
Video Graphics Array
Encyclopedia
Video Graphics Array refers specifically to the display hardware first introduced with the IBM PS/2
line of computers in 1987, but through its widespread adoption has also come to mean either an analog
computer display standard
, the 15-pin D-subminiature
VGA connector
or the 640×480 resolution itself. While this resolution was superseded in the personal computer
market in the 1990s, it is becoming a popular resolution on mobile devices.
VGA was the last graphical standard introduced by IBM that the majority of PC clone
manufacturers conformed to, making it today the lowest common denominator
that all PC
graphics hardware can be expected to implement without device-specific driver
software. For example, the Microsoft Windows
splash screen
appears while the machine is still operating in VGA mode, which is the reason that this screen always appears in reduced resolution and color depth.
VGA was officially followed by IBM's Extended Graphics Array (XGA) standard, but it was effectively superseded by numerous slightly different extensions to VGA made by clone manufacturers that came to be known collectively as Super VGA
.
 VGA is referred to as an "array" instead of an "adapter" because it was implemented from the start as a single chip (an ASIC
VGA is referred to as an "array" instead of an "adapter" because it was implemented from the start as a single chip (an ASIC
), replacing the Motorola 6845
and dozens of discrete logic chips that covered the full-length ISA
boards of the MDA, CGA
, and EGA
. Its single-chip implementation also allowed the VGA to be placed directly on a PC
′s motherboard
with a minimum of difficulty (it only required video memory, timing crystal
s and an external RAMDAC
), and the first IBM PS/2
models were equipped with VGA on the motherboard. (Contrast this with all of the "family one" IBM PC desktop models—the PC, PC/XT
, and PC AT—which required a display adapter installed in a slot in order to connect a monitor.)
The VGA supports both All Points Addressable
graphics modes, and alphanumeric text mode
s. Standard graphics modes are:
The VGA specifications are as follows:
As well as the standard modes, VGA can be configured to emulate many of the modes of its predecessors (EGA, CGA, and MDA). Compatibility is almost full at BIOS
level, but even at register level, a very high value of compatibility is reached. VGA is not compatible with the special IBM PCjr
or HGC
video modes.
For most common VGA mode 640×480 "60 Hz" non-interlaced
the horizontal timings are:
(Total horizontal sync time 6.60 µs)
 The vertical timings are:
The vertical timings are:
(Total vertical sync time 1.43 ms)
640 × 400 @ 70 Hz is video mode used for booting most x86 personal computer
s.
640 × 480 @ 60 Hz is the default MS-Windows graphics mode with 16 colors.
The actual timings vary slightly. For example, for 640×480 @ 60 FPS, a 25.17 µs active video time with a pixel frequency of 25.174 MHz gives 633 pixels rather than the expected 640.
offers some text mode
s for a VGA adapter, which have 80×25, 40×25, 80×43 or 80×50 text grid. Each cell may choose from one of 16 available colors for its foreground and eight colors for the background; the eight background colors allowed are the ones without the high-intensity bit set. Each character may also be made to blink; all that are set to blink will blink in unison. The blinking option for the entire screen can be exchanged for the ability to use all 16 colors for background. All of these options are the same as those on the CGA adapter as introduced by IBM.
Like EGA, VGA supports 512 simultaneous characters on screen by disabling one color bit. The glyphs on 80×25 mode are normally made of 9×16 pixels. Users may define their own character set by loading a custom font onto the card. As character data is eight bits wide, some characters are normally made nine bits wide by repeating the last vertical line, especially those defining horizontal IBM box drawing characters
.
. Usually, once the video card's drivers are loaded (for example, by continuing to boot into the operating system), they will override this detection and the monitor will return to color.
 The video memory of the VGA is mapped to the PC's memory via a window in the range between segments 0xA0000
The video memory of the VGA is mapped to the PC's memory via a window in the range between segments 0xA0000
and 0xBFFFF in the PC's real mode
address space (A000:0000 and B000:FFFF in segment:offset notation). Typically, these starting segments are:
Due to the use of different address mappings for different modes, it is possible to have a monochrome adapter (i.e. MDA or Hercules
) and a color adapter such as the VGA, EGA
, or CGA
installed in the same machine. At the beginning of the 1980s, this was typically used to display Lotus 1-2-3
spreadsheets in high-resolution text on a monochrome display and associated graphics on a low-resolution CGA display simultaneously. Many programmers also used such a setup with the monochrome card displaying debugging information while a program ran in graphics mode on the other card. Several debuggers, like Borland's Turbo Debugger
, D86
(by Alan J. Cox) and Microsoft's CodeView
could work in a dual monitor setup. Either Turbo Debugger or CodeView could be used to debug Windows. There were also DOS device drivers such as ox.sys, which implemented a serial interface simulation on the monochrome display and, for example, allowed the user to receive crash messages from debugging versions of Windows without using an actual serial terminal. It is also possible to use the "MODE MONO" command at the DOS
prompt to redirect the output to the monochrome display. When a monochrome adapter was not present, it was possible to use the 0xB000 – 0xB7FF address space as additional memory for other programs (for example by adding the line "DEVICE=EMM386.EXE I=B000-B7FF" into config.sys, this memory would be made available to programs that can be "loaded high" – loaded into high memory
.)
