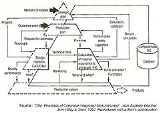
Computer Integrated Manufacturing
Encyclopedia
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the use of machines, tools and labor to produce goods for use or sale. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech, but is most commonly applied to industrial production, in which raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale...
approach of using computer
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
s to control the entire production process
Process (engineering)
In engineering a process is a set of interrelated tasks that, together, transform inputs into outputs. These tasks may be carried out by people, nature, or machines using resources; so an engineering process must be considered in the context of the agents carrying out the tasks, and the resource...
. This integration allows individual processes to exchange information with each other and initiate actions. Through the integration of computers, manufacturing can be faster and less error-prone, although the main advantage is the ability to create automated manufacturing processes. Typically CIM relies on closed-loop control processes, based on real-time input from sensors. It is also known as flexible design and manufacturing.
Overview
The term "computer-integrated manufacturing" is both a method of manufacturing and the name of a computer-automated system in which individual engineering, production, marketing, and support functions of a manufacturingManufacturing
Manufacturing is the use of machines, tools and labor to produce goods for use or sale. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech, but is most commonly applied to industrial production, in which raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale...
enterprise are organized. In a CIM system functional areas such as design, analysis, planning, purchasing, cost accounting, inventory control, and distribution are linked through the computer with factory floor functions such as materials handling and management, providing direct control and monitoring of all the operations.
As a method of manufacturing, three components distinguish CIM from other manufacturing methodologies:
- Means for data storage, retrieval, manipulation and presentation;
- Mechanisms for sensing state and modifying processes;
- Algorithms for uniting the data processing component with the sensor/modification component.
CIM is an example of the implementation of information and communication technologies
Information and communication technologies
Information and communications technology or information and communication technology, usually abbreviated as ICT, is often used as an extended synonym for information technology , but is usually a more general term that stresses the role of unified communications and the integration of...
(ICTs) in manufacturing.
CIM implies that there are at least two computers exchanging information, e.g. the controller of an arm robot and a micro-controller of a CNC machine.
Some factors involved when considering a CIM implementation are the production volume, the experience of the company or personnel to make the integration, the level of the integration into the product itself and the integration of the production processes. CIM is most useful where a high level of ICT is used in the company or facility, such as CAD/CAM systems, the availability of process planning and its data.
History
The idea of "digital manufacturing" was prominent the 1980s, when computer-integrated manufacturing was developed and promoted by machine tool manufacturers and the Computer and Automated Systems Association and Society of Manufacturing EngineersSociety of Manufacturing Engineers
The Society of Manufacturing Engineers is a non-profit organization.-History of the Society:Founded in 1932 with 33 members, the organization was originally named The Society of Tool Engineers . A year later, it was renamed the American Society of Tool Engineers...
(CASA/SME).
- "CIM is the integration of total manufacturing enterprise by using integrated systems and data communication coupled with new managerial philosophies that improve organizational and personnel efficiency." ERHUM
Computer-integrated manufacturing topics
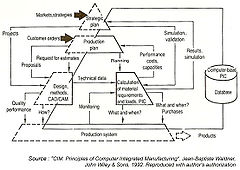
Key challenges
There are three major challenges to development of a smoothly operating computer-integrated manufacturing system:- Integration of components from different suppliers: When different machines, such as CNC, conveyors and robots, are using different communications protocols. In the case of AGVAutomated Guided VehicleAn automated guided vehicle or automatic guided vehicle is a mobile robot that follows markers or wires in the floor, or uses vision or lasers. They are most often used in industrial applications to move materials around a manufacturing facility or a warehouse...
s, even differing lengths of time for charging the batteries may cause problems.
- Data integrityData integrityData Integrity in its broadest meaning refers to the trustworthiness of system resources over their entire life cycle. In more analytic terms, it is "the representational faithfulness of information to the true state of the object that the information represents, where representational faithfulness...
: The higher the degree of automation, the more critical is the integrity of the data used to control the machines. While the CIM system saves on labor of operating the machines, it requires extra human labor in ensuring that there are proper safeguards for the data signals that are used to control the machines.
- Process controlProcess controlProcess control is a statistics and engineering discipline that deals with architectures, mechanisms and algorithms for maintaining the output of a specific process within a desired range...
: Computers may be used to assist the human operators of the manufacturing facility, but there must always be a competent engineer on hand to handle circumstances which could not be foreseen by the designers of the control software.
Subsystems in computer-integrated manufacturing
A computer-integrated manufacturing system is not the same as a "lights-out" factory, which would run completely independent of human intervention, although it is a big step in that direction. Part of the system involves flexible manufacturingFlexible manufacturing system
A flexible manufacturing system is a manufacturing system in which there is some amount of flexibility that allows the system to react in the case of changes, whether predicted or unpredicted...
