standard
Computer display standard
Computer display standards are often a combination of aspect ratio, display resolution, color depth, and refresh rate.This article describes the different display standards for computer displays.-History:...
specification which is between CGA
Color Graphics Adapter
The Color Graphics Adapter , originally also called the Color/Graphics Adapter or IBM Color/Graphics Monitor Adapter, introduced in 1981, was IBM's first color graphics card, and the first color computer display standard for the IBM PC....
and VGA
Video Graphics Array
Video Graphics Array refers specifically to the display hardware first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, but through its widespread adoption has also come to mean either an analog computer display standard, the 15-pin D-subminiature VGA connector or the 640×480 resolution...
in terms of color and space resolution. Introduced in October 1984 by IBM shortly after (but not exclusively for) its new PC/AT
IBM Personal Computer/AT
The IBM Personal Computer AT, more commonly known as the IBM AT and also sometimes called the PC AT or PC/AT, was IBM's second-generation PC, designed around the 6 MHz Intel 80286 microprocessor and released in 1984 as machine type 5170...
, EGA produces a display of 16 simultaneous colors from a palette of 64 at a resolution of up to 640×350 pixels. The EGA card includes a 16 KB
Kibibyte
The kibibyte is a multiple of the unit byte for quantities of digital information. The binary prefix kibi means 1024; therefore, 1 kibibyte is . The unit symbol for the kibibyte is KiB. The unit was established by the International Electrotechnical Commission in 1999 and has been accepted for use...
ROM
Read-only memory
Read-only memory is a class of storage medium used in computers and other electronic devices. Data stored in ROM cannot be modified, or can be modified only slowly or with difficulty, so it is mainly used to distribute firmware .In its strictest sense, ROM refers only...
to extend the system BIOS
BIOS
In IBM PC compatible computers, the basic input/output system , also known as the System BIOS or ROM BIOS , is a de facto standard defining a firmware interface....
for additional graphics functions, and includes the Motorola
Motorola
Motorola, Inc. was an American multinational telecommunications company based in Schaumburg, Illinois, which was eventually divided into two independent public companies, Motorola Mobility and Motorola Solutions on January 4, 2011, after losing $4.3 billion from 2007 to 2009...
MC6845 video address generator
Video Display Controller
A Video Display Controller or VDC is an integrated circuit which is the main component in a video signal generator, a device responsible for the production of a TV video signal in a computing or game system...
as used in the CGA.
Each of the 16 colors can be assigned a unique RGB color code via a palette
Palette (computing)
In computer graphics, a palette is either a given, finite set of colors for the management of digital images , or a small on-screen graphical element for choosing from a limited set of choices, not necessarily colors .Depending on the context In computer graphics, a palette is either a given,...
mechanism in the 640×350 high-resolution mode; the 64 palette colors are a balanced RGB color set comprising all possible combinations of two bits per pixel for red, green and blue. EGA also includes full 16-color versions of the CGA 640×200 and 320×200 graphics modes; only the 16 CGA/RGBI colors are available in these modes. EGA 4-bit (16 colors) graphic modes
All Points Addressable
All Points Addressable , in the context of a video monitor, dot matrix or any display device consisting of a pixel array, refers to an arrangement bits or cells which can be individually manipulated, as opposed to rewriting the whole array every time a pixel changes.Generally, text modes are not...
are also notable for a sophisticated use of bit plane
BIT plane
This article is about Natalie Jeremijenko and the Bureau of Inverse Technology's project. For the company, see Bitplane. For the digital information term, see bit plane....
s and mask registers
Hardware register
In digital electronics, especially computing, a hardware register stores bits of information, in a way that all the bits can be written to or read out simultaneously.The hardware registers inside a central processing unit are called processor registers....
together with CPU bitwise operation
Bitwise operation
A bitwise operation operates on one or more bit patterns or binary numerals at the level of their individual bits. This is used directly at the digital hardware level as well as in microcode, machine code and certain kinds of high level languages...
s, which constitutes an early graphics accelerator inherited by VGA
Video Graphics Array
Video Graphics Array refers specifically to the display hardware first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, but through its widespread adoption has also come to mean either an analog computer display standard, the 15-pin D-subminiature VGA connector or the 640×480 resolution...
and numerous compatible hardware.
