.gif)
Excitation (magnetic)
Encyclopedia

Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
consists of a rotor
Rotor (electric)
The rotor is the non-stationary part of a rotary electric motor, electric generator or alternator, which rotates because the wires and magnetic field of the motor are arranged so that a torque is developed about the rotor's axis. In some designs, the rotor can act to serve as the motor's armature,...
spinning in a magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
. The magnetic field may be produced by permanent magnets or by field coil
Field coil
A field coil is a component of an electro-magnetic machine, typically a rotating electrical machine such as a motor or generator. A current-carrying coil is used to generate a magnetic field....
s. In the case of a machine with field coils, a current must flow in the coils to generate the field, otherwise no power is transferred to or from the rotor. The process of generating a magnetic field by means of an electric current is called excitation.
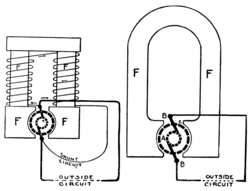
Excitation in generators
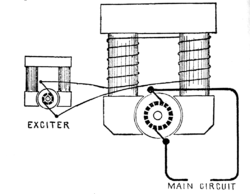
Amplifier principle
Except for permanent magnet generatorMagneto (generator)
A magneto is an electrical generator that uses permanent magnets to produce alternating current. Unlike a dynamo, there is no commutator and so they cannot produce direct current...
s, a generator produces output voltage proportional to the magnetic field, which is proportional to the excitation current; if there is no excitation current there is zero voltage. A generator
Generator
Generator may refer to:* Electrical generator* Engine-generator, an electrical generator, but with its own engine.* Generator , any of several closely related usages in mathematics.Computing:...
can thus be considered as an amplifier: a small amount of power may control a large amount of power. This principle is very useful for voltage control: if the system voltage is low, excitation can be increased; if the system voltage is high, excitation can be decreased. A synchronous condenser operates on the same principle, but there is no "prime mover" power input; however, the "flywheel effect" means that it can send or receive power over short periods of time. To avoid damage to the machine through erratic current changes, a ramp generator
Ramp generator
In electronics and electrical engineering, a ramp generator is a function generator that increases its output voltage up to a specific value, called a ramp. Among multitude of other uses, it is used in electrical generators or electric motors to avoid jolts when changing a load...
is often used.
Separate excitation
For large, or older, generators, it is usual for a separate exciter dynamo to be operated in conjunction with the main power generator. This is a small permanent-magnet or battery-excited dynamo that produces the field current for the larger generator.Self excitation
Modern generators with field coils are self-excited, where some of the power output from the rotor is used to power the field coils. The rotor iron retains a residual magnetismMagnetism
Magnetism is a property of materials that respond at an atomic or subatomic level to an applied magnetic field. Ferromagnetism is the strongest and most familiar type of magnetism. It is responsible for the behavior of permanent magnets, which produce their own persistent magnetic fields, as well...
when the generator is turned off. The generator is started with no load connected; the initial weak field creates a weak voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
in the stator coils, which in turn increases the field current, until the machine "builds up" to full voltage.
Starting
Self-excited generators must be started without any external load attached. An external load will continuously drain off the buildup voltage and prevent the generator from reaching its proper operating voltage.
Field flashing
If the machine does not have enough residual magnetism to build up to full voltage, usually provision is made to inject current into the rotor from another source. This may be a battery
Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
, a house unit providing direct current
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
, or rectified
Rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
current from a source of alternating current
Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
power. Since this initial current is required for a very short time, it is called "field flashing". Even small portable generator sets
Engine-generator
An engine-generator is the combination of an electrical generator and an engine mounted together to form a single piece of equipment. This combination is also called an engine-generator set or a gen-set...
may occasionally need field flashing to restart.
The critical field resistance is the maximum field circuit resistance for a given speed with which the shunt generator would excite. The shunt generator will build up voltage only if field circuit resistance is less than critical field resistance. It is a tangent to the open circuit characteristics of the generator at a given speed.
See also
- AlternatorAlternatorAn alternator is an electromechanical device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating current.Most alternators use a rotating magnetic field but linear alternators are occasionally used...
- Electric generator
- Electric motorElectric motorAn electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
- Magneto (generator)Magneto (generator)A magneto is an electrical generator that uses permanent magnets to produce alternating current. Unlike a dynamo, there is no commutator and so they cannot produce direct current...

