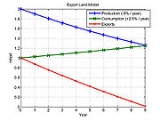
Export Land Model
Encyclopedia
The Export Land Model, or Export-Land Model, refers to work done by Dallas geologist Jeffrey Brown, building on the work of others, and discussed widely on The Oil Drum
. It models the decline in oil
export
s that result when an exporting nation experiences both a peak in oil production
and an increase in domestic oil consumption
. In such cases, exports decline at a far faster rate than the decline in oil production alone.
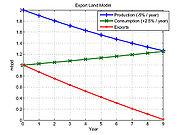 The Export Land Model is important to petroleum importing nations because when the rate of global petroleum production peaks and begins to decline, the petroleum available on the world market will decline much more steeply than the decline in total production.
The Export Land Model is important to petroleum importing nations because when the rate of global petroleum production peaks and begins to decline, the petroleum available on the world market will decline much more steeply than the decline in total production.
and oil consumption in Export-Land countries, creating a positive feedback
process between declining exports and higher prices. Eventually, however, the level of export decline outpaces the increasing oil price, slowing domestic growth. In some cases, an Export Land eventually becomes a net importer. It is unlikely that an Export Land would constrain domestic consumption to help importing countries. In fact, many oil exporting countries subsidize domestic consumption below price levels defined by the world market
.
Several real-world nations exhibit the characteristics of the Export Land Model as pictured in the image gallery above. These four nations exhibit increasing domestic consumption along with declining production. Indonesia has already shifted from oil exporter to oil importer while Egypt is hovering on the brink. Malaysia and Mexico also have the hallmarks of the Export Land Model.
Within 5 years, Mexico (the second biggest exporter of oil to the US) may become a net oil importer. Other nations where this may soon happen include Iran, Algeria and Malaysia.
A recent report from CIBC World Markets
also indicates that as much as 40% of Saudi Arabia
's expected production increases will be offset by rising internal demand by 2010, and Iran
ian exports will decline by more than 50% for similar reasons. This report indicates that similar market pressures could reduce net worldwide oil exports by 2.5 Moilbbl/d (about 3%).
Nations may also reach their peak of oil production without fitting the Export Land model. For example, the United Kingdom began importing oil in 2006, after decades of exporting, due to declining production. But as domestic consumption in the UK has remained essentially unchanged for the last 20 years, their rising import levels essentially match their falling production levels. Similarly, Norway's exports began declining in 2001, but at the same rate as their production because their domestic consumption was also not growing. Unlike many exporters, these two countries don't subsidize local market oil price and have high fuel prices by world standards, thus one of the premises of the export land model (that domestic consumption should not be affected by world market price) does not apply to those countries.
The Oil Drum
The Oil Drum is a web-based, interactive energy, peak oil and sustainability think tank and community devoted to the discussion of energy issues and their impact on society. The Oil Drum is facilitated by the Institute for the Study of Energy and Our Future, a Colorado non-profit corporation...
. It models the decline in oil
Petroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
export
Export
The term export is derived from the conceptual meaning as to ship the goods and services out of the port of a country. The seller of such goods and services is referred to as an "exporter" who is based in the country of export whereas the overseas based buyer is referred to as an "importer"...
s that result when an exporting nation experiences both a peak in oil production
Peak oil
Peak oil is the point in time when the maximum rate of global petroleum extraction is reached, after which the rate of production enters terminal decline. This concept is based on the observed production rates of individual oil wells, projected reserves and the combined production rate of a field...
and an increase in domestic oil consumption
Consumption (economics)
Consumption is a common concept in economics, and gives rise to derived concepts such as consumer debt. Generally, consumption is defined in part by comparison to production. But the precise definition can vary because different schools of economists define production quite differently...
. In such cases, exports decline at a far faster rate than the decline in oil production alone.

