
Enterprise integration
Encyclopedia
Enterprise architecture
An enterprise architecture is a rigorous description of the structure of an enterprise, which comprises enterprise components , the externally visible properties of those components, and the relationships between them...
, which focused on the study of topics such as system interconnection, electronic data interchange, product data exchange and distributed computing environments.
It is a concept in Enterprise engineering
Enterprise engineering
Enterprise engineering is a subdiscipline of systems engineering, which applies the knowledge and methods of systems engineering to the design of businesses. The discipline examines each aspect of the enterprise, including business processes, information flows, and organizational structure...
to provide the right information at the right place and at the right time and thereby enable communication between people, machines and computers and their efficient co-operation and co-ordination.
Overview
Enterprise Integration, according Brosey et al. (2001), "aims to connect and combines people, processes, systems, and technologies to ensure that the right people and the right processes have the right information and the right resources at the right time".Enterprise Integration is focused on optimizing operations in a world which could be considered full of continuous and largely unpredictable change. Changes occur in single manufacturing companies just as well as in an "everchanging set of extended or virtual enterprises". It enables the actors to make "quick and accurate decisions and adaptation of operations to respond to emerging threats and opportunities".
History
Enterprise integration has been discussed since the early days of computers in industry and especially in the manufacturing industry with Computer Integrated ManufacturingComputer Integrated Manufacturing
Computer-integrated manufacturing is the manufacturing approach of using computers to control the entire production process. This integration allows individual processes to exchange information with each other and initiate actions...
(CIM) as the acronym for operations integration. In spite of the different understandings of the scope of integration in CIM it has always stood for information integration
Information integration
Information integration is the merging of information from disparate sources with differing conceptual, contextual and typographical representations. It is used in data mining and consolidation of data from unstructured or semi-structured resources...
across at least parts of the enterprise. Information integration essentially consists of providing the right information, at the right place, at the right time.
In the 1990s enterprise integration and enterprise engineering
Enterprise engineering
Enterprise engineering is a subdiscipline of systems engineering, which applies the knowledge and methods of systems engineering to the design of businesses. The discipline examines each aspect of the enterprise, including business processes, information flows, and organizational structure...
became a focal point of discussions with active contribution of many disciplines. The state of the art in enterprise engineering and integration end 1990s, according to Jim Nell and Kurt Kosanke (1997), has been rather confusing. On one hand it claims to provide solutions for many of the issues identified in enterprise integration. On the other hand the solutions seem to compete with each other, use conflicting terminology and do not provide any clues on their relations to solutions on other issues. Workflow modelling, business process modelling, business process reengineering
Business process reengineering
Business process re-engineering is the analysis and design of workflows and processes within an organization.According to Davenport a business process is a set of logically related tasks performed to achieve a defined business outcome....
(BPR), and concurrent engineering
Concurrent engineering
Concurrent engineering is a work methodology based on the parallelization of tasks . It refers to an approach used in product development in which functions of design engineering, manufacturing engineering and other functions are integrated to reduce the elapsed time required to bring a new product...
all aim toward identifying and providing the information needed in the enterprise operation. In addition, numerous integrating-platforms concepts are promoted with only marginal or no recognition or support of information identification. Tools claiming to support enterprise modelling
Enterprise modelling
Enterprise modelling is the abstract representation, description and definition of the structure, processes, information and resources of an identifiable business, government body, or other large organization....
exist in very large numbers, but the support is rather marginal, especially if models are to be used by the end user, for instance, in decision support.
Enterprise modeling
In his 1996 book "Enterprise Modeling and Integration: Principles and Applications" François VernadatFrançois Vernadat
François B. Vernadat is a French and Canadian computer scientist, who has contributed to Enterprise Modelling, Integration and Networking over the last 25 years specialising in enterprise architectures, business process modelling, information systems design and analysis, systems integration and...
states, that "enterprise modeling is concerned with assessing various aspects of an enterprise in order to better understand, restructure or design enterprise operations. It is the basis of business process reengineering
Business process reengineering
Business process re-engineering is the analysis and design of workflows and processes within an organization.According to Davenport a business process is a set of logically related tasks performed to achieve a defined business outcome....
and the first step to achieving enterprise integration. Enterprise integration according to Vernadat is a rapidly developing technical field which has already shown proven solutions for system interconnection, electronic data interchange, product data exchange and distributed computing environments. His book combines these two methodologies and advocates a systematic engineering approach called Enterprise Engineering, for modeling, analysing, designing and implementing integrated enterprise systems".