 The VGA color system is backward compatible
The VGA color system is backward compatible
with the EGA and CGA adapters, and adds another level of configuration on top of that. CGA was able to display up to 16 colors, and EGA extended this by allowing each of the 16 colors to be chosen from a 64-color palette (these 64 colors are made up of two bits each for red, green and blue: two bits × three channels = six bits = 64 different values). VGA further extends this scheme by increasing the EGA palette from 64 entries to 256. Two more blocks of 64 colors with progressively darker shades were added, along with eight "blank" entries that were set to black.
In addition to the extended palette, each of the 256 entries could be assigned an arbitrary color value through the VGA DAC
. The EGA BIOS only allowed two bits per channel to represent each entry, while VGA allowed six bits to represent the intensity of each of the three primaries (red, blue and green). This provided a total of 64 different intensity levels for red, green and blue, resulting in 262,144 possible colors, any 256 of which could be assigned to the palette (and in turn out of those 256, any 16 of them could be displayed in CGA video modes).
This method allowed new VGA colors to be used in EGA and CGA graphics modes, providing one remembered how the different palette systems are laid together. To set the text color to very dark red in text mode, for instance, it will need to be set to one of the CGA colors (for example, the default color, #7: light grey.) This color then maps to one in the EGA palette—in the case of CGA color 7, it maps to EGA palette entry 42. The VGA DAC must then be configured to change color 42 to dark red, and then immediately anything displayed on the screen in light-grey (CGA color 7) will become dark red. This feature was often used in 256-color VGA DOS games when they first loaded, by smoothly fading out the text screen to black. (The game Descent
, from 1995, is an example.)
While CGA and EGA-compatible modes only allowed 16 colors to be displayed at any one time, other VGA modes, such as the widely used mode 13h
, allowed all 256 palette entries to be displayed on the screen at the same time, and so in these modes any 256 colors could be shown out of the 262,144 colors available.
(first coined by Michael Abrash
) or "tweaked VGA" was used to make programming techniques and graphics resolutions available that were not otherwise possible in the standard Mode 13h. This was done by "unchaining" the 256 KB VGA memory into four separate "planes", which would make all of VGA's 256 KB of RAM available in 256-color modes. There was a trade-off for extra complexity and performance loss in some types of graphics operations, but this was mitigated by other operations becoming faster in certain situations:
Sometimes the monitor refresh rate
had to be reduced to accommodate these modes, increasing eye strain
. They were also incompatible with some older monitors, producing display problems such as picture detail disappearing into overscan
, flicker
ing, vertical roll, and lack of horizontal sync
depending on the mode being attempted. Because of this, most VGA tweaks used in commercial products were limited to "monitor-safe" combinations, such as 320×240 (square pixels, three video pages), 320×400 (double resolution, two video pages), and 360×480 (highest resolution compatible with standard VGA monitors, one video page).
Currently, the highest known tweaked VGA resolution is 400×600×256 (400×600 pixel × 256 colors). It is used in Fractint
, a popular fractal generator.
IBM Personal System/2
The Personal System/2 or PS/2 was IBM's third generation of personal computers. The PS/2 line, released to the public in 1987, was created by IBM in an attempt to recapture control of the PC market by introducing an advanced proprietary architecture...
line of computers in 1987, but through its widespread adoption has also come to mean either an analog
Analogue electronics
Analogue electronics are electronic systems with a continuously variable signal, in contrast to digital electronics where signals usually take only two different levels. The term "analogue" describes the proportional relationship between a signal and a voltage or current that represents the signal...
computer display standard
Computer display standard
Computer display standards are often a combination of aspect ratio, display resolution, color depth, and refresh rate.This article describes the different display standards for computer displays.-History:...
, the 15-pin D-subminiature
D-subminiature
The D-subminiature or D-sub is a common type of electrical connector. They are named for their characteristic D-shaped metal shield. When they were introduced, D-subs were among the smaller connectors used on computer systems....