Theory
As world oil exports approach (or pass) a global peak, the price of exported oil increases and further stimulates domestic economic growthEconomic growth
In economics, economic growth is defined as the increasing capacity of the economy to satisfy the wants of goods and services of the members of society. Economic growth is enabled by increases in productivity, which lowers the inputs for a given amount of output. Lowered costs increase demand...
and oil consumption in Export-Land countries, creating a positive feedback
Positive feedback
Positive feedback is a process in which the effects of a small disturbance on a system include an increase in the magnitude of the perturbation. That is, A produces more of B which in turn produces more of A. In contrast, a system that responds to a perturbation in a way that reduces its effect is...
process between declining exports and higher prices. Eventually, however, the level of export decline outpaces the increasing oil price, slowing domestic growth. In some cases, an Export Land eventually becomes a net importer. It is unlikely that an Export Land would constrain domestic consumption to help importing countries. In fact, many oil exporting countries subsidize domestic consumption below price levels defined by the world market
Financial market
In economics, a financial market is a mechanism that allows people and entities to buy and sell financial securities , commodities , and other fungible items of value at low transaction costs and at prices that reflect supply and demand.Both general markets and...
.
Hypothetical example
Given a hypothetical oil producing country (known by the model as an Export Land) that produces 2 Moilbbl/d, consumes 1 Moilbbl/d, and exports 1 Moilbbl/d to oil consuming countries around the world, the model would be applied as such (illustrated in the graph above):- Export Land hits the point of Peak Oil production, and over a five year period production drops by 25%. Over the same time period, Export Land's consumption increases by 20% to 1.2 mbpd. This causes Export Land's net exports over the five year period to fall from 1 mbpd to 0.3 mbpd, a decrease of 70% -- resulting from a combination of increasing domestic consumption in Export Land and a 25% drop in production. Counter-intuitively, the fractional decline in exports is much greater than the sum of the fractional increase in domestic consumption and the fractional decline in production.
Real-world examples
| Country | Production | Consumption | net exports | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2002 | 2007 | 2002 | 2007 | 2002 | 2007 | |
| Argentina Argentina Argentina , officially the Argentine Republic , is the second largest country in South America by land area, after Brazil. It is constituted as a federation of 23 provinces and an autonomous city, Buenos Aires... |
806 | 698 | 364 | 492 | 442 | 206 |
| Bahrain Bahrain ' , officially the Kingdom of Bahrain , is a small island state near the western shores of the Persian Gulf. It is ruled by the Al Khalifa royal family. The population in 2010 stood at 1,214,705, including 235,108 non-nationals. Formerly an emirate, Bahrain was declared a kingdom in 2002.Bahrain is... |
49 | 48 | 23 | 35 | 25 | 14 |
| Colombia Colombia Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia , is a unitary constitutional republic comprising thirty-two departments. The country is located in northwestern South America, bordered to the east by Venezuela and Brazil; to the south by Ecuador and Peru; to the north by the Caribbean Sea; to the... |
601 | 561 | 222 | 228 | 379 | 333 |
| Egypt Egypt Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world... |
751 | 710 | 534 | 651 | 217 | 59 |
| Indonesia Indonesia Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an... |
1289 | 969 | 1137 | 1157 | 152 | -188 |
| Malaysia | 757 | 755 | 489 | 514 | 268 | 241 |
| Syria Syria Syria , officially the Syrian Arab Republic , is a country in Western Asia, bordering Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest.... |
548 | 394 | 256 | 262 | 292 | 132 |
| Turkmenistan Turkmenistan Turkmenistan , formerly also known as Turkmenia is one of the Turkic states in Central Asia. Until 1991, it was a constituent republic of the Soviet Union, the Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic . Turkmenistan is one of the six independent Turkic states... |
192 | 180 | 78 | 117 | 114 | 62 |
| Vietnam Vietnam Vietnam – sometimes spelled Viet Nam , officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam – is the easternmost country on the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by China to the north, Laos to the northwest, Cambodia to the southwest, and the South China Sea –... |
339 | 350 | 192 | 294 | 146 | 56 |
| Yemen Yemen The Republic of Yemen , commonly known as Yemen , is a country located in the Middle East, occupying the southwestern to southern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the north, the Red Sea to the west, and Oman to the east.... |
438 | 360 | 112 | 143 | 326 | 217 |
Several real-world nations exhibit the characteristics of the Export Land Model as pictured in the image gallery above. These four nations exhibit increasing domestic consumption along with declining production. Indonesia has already shifted from oil exporter to oil importer while Egypt is hovering on the brink. Malaysia and Mexico also have the hallmarks of the Export Land Model.
