
Exhaled nitric oxide
Encyclopedia
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
, exhaled nitric oxide (eNO) can be measured in a breath test
Breath test
A breath test is a type of test performed on air generated from the act of exhalation.Types include:*Breathalyzer - By far the most common usage of this term relates to the legal breath test to determine if a person is driving under the influence of alcohol.*Hydrogen breath test - it is becoming...
for asthma
Asthma
Asthma is the common chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and bronchospasm. Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath...
or other conditions characterized by airway
Airway
The pulmonary airway comprises those parts of the respiratory system through which air flows, conceptually beginning at the nose and mouth, and terminating in the alveoli...
inflammation
Inflammation
Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process...
. Nitric oxide
Nitric oxide
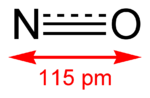
Nitric oxide, also known as nitrogen monoxide, is a diatomic molecule with chemical formula NO. It is a free radical and is an important intermediate in the chemical industry...
(NO) is a gaseous molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
produced by certain cell
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
types in an inflammatory response. The fraction of exhaled NO (FENO)is a promising biomarker for the diagnosis, follow-up and as a guide to therapy in adults and children with asthma. The breath test has recently become available in many well-equipped hospitals in developed countries, although its exact role remains unclear.
Biology
In humans, nitric oxide is produced from L-arginine by three enzymes called nitric oxide synthaseNitric oxide synthase
Nitric oxide synthases are a family of enzymes that catalyze the production of nitric oxide from L-arginine. NO is an important cellular signaling molecule, having a vital role in many biological processes...
s (NOS): inducible (iNOS), endothelial (eNOS
Endothelial NOS
Endothelial NOS , also known as nitric oxide synthase 3 or constitutive NOS , is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NOS3 gene....
), and neuronal (nNOS). The latter two are constantly active in endothelial cells and neuron
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
s respectively, whereas iNOS' action can be induced in states like inflammation (for example, by cytokines). In inflammation, several cells use iNOS to produce NO, including eosinophils. As such, eNO has been dubbed an inflammometer.
Although iNOS is thought to be the main contributor to exhaled NO in asthmatics, studies in mice also point to a role for nNOS.
It was initially thought that exhaled NO derived mostly from the sinuses, which contain high levels of NO. It has subsequently been shown that the lower airways contribute most of the exhaled NO, and that contamination from the sinuses is minimal.
Asthma
Patients with asthmaAsthma
Asthma is the common chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and bronchospasm. Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath...
have higher eNO levels than other people. Their levels also rise together with other clinical and laboratory parameters of asthma (for example, the amount of eosinophils in their sputum
Sputum
Sputum is mucus that is coughed up from the lower airways. It is usually used for microbiological investigations of respiratory infections....
). In conditions that trigger inflammation such as upper respiratory tract infection
Upper respiratory tract infection
Upper respiratory tract infections are the illnesses caused by an acute infection which involves the upper respiratory tract: nose, sinuses, pharynx or larynx...
s or the inhalation of allergen
Allergen
An allergen is any substance that can cause an allergy. In technical terms, an allergen is a non-parasitic antigen capable of stimulating a type-I hypersensitivity reaction in atopic individuals....
s or plicatic acid
Plicatic acid
Plicatic acid is a carboxylic acid from the resin acid group. It is naturally found in thuja and cypress resin. It is the main irritant and contact allergen present in thuja wood...
, eNO levels rise. The eNO levels also tend to vary according to the results of lung function test results such as the degree of bronchial hyperresponsiveness
Bronchial hyperresponsiveness
Bronchial hyperresponsiveness is a state characterised by easily triggered bronchospasm ....
. Furthermore, drugs used to treat asthma (such as inhaled glucocorticoids or leukotriene receptor antagonists) also reduce eNO levels.
Clinical trial
Clinical trial
Clinical trials are a set of procedures in medical research and drug development that are conducted to allow safety and efficacy data to be collected for health interventions...
s have looked at whether tailoring asthma therapy based on eNO values is better than conventional care, in which therapy is gauged by symptoms and the results of lung function tests. To date, the results in both adults and children have been modest and this technique can not be universally recommended. It has also been noted that factors other than inflammation can increase eNO levels, for example airway acidity.
The fraction of eNO has been found to be a better test to identify asthmatics than basic lung function testing (for airway obstruction). Its specificity
Sensitivity and specificity
Sensitivity and specificity are statistical measures of the performance of a binary classification test, also known in statistics as classification function. Sensitivity measures the proportion of actual positives which are correctly identified as such Sensitivity and specificity are statistical...
is comparable to bronchial challenge test
Bronchial challenge test
A bronchial challenge test is a medical test used to assist in the diagnosis of asthma. The patient breathes in nebulized methacholine or histamine. Thus the test may also be called a methacholine challenge test or histamine challenge test respectively. Both drugs provoke bronchoconstriction, or...
ing, although less sensitive
Sensitivity and specificity
Sensitivity and specificity are statistical measures of the performance of a binary classification test, also known in statistics as classification function. Sensitivity measures the proportion of actual positives which are correctly identified as such Sensitivity and specificity are statistical...
. This means that eNO might not be as useful to rule in a diagnosis of asthma as it might be useful to rule it out.