VGA connector
VGA connector
A Video Graphics Array connector is a three-row 15-pin DE-15 connector. The 15-pin VGA connector is found on many video cards, computer monitors, and some high definition television sets...
or the 640×480 resolution itself. While this resolution was superseded in the personal computer
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
market in the 1990s, it is becoming a popular resolution on mobile devices.
VGA was the last graphical standard introduced by IBM that the majority of PC clone
IBM PC compatible
IBM PC compatible computers are those generally similar to the original IBM PC, XT, and AT. Such computers used to be referred to as PC clones, or IBM clones since they almost exactly duplicated all the significant features of the PC architecture, facilitated by various manufacturers' ability to...
manufacturers conformed to, making it today the lowest common denominator
Lowest common denominator
In mathematics, the lowest common denominator or least common denominator is the least common multiple of the denominators of a set of vulgar fractions...
that all PC
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
graphics hardware can be expected to implement without device-specific driver
Device driver
In computing, a device driver or software driver is a computer program allowing higher-level computer programs to interact with a hardware device....
software. For example, the Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
splash screen
Splash screen
A splash screen is an image that appears while a game or program is loading. It may also be used to describe an introduction page on a website. Splash screens sometimes do not cover the entire screen, but only a rectangle near the center...
appears while the machine is still operating in VGA mode, which is the reason that this screen always appears in reduced resolution and color depth.
VGA was officially followed by IBM's Extended Graphics Array (XGA) standard, but it was effectively superseded by numerous slightly different extensions to VGA made by clone manufacturers that came to be known collectively as Super VGA
Super Video Graphics Array
Super Video Graphics Array or Ultra Video Graphics Array, almost always abbreviated to Super VGA, Ultra VGA or just SVGA or UVGA is a broad term that covers a wide range of computer display standards....
.
Hardware

ASIC
ASIC may refer to:* Application-specific integrated circuit, an integrated circuit developed for a particular use, as opposed to a customised general-purpose device.* ASIC programming language, a dialect of BASIC...
), replacing the Motorola 6845
Motorola 6845
The Motorola 6845 is a video address generator first introduced by Motorola and used among others in the Videx VideoTerm display cards for the Apple II computers, the MDA and CGA video adapters for the IBM PC, in the Amstrad CPC and the BBC Micro. Its functionality was duplicated and extended by...
and dozens of discrete logic chips that covered the full-length ISA
Industry Standard Architecture
Industry Standard Architecture is a computer bus standard for IBM PC compatible computers introduced with the IBM Personal Computer to support its Intel 8088 microprocessor's 8-bit external data bus and extended to 16 bits for the IBM Personal Computer/AT's Intel 80286 processor...
boards of the MDA, CGA
Color Graphics Adapter
The Color Graphics Adapter , originally also called the Color/Graphics Adapter or IBM Color/Graphics Monitor Adapter, introduced in 1981, was IBM's first color graphics card, and the first color computer display standard for the IBM PC....
, and EGA
Enhanced Graphics Adapter
The Enhanced Graphics Adapter is the IBM PC computer display standard specification which is between CGA and VGA in terms of color and space resolution. Introduced in October 1984 by IBM shortly after its new PC/AT, EGA produces a display of 16 simultaneous colors from a palette of 64 at a...
. Its single-chip implementation also allowed the VGA to be placed directly on a PC
IBM PC compatible
IBM PC compatible computers are those generally similar to the original IBM PC, XT, and AT. Such computers used to be referred to as PC clones, or IBM clones since they almost exactly duplicated all the significant features of the PC architecture, facilitated by various manufacturers' ability to...
′s motherboard
Motherboard
In personal computers, a motherboard is the central printed circuit board in many modern computers and holds many of the crucial components of the system, providing connectors for other peripherals. The motherboard is sometimes alternatively known as the mainboard, system board, or, on Apple...
with a minimum of difficulty (it only required video memory, timing crystal
Crystal oscillator
A crystal oscillator is an electronic oscillator circuit that uses the mechanical resonance of a vibrating crystal of piezoelectric material to create an electrical signal with a very precise frequency...
s and an external RAMDAC
RAMDAC
Random Access Memory Digital-to-Analog Converter is a combination of three fast DACs with a small SRAM used in computer graphics display adapters to store the color palette and to generate the analog signals to drive a color monitor...
