
Estradiol 17alpha-dehydrogenase
Encyclopedia
In enzymology, an estradiol 17alpha-dehydrogenase is an enzyme
that catalyzes
the chemical reaction
The three substrates
of this enzyme are estradiol-17alpha, NAD+
, and NADP+
, whereas its four products
are estrone
, NADH
, NADPH
, and H+
.
This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductase
s, specifically those acting on the CH-OH group of donor with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is 17alpha-hydroxysteroid:NAD(P)+ 17-oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include 17alpha-estradiol dehydrogenase, 17alpha-hydroxy steroid dehydrogenase, 17alpha-hydroxy steroid oxidoreductase, 17alpha-hydroxysteroid oxidoreductase, and estradiol 17alpha-oxidoreductase. This enzyme participates in androgen
and estrogen
metabolism.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
- estradiol-17alpha + NAD(P)+
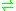 estrone + NAD(P)H + H+
estrone + NAD(P)H + H+
The three substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are estradiol-17alpha, NAD+
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, abbreviated NAD, is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, since it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide.In metabolism, NAD is involved...
, and NADP+
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or TPN in older notation , is a coenzyme used in anabolic reactions, such as lipid and nucleic acid synthesis, which require NADPH as a reducing agent....
, whereas its four products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
are estrone
Estrone
Estrone is an estrogenic hormone secreted by the ovary as well as adipose tissue.Estrone is one of several natural estrogens, which also include estriol and estradiol...
, NADH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, abbreviated NAD, is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, since it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide.In metabolism, NAD is involved...
, NADPH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or TPN in older notation , is a coenzyme used in anabolic reactions, such as lipid and nucleic acid synthesis, which require NADPH as a reducing agent....
, and H+
Hydrogen ion
Hydrogen ion is recommended by IUPAC as a general term for all ions of hydrogen and its isotopes.Depending on the charge of the ion, two different classes can be distinguished: positively charged ions and negatively charged ions....
.
This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductase
Oxidoreductase
In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule to another...
s, specifically those acting on the CH-OH group of donor with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is 17alpha-hydroxysteroid:NAD(P)+ 17-oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include 17alpha-estradiol dehydrogenase, 17alpha-hydroxy steroid dehydrogenase, 17alpha-hydroxy steroid oxidoreductase, 17alpha-hydroxysteroid oxidoreductase, and estradiol 17alpha-oxidoreductase. This enzyme participates in androgen
Androgen
Androgen, also called androgenic hormone or testoid, is the generic term for any natural or synthetic compound, usually a steroid hormone, that stimulates or controls the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors...
and estrogen
Estrogen
Estrogens , oestrogens , or œstrogens, are a group of compounds named for their importance in the estrous cycle of humans and other animals. They are the primary female sex hormones. Natural estrogens are steroid hormones, while some synthetic ones are non-steroidal...
metabolism.

