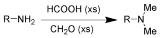
Eschweiler-Clarke reaction
Overview
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
whereby a primary (or secondary) amine
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
is methylated using excess formic acid
Formic acid
Formic acid is the simplest carboxylic acid. Its chemical formula is HCOOH or HCO2H. It is an important intermediate in chemical synthesis and occurs naturally, most notably in the venom of bee and ant stings. In fact, its name comes from the Latin word for ant, formica, referring to its early...
and formaldehyde
Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula CH2O. It is the simplest aldehyde, hence its systematic name methanal.Formaldehyde is a colorless gas with a characteristic pungent odor. It is an important precursor to many other chemical compounds, especially for polymers...
. Reductive amination
Reductive amination
Reductive amination is a form of amination that involves the conversion of a carbonyl group to an amine via an intermediate imine...
reactions such as this one will not produce quaternary ammonium salts, but instead will stop at the tertiary amine stage. It is named for the German chemist Wilhelm Eschweiler (1860–1936) and the British chemist Hans Thacher Clarke
Hans Thacher Clarke
Hans Thacher Clarke was one of the world's leading biochemists.His father, Joseph Thacher Clarke, was an archaeologist who was friendly with George Eastman of the Kodak company...
(1887-1972).
The first methylation of the amine begins with imine
Imine
An imine is a functional group or chemical compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond, with the nitrogen attached to a hydrogen atom or an organic group. If this group is not a hydrogen atom, then the compound is known as a Schiff base...
formation with formaldehyde.
Unanswered Questions