Enterprise integration needs
With this understanding the different needs in enterprise integration can be identified:- Identify the right information: requires a precise knowledge of the information needed and created by the different activities in the enterprise operation. Knowledge which has to be structured in the form of an accurate model of the enterprise operation. A model which describes product and administrative information, resources and organisational aspects of the operational processes and allows what-if analysis in order to optimize these processes.
- Provide the right information at the right place: requires information sharing systems and integration platforms capable of handling information transaction across heterogeneous environments. Environments which consists of heterogeneous hardware, different operating systems and monolithic software applications (legacy systems). Environments which cross organizational boundaries and link the operation of different organisations on a temporal basis and with short set-up times and limited time horizon (extended and virtual enterprises).
- Up-date the information in real time to reflect the actual state of the enterprise operation: requires not only the up-date of the operational data (information created during the operation), but adapting to environmental changes as well. Changes which may originate from new customer demands, new technology, new legislation or new philosophies of the society at large. Changes which may require modification of the operational processes, the human organization or even the overall scope and goals of the enterprise.
- Co-ordinate business processes: requires precise modelling of the enterprise operation in terms of business processes, their relations with each other, with information, resources and organisation. This goes far beyond exchange of information and information sharing. It takes into account decisional capabilities and know-how within the enterprise for real time decision support and evaluation of operational alternatives.
- Organize and adapt the enterprise: requires very detailed and up-to-date knowledge of both the current state of the enterprise operation and its environment (market, technology, society). Knowledge which has to be available a priori and very well structured to allow easy identification of and access to relevant information.
Identification and use of information
Explicit knowledge on information needs during the operation of the enterprise can be provided by a model of the operational processes. A model which identifies the operational tasks, their required information supply and removal needs as well as the point in time of required information transactions. In order to enable consistent modelling of the enterprise operation the modelling process has to be guided and supported by a reference architecture, a methodology and IT based tools.The Generalised Enterprise Reference Architecture and Methodology
Generalised Enterprise Reference Architecture and Methodology
Generalised Enterprise Reference Architecture and Methodology is a generalised Enterprise Architecture framework for enterprise integration and business process engineering. It identifies the set of components recommended for use in enterprise engineering.This framework is developed in the 1990s...
(GERAM) framework defined by the IFAC/IFIP Task Force provides the necessary guidance of the modelling process, see figure, and enables semantic unification of the model contents as well. The framework identifies the set of components necessary and helpful for enterprise modelling. The general concepts identified and defined in the reference architecture consist of life cycle, life history, model views among others. these concept help the user to create and maintain the process models of the operation and use them in her/his daily work. The modelling tools will support both model engineering and model use by providing an appropriate methodology and language for guiding the user and model representation, respectively.
Transfer of information
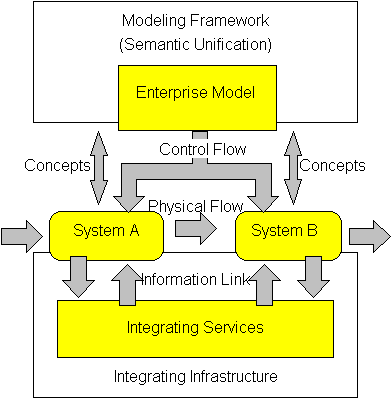
To enable an integrated real time support of the operation, both the process descriptions and the actual information have to be available in real time for decision support, operation monitoring and control, and model maintenance.The figure illustrates the concept of an integrating infrastructure linking the enterprise model to the real world systems. Integrating services act as a harmonising platform across the heterogeneous system environments (IT and others) and provide the necessary execution support for the model. The process dynamics captured in the enterprise model act as the control flow for model enactment. Therefore access to information and its transfer to and from the location of use is controlled by the model and supported by the integrating infrastructure. The harmonising characteristics of the integrating infrastructure enables transfer of information across and beyond the organisation. Through the semantic unification of the modelling framework interoperability of enterprise models is assured as well.