, where the factory can be quickly modified to produce different products, or where the volume of products can be changed quickly with the aid of computers. Some or all of the following subsystems may be found in a CIM operation:
Computer-aided techniques:
- CAD (computer-aided designComputer-aided designComputer-aided design , also known as computer-aided design and drafting , is the use of computer technology for the process of design and design-documentation. Computer Aided Drafting describes the process of drafting with a computer...
) - CAE (computer-aided engineeringComputer-aided engineeringComputer-aided engineering is the broad usage of computer software to aid in engineering tasks. It includes computer-aided design , computer-aided analysis , computer-integrated manufacturing , computer-aided manufacturing , material requirements planning , and computer-aided planning .- Overview...
) - CAM (computer-aided manufacturingComputer-aided manufacturingComputer-aided manufacturing is the use of computer software to control machine tools and related machinery in the manufacturing of workpieces. This is not the only definition for CAM, but it is the most common; CAM may also refer to the use of a computer to assist in all operations of a...
) - CAPP (computer-aided process planning)
- CAQ (computer-aided quality assurance)
- PPC (production planning and controlProject management softwareProject management software is a term covering many types of software, including estimation and planning, scheduling, cost control and budget management, resource allocation, collaboration software, communication, quality management and documentation or administration systems, which are used to...
) - ERP (enterprise resource planningEnterprise resource planningEnterprise resource planning systems integrate internal and external management information across an entire organization, embracing finance/accounting, manufacturing, sales and service, customer relationship management, etc. ERP systems automate this activity with an integrated software application...
) - A business system integrated by a common database.
Devices and equipment required:
- CNC, Computer numerical controlled machine tools
- DNCDirect Numerical ControlDirect numerical control , also known as distributed numerical control , is a common manufacturing term for networking CNC machine tools...
, Direct numerical control machine tools - PLCsProgrammable logic controllerA programmable logic controller or programmable controller is a digital computer used for automation of electromechanical processes, such as control of machinery on factory assembly lines, amusement rides, or light fixtures. PLCs are used in many industries and machines...
, Programmable logic controllers - RobotRobotA robot is a mechanical or virtual intelligent agent that can perform tasks automatically or with guidance, typically by remote control. In practice a robot is usually an electro-mechanical machine that is guided by computer and electronic programming. Robots can be autonomous, semi-autonomous or...
ics - ComputerComputerA computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
s - Software
- ControllersController (computing)In computing and especially in computer hardware, controller is a chip, an expansion card, or a stand-alone device that interfaces with a peripheral device...
- NetworksComputer networkA computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information....
- InterfacingInterfacingInterfacing is a textile used on the unseen or "wrong" side of fabrics to make an area of a garment more rigid.Interfacings can be used to:*stiffen or add body to fabric, such as the interfacing used in shirt collars...
- Monitoring equipment
Technologies:
- FMS, (flexible manufacturing systemFlexible manufacturing systemA flexible manufacturing system is a manufacturing system in which there is some amount of flexibility that allows the system to react in the case of changes, whether predicted or unpredicted...
) - ASRS, automated storage and retrieval systemAutomated Storage and Retrieval SystemAn automated storage and retrieval system consists of a variety of computer-controlled methods for automatically placing and retrieving loads from specific storage locations...
- AGV, automated guided vehicleAutomated Guided VehicleAn automated guided vehicle or automatic guided vehicle is a mobile robot that follows markers or wires in the floor, or uses vision or lasers. They are most often used in industrial applications to move materials around a manufacturing facility or a warehouse...
- RoboticsRoboticsRobotics is the branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation, structural disposition, manufacture and application of robots...
- Automated conveyance systems
Others:
- Lean manufacturingLean manufacturingLean manufacturing, lean enterprise, or lean production, often simply, "Lean," is a production practice that considers the expenditure of resources for any goal other than the creation of value for the end customer to be wasteful, and thus a target for elimination...
CIMOSA
CIMOSACIMOSA
CIMOSA stands for "Computer Integrated Manufacturing Open System Architecture", is a enterprise modeling framework, which aims to support the enterprise integration of machines, computers and people...
(Computer Integrated Manufacturing Open System Architecture), is a 1990s European proposal for an open system architecture for CIM developed by the AMICE Consortium
AMICE Consortium
AMICE Consortium was a European organization of major companies, including users, vendors,consulting companies, and academia, from 1985 to 1995, concerned with Computer Integrated Manufacturing...
as a series of ESPRIT projects. The goal of CIMOSA was "to help companies to manage change and integrate their facilities and operations to face world wide competition. It provides a consistent architectural framework for both enterprise modeling and enterprise integration
Enterprise integration
Enterprise integration is a technical field of Enterprise Architecture, which focused on the study of topics such as system interconnection, electronic data interchange, product data exchange and distributed computing environments....
as required in CIM environments".