), and the first IBM PS/2
IBM Personal System/2
The Personal System/2 or PS/2 was IBM's third generation of personal computers. The PS/2 line, released to the public in 1987, was created by IBM in an attempt to recapture control of the PC market by introducing an advanced proprietary architecture...
models were equipped with VGA on the motherboard. (Contrast this with all of the "family one" IBM PC desktop models—the PC, PC/XT
IBM Personal Computer XT
The IBM Personal Computer XT, often shortened to the IBM XT, PC XT, or simply XT, was IBM's successor to the original IBM PC. It was released as IBM Machine Type number 5160 on March 8, 1983, and came standard with a hard drive...
, and PC AT—which required a display adapter installed in a slot in order to connect a monitor.)
The VGA supports both All Points Addressable
All Points Addressable
All Points Addressable , in the context of a video monitor, dot matrix or any display device consisting of a pixel array, refers to an arrangement bits or cells which can be individually manipulated, as opposed to rewriting the whole array every time a pixel changes.Generally, text modes are not...
graphics modes, and alphanumeric text mode
Text mode
Text mode is a kind of computer display mode in which the content of the screen is internally represented in terms of characters rather than individual pixels. Typically, the screen consists of a uniform rectangular grid of character cells, each of which contains one of the characters of a...
s. Standard graphics modes are:
- 640×480Display resolutionThe display resolution of a digital television or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by all different factors in cathode ray tube , flat panel or projection...
in 16 colors - 640×350 in 16 colors
- 320×200 in 16 colors
- 320×200 in 256 colors (Mode 13hMode 13hMode 13h is the IBM VGA BIOS mode number for a specific standard 256 color mode on IBM's VGA graphics hardware. It features a resolution of 320×200 pixels and was used extensively in computer games and art/animation software of the late 1980s and early- to mid-1990s...
)
The VGA specifications are as follows:
- 256 KBKilobyteThe kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Although the prefix kilo- means 1000, the term kilobyte and symbol KB have historically been used to refer to either 1024 bytes or 1000 bytes, dependent upon context, in the fields of computer science and information...
Video RAMRandom-access memoryRandom access memory is a form of computer data storage. Today, it takes the form of integrated circuits that allow stored data to be accessed in any order with a worst case performance of constant time. Strictly speaking, modern types of DRAM are therefore not random access, as data is read in...
(The very first cards could be ordered with 64 KB or 128 KB of RAM at the cost of losing some video modes.) - 16-color and 256-color modes
- 262,144-value color palette (six bits each for red, green, and blue)
- Selectable 25.175 MHz or 28.322 MHz master clock
- Maximum of 800 horizontal pixelPixelIn digital imaging, a pixel, or pel, is a single point in a raster image, or the smallest addressable screen element in a display device; it is the smallest unit of picture that can be represented or controlled....
s - Maximum of 600 lines
- Refresh rates at up to 70 HzHertzThe hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
- Vertical blank interruptVertical blank interruptA vertical blank interrupt is a programming technique used in some systems, notably video games and consoles, to allow program code to be run in the periods when the display hardware is turned off, waiting for the TV to complete its vertical blank.Since the vertical blank period occurs at the...
(Not all clone cards support this.) - Planar mode: up to 16 colors (4-bit planes)
- Packed-pixel mode: 256 colors (Mode 13hMode 13hMode 13h is the IBM VGA BIOS mode number for a specific standard 256 color mode on IBM's VGA graphics hardware. It features a resolution of 320×200 pixels and was used extensively in computer games and art/animation software of the late 1980s and early- to mid-1990s...
) - Hardware smooth scrollingScrollingIn computer graphics, filmmaking, television production, and other kinetic displays, scrolling is sliding text, images or video across a monitor or display. "Scrolling", as such, does not change the layout of the text or pictures, or but incrementally moves the user's view across what is...
support - Some "RasterRaster graphicsIn computer graphics, a raster graphics image, or bitmap, is a data structure representing a generally rectangular grid of pixels, or points of color, viewable via a monitor, paper, or other display medium...
Ops" support - Barrel shifterBarrel shifterA barrel shifter is a digital circuit that can shift a data word by a specified number of bits in one clock cycle. It can be implemented as a sequence of multiplexers , and in such an implementation the output of one mux is connected to the input of the next mux in a way that depends on the shift...