Other conditions
The role for eNO in other conditions is even less well established compared to asthma.Since asthma can be a cause of chronic coughing (it may even be the sole manifestation, such as in cough-variant asthma), studies have looked at whether eNO can be used in the diagnosis of chronic cough.
Exhaled NO is minimally increased in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, but levels may rise in sudden worsenings of the disease (acute exacerbations) or disease progression. Early findings indicate a possible role for eNO in predicting the response to inhaled glucocorticoids and the degree of airway obstruction reversibility.
Children with cystic fibrosis have been found to have low eNO levels. In subjects with bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis is a disease state defined by localized, irreversible dilation of part of the bronchial tree caused by destruction of the muscle and elastic tissue. It is classified as an obstructive lung disease, along with emphysema, bronchitis, asthma, and cystic fibrosis...
(a state of localized, irreversible dilatation of part of the bronchial tree) not due to cystic fibrosis, high levels have been found. Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis , also called sarcoid, Besnier-Boeck disease or Besnier-Boeck-Schaumann disease, is a disease in which abnormal collections of chronic inflammatory cells form as nodules in multiple organs. The cause of sarcoidosis is unknown...
could also feature increased eNO. Low levels have been found in primary ciliary dyskinesia
Primary ciliary dyskinesia
Primary ciliary dyskinesia , also known as immotile ciliary syndrome or Kartagener Syndrome ', is a rare, ciliopathic, autosomal recessive genetic disorder that causes a defect in the action of the cilia lining the respiratory tract and fallopian tube, and also of the flagella of sperm in...
, bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia is a chronic lung disorder that is most common among children who were born prematurely, with low birthweights and who received prolonged mechanical ventilation to treat respiratory distress syndrome...
, and pulmonary arterial hypertension. In the latter condition, inhaled NO is used as a diagnostic test of the response of the pulmonary arteries to vasodilators (agents that relax the blood vessels).
Exposure to air pollution has been associated with decreased, and increased eNO levels.
Measurement techniques

Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
that produces light
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
; this is called a chemiluminescence reaction. The NO in the breath sample reacts with ozone
Ozone
Ozone , or trioxygen, is a triatomic molecule, consisting of three oxygen atoms. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope...
to form nitrogen dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide is the chemical compound with the formula it is one of several nitrogen oxides. is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of nitric acid, millions of tons of which are produced each year. This reddish-brown toxic gas has a characteristic sharp, biting odor and is a prominent...
in an excited state
Excited state
Excitation is an elevation in energy level above an arbitrary baseline energy state. In physics there is a specific technical definition for energy level which is often associated with an atom being excited to an excited state....
. When this returns to its ground state, it emits light in quantities that are proportional
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is a branch of chemistry that deals with the relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions. In a balanced chemical reaction, the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of whole numbers...
to the amount of exhaled NO.
The subject can exhale directly into a measurement device ('online' technique), or into a reservoir that can afterwards be connected to the analyser ('offline' technique). With the former technique, the early and later NO in the breath sample can be analysed separately. The test requires little coordination from the subject, and children older than 4 can be tested successfully.
Reference range
The upper normal level of eNO in different studies ranges from 20 to 30 parts per billion. However, several major features influence the reference values. Men have higher eNO values than women. Smoking notoriously lowers eNO values, and even former smoking status can influence results. The levels are higher in people with an atopic constitution (a tendency towards allergies). The fraction of eNO is also flow-dependent (higher at lower flow rates and vice versa), so measurements are normally measured at 50 ml/s. Age or height could also considerably confound eNO values in children. The magnitude of these effects lies in the order of 10%, so even single cut-off values might be useful.History
Until the 1980s, nitric oxide, a product of fossil fuelFossil fuel
Fossil fuels are fuels formed by natural processes such as anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms. The age of the organisms and their resulting fossil fuels is typically millions of years, and sometimes exceeds 650 million years...
combustion, was thought only to play a role the detrimental effects of air pollution
Air pollution
Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or biological materials that cause harm or discomfort to humans or other living organisms, or cause damage to the natural environment or built environment, into the atmosphere....
on the respiratory tract
Respiratory tract
In humans the respiratory tract is the part of the anatomy involved with the process of respiration.The respiratory tract is divided into 3 segments:*Upper respiratory tract: nose and nasal passages, paranasal sinuses, and throat or pharynx...
. In 1987, experiments with coronary arteries showed that nitric oxide was the long sought endothelium-derived relaxing factor
Endothelium-derived relaxing factor
Endothelium-derived relaxing factor is produced and released by the endothelium to promote smooth muscle relaxation. The best-characterized is nitric oxide . Some sources equate EDRF and nitric oxide....
. After scientists realised that NO played a biological role, its role as a cell signalling molecule and neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
became clear from abundant studies.
NO was first detected in exhaled breath samples in 1991. In 1992, NO was voted molecule of the year by the scientific journal Science
Science (journal)
Science is the academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science and is one of the world's top scientific journals....
. In 1993, researchers from the Karolinska Institute in Sweden were the first to report increased eNO in asthmatics.
Today, NO is not only used in breath tests but also as a therapeutic agent for conditions such as pulmonary arterial hypertension and possibly for the acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome , also known as respiratory distress syndrome or adult respiratory distress syndrome is a serious reaction to various forms of injuries to the lung....
.