CIMOSA provides a solution for business integration with four types of products:
- The CIMOSA Enterprise Modeling Framework, which provides a reference architecture for enterprise architectureEnterprise architectureAn enterprise architecture is a rigorous description of the structure of an enterprise, which comprises enterprise components , the externally visible properties of those components, and the relationships between them...
- CIMOSA IIS, a standard for physical and application integration.
- CIMOSA Systems Life Cycle, is a life cycle model for CIM development and deployment.
- Inputs to standardization, basics for international standard development.
CIMOSA according to Vernadat (1996), coined the term business process
Business process
A business process or business method is a collection of related, structured activities or tasks that produce a specific service or product for a particular customer or customers...
and introduced the process-based approach for integrated enterprise modeling based on a cross-boundaries approach, which opposed to traditional function
Function model
A function model or functional model in systems engineering and software engineering is a structured representation of the functions within the modeled system or subject area....
or activity-based approaches. With CIMOSA also the concept of an "Open System Architecture" (OSA) for CIM was introduced, which was designed to be vendor-independent, and constructed with standardised CIM modules. Here to the OSA is "described in terms of their function, information, resource, and organizational aspects. This should be designed with structured engineering methods and made operational in a modular and evolutionary architecture for operational use".
Application
There are multiple areas of usage:- In mechanical engineeringMechanical engineeringMechanical engineering is a discipline of engineering that applies the principles of physics and materials science for analysis, design, manufacturing, and maintenance of mechanical systems. It is the branch of engineering that involves the production and usage of heat and mechanical power for the...
- In electronic design automationElectronic design automationElectronic design automation is a category of software tools for designing electronic systems such as printed circuit boards and integrated circuits...
(printed circuit boardPrinted circuit boardA printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
(PCB) and integrated circuitIntegrated circuitAn integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
design data for manufacturing)
See also
- Direct numerical controlDirect Numerical ControlDirect numerical control , also known as distributed numerical control , is a common manufacturing term for networking CNC machine tools...
- Enterprise integrationEnterprise integrationEnterprise integration is a technical field of Enterprise Architecture, which focused on the study of topics such as system interconnection, electronic data interchange, product data exchange and distributed computing environments....
- Enterprise resource planningEnterprise resource planningEnterprise resource planning systems integrate internal and external management information across an entire organization, embracing finance/accounting, manufacturing, sales and service, customer relationship management, etc. ERP systems automate this activity with an integrated software application...
- Flexible manufacturing systemFlexible manufacturing systemA flexible manufacturing system is a manufacturing system in which there is some amount of flexibility that allows the system to react in the case of changes, whether predicted or unpredicted...
- Integrated Computer-Aided ManufacturingIntegrated Computer-aided manufacturingIntegrated Computer-Aided Manufacturing is a US Air Force program to develop tools, techniques, and processes to support manufacturing integration and has influenced the computer-integrated manufacturing and computer-aided manufacturing project efforts of many companies.The ICAM program was...
- Integrated manufacturing databaseIntegrated manufacturing databaseAn integrated database system can be used by small and large businesses as a means to incorporate IT in the manufacturing process. It updates, stores and records information, with a view to rapid retrieval.Some examples of could include:...
- Manufacturing process managementManufacturing Process ManagementManufacturing process management is a collection of technologies and methods used to define how products are to be manufactured. MPM differs from ERP/MRP which is used to plan the ordering of materials and other resources, set manufacturing schedules, and compile cost data.A cornerstone of MPM is...
- Product lifecycle managementProduct lifecycle managementIn industry, product lifecycle management is the process of managing the entire lifecycle of a product from its conception, through design and manufacture, to service and disposal...
Further reading
- Yoram Korem, Computer Control of Manufacturing Systems, McGraw Hill, Inc. 1983, 287 pp, ISBN 0-07-035341-7
- Singh, V (1997). The Cim Debacle: Methodologies to Facilitate Software Interoperability. Springer. ISBN 9813083212.
- A. de Toni and S. Tonchia, Manufacturing Flexibility: a literature review International Journal of Production Research, 1998, vol. 36, no. 6, 1587-617.
- Jean-Baptiste Waldner (1992), Principles of Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 047193450X
- Jean-Baptiste Waldner (1990), CIM, les nouvelles perspectives de la production, DUNOD- BORDAS, ISBN 9782040198206