- SplitSplit screen (computer graphics)Split screen is a display technique in computer graphics that consists of dividing graphics and/or text into non-movable adjacent parts, typically two or four rectangular areas. This is done in order to allow the simultaneous presentation of related graphical and textual information on a computer...
screen support - 0.7 VVoltThe volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
peak-to-peakAmplitudeAmplitude is the magnitude of change in the oscillating variable with each oscillation within an oscillating system. For example, sound waves in air are oscillations in atmospheric pressure and their amplitudes are proportional to the change in pressure during one oscillation... - 75 ohmOhmThe ohm is the SI unit of electrical resistance, named after German physicist Georg Simon Ohm.- Definition :The ohm is defined as a resistance between two points of a conductor when a constant potential difference of 1 volt, applied to these points, produces in the conductor a current of 1 ampere,...
double-terminated impedanceElectrical impedanceElectrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
(18.7 mA – 13 mW)
As well as the standard modes, VGA can be configured to emulate many of the modes of its predecessors (EGA, CGA, and MDA). Compatibility is almost full at BIOS
BIOS
In IBM PC compatible computers, the basic input/output system , also known as the System BIOS or ROM BIOS , is a de facto standard defining a firmware interface....
level, but even at register level, a very high value of compatibility is reached. VGA is not compatible with the special IBM PCjr
IBM PCjr
The IBM PCjr was IBM's first attempt to enter the home computer market. The PCjr, IBM model number 4860, retained the IBM PC's 8088 CPU and BIOS interface for compatibility, but various design and implementation decisions led the PCjr to be a commercial failure.- Features :Announced November 1,...
or HGC
Hercules Graphics Card
The Hercules Graphics Card was a computer graphics controller made by Hercules Computer Technology, Inc. which, through its popularity, became a widely supported display standard. It was common on IBM PC compatibles connected to a monochrome monitor . It supported one high resolution text mode and...
video modes.
Signal
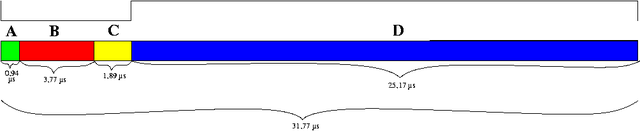
The intended value for the horizontal frequency of VGA is exactly double the value used in the NTSC-M video system. The formula for the VGA horizontal frequency is thus (60 ÷ 1001) × 525 kHz = 4500 ÷ 143 kHz ≈ 31.4686 kHz. All other frequencies used by the VGA card are derived from this value by integer multiplication or division. Since the exactness of quartz oscillators is limited, real cards will have slightly higher or lower frequency.For most common VGA mode 640×480 "60 Hz" non-interlaced
Progressive scan
Progressive scanning is a way of displaying, storing, or transmitting moving images in which all the lines of each frame are drawn in sequence...
the horizontal timings are:
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pixel clock frequency | 25.175 | MHz Hertz The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications.... |
| Horizontal frequency | 31.4686 | kHz Hertz The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications.... |
| Horizontal pixels | 640 | |
| Horizontal sync polarity | Negative | |
| Total time for each line | 31.77 | µs 1 E-6 s A microsecond is an SI unit of time equal to one millionth of a second. Its symbol is µs.A microsecond is equal to 1000 nanoseconds or 1/1000 millisecond... |
| Front porch Front Porch Front Porch, Inc. provides services to Internet Service Providers. Front Porch technology enables an Internet Service Provider to insert its own messages to be presented to users as they use their web browsers, such as customer service notices or online advertising... (A) |
0.94 | µs |
| Sync pulse length (B) | 3.77 | µs |
| Back porch (C) | 1.89 | µs |
| Active video (D) | 25.17 | µs |
(Total horizontal sync time 6.60 µs)

| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical lines | 480 | |
| Vertical sync polarity | Negative | |
| Vertical frequency | 59.94 | Hz |
| Front porch (E) | 0.35 | ms Millisecond A millisecond is a thousandth of a second.10 milliseconds are called a centisecond.... |
| Sync pulse length (F) | 0.06 | ms |
| Back porch (G) | 1.02 | ms |
| Active video (H) | 15.25 | ms |
(Total vertical sync time 1.43 ms)
640 × 400 @ 70 Hz is video mode used for booting most x86 personal computer
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
s.
640 × 480 @ 60 Hz is the default MS-Windows graphics mode with 16 colors.
The actual timings vary slightly. For example, for 640×480 @ 60 FPS, a 25.17 µs active video time with a pixel frequency of 25.174 MHz gives 633 pixels rather than the expected 640.
