
Error vector magnitude
Encyclopedia
The error vector magnitude or EVM (sometimes also called receive constellation error or RCE) is a measure used to quantify the performance of a digital radio transmitter or receiver. A signal sent by an ideal transmitter or received by a receiver would have all constellation points
precisely at the ideal locations, however various imperfections in the implementation (such as carrier leakage, low image rejection ratio
, phase noise
etc.) cause the actual constellation points to deviate from the ideal locations. Informally, EVM is a measure of how far the points are from the ideal locations.
Transmitter EVM can be measured by specialised equipment, which demodulates
the received signal in a similar way to how a real radio
demodulator does it. One of the stages in a typical phase-shift keying
demodulation process produces a stream of I-Q points which can be used as a reasonably reliable estimate for the ideal transmitted signal in EVM calculation.
(RMS) average is used.
The error vector magnitude is equal to the ratio of the power of the error vector to the root mean square
(RMS) power of the reference. It is defined in dB
as:
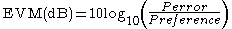
where Perror is the RMS power of the error vector. For single carrier modulations, Preference is, by convention, the power of the outermost (highest power) point in the reference signal constellation. More recently, for multi-carrier modulations, Preference is defined as the reference constellation average power.
EVM is defined as a percentage
in a compatible way:
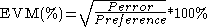
with the same definitions.
EVM, as conventionally defined for single carrier modulations, is a ratio of a mean power to a peak power. Because the relationship between the peak and mean signal power is dependent on constellation geometry, different constellation types (e.g. 16-QAM and 64-QAM), subject to the same mean level of interference, will report different EVM values.
EVM, as defined for multi carrier modulations, is arguably the more satisfactory measurement because it is a ratio of two mean powers and is insensitive to the constellation geometry. In this form, EVM is closely related to Modulation error ratio
, the ratio of mean signal power to mean error power.
Constellation diagram
A constellation diagram is a representation of a signal modulated by a digital modulation scheme such as quadrature amplitude modulation or phase-shift keying. It displays the signal as a two-dimensional scatter diagram in the complex plane at symbol sampling instants...
precisely at the ideal locations, however various imperfections in the implementation (such as carrier leakage, low image rejection ratio
Image rejection ratio
In radio, the image rejection ratio, or image frequency rejection ratio, is the ratio of the intermediate-frequency signal level produced by the desired input frequency to that produced by the image frequency. The image rejection ratio is usually expressed in dB...
, phase noise
Phase noise
Phase noise is the frequency domain representation of rapid, short-term, random fluctuations in the phase of a waveform, caused by time domain instabilities...
etc.) cause the actual constellation points to deviate from the ideal locations. Informally, EVM is a measure of how far the points are from the ideal locations.
Transmitter EVM can be measured by specialised equipment, which demodulates
Demodulation
Demodulation is the act of extracting the original information-bearing signal from a modulated carrier wave.A demodulator is an electronic circuit that is used to recover the information content from the modulated carrier wave.These terms are traditionally used in connection with radio receivers,...
the received signal in a similar way to how a real radio
Radio
Radio is the transmission of signals through free space by modulation of electromagnetic waves with frequencies below those of visible light. Electromagnetic radiation travels by means of oscillating electromagnetic fields that pass through the air and the vacuum of space...
demodulator does it. One of the stages in a typical phase-shift keying
Phase-shift keying
Phase-shift keying is a digital modulation scheme that conveys data by changing, or modulating, the phase of a reference signal ....
demodulation process produces a stream of I-Q points which can be used as a reasonably reliable estimate for the ideal transmitted signal in EVM calculation.
Definition
An error vector is a vector in the I-Q plane between the ideal constellation point and the point received by the receiver. In other words, it is the difference between actual received symbols and ideal symbols. The average power of the error vector, normalized to signal power, is the EVM. For the percentage format, root mean squareRoot mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
(RMS) average is used.
The error vector magnitude is equal to the ratio of the power of the error vector to the root mean square
Root mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
(RMS) power of the reference. It is defined in dB
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
as:
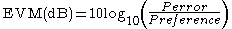
where Perror is the RMS power of the error vector. For single carrier modulations, Preference is, by convention, the power of the outermost (highest power) point in the reference signal constellation. More recently, for multi-carrier modulations, Preference is defined as the reference constellation average power.
EVM is defined as a percentage
Percentage
In mathematics, a percentage is a way of expressing a number as a fraction of 100 . It is often denoted using the percent sign, “%”, or the abbreviation “pct”. For example, 45% is equal to 45/100, or 0.45.Percentages are used to express how large/small one quantity is, relative to another quantity...
in a compatible way:
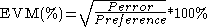
with the same definitions.
EVM, as conventionally defined for single carrier modulations, is a ratio of a mean power to a peak power. Because the relationship between the peak and mean signal power is dependent on constellation geometry, different constellation types (e.g. 16-QAM and 64-QAM), subject to the same mean level of interference, will report different EVM values.
EVM, as defined for multi carrier modulations, is arguably the more satisfactory measurement because it is a ratio of two mean powers and is insensitive to the constellation geometry. In this form, EVM is closely related to Modulation error ratio
Modulation error ratio
The modulation error ratio or MER is a measure used to quantify the performance of a digital radio transmitter or receiver in a communications system using digital modulation...
, the ratio of mean signal power to mean error power.
See also
- Modulation error ratioModulation error ratioThe modulation error ratio or MER is a measure used to quantify the performance of a digital radio transmitter or receiver in a communications system using digital modulation...
- Carrier to Noise Ratio
- Signal-to-noise ratioSignal-to-noise ratioSignal-to-noise ratio is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. It is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power. A ratio higher than 1:1 indicates more signal than noise...