Within 5 years, Mexico (the second biggest exporter of oil to the US) may become a net oil importer. Other nations where this may soon happen include Iran, Algeria and Malaysia.
A recent report from CIBC World Markets
CIBC World Markets
CIBC World Markets is the investment banking subsidiary of the Canadian Imperial Bank of Commerce. The firm operates as an investment bank both in the domestic and international equity and debt capital markets...
also indicates that as much as 40% of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia , commonly known in British English as Saudi Arabia and in Arabic as as-Sa‘ūdiyyah , is the largest state in Western Asia by land area, constituting the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and the second-largest in the Arab World...
's expected production increases will be offset by rising internal demand by 2010, and Iran
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
ian exports will decline by more than 50% for similar reasons. This report indicates that similar market pressures could reduce net worldwide oil exports by 2.5 Moilbbl/d (about 3%).
Nations may also reach their peak of oil production without fitting the Export Land model. For example, the United Kingdom began importing oil in 2006, after decades of exporting, due to declining production. But as domestic consumption in the UK has remained essentially unchanged for the last 20 years, their rising import levels essentially match their falling production levels. Similarly, Norway's exports began declining in 2001, but at the same rate as their production because their domestic consumption was also not growing. Unlike many exporters, these two countries don't subsidize local market oil price and have high fuel prices by world standards, thus one of the premises of the export land model (that domestic consumption should not be affected by world market price) does not apply to those countries.
See also
- Energy developmentEnergy developmentEnergy development is the effort to provide sufficient primary energy sources and secondary energy forms for supply, cost, impact on air pollution and water pollution, mitigation of climate change with renewable energy....
- Energy securityEnergy securityEnergy security is a term for an association between national security and the availability of natural resources for energy consumption. Access to cheap energy has become essential to the functioning of modern economies. However, the uneven distribution of energy supplies among countries has led...
- Gross domestic product per barrelGross domestic product per barrelEnergy efficiency as it relates to oil usage can be described by the gross domestic product per barrel of oil used . The original data for this is taken from two sources, the and the List of countries by GDP article from Wikipedia...
- Oil price increases since 2003
- Oil reservesOil reservesThe total estimated amount of oil in an oil reservoir, including both producible and non-producible oil, is called oil in place. However, because of reservoir characteristics and limitations in petroleum extraction technologies, only a fraction of this oil can be brought to the surface, and it is...
- World energy resources and consumptionWorld energy resources and consumption]World energy consumption in 2010: over 5% growthEnergy markets have combined crisis recovery and strong industry dynamism. Energy consumption in the G20 soared by more than 5% in 2010, after the slight decrease of 2009. This strong increase is the result of two converging trends...
External links
- An Extension of the World Import/Export Land Model
- Declining Net Oil Exports--A Temporary Decline or a Long Term Trend?
- Economist Jeff Rubin and the Export Land Model - CNBC
- Energy Export Databrowser - Visual review of production and consumption trends for individual nations; data from the British Petroleum Statistical Review
- Five Geopolitical Feedback-Loops in Peak Oil
- Hubbert Linearization Analysis of the Top Three Net Oil Exporters
- Net Oil Exports and the "Iron Triangle"
- Oil export - import model for the UK - lecture at UCSBUniversity of California, Santa BarbaraThe University of California, Santa Barbara, commonly known as UCSB or UC Santa Barbara, is a public research university and one of the 10 general campuses of the University of California system. The main campus is located on a site in Goleta, California, from Santa Barbara and northwest of Los...
by Jeffrey Brown on the Export Land Model - Quantitative Assessment of Future Net Oil Exports by the Top Five Net Oil Exporters
- Another Take On Peak Oil: Exports, Not Production, Indicate Crisis

