
Exponential utility
Encyclopedia
In economics
exponential discounting is a specific form of the discount function
, used in the analysis of choice over time
(with or without uncertainty
). Formally, exponential discounting occurs when total utility
is given by
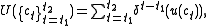
where ct is consumption
at time t,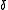 is the exponential discount factor, and u is the instantaneous utility function.
is the exponential discount factor, and u is the instantaneous utility function.
In continuous time, exponential discounting is given by
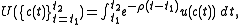
Exponential discounting implies that the marginal rate of substitution
between consumption at any pair of points in time depends only on how far apart those two points are. Exponential discounting is not dynamically inconsistent.
For its simplicity, the exponential discounting assumption is the most commonly used in economics. However, alternatives like hyperbolic discounting
have more empirical support.
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
exponential discounting is a specific form of the discount function
Discount function
A discount function is used in economic models to describe the weights placed on rewards received at different points in time. For example, if time is discrete and utility is time-separable, with the discount function...
, used in the analysis of choice over time
Intertemporal choice
Intertemporal choice is the study of the relative value people assign to two or more payoffs at different points in time. Most choices require decision-makers to trade-off costs and benefits at different points in time. These decisions maybe about savings, work effort, education, nutrition,...
(with or without uncertainty
Uncertainty
Uncertainty is a term used in subtly different ways in a number of fields, including physics, philosophy, statistics, economics, finance, insurance, psychology, sociology, engineering, and information science...
). Formally, exponential discounting occurs when total utility
Utility
In economics, utility is a measure of customer satisfaction, referring to the total satisfaction received by a consumer from consuming a good or service....
is given by
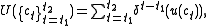
where ct is consumption
Consumption (economics)
Consumption is a common concept in economics, and gives rise to derived concepts such as consumer debt. Generally, consumption is defined in part by comparison to production. But the precise definition can vary because different schools of economists define production quite differently...
at time t,
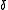 is the exponential discount factor, and u is the instantaneous utility function.
is the exponential discount factor, and u is the instantaneous utility function.In continuous time, exponential discounting is given by
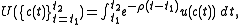
Exponential discounting implies that the marginal rate of substitution
Marginal rate of substitution
In economics, the marginal rate of substitution is the rate at which a consumer is ready to give up one good in exchange for another good while maintaining the same level of utility.-Marginal rate of substitution as the slope of indifference curve:...
between consumption at any pair of points in time depends only on how far apart those two points are. Exponential discounting is not dynamically inconsistent.
For its simplicity, the exponential discounting assumption is the most commonly used in economics. However, alternatives like hyperbolic discounting
Hyperbolic discounting
In behavioral economics, hyperbolic discounting is a time-inconsistent model of discounting.Given two similar rewards, humans show a preference for one that arrives sooner rather than later. Humans are said to discount the value of the later reward, by a factor that increases with the length of the...
have more empirical support.