Standard text modes
The BIOSBIOS
In IBM PC compatible computers, the basic input/output system , also known as the System BIOS or ROM BIOS , is a de facto standard defining a firmware interface....
offers some text mode
Text mode
Text mode is a kind of computer display mode in which the content of the screen is internally represented in terms of characters rather than individual pixels. Typically, the screen consists of a uniform rectangular grid of character cells, each of which contains one of the characters of a...
s for a VGA adapter, which have 80×25, 40×25, 80×43 or 80×50 text grid. Each cell may choose from one of 16 available colors for its foreground and eight colors for the background; the eight background colors allowed are the ones without the high-intensity bit set. Each character may also be made to blink; all that are set to blink will blink in unison. The blinking option for the entire screen can be exchanged for the ability to use all 16 colors for background. All of these options are the same as those on the CGA adapter as introduced by IBM.
Like EGA, VGA supports 512 simultaneous characters on screen by disabling one color bit. The glyphs on 80×25 mode are normally made of 9×16 pixels. Users may define their own character set by loading a custom font onto the card. As character data is eight bits wide, some characters are normally made nine bits wide by repeating the last vertical line, especially those defining horizontal IBM box drawing characters
Box drawing characters
Box drawing characters, also known as line drawing characters, or pseudographics, are widely used in text user interfaces to draw various frames and boxes...
.
Monochrome modes
VGA adapters usually support both monochrome and color modes, though the monochrome mode is almost never used, and support for the full set of MDA text mode attributes (intense, underline) is often missing. Black and white text on nearly all modern VGA adapters is drawn by using gray colored text on a black background in color mode. VGA monochrome monitors intended primarily for text were sold, but most of them will work at least adequately with a VGA adapter in color mode. Occasionally, a faulty connection between a modern monitor and video card will cause the VGA part of the card to detect the monitor as monochrome; this will cause the BIOS and initial boot sequence to appear in greyscaleGrayscale
In photography and computing, a grayscale or greyscale digital image is an image in which the value of each pixel is a single sample, that is, it carries only intensity information...
. Usually, once the video card's drivers are loaded (for example, by continuing to boot into the operating system), they will override this detection and the monitor will return to color.
Addressing details

Hexadecimal
In mathematics and computer science, hexadecimal is a positional numeral system with a radix, or base, of 16. It uses sixteen distinct symbols, most often the symbols 0–9 to represent values zero to nine, and A, B, C, D, E, F to represent values ten to fifteen...
and 0xBFFFF in the PC's real mode
Real mode
Real mode, also called real address mode, is an operating mode of 80286 and later x86-compatible CPUs. Real mode is characterized by a 20 bit segmented memory address space and unlimited direct software access to all memory, I/O addresses and peripheral hardware...
address space (A000:0000 and B000:FFFF in segment:offset notation). Typically, these starting segments are:
- 0xA0000 for EGA/VGA graphics modes (64 KBKibibyteThe kibibyte is a multiple of the unit byte for quantities of digital information. The binary prefix kibi means 1024; therefore, 1 kibibyte is . The unit symbol for the kibibyte is KiB. The unit was established by the International Electrotechnical Commission in 1999 and has been accepted for use...
) - 0xB0000 for monochrome text mode (32 KB)
- 0xB8000 for color text mode and CGA-compatible graphics modes (32 KB)
Due to the use of different address mappings for different modes, it is possible to have a monochrome adapter (i.e. MDA or Hercules
Hercules Graphics Card
The Hercules Graphics Card was a computer graphics controller made by Hercules Computer Technology, Inc. which, through its popularity, became a widely supported display standard. It was common on IBM PC compatibles connected to a monochrome monitor . It supported one high resolution text mode and...
) and a color adapter such as the VGA, EGA
Enhanced Graphics Adapter
The Enhanced Graphics Adapter is the IBM PC computer display standard specification which is between CGA and VGA in terms of color and space resolution. Introduced in October 1984 by IBM shortly after its new PC/AT, EGA produces a display of 16 simultaneous colors from a palette of 64 at a...
, or CGA
Color Graphics Adapter
The Color Graphics Adapter , originally also called the Color/Graphics Adapter or IBM Color/Graphics Monitor Adapter, introduced in 1981, was IBM's first color graphics card, and the first color computer display standard for the IBM PC....
installed in the same machine. At the beginning of the 1980s, this was typically used to display Lotus 1-2-3
Lotus 1-2-3
Lotus 1-2-3 is a spreadsheet program from Lotus Software . It was the IBM PC's first "killer application"; its huge popularity in the mid-1980s contributed significantly to the success of the IBM PC in the corporate environment.-Beginnings:...
spreadsheets in high-resolution text on a monochrome display and associated graphics on a low-resolution CGA display simultaneously. Many programmers also used such a setup with the monochrome card displaying debugging information while a program ran in graphics mode on the other card. Several debuggers, like Borland's Turbo Debugger
Turbo Debugger
Turbo Debugger was a machine-level debugger for MS-DOS executables, intended mainly for debugging Borland Turbo Pascal , and later Turbo C programs, sold by Borland...