Enterprise Integration Act of 2002
The Public Law 107-277 (116 Stat. 1936-1938), known as the Enterprise Integration Act of 2002, authorizes the National Institute of Standards and TechnologyNational Institute of Standards and Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology , known between 1901 and 1988 as the National Bureau of Standards , is a measurement standards laboratory, otherwise known as a National Metrological Institute , which is a non-regulatory agency of the United States Department of Commerce...
to work with major manufacturing industries on an initiative of standards development and implementation for electronic enterprise integration, etc. It requires the Director of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) to establish an initiative for advancing enterprise integration within the United States which shall:
- involve the various units of NIST, including NIST laboratories, the Manufacturing Extension Partnership program, and the Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Program, and consortia that include government and industry;
- build upon ongoing efforts of NIST and the private sector; and
- address the enterprise integration needs of each major U.S. manufacturing industry at the earliest possible date.
See also
- AMICE ConsortiumAMICE ConsortiumAMICE Consortium was a European organization of major companies, including users, vendors,consulting companies, and academia, from 1985 to 1995, concerned with Computer Integrated Manufacturing...
- Integration ConsortiumIntegration ConsortiumThe Integration Consortium is a global non-profit community that shares knowledge and best practices related to enterprise application integration...
- Canonical ModelCanonical ModelCanonical Model is a design pattern used to communicate between different data formats. A form of Enterprise Application Integration, it is intended to reduce costs and standardize on agreed data definitions associated with integrating business systems. A Canonical Model is any model that is...
- CIMOSACIMOSACIMOSA stands for "Computer Integrated Manufacturing Open System Architecture", is a enterprise modeling framework, which aims to support the enterprise integration of machines, computers and people...
- Configuration ManagementConfiguration managementConfiguration management is a field of management that focuses on establishing and maintaining consistency of a system or product's performance and its functional and physical attributes with its requirements, design, and operational information throughout its life.For information assurance, CM...
- Data integrationData integrationData integration involves combining data residing in different sources and providing users with a unified view of these data.This process becomes significant in a variety of situations, which include both commercial and scientific domains...
- Enterprise application integrationEnterprise application integrationEnterprise Application Integration is defined as the use of software and computer systems architectural principles to integrate a set of enterprise computer applications.- Overview :...
- Enterprise Information IntegrationEnterprise Information IntegrationEnterprise Information Integration , is a process of information integration, using data abstraction to provide a unified interface for viewing all the data within an organization, and a single set of structures and naming conventions to represent this data; the goal of EII is to get a large set of...
- Generalised Enterprise Reference Architecture and MethodologyGeneralised Enterprise Reference Architecture and MethodologyGeneralised Enterprise Reference Architecture and Methodology is a generalised Enterprise Architecture framework for enterprise integration and business process engineering. It identifies the set of components recommended for use in enterprise engineering.This framework is developed in the 1990s...
- Semantic integrationSemantic integrationSemantic integration is the process of interrelating information from diverse sources, for example calendars and to do lists; email archives; physical, psychological, and social presence information; documents of all sorts; contacts ; search results; and advertising and marketing relevance derived...
- Semantic UnificationSemantic unificationSemantic unification, in philosophy, linguistics, and computer science, is the process of unifying lexically different concept representations that are judged to have the same semantic content ....
Further reading
- Peter BernusPeter BernusPeter Bernus is an Hungarian Australian scientist and Associate Professor of Enterprise Architecture at the School of Information and Communication Technology, Griffith University, Brisbane, Australia.- Biography :...
and L. Nemes (ed.). (1995). Modelling and Methodologies for Enterprise Integration: Proceedings of the IFIP TC5 Working Conference on Models and Methodologies for Enterprise Integration, Queensland, Australia, November 1995. Chapman & Hall. ISBN 0412756307. - Peter BernusPeter BernusPeter Bernus is an Hungarian Australian scientist and Associate Professor of Enterprise Architecture at the School of Information and Communication Technology, Griffith University, Brisbane, Australia.- Biography :...
et al. (1996). Architectures for Enterprise Integration. Springer. ISBN 0412731401 - Fred A. Cummins (2002). Enterprise Integration: An Architecture for Enterprise Application and Systems Integration. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0471400106
- Charles J. Petrie (1992). Enterprise Integration Modeling: Proceedings of the First International Conference. MIT Press. ISBN 0262660806
- Kent Sandoe, Gail Corbitt, Raymond Boykin, Aditya Saharia (2001). Enterprise Integration. Wiley, ISBN 047135993.
External links
- IFIP/IFAC Task Force on Enterprise Integration, a short overview of their activities in the 1990s.