The original CGA modes are also present, though EGA is not 100% hardware compatible with CGA. EGA can drive an MDA
Monochrome Display Adapter
The Monochrome Display Adapter introduced in 1981 was IBM's standard video display card and computer display standard for the PC. The MDA did not have any pixel-addressable graphics modes...
monitor by a special setting of switches on the board; only 640×350 high-resolution monochrome graphics and the standard MDA text mode are available in this mode.
EGA cards use the PC ISA
Industry Standard Architecture
Industry Standard Architecture is a computer bus standard for IBM PC compatible computers introduced with the IBM Personal Computer to support its Intel 8088 microprocessor's 8-bit external data bus and extended to 16 bits for the IBM Personal Computer/AT's Intel 80286 processor...
bus and were available starting in 8-bit versions. The base IBM EGA card came with 64 KB of video memory
Video memory
Video memory is a term generally used in computers to describe some form of writable memory, usually RAM, dedicated to the purpose of holding the information necessary for a graphics card to drive a display device...
installed, only enough for 4 colors in high-resolution graphics. Expansion to 256 KB required a daughterboard
Daughterboard
A daughterboard, daughtercard or piggyback board is a circuit board meant to be an extension or "daughter" of a motherboard , or occasionally of another card...
. Eventually, most EGA cards and clones would come with 256 KB of memory. A few third-party EGA clones (notably the ATI Technologies
ATI Technologies
ATI Technologies Inc. was a semiconductor technology corporation based in Markham, Ontario, Canada, that specialized in the development of graphics processing units and chipsets. Founded in 1985 as Array Technologies Inc., the company was listed publicly in 1993 and was acquired by Advanced Micro...
and Paradise
Western Digital
Western Digital Corporation is one of the largest computer hard disk drive manufacturers in the world. It has a long history in the electronics industry as an integrated circuit maker and a storage products company. Western Digital was founded on April 23, 1970 by Alvin B...
boards) feature a range of extended graphics modes (e.g., 640×400, 640×480 and 720×540), as well as automatic monitor type detection, and sometimes also a special 400-line interlace mode for use on CGA monitors.
The EGA standard was made obsolete by the introduction of VGA by IBM in April 1987 with the PS/2
IBM Personal System/2
The Personal System/2 or PS/2 was IBM's third generation of personal computers. The PS/2 line, released to the public in 1987, was created by IBM in an attempt to recapture control of the PC market by introducing an advanced proprietary architecture...
computer line.
|-
|Sample of text mode
Text mode
Text mode is a kind of computer display mode in which the content of the screen is internally represented in terms of characters rather than individual pixels. Typically, the screen consists of a uniform rectangular grid of character cells, each of which contains one of the characters of a...
characters
with cursor.
|}>
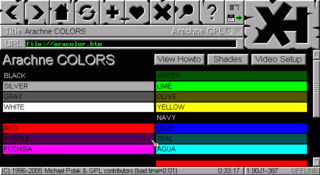
Color palette
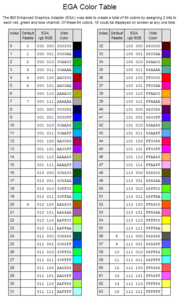
Video Graphics Array
Video Graphics Array refers specifically to the display hardware first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, but through its widespread adoption has also come to mean either an analog computer display standard, the 15-pin D-subminiature VGA connector or the 640×480 resolution...
standard built on this by allowing each of the 64 colors to be further customized.