, D86
A86 (software)
A86 is a compact commercial assembler developed for the Intel x86 family of microprocessors by Eric Isaacson. The assembler can directly produce a Windows/DOS compatible .COM or .OBJ file from a simple text source file. It uses a slightly simpler syntax for source code than that used by other...
(by Alan J. Cox) and Microsoft's CodeView
CodeView
CodeView was a standalone debugger created by David Norris at Microsoft in 1985 as part of its development toolset. It originally shipped with Microsoft C 4.0 and later. It also shipped with Visual Basic for MS-DOS, Microsoft Basic PDS, and a number of other Microsoft language products...
could work in a dual monitor setup. Either Turbo Debugger or CodeView could be used to debug Windows. There were also DOS device drivers such as ox.sys, which implemented a serial interface simulation on the monochrome display and, for example, allowed the user to receive crash messages from debugging versions of Windows without using an actual serial terminal. It is also possible to use the "MODE MONO" command at the DOS
DOS
DOS, short for "Disk Operating System", is an acronym for several closely related operating systems that dominated the IBM PC compatible market between 1981 and 1995, or until about 2000 if one includes the partially DOS-based Microsoft Windows versions 95, 98, and Millennium Edition.Related...
prompt to redirect the output to the monochrome display. When a monochrome adapter was not present, it was possible to use the 0xB000 – 0xB7FF address space as additional memory for other programs (for example by adding the line "DEVICE=EMM386.EXE I=B000-B7FF" into config.sys, this memory would be made available to programs that can be "loaded high" – loaded into high memory
High memory
High Memory is the part of physical memory in a computer which is not directly mapped by the page tables of its operating system kernel. The phrase is also sometimes used as shorthand for the High Memory Area, which is a different concept entirely....
.)
The VGA color palette

Backward compatibility
In the context of telecommunications and computing, a device or technology is said to be backward or downward compatible if it can work with input generated by an older device...
with the EGA and CGA adapters, and adds another level of configuration on top of that. CGA was able to display up to 16 colors, and EGA extended this by allowing each of the 16 colors to be chosen from a 64-color palette (these 64 colors are made up of two bits each for red, green and blue: two bits × three channels = six bits = 64 different values). VGA further extends this scheme by increasing the EGA palette from 64 entries to 256. Two more blocks of 64 colors with progressively darker shades were added, along with eight "blank" entries that were set to black.
In addition to the extended palette, each of the 256 entries could be assigned an arbitrary color value through the VGA DAC
Digital-to-analog converter
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter is a device that converts a digital code to an analog signal . An analog-to-digital converter performs the reverse operation...
. The EGA BIOS only allowed two bits per channel to represent each entry, while VGA allowed six bits to represent the intensity of each of the three primaries (red, blue and green). This provided a total of 64 different intensity levels for red, green and blue, resulting in 262,144 possible colors, any 256 of which could be assigned to the palette (and in turn out of those 256, any 16 of them could be displayed in CGA video modes).
This method allowed new VGA colors to be used in EGA and CGA graphics modes, providing one remembered how the different palette systems are laid together. To set the text color to very dark red in text mode, for instance, it will need to be set to one of the CGA colors (for example, the default color, #7: light grey.) This color then maps to one in the EGA palette—in the case of CGA color 7, it maps to EGA palette entry 42. The VGA DAC must then be configured to change color 42 to dark red, and then immediately anything displayed on the screen in light-grey (CGA color 7) will become dark red. This feature was often used in 256-color VGA DOS games when they first loaded, by smoothly fading out the text screen to black. (The game Descent
Descent (video game)
Descent is a 3D first-person shooter video game developed by Parallax Software and released by Interplay Entertainment Corp. in 1995. The game features six degrees of freedom gameplay and garnered several expansion packs...
, from 1995, is an example.)
While CGA and EGA-compatible modes only allowed 16 colors to be displayed at any one time, other VGA modes, such as the widely used mode 13h
Mode 13h
Mode 13h is the IBM VGA BIOS mode number for a specific standard 256 color mode on IBM's VGA graphics hardware. It features a resolution of 320×200 pixels and was used extensively in computer games and art/animation software of the late 1980s and early- to mid-1990s...
, allowed all 256 palette entries to be displayed on the screen at the same time, and so in these modes any 256 colors could be shown out of the 262,144 colors available.
Programming tricks
An undocumented but popular technique nicknamed Mode XMode X
Mode X is an alternative video graphics display mode of the IBM VGA graphics hardware that was popularized by Michael Abrash, first published in July 1991 in Dr...
(first coined by Michael Abrash
Michael Abrash
Michael Abrash is a technical writer specializing in optimization and 80x86 assembly language programming, a reputation cemented by his 1990 book Zen of Assembly Language Volume 1: Knowledge. The original 8086 processor, the focus of the book, was several generations behind the state of the art by...
) or "tweaked VGA" was used to make programming techniques and graphics resolutions available that were not otherwise possible in the standard Mode 13h. This was done by "unchaining" the 256 KB VGA memory into four separate "planes", which would make all of VGA's 256 KB of RAM available in 256-color modes. There was a trade-off for extra complexity and performance loss in some types of graphics operations, but this was mitigated by other operations becoming faster in certain situations:
- Single-color polygon filling could be accelerated due to the ability to set four pixels with a single write to the hardware.
- The video adapter could assist in copying video RAM regions, which was sometimes faster than doing this with the relatively slow CPU-to-VGA interface.
- Several higher-resolution display modes were possible: at 16 colors, 704×528, 736×552, 768×576, and even 800×600. Software such as Xlib (a VGA graphics library for C in the early 1990s) and ColoRIX (a 256-color graphics program), also supported tweaked 256-color modes using many combinations of widths of 256, 320, and 360 pixels, and heights of 200, 240, 256, 400, and 480 lines (the upper limit being 640×400 which used 250 KB of VGA's 256 KB video ram). However, 320×240 was the best known and most-frequently used since it was a typical 4:3 aspect ratio resolution with square pixels.
- The use of multiple video pages in hardware allowed the programmer to perform double bufferingDouble bufferingIn computer science, multiple buffering is the use of more than one buffer to hold a block of data, so that a "reader" will see a complete version of the data, rather than a partially-updated version of the data being created by a "writer"...
, triple buffering or split screens, which, while available in VGA's 320×200 16-color mode, was not possible using stock Mode 13hMode 13hMode 13h is the IBM VGA BIOS mode number for a specific standard 256 color mode on IBM's VGA graphics hardware. It features a resolution of 320×200 pixels and was used extensively in computer games and art/animation software of the late 1980s and early- to mid-1990s...
.
Sometimes the monitor refresh rate
Refresh rate
The refresh rate is the number of times in a second that a display hardware draws the data...
had to be reduced to accommodate these modes, increasing eye strain
Asthenopia
Asthenopia or eye strain is an ophthalmological condition that manifests itself through nonspecific symptoms such as fatigue, pain in or around the eyes, blurred vision, headache and occasional double vision...
. They were also incompatible with some older monitors, producing display problems such as picture detail disappearing into overscan
Overscan
Overscan is extra image area around the four edges of a video image that may not be seen reliably by the viewer. It exists because television sets in the 1930s through 1970s were highly variable in how the video image was framed within the cathode ray tube .-Origins of overscan:Early televisions...
, flicker
Flicker (screen)
Flicker is a visible fading between cycles displayed on video displays, especially the refresh interval on cathode ray tube based computer screens. Flicker occurs on CRTs when they are driven at a low refresh rate, allowing the brightness to drop for time intervals sufficiently long to be noticed...
ing, vertical roll, and lack of horizontal sync
Horizontal scan rate
Horizontal scan rate, or horizontal frequency, usually expressed in kilohertz, is the frequency at which a CRT moves the electron beam from the left side of the display to the right and back, and therefore describes the number of horizontal lines displayed per second...
depending on the mode being attempted. Because of this, most VGA tweaks used in commercial products were limited to "monitor-safe" combinations, such as 320×240 (square pixels, three video pages), 320×400 (double resolution, two video pages), and 360×480 (highest resolution compatible with standard VGA monitors, one video page).
Currently, the highest known tweaked VGA resolution is 400×600×256 (400×600 pixel × 256 colors). It is used in Fractint
Fractint
FractInt is a freeware program that can render and display many kinds of fractals.-Name:Its name comes from the words fractal and integer, since the first versions of it computed fractals by using only integer arithmetic , which led to much faster rendering on x86 computers without math coprocessors...
, a popular fractal generator.
See also
- Graphic display resolutionsGraphic display resolutionsThe graphics display resolution describes the width and height dimensions of a display, such as a computer monitor, in pixels. Certain combinations of width and height are standardized and typically given a name and an initialism that is descriptive of its dimensions...
- List of video connectors
- List of monochrome and RGB palettes
- List of 16-bit computer hardware palettes