| Default EGA 16-color palette (set up to match the standard CGA Color Graphics Adapter The Color Graphics Adapter , originally also called the Color/Graphics Adapter or IBM Color/Graphics Monitor Adapter, introduced in 1981, was IBM's first color graphics card, and the first color computer display standard for the IBM PC.... colors) |
||
|---|---|---|
| Color | rgbRGB | Decimal |
| 0 – black (#000000) | 000000 | 0 |
| 1 – blue (#0000AA) | 000001 | 1 |
| 2 – green (#00AA00) | 000010 | 2 |
| 3 – cyan (#00AAAA) | 000011 | 3 |
| 4 – red (#AA0000) | 000100 | 4 |
| 5 – magenta (#AA00AA) | 000101 | 5 |
| 6 – brown (#AA5500) | 010100 | 20 |
| 7 – white / light gray (#AAAAAA) | 000111 | 7 |
| 8 – dark gray / bright black (#555555) | 111000 | 56 |
| 9 – bright blue (#5555FF) | 111001 | 57 |
| 10 – bright green (#55FF55) | 111010 | 58 |
| 11 – bright cyan (#55FFFF) | 111011 | 59 |
| 12 – bright red (#FF5555) | 111100 | 60 |
| 13 – bright magenta (#FF55FF) | 111101 | 61 |
| 14 – bright yellow (#FFFF55) | 111110 | 62 |
| 15 – bright white (#FFFFFF) | 111111 | 63 |
Specifications
The EGA uses a female 9-pin D-subminiature (DE-9) connector which looks identical to the CGA connector. The hardware signal interface, including the pin configuration, is largely compatible with CGA. The differences are in the repurposing of three pins for the EGA's secondary RGB signals: the CGA Intensity pin (pin 6) has been changed to Secondary Green (Intensity); the second ground of CGA (pin 2) has been changed to Secondary Red (Intensity), and pin 7 (Reserved on the CGA) is used for Secondary Blue (Intensity). If the EGA is operated in the modes having the same scan rates as CGA, a connected CGA monitor should operate correctly, though if the monitor connects pin 2 to ground, the shorting of the EGA's Secondary Red (Intensity) output to ground could conceivably damage the EGA adapter. Similarly, if the CGA monitor is wired with pin 2 as its sole ground (which is poor design), it will not work with the EGA, though it will work with a CGA. Finally, because of the use of the CGA's Intensity pin as Secondary Green, on a CGA monitor connected to an EGA, all CGA colors will display correctly, but all other EGA colors will incorrectly display as the standard CGA color which has the same values for the g, R, G, and B bits (ignoring the r and b bits.) Conversely, an EGA monitor should work with a CGA adapter, but the Secondary Red signal will be grounded (always 0) and the Secondary Blue will be floating (unconnected), causing all high-intensity CGA colors except brown to display incorrectly and all colors to perhaps (but probably not) have a blue tint due to the indeterminate state of the unconnected Secondary Blue.The IBM 5154 EGA monitor has a special IBM 5153 CGA compability mode when operating with CGA sync signals, and it will automaticly change to the CGA pinout to avoid all of the mentioned problems when operating in this mode.
Connector
Female DE-9, on EGA (computer).Pin numbers (looking at socket): top row is pins 1-5, bottom row is pins 6 to 9, both numbered from right to left in this illustration.
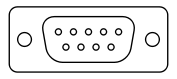
| Pin | Name | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground |
| 2 | SR | Secondary Red (Intensity) |
| 3 | PR | Primary Red |
| 4 | PG | Primary Green |
| 5 | PB | Primary Blue |
| 6 | SG | Secondary Green (Intensity) |
| 7 | SB | Secondary Blue (Intensity) |
| 8 | H | Horizontal Sync |
| 9 | V | Vertical Sync |
Signal
| Type | Digital, TTL |
|---|---|
| 640 × 350, other modes available | |
| H-freq | 15.7 or 21.8 kHz |
| V-freq | 60 Hz |
| Colors | 6-bit (64) |
See also
- Graphics card
- Graphic display resolutionsGraphic display resolutionsThe graphics display resolution describes the width and height dimensions of a display, such as a computer monitor, in pixels. Certain combinations of width and height are standardized and typically given a name and an initialism that is descriptive of its dimensions...
- Graphics processing unitGraphics processing unitA graphics processing unit or GPU is a specialized circuit designed to rapidly manipulate and alter memory in such a way so as to accelerate the building of images in a frame buffer intended for output to a display...
- List of display interfaces
- List of monochrome and RGB palettes — 6-bit RGB section
- List of 16-bit computer hardware palettes — EGA section
- Professional Graphics ControllerProfessional Graphics ControllerProfessional Graphics Controller was a graphics card manufactured by IBM for the PC. It consisted of three interconnected PCBs, and contained its own processor and memory....
- VGA compatible text modeVGA compatible text modeThe implementation of computer monitor text mode on VGA compatible hardware is quite complex. Its use on PC compatible computers was widespread in 1980s–1990s , but persists today for some applications even on modern desktop computers...
— EGA’s own modes are just a subset, and all features are nearly the same

